Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
6 Safflower Oil Benefits (incl. weight, skin) + Side Effects

Safflower oil is equally popular for cooking and as it is for boosting weight loss and skin health. Research backs up some of the claims but also suggests that this oil may be good for the heart, brain, and blood vessels. Its serotonin-like polyphenols reduce inflammation and may enhance cognition. Read on to learn more about safflower oil, with mechanisms, dosage, and side effects. What Is Safflower Oil?
Carthamus tinctorius , known as safflower or false saffron, is one of the oldest known crops . It was first cultivated 4,000 years ago [ 1 , 2 ].
This thistle-like plant is part of the daisy family ( Asteraceae ) and thrives in hot and dry climates. Safflower oil was first cultivated in China, India, Iran, and Egypt. It was then introduced to western countries between the 5th and 14th centuries [ 3 , 4 ].
The safflower plant is grown primarily as an oilseed crop , but its flowers have also been cultivated for culinary, textile, and medicinal purposes [ 4 , 3 ].
Safflower oil is popular for cooking and deep frying due to its high smoke point. It is a clear oil with a neutral taste that makes it a common addition to salads. Nutritionally, safflower oil is similar to sunflower oil. However, it contains some unique bioactive compounds that sunflower oil lacks [ 5 ]. Bioactive Components
The oil content of safflower seeds ranges from 23 – 40% [ 6 , 4 ]. Mostly polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acids: linoleic acid 55 – 82%
Very small amounts of saturated fatty acids (palmitic acid up to 7% and stearic acids 1 – 6%)
Phospholipids
Linoleic and oleic acids in safflower oil provide concentrated sources of omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids, respectively [ 9 , 2 ].
Cultivation programs in the 1960s created a safflower oil high in oleic acid (70 – 80%) and low in linoleic acid. Due to its high oleic acid content, this oil has a longer shelf life. Many other plant oils are naturally rich in oleic acid. But this special type of safflower oil is richer in oleic acid than olive oil , the usual best source of this omega-9 fatty acid (with ~66% oleic acid) [ 2 ].
Safflower oil is rich in antioxidant polyphenols (lignans, flavones, and serotonins), which have wide-ranging health benefits. Lignans and flavone polyphenols are phytoestrogens, plant compounds that can mimic estrogen [ 10 , 11 ]. Mechanism of Action
In cell studies, safflower oil blocked a key inflammatory pathway called NF-κB and turn off genes that increase immune-activating cytokines, making it a potentially potent anti-inflammatory [ 12 , 13 , 7 ].
It also reduced inflammatory enzymes that can damage the placenta in pregnant diabetic rats [ 14 ].
Safflower oil improved bone mass in animals by increasing growth hormones ( IGF-I , IGF-II) and their proteins [ 15 ].
It protected against small intestine ulcers from NSAID drugs (like Motrin) in mice [ 16 ].
Phospholipids in safflower oil lowered blood and liver cholesterol in rats by reducing cholesterol absorption in the small intestine [ 8 ].
Polyphenols in safflower seed oil have demonstrated activity against:
Safflower polyphenols prevented LDL from being transformed into oxidized LDL, which can block arteries. These active compounds prevented plaque buildup even in mice genetically lacking APOE . Its polyphenols also prevent arteries from becoming thick and rigid [ 18 , 17 ]. Antioxidant Activity
Polyphenols from safflower oil enhanced antioxidant defense and reduced damage in numerous cellular and animal studies [ 20 , 18 , 21 , 22 ].
Antioxidant serotonins from safflower oil neutralized free radicals and inflammatory cytokines in human white blood cells exposed to LPS . LPS is a bacterial toxin that often enters the bloodstream of people with leaky gut and can trigger inflammation in the whole body [ 22 ]. Potential Benefits of Safflower Oil
Safflower oil is safe to consume in food, but it has not been approved by the FDA for medical use. Speak with your doctor before making significant changes to your diet or supplements. 1) Heart Health
Safflower oil reduced triglycerides , LDL , and total cholesterol in a large meta-analysis of human trials. When it comes to the breakdown of its effects compared to other oils and fats, safflower oil was [ 23 ]: Better at reducing LDL than saturated fats like butter or lard (a mix of saturated and unsaturated fats)
Better at reducing triglycerides than butter or beef fat
Worse at increasing HDL cholesterol than most other oils or fats, including sunflower, olive, palm, coconut oil, and beef fat
In one clinical trial, 8g/day of safflower oil reduced inflammation and increased HDL in 35 obese, post-menopausal women with type 2 diabetes over 16 weeks. But keep in mind that many other oils and fats may be more effective at increasing HDL [ 24 ].
In another clinical trial, 24g/day of safflower oil reduced total cholesterol and LDL in 37 healthy adults [ 25 ].In multiple animal studies, diets rich in safflower oil or safflower phospholipids reduced blood and/or liver cholesterol and increased HDL levels. For example, safflower oil decreased liver cholesterol by an impressive 44% in lambs. Triglyceride levels varied in most animal studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 8 , 29 , 30 ].Compared to beef tallow, diets high in safflower oil were much more effective at reducing blood triglycerides in rats [ 31 ].Two serotonin polyphenols from safflower oil improved recovery and reduced damage after heart attacks in a heart tissue study [ 21 ].However, high-oleic-acid safflower oil (30mL/day) had no beneficial effect on lipid levels in one study on twelve post-menopausal women [ 32 ].The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of safflower oil for any of the below-listed uses. Remember to speak with a doctor before making significant changes to your diet, and never use safflower oil as a replacement for something your doctor recommends […]
Artificial Blue Light: Negative / Positive Health Effects
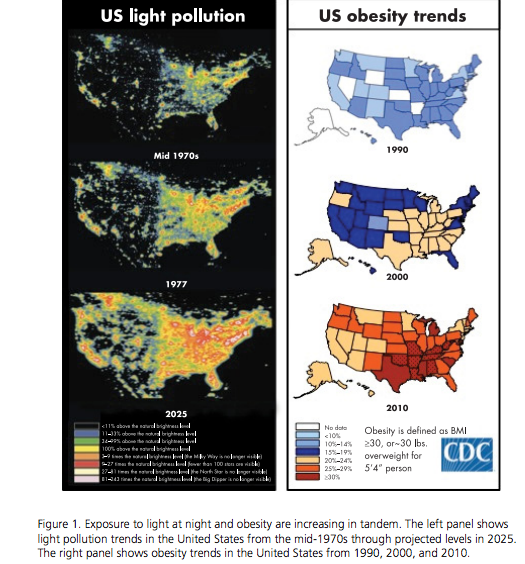
Nighttime blue light exposure can derange the circadian rhythm. It may be a culprit behind many modern chronic health issues, including obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. On the other hand, blue light exposure during the day is very beneficial. Read this post to learn how to hack your blue light exposure for your benefit.
What Is Blue Light?
Light is electromagnetic radiation of a variety of wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum.
There is both visible and non-visible light. Non-visible light includes ultraviolet ( UV ) and infrared light, while visible light includes the whole spectrum of the rainbow, including blue light. Within the visible light spectrum, each wavelength is represented by a color.
Of all the colors of the visible light spectrum, blue light (wavelength 446-477 nm) has the strongest impact on physiology and the circadian rhythm because our pigments react to this wavelength [ 1 , 2 , 3 ].
Humans have evolved to rise with the sun and go to sleep after sunset. Before the advent of technology, humans only used sources that emitted yellow, orange, and red light, such as fire, candles, and lamps. These lights have much less impact on our circadian rhythm and sleep-wake cycles than blue light [ 4 , 5 ].
Nowadays, advances in lighting and other technologies like television, computers, and digital clocks among others, have introduced more blue-white light to our environment. In addition, these lights are available at all hours, which can affect our health and wellbeing [ 5 ].
The higher-efficiency “green” light bulbs are not necessarily as beneficial for humans as they supposedly are for the Earth. Compact fluorescent light (CFL) bulbs contain about 25% of blue light, while this percentage reaches 35% in LEDs [ 5 ].
Generally, blue light is beneficial during the day, but harmful at night. What Are the Physiological Effects of Blue Light?
Light exposure anchors human body functions to the rise and fall of the sun. When sunlight, which contains blue light, hits the retina, the photoreceptor cells transmit nerve impulses to the hypothalamus . The hypothalamus is the command central for hunger , thirst, temperature regulation, hormone secretion, and sleep patterns, which fluctuate according to our circadian rhythm [ 6 ]. Photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye (retinal cells, rod and cone cells). The arrangement of retinal cells is shown in a cross-section.
When light hits the eye, it hits the retina. This light-sensitive tissue is actually considered part of the central nervous system (CNS) and is connected to the brain via the optic nerve. There are several layers of nerve cells in the retina, but the ones that are sensitive to light are those with photoreceptor cells. Rods and cones are the light-sensing cells that allow us to see, while the retinal ganglion cells are important for circadian rhythm entrainment [ 7 ].
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus coordinates light exposure with bodily functions through hormonal, autonomic (involuntary nerve impulses), and feeding-related cues [ 7 ]. Source: [ 8 ] 1) Potential Negative Effects of Blue Light Exposure During the Night
The following adverse effects are commonly associated with increased exposure to blue night during the night. Note, however, that the majority of studies covered in this section deal with associations only, which means that a cause-and-effect relationship hasn’t been established. Other environmental and genetic factors may play a more important role. 1) Disrupting Circadian Rhythm
Normally, darkness at night allows a normal output of melatonin between 2:00 and 4:00 am. Then, bright daylight follows resetting the clock and beginning a new 24-hour day [ 9 ].
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells contain melanopsin (a light sensor protein), whose job is to synchronize the body’s circadian clock to light [ 10 ].
Exposure to blue light at night signals the body that it is daytime , consequently, messing up the circadian rhythm, which is crucial to many body processes. To entrain the circadian rhythm , it is important to both get sunlight in the morning and avoid artificial light at night [ 11 ]. 1) May Lower Melatonin Production
Melatonin is an important hormone that controls the sleep-wake cycle. Light at night, especially blue light , suppresses melatonin production [ 12 , 9 , 13 ].
Even dim light can interfere with a person’s circadian rhythm and melatonin secretion. A mere 8 lux (2x the brightness of a night light) can inhibit melatonin. The brighter the light and the longer the exposure time, the less melatonin the eye cells produce [ 14 , 15 ].
A theoretical model of different types of light and exposures indicates the following time needed for melatonin suppression [ 16 ]: Monochromatic red light at 100 lux , a reasonable living room lighting level, would take 403 hours of exposure to suppress melatonin by 50%
Candle: 66 min suppresses melatonin by 50%
60-watt incandescent bulb : 39 min suppresses melatonin by 50%
58-watt deluxe daylight fluorescent light: 15 min suppresses melatonin by 50%
Pure white high-output LED : 13 min suppresses melatonin by 50%
The extent to which light at night suppresses melatonin depends on both the wavelength (blue being the worst) and the intensity of the light [ 13 , 9 ].
For example, after 1 hr of light at midnight, melatonin could be suppressed up to 71% , 67%, 44%, 38%, and 16% with intensities of 3,000, 1,000, 500, 350, and 200 lux, respectively [ 17 ].
Melatonin levels are reduced most with dilated pupils exposed to 90 min of monochromatic blue light from 2:00 to 3:30 AM at a brightness of 0.1 lux, which is equivalent to the light of a full moon [ 9 ]. Blue light, even at a dim, moonlight level (0.1 lux), suppressed melatonin production more than any other wavelength in a study in rats [ 9 ]. People with light-colored eyes (blue or green, for example) are more susceptible to melatonin suppression by blue light than those with darker eyes [ 18 ]. 2) May Raise Cortisol Exposure to either […]
Benefits of Proline-Rich Polypeptides (PRP) + Risks
Proline-Rich Polypeptides (PRPs) are part of colostrum or “first milk”. They are crucial for the development of newborns and support the immune and nervous systems. When supplemented, PRPs may enhance cognition in the elderly. Read on to learn the beneficial roles of PRPs and the potential side effects of supplementation. What are Proline-Rich Polypeptides?
Proline-rich polypeptides (PRPs), also known as Colostrinin, are derived from colostrum – the milk given to a newborn mammal as its first nourishment [ 1 ].
PRPs are not species-specific i.e PRPs derived from cow milk works on all mammals [ 2 ].
Since the immune system of a newborn is not fully developed, PRPs play an important role in immunity with their antiviral, antibacterial, anti-tumor, and immunoregulatory activities [ 1 ].
PRPs could be important, not only for the development of the immune and nervous systems of newborns but also in improving the health status of elderly persons [ 1 ].
As we will discuss, PRPs influence a wide variety of biological functions , such as the regulation of cell and tissue processes and the interactions of signal and regulatory proteins [ 1 ]. Snapshot
Proponents:
Improve brain function and memory
Regulate the immune system and inflammation
Have antiviral properties
Protect the brain and nerves
Combat cellular damage & aging
Skeptics:
Supplementation is poorly researched
May not be suitable for people with dairy intolerance
Not recommended for pregnant women
Benefits & Roles of Proline-Rich Polypeptides (PRPs)
Please note : the roles and benefits of PRPs supplied through mother’s milk may not translate to PRP supplementation. Cognitive Function
In a clinical trial with 46 mild Alzheimer’s patients, those who were given colostrinin (PRPs) either improved or didn’t worsen. None of the patients given placebo or selenium showed improvements [ 3 ].
In two studies of 138 Alzheimer’s patients, long-term colostrinin use (4-28 months) slowed down the decline in memory, cognitive function, and daily activity [ 4 , 5 ].
Animal studies discovered that PRPs had beneficial effects on the cognitive functioning and memory of older rats [ 6 , 7 ].
Chicks who had PRP-rich Colostrum injected into a part of their brain responsible for learning showed a marked improvement in memory function [ 8 ].
That said, regular colostrum supplements on the market may only contain PRPs in negligible amounts. Some manufacturers do list it specifically as an ingredient, but its therapeutic dosage for cognitive dysfunction based on the published studies is unclear [ 3 ].
No clinical evidence supports the use of PRPs for any of the conditions listed in this section. Below is a summary of the existing animal and cell-based studies; they should guide further investigational efforts but should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit. Regulate the Immune System
PRPs encourage the growth of white blood cells before stimulating the white blood cells to become either helper T-cells or suppressor T-cells [ 9 ].
PRPs stimulate the activity of natural killer cells , the cells that actually attack and kill pathogens, as well as cancerous cells [ 10 ].The net immune system effect of PRPs depend on the actual state of the animals studied. But broadly speaking, PRPs seem to restore the balance in cellular immune functions [ 6 ]. Regulate Inflammation PRPs can stimulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-a and Interferon-gamma ( Th1 cytokine ) in white blood cells, peritoneal cells, and placental and amniotic membranes [ 11 , 12 , 13 ].They can increase the production of IL-6 and IL-10 in blood cell cultures [ 14 ].PRPs raise the permeability of blood vessels in the skin in order to allow the passage of blood cells and cytokines into the infected area in which they are needed – this is a vital step in the inflammatory response [ 15 ].They may also regulate inflammation by altering genetic expression [ 16 ]. Antiviral Effects PRPs have been experimentally shown to provide immunity against several viruses , including:Of particular note is PRPs ability to inhibit the replication of the Epstein-Barr virus and the human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) – both of which have been linked with autoimmune conditions and chronic fatigue syndrome [ 24 , 25 ]. Cellular Damage & Aging When studied in mice, PRPs lowered reactive oxygen species ( ROS ), which cause cellular stress and damage [ 7 ].PRPs reduce the chance of random mutations and mutations caused by ROS and toxins [ 28 ].They are important for suppressing the uncontrolled activation of cells [ 1 , 7 ]. Brain Protection One experiment showed that PRPs possessed neuroprotective properties in mice with aluminum toxicity or neuronal damage from venom and toxins [ 29 ].One review suggested that colostrinin may partly be responsible for brain-protective effects of certain dairy products [ 30 ]. PRP Risks and Side Effects Keep in mind that the safety profile of PRPs is relatively unknown, given the lack of well-designed clinical studies. The list of side effects below is not a definite one, and you should consult your doctor about other potential side effects, based on your health condition and possible drug or supplement interactions. In clinical trials, PRPs were generally safe and well-tolerated. Only one study reported any adverse side effects of PRP supplementation. These included mild anxiety, excessive talkativeness, and insomnia that only lasted for 3 to 4 days [ 7 ]. Children and pregnant women should avoid PRP supplements until we know more about their safety.
9 Health Benefits of Raw Honey + Effects on Blood Sugar

Honey contains hidden nutritional and medicinal values. Raw, unprocessed types are nutritious, antimicrobial, and good for the skin & hair. The Bible itself suggests eating honey. But what does the science say? Read this post to learn the health benefits of honey and its effects on blood sugar levels. What is Honey?
Honey is a sweet food made by bees taking nectar from flowers. There are different types of honey, but the most common kind comes from the genus Apis, known as honeybees. Honeybees convert the nectar to honey by a regurgitation process and evaporation.
As you can imagine, depending on the available plants, the taste, constituents, and benefits of honey are different [ 1 ].
Depending on the type, honey can be a pain reliever, antibacterial, or pure sugar (like artificial honey). Snapshot
Proponents:
Good for the skin & hair
Antioxidant
Provides energy and nutrients
May relieve cough and allergies
May balance cholesterol levels
Supports wound healing
Lacks solid clinical research
Excess consumption might cause stomach upset
High in sugar
Loses nutrients when heated or commercially processed
Conflicting effects on blood sugar
Raw vs. Heated Honey
Raw honey retains more of its beneficial bioactive compounds . It is especially rich in flavonoids and other polyphenol antioxidants that can reduce inflammation, protect the brain, fight viruses and bacteria, and boost cognition [ 2 , 3 ].
The concentration of honey is also very important. The bacteria-fighting potency among the different kinds of honey can vary up to 100-fold, depending on its geographical, seasonal and plant source as well as harvesting, processing and storage conditions [ 2 ].
Manuka honey has been widely researched and it’s renowned worldwide for its antibacterial effects. Mountain, tualang, Capilano, and eco-honeys also have high bacteria-fighting potency [ 2 ].
However, commercially available honey is often heat-processed. Higher temperatures can reduce the quality of honey and cause it to lose many beneficial enzymes, nutrients, and antioxidants . Heating honey together with ghee doesn’t reduce the concentration of beneficial substances but can cause harmful products to build up [ 4 ].
For this reason, you may want to find high-quality, natural, raw honey. Health Benefits of Honey
1) Fights Microbes
In rats, infected skin wounds treated daily with honey for 7 days had a better outcome than saltwater treatments.
After 7 days, the bacteria culture showed that honey was effective in the management of infected skin wounds by significantly inhibiting bacterial growth and having a positive influence on wound repair [ 5 ].
When the concentrations of honey were increased, the antibacterial effects against Staph bacteria and E.Coli were enhanced [ 6 ].Various kinds of honey show antimicrobial effects against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria as well as multidrug-resistant strains [ 7 ].Melaleuca honey is capable of inhibiting MRSA [ 8 ].A literature review found that honey is a great antimicrobial because of its high viscosity that provides a barrier to prevent infections. The antimicrobial property comes from the enzymatic production of hydrogen peroxide [ 9 ]. Fungal Infections In 70 women with vaginal candidiasis, honey + yogurt were similar to clotrimazole cream and even better at relieving some symptoms [ 10 ].Substituting sugars with honey in processed food can inhibit the harmful and genotoxic effects of mycotoxins, and improve the gut microflora. Honey increased colon Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli count the mice [ 11 ]. 2) Supplies Vitamins, Minerals, and Enzymes A pilot study was performed in 10 healthy people consuming multi-floral honey daily for two weeks (1.2 g/kg BW). Honey consumption increased blood antioxidants, Vitamin C , beta-carotene ( Vitamin A ), glutathione reductase, iron , white blood cells , zinc , magnesium , hemoglobin , and copper .On the other hand, honey decreased blood ferritin , IgE, aspartate aminotransferase , alanine aminotransferase , lactic acid dehydrogenase, creatine kinase, and fasting blood sugar [ 12 ]. 3) Improves Wound Healing In a review of 6 clinical trials, honey was more effective as a wound dressing than silver as measured by the number of days the wound needed to heal [ 13 ].In patients with diabetic foot ulcers, honey was able to reduce the rate of amputation.172 patients with non-healing diabetic foot ulcers received a thick layer of honey on their wound. Wounds became healthy within 7-35 days. Of those 172 patients, only 3 had to get their big toe amputated and 2 had below the knee amputations. This study concluded that honey greatly decreased the rate of amputations [ 14 ].In patients with diabetic foot ulcers, a regular saline dressing was compared to the effect of Beri-honey-impregnated dressings. 136/179 wounds were completely healed with honey compared to 97/169 that healed with saline dressings. The mean healing time for honey was 18 days compared to the 29 days for the saline dressings [ 15 ].Skin grafts are used to cover burn injuries and honey has been shown to increase the adherence of skin grafts to wound beds. In a clinical trial, 30 patients used honey as their graft and 30 used a regular dressing or suturing.The patients treated with honey reported a significantly reduced infection rate on day 5 and had reduced pain. They also had a shorter mean hospital stay. This study concluded that medical honey can be used for the fixation of a split-thickness skin graft [ 16 ].In rats, honey (combined with milk and aloe vera ) induced cell proliferation which increased the wound closure rate, blood vessel count and the collagen fiber density [ 17 ].However, in 19 trials it was found that for burns, compression bands alone were just as effective as honey [ 18 ]. 4) Nourishes the Skin and Hair According to a clinical review, honey can be used in rejuvenating the skin as well as slowing down the formation of wrinkles. It also helps make hair smooth and regulates the pH while preventing pathogen infections [ 19 ].Another article suggested using honey as a face wash and facial cleansing scrub for pimples and dry skin [ 20 ].A […]
5 Buspirone Uses, Side Effects, Dosage + Natural Options

Buspirone is a prescription medication indicated primarily for anxiety but may also be used “off-label” for depression and other mental disorders. Read on to learn the uses and side effects of buspirone + natural complementary approaches to anxiety.
Disclaimer: This post is not a recommendation or endorsement for buspirone. This medication is only FDA-approved for the treatment of certain specific medical disorders, and can only be taken by prescription and with oversight from a licensed medical professional. We have written this post for informational purposes only, and our goal is solely to inform people about the science behind buspirone’s effects, mechanisms, and current medical uses. What is Buspirone?
Buspirone is an anti- anxiety medication (anxiolytic) that is sold under the brand name Buspar. It is chemically and pharmacologically distinct from other anti-anxiety drugs such as benzodiazepines and offers reduced anxiety without physical dependence or withdrawal symptoms [ 1 , 2 ].
Buspirone is most commonly used for generalized anxiety disorder but is also prescribed occasionally for anxiety related to other brain-related disorders such as depression , attention deficit disorder, social phobia, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s [ 3 , 4 ]. Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of buspirone is not fully understood. It is known that buspirone binds to serotonin ( 5-HT1A ) receptors and partially mimics the action of serotonin. Serotonin is a chemical in the brain that promotes feelings of well-being and happiness [ 3 , 5 ].
Buspirone is also able to partially block the action of some dopamine receptors ( DRD2 ) [ 3 , 5 ].
When buspirone is broken down by the body, one of the major byproducts called 1-PP becomes quite concentrated in the blood. 1-PP can block the activity of a receptor that epinephrine/adrenaline activates (α2-adrenergic), which could account for some of the anti-depressant effects of buspirone [ 6, 7, 8, 5 ].
When taken by mouth (20 mg) it is rapidly absorbed and reaches its peak concentration within the blood in less than an hour . It takes 2.5 hours for half of the initial dose to be removed from the body ( half-life ). However, like most anti-anxiety medications, it may take 3-4 weeks until you start to feel relief from symptoms [ 5 , 3 ]. Approved Medical Uses
1) Anxiety
Buspirone treatment is more effective than placebo in treating and maintaining stability for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) based on a ten-week trial in 125 patients [ 9 ].
GAD is persistent, uncontrollable worry that requires professional therapy or medication to be resolved [ 3 , 10 ].
Buspirone is as effective as benzodiazepines, such as diazepam or lorazepam for treating generalized anxiety. This was shown in a study of 367 menstruating female patients, and 2 studies with 84 adults [ 11 , 12 , 13 ].
It is equal to or better (after 2 and 4 weeks) than sertraline (an SSRI) for GAD, based on a study of 46 people [ 14 ].
Based on the above results, the FDA has officially approved buspirone for the treatment of generalized anxiety. Off-Label Uses
Occasionally, doctors will prescribe drugs like buspirone to help treat conditions that fall outside of the official uses approved by the FDA – also known as “ off-label ” drug use. Usually, this is done because there is actually decent evidence that the drug may help, although not enough to get full FDA approval [ 15 ]. However, keep in mind that the decision to use medications in this way can only be made by a licensed medical professional.
2) Depression
Buspirone is more effective for treating major depressive disorder than placebo, based on a meta-analysis looking at the results of 15 randomized controlled trials with a total of 2,469 patients [ 16 ].
Two large studies performed in 300 adults for 8 weeks with both major depression and moderate anxiety resulted in significant improvement in symptoms for a majority of treated patients [ 17 , 18 ].
Taking buspirone for 8 weeks improved major depression in 61% of 177 elderly patients (double-blind randomized controlled trial) [ 19 ].
A randomized study of 286 adults being treated for depression with citalopram, found that augmentation with 60 mg/day buspirone resulted in a 30% remission rate based on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression [ 20 ].
Buspirone increases cortisol secretion (via 5HT1A ), which may improve depressive symptoms [ 21 ]. 3) Substance Abuse
The use of buspirone to help overcome substance abuse has had somewhat disappointing results, as conflicting data have been published for substance abuse of many types.
Buspirone was useful in helping high anxiety patients stop smoking in a study with 101 people. Participants that were considered to be low anxiety did not experience any benefit from taking buspirone [ 22 ].
However, it did not help 35 crack cocaine users (60 mg/d) in their addiction [ 23 ].
The effects of buspirone treatment on marijuana dependence have been conflicting. One study of 50 adults found it helped, while it didn’t with another study of 175 people [ 24 , 25 ].
Buspirone did not help methamphetamine use in 8 participants [ 26 ].In primates, buspirone was found to be helpful in reducing nicotine and cocaine addiction [ 27 ]. Other Potential Uses Buspirone has also been studied for other health conditions. However, keep in mind that the evidence supporting these potential applications is still only preliminary, and a lot more additional research will be needed before any of these applications are approved. Therefore, take all of the information below with a grain of salt. 4) Sexual Risk-Taking in Cocaine Users There is an association between cocaine use and sexually transmitted diseases that are attributed to an increase in sexual desire and a decrease in self-control when using cocaine. Buspirone improves impulse control in rats and reduced the reinforcing effects of cocaine in preclinical trials [ 28 , 29 ].Nine cocaine users were treated with 30 mg/day of buspirone for 3 days (repeated measures, inpatient protocol). Buspirone […]
Eucalyptus Oil Health Benefits + Dangers & How to Use
The sharp aroma of its trees or perhaps the common household item VapoRub are probably images that first come to mind when someone mentions eucalyptus. The common belief that eucalyptus oil is an effective decongestant is true, but it can also be dangerous. Read on to learn the benefits, dangers, and how to use it for the best results. What is Eucalyptus Oil?
Derived from Eucalyptus Globulus , eucalyptus essential oil is a liquid rich in 1,8-cineol (eucalyptol) and other beneficial components [ 1 , 2 ].
At diluted concentrations, the oil is effective against infections. It can kill harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It also has antioxidant and muscle-relaxing effects [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
People use eucalyptus oil to reduce symptoms of colds, the flu, and other respiratory problems like asthma, bronchitis, and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) [ 3 ].
Different species of eucalyptus differ widely regarding chemical composition, but all contain a high concentration of 1,8-cineol [ 6 ].
Eucalyptus oil can be inhaled, ingested, and put on the skin topically in highly diluted forms. Do not use a pure/undiluted solution on your skin or ingest it [ 3 ].
Proponents: Long history of traditional use
Relieves nasal and chest congestion
May reduce pain
Has a relaxing effect
Skeptics: Toxic in pure form and higher doses
Clinical research is limited
Can irritate the skin
Eucalyptus oil’s primary constituents are 1,8-cineole and α-pinene.
1,8-cineol is responsible for the thinning of mucus in the respiratory tract and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects [ 7 ].
Αlpha-pinene is what gives eucalyptus oil its antimicrobial properties against bacteria and viruses [ 8 ].
They both inhibit the growth of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria [ 9 ]. 1) Nasal and Chest Congestion
Inhaling eucalyptus oil vapors can help relieve uncontrollable coughing, as the vapors provide a calming and soothing effect [ 10 ].
According to pre-clinical trials, eucalyptus oil loosens mucus buildup, which reduces the possibility of extreme allergy attacks. This is accomplished by reducing cytokine levels in the bloodstream and consequently producing less mucus buildup in the sinuses [ 3 , 11 ].
Traditionally, eucalyptus oil inhalation has been used to relieve nasal congestion caused by asthma, respiratory infections, colds, and other conditions [ 3 ].
In 242 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), oral intake of eucalyptus oil helped prevent the sudden worsening of symptoms involving shortness of breath and mucus production [ 12 ].
In two trials of over 500 subjects, a combination of diluted pine, lime, and eucalyptus oil extracts by oral intake helped to reduce frequent bronchitis flare-ups [ 13 , 14 ].
Eucalyptol (cineol), a constituent of eucalyptus oil, significantly reduced the use of oral steroids in 32 patients with severe asthma [ 15 ]. 2) Pain
Eucalyptus oil is an efficient rubefacient, which means it mildly irritates the skin to reduce joint or muscle pain [ 16 ].
Rubbing a few drops of diluted eucalyptus oil at the temples region or forehead region can provide pain relief. The same effects can also be felt by inhaling the oil’s vapors, known as aromatherapy [ 17 ].
Along with other essential oils, it helped reduce nerve pain by combining aromatherapy and massage in 46 diabetic patients [ 18 ].In a study of 52 knee replacement patients, inhaling eucalyptus oil after total knee replacement surgery significantly reduced pain and blood pressure, allowing for faster recovery [ 19 ]. No valid clinical evidence supports the use of eucalyptus oil for any of the conditions in this section. Below is a summary of up-to-date animal studies, cell-based research, or low-quality clinical trials which should spark further investigation. However, you shouldn’t interpret them as supportive of any health benefit. 3) Relaxation Inhaling eucalyptus oil can help increase concentration and also provide a calming, soothing effect.In a study of 32 participants, a combination of diluted ethanol, eucalyptus oil, and peppermint oil rubbed near the temples and forehead area can help induce a muscle and mentally relaxing effect. The participants also had an increase in brain function [ 20 ]. No clinical evidence supports the use of eucalyptus oil for any of the conditions listed in this section. Below is a summary of the existing animal and cell-based studies; they should guide further investigational efforts but should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit. In animal and cell-based experiments, eucalyptus oil increased monocyte-derived macrophages in the blood, thus increasing immunity and faster recovery from infections. Macrophages are white blood cells that work by engulfing harmful organisms [ 21 ]. Microbial Infections Eucalyptus oil combined with thermal treatment effectively prevented food spoilage caused by yeast and bacteria. This is because of the oil’s bactericidal (killing the bacteria) and bacteriostatic (prevention of bacterial reproduction) properties [ 22 ].Eucalyptus oil can help inhibit germination and spore production of fungi, and thus has antifungal properties [ 23 ]. Side Effects & Precautions This list does not cover all possible side effects. Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any other side effects. In the US, you may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch . In Canada, you may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345. Eucalyptus oil is likely safe in the amounts present in foods and possibly safe when used in appropriate doses, orally or topically. However, severe adverse effects may occur if one overdoses or has an allergic reaction to the substance .Possible side effects include [ 24 ]: Burning sensation in the mouth Burning throat Stomach pain Vomiting Dizziness and/or disorientation Itchy hives Swelling of face, hands, mouth, or throat Tingling mouth or throat Chest tightening Breathing trouble Warnings For children under 2 years, eucalyptus ointments/salves or oil are not advised.Do not give cough drops containing eucalyptus oil to children under 6 years of age.Eucalyptus oil can slow down how fast the liver breaks down medications, so be cautious and consult physicians regarding specific drug interactions [ 25 , 26 ]. Overdose Consuming more than […]
Keto Diet: Benefits & How to Know if It’s Right For You

The ketogenic diet (or keto diet) has been touted for its many potential health benefits such as weight loss, cognitive enhancement, and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. In this post, we cover: Different ways to get into ketosis
Physiology and pathways that are changed when you are in ketosis, which explains how the ketogenic diet may derive its benefits
Genetic factors that may affect the safety and effectiveness of ketosis
Health conditions that may be helped by the ketogenic diet
Negative effects of ketosis and how to mitigate them
What Is the Keto Diet?
Keto diets are defined by a low-carbohydrate (typically under 50 grams/day) and high-fat intake, leading to an elevation of free fatty acids and ketone bodies in the blood [ 1 ].
The first ketogenic diets in the medical literature are noted in publications from the 1920s, although wider popularity and increased research was not observed until the 1960s [ 1 ].
Variations of this diet have remained popular for the past 20-30 years, with proponents claiming that these diets boost weight loss and energy while protecting from certain metabolic diseases [ 1 ].
A ketogenic diet and fasting seem to affect the body similarly. Both deplete the body’s glucose reserves, so the body may start turning fatty acids into ketones [ 2 ]. The Physiology of Ketosis
Mechanisms
Beta-hydroxybutyrate is a signaling molecule that can activate HDACs and thereby increase or decrease important genes during ketosis [ 3 ]. Biochemical Pathway, Hormones, or Benefits Ketogenic Diet Calorie Restriction or Fasting References How to Get Into Ketosis
When the body doesn’t have enough carbohydrates from food, it burns fat to produce energy. This results in the production of ketones or ketone bodies [ 17 ].
In non-diabetics, ketosis can be achieved through 4 ways: Prolonged physical exercise in a fasted state, depending on intensity and duration [ 19 , 20 ]
Nutritional ketosis, i.e. by consuming a very low carbohydrate diet
Supplementation, such as with medium-chain triglycerides or exogenous ketones (ketone esters or ketone ester salts) [ 21 ]
There are 3 different types of ketone bodies, including [ 22 ]: Beta-hydroxybutyrate, the main ketone body that circulates in the blood
Acetoacetate , the main ketone body produced by the liver
Acetone , a very volatile ketone that is generally eliminated through exhalation and is what gives the sweet ketone breath in people in ketosis
In rats, acetoacetate concentration in the blood and brain is very low. A study found that its concentration in the brain was less than 4% of that in the whole blood and 2.6% of that in plasma. However, the brain/blood ratio was highest in starved rats [ 23 ].
In this study, the concentration of beta-hydroxybutyrate in the blood and brain was 5-10 times greater than that of acetoacetate [ 23 ]. Exogenous Ketones
Ketone body supplements can provide 8-12 grams of beta-hydroxybutyrate and 1 gram of sodium per serving, which can rapidly increase ketone body availability.
While a ketogenic diet or fasting can take days to raise blood ketone levels, exogenous ketones can reach peak levels in 1-2 hours.
Upon ingestion, ketone esters, such as (R)-3-hydroxybutyl and (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate, have emerged as a more practical and applicable way to increase ketone bodies, especially for athletes.
Ketone esters are cleaved and absorbed in the gut, from where they can either enter circulation or undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver [ 24 ]. Keto-Adaptation
Keto-adaptation refers to the process where cells transition from relying on glucose to relying on fat burning for energy production [ 25 ].After prolonged fasting (over 2 weeks) or diet-induced ketosis, cells adapt to using fatty acids and ketone bodies (keto-adaptation), resulting in a significant reduction in glucose requirement [ 26 ].Typically, ketone bodies are present in low amounts in the blood. After the first 2-3 days of fasting or being on a very low-carbohydrate diet, the liver starts to produce ketones so ketone levels remain around 2-3 mM [ 25 ].Keto-adaptation is complete when, after weeks of carbohydrate depletion, cells in the body cut down their uptake of ketone bodies. This results in an increase of ketone body concentration in the blood to ~8 mM [ 27 ].Keto-adaptation allows the brain to effectively take up and use the ketone bodies because the protein that transports them through the blood-brain barrier is more effective at higher concentrations (Km = 7 mM) [ 28 ]. Nutritional Ketosis vs Diabetic Ketoacidosis Nutritional ketosis is very different from diabetic ketoacidosis .In non-diabetics, blood sugar remains normal during ketosis. When the carbohydrate stores are depleted by the end of the first day on a ketogenic diet, the liver starts to produce glucose from other sources, such as pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids. This helps maintain normal blood sugar levels [ 26 ].In healthy people eating a ketogenic diet or fasting for long periods of time, ketone levels can reach up to 8 mmol/L, which is a safe level [ 18 ].Ketone bodies can inhibit their own production, typically preventing these substances from building up to levels that cause ketoacidosis in type 1 diabetics (approximately 20 mmol/L) [ 29 , 18 ]. Genetic Factors that Determine Whether You Should Adopt a Ketogenic Diet PPAR-alpha activity is required for ketosis. Mice lacking PPAR-alpha have reduced ability to enter ketosis [ 9 , 8 ].People with ApoE 3 (CT for RS429358 ) and ApoE4 genotypes (CC for rs7412 ) may have very high cholesterol when they consume a diet high in saturated fat . The keto diet is contraindicated in this case, since it increases their risk of heart disease [ 30 ].Epileptic patients with certain variants at KCNJ11 (rs8175351, rs5219 , rs5215 ) and BAD (rs34882006, rs2286615) genes had lower responses to ketogenic diet treatments after three months in a study on over 500 people [ 31 ]. Snapshot Proponents Often prescribed to reduce seizures in people with epilepsy May help lose weight May lower blood fat levels May improve blood sugar […]
15 Resistant Starch Health Benefits + Limitations
Eating pure starch may not seem like the healthiest choice. However, resistant starch is an exception: it feeds gut probiotics, balances blood sugar, improves metabolism, and more. Read on to learn the health benefits and side effects of resistant starch. If you are interested in hacking your gut microbiome , this post is a must-read. Mechanisms
Potential health benefits of resistant starch stem from the following properties: By acting as a dietary fiber, resistant starch slows down digestion and absorption in the small intestine and bulks up the stool in the large intestine [ 1 ]
By supporting the production of short-chain fatty acids ( butyrate , acetate, propionate) and other beneficial metabolites in the large intestine [ 3 ]
Short-chain fatty acids support intestinal barrier function (i.e., help repair leaky gut), and healthy secretions of hormones and enzymes in the gut [ 3 ]
Resistant Starch and Metabolic Health
1) May Balance Blood Glucose
Supplementing the diet with resistant corn starch helped control blood glucose levels in overweight individuals [ 4 ].
One study found that consuming high-amylose maize resistant starch daily for six weeks improved glucose balance in 18 overweight adults. Glucose balance is the process of maintaining normal blood glucose levels [ 5 ].
According to preliminary research, there are many ways in which resistant starch may help normalize blood glucose, including: By activating glycogen synthesis genes, it causes the body to store more carbohydrates in our muscles and liver [ 6 ].
Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance occurs when cells fail to respond to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels, and it is associated with a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Resistant starch intake may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the amount of insulin required to manage blood sugar in both animals and humans. It may help by: Increasing the excretion of certain bile acids into the gut, which helps decrease insulin resistance through GLP-1 [ 8 , 9 ].
Reducing fat tissue macrophages, which are immune cells that drive the development of insulin resistance [ 7 , 3 , 10 , 11 , 12 ].
Short-chain fatty acids (fermentation products of resistant starch) signal to the brain and liver to reduce glucose production, which may improve insulin sensitivity [ 13 ].
Increasing adiponectin , which improves insulin sensitivity by increasing fatty acid oxidation and inhibiting liver glucose production [ 14 ].
Increasing ghrelin , which inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from the pancreas [ 15 ].
Type 2 Diabetes
Resistant starch potentially reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in animals and overweight adults by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing blood glucose, and reducing blood fat levels [ 16 , 4 , 12 ].
Supplementing the diet with resistant starch may prevent complications resulting from excess blood sugar in patients with type 2 diabetes. One study of 56 women with type 2 diabetes found that resistant starch improved blood glucose levels, reduced toxins released by bacteria, and increased antioxidants [ 17 , 18 ].
In diabetics, resistant starch consumption also protects the blood vessels from oxidative damage due to high blood sugar and improves endothelial function [ 19 , 18 ]. 2) May Improve Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a group of factors that increase the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. These include large waistline, low HDL cholesterol, high blood pressure, high triglycerides , and blood sugar levels [ 20 ].
In one study of 20 healthy adults, resistant starch decreased the amount of insulin released after food intake, which makes it a promising complementary approach to metabolic syndrome [ 21 ].
Adding resistant starch to the diets of patients with metabolic syndrome improved cholesterol, triglyceride levels, and insulin sensitivity [ 22 , 10 ].
When added to standard treatment, resistant starch decreased LDL and total cholesterol levels while increasing HDL in 19 subjects with metabolic syndrome [ 23 ]. 3) Supports Heart Health
In a double-blind study of 86 individuals, resistant starch type 4 reduced abnormal fat levels in the blood [ 22 ].
The hardening of blood vessels is often a precursor to heart disease. Resistant starch potentially reduces the risk factors involved in the hardening of blood vessels in overweight individuals [ 4 ].Resistant starch reduced cholesterol and triglyceride levels in multiple animal studies [ 1 , 24 , 25 ]. 4) May Protect the Kidneys Supplementing the diet with resistant starch decreased toxic metabolite (indoxyl sulfate and p-cresol sulfate) levels in 56 patients on kidney dialysis [ 26 ].A diet with high-amylose maize starch slowed down chronic kidney disease (CKD) by decreasing oxidative stress , reducing inflammation, and preventing colon lining damage in rats [ 27 ]. 5) May Support Weight Control Please note that the effects of resistant starch on weight control stem from preliminary low-quality research. Although it may theoretically support metabolism and weight control in multiple ways, solid clinical evidence is lacking. Weight Gain and Metabolism In obesity-prone rats, dietary resistant starch and regular exercise prevented weight gain by reducing energy (food) requirements [ 28 ].It reduces fat accumulation and blood glucose levels and increases the breakdown of fat through fermentation in the intestines, thus potentially improving weight control [ 29 , 30 ].Resistant starch may stimulate fat burning by: Forcing the body to burn fat by lowering blood glucose [ 31 ]. Consuming dietary resistant starch increases the appetite-reducing hormone peptide YY ( PYY ), which promotes satiety and fullness [ 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 ].A study of 20 healthy adults found that consuming resistant starch over a 24-hour period significantly reduced the amount of food eaten. Although food intake was lower, there was no association between food consumption and how subjects rated their appetite [ 21 ]. Resistant Starch and Digestive Health 6) Acts as Prebiotic Prebiotics stimulate the growth of beneficial or probiotic gut bacteria .By increasing the number of good bacteria in the large intestine, resistant starches may offer several health benefits, such as […]
Health Benefits of Dietary Nucleotides: + Side Effects

You are what you eat – there may be more truth to the phrase than we realize. Nucleotides are organic molecules found in most of the foods that we eat. Our body then uses these nucleotides to build our DNA. Can certain people benefit from nucleotide supplements? Read on to learn about the potential health benefits and the evidence behind them. What are Nucleotides?
Nucleotides are organic compounds that are essential in all living organisms. They act as building blocks for DNA and RNA, which contain all of our genetic information.
Nucleotides also play a critical role in metabolism and energy. They transport energy in the form of ATP to power different parts of the cell. This energy is used to create new proteins, cells, and other vital components [ 1+ ].
There are several different ways we obtain nucleotides. The primary source is from our own bodies. The human body naturally produces nucleotides by either creating them from scratch or salvaging parts from cells [ 2 ].
Food is another important source of nucleotides. They are naturally found in meats, fruits, and vegetables. Foods that have high cell density (organ meats, fish, and seeds) contain the highest nucleotide levels [ 2+ ].
Nucleotide supplements are also available. However, these supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use. Supplements generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing.
Normally, we receive all the nucleotides we need from our body and diet. Limited studies suggest that we may need additional nucleotides when our bodies are stressed – possibly from infection, injury, or during rapid growth. The evidence is still insufficient to support supplementation in these instances [ 2 ].
Some scientists hypothesize that areas in the body that experience a high turnover of cells may benefit the most from nucleotides. Cells in the immune system , liver, and gut tend to have very short lives and new cells must be constantly made. This results in a high demand for nucleotides in these areas of the body, at least in animal experiments. Human data are lacking [ 3 ].
Few studies have explored the purported benefits of nucleotide supplements. Anecdotally, nucleotides improve the immune system and repair cells in the liver and gut. Clinical trials are needed to verify these claims [ 1+ , 2 ]. Snapshot
Proponents
Naturally found in food
Claimed to boost the immune system
May support liver and gut health
Skeptics
Not well studied in humans
Long-term safety and side effects unknown
May increase uric acid levels
Effects of specific nucleotides mostly unexplored
Nucleotide Building Blocks
Each nucleotide consists of 3 main parts: a sugar molecule, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group [ 4+ ].
The sugar molecule acts as a backbone for the nucleotide. Depending on the chemical structure of the sugar molecule, it is classified as either ribose or deoxyribose. Ribose is used to build RNA, while deoxyribose is used in DNA [ 4+ ].
Attached to one side of the sugar molecule is a phosphate group. The phosphate group helps link the sugar molecule to other nucleotides, allowing them to form long chains. Phosphate groups can also provide energy when multiple ones are attached [ 4+ ].
The nitrogen-containing base is attached to the other side of the sugar molecule. In our DNA there are 4 types of nitrogen bases, represented by the letters A, T, C, and G. These different bases form the genetic language of our DNA. We have all the same bases in our RNA as in our DNA except for one: in RNA, the base labeled as T is replaced by U [ 4+ ].
All in all, this gives us 5 bases for nucleotides:
If there is no phosphate group, the molecule is called a nucleoside (indicated in parentheses above, e.g. adenosine). Basically, scientists say that the body uses these nucleosides only to make nucleotides [ 4+ ].
Supplements can contain a mix of all 5 nucleotides if they’re a DNA/RNA complex. This means that they should have all the following: Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) Thymidine Monophosphate (TMP) Guanosine Monophosphate (GMP) Uridine Monophosphate (UMP) If the supplement is RNA-only, then it won’t have TMP. Some nucleotides like UMP are also sold individually. How Are Nucleotides Created? Research reveals that our bodies have two ways of creating nucleotides. The first pathway involves building brand new ones from amino acids. Creating nucleotides through this pathway requires a lot of energy [ 2+ ].The salvage pathway creates nucleotides from other pre-built nucleosides and bases. This method requires far less energy and is preferred by areas of the body that have high nucleotide demands, like the gut [ 10 ].Food is another important source of nucleotides. Our stomachs contain enzymes that break down proteins and cells into nucleotides. We also have enzymes that convert nucleotides to nucleosides, which are better absorbed [ 11+ ].Once nucleotides are created by the body or absorbed from food, they can be used for a variety of functions. Multiple nucleotides can be chained together to form strands of DNA. Nucleotides can also be converted to other forms that help in metabolism and regulation [ 4+ ]. Potential Health Benefits of Nucleotides The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of dietary nucleotides for any of the below-listed uses. Remember to speak with a doctor before taking dietary nucleotide supplements, which should never be used as a replacement for approved medical therapies. 1) Immune Support Some scientists think that nucleotides may help support the immune system, where cell turnover is high. Some cells in the immune system live for only 1-3 days, meaning new cells need to be constantly created. Theoretically, nucleotides can provide ready-to-use parts, saving the body time and energy [ 3+ ].Human research on nucleotides and the immune system mainly focused on infants. This is […]
21 Foods that May Be Good For the Liver
Your liver is vital to your health. When working well, the liver efficiently detoxifies chemicals and built-up metabolic waste. It also stores sugar as glycogen, breaks down old red blood cells , and produces hormones and proteins. Natural medicine can go a long way in improving liver health. Read on for a full breakdown of the best liver-protective foods and supplements. Foods that Are Good for the Liver
People who have liver problems are often told to closely examine their diet and supplements regimen. The same goes for anyone who wants to support their liver health.
Many “fad” diets restrict important food groups. Some go as far as to exclude many healthy fats, which is often detrimental to overall health.
As a general rule, it’s important not to stress the liver by eating more than the body needs. However, a plethora of research highlights the importance of getting a variety of nutritious, antioxidant-rich foods, and healthy fats [ 1 , 2 ].
Remember to speak with your doctor before making any major changes in your diet.
The following natural substances have shown promise for supporting liver health in limited, low-quality clinical trials or animal studies. Additionally, some human studies look only for associations, which means that a cause-and-effect relationship can’t be established.
Therefore, there is currently insufficient evidence to support the use of the foods listed below in the context of liver disease, and they should never replace what your doctor prescribes.
Remember to talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement or making significant changes to your diet. 1) Seafood
Seafood has taurine , which seems to protect against oxidative stress -induced liver damage and fibrosis in rats [ 3 ].
Seafood is also rich in omega 3 fatty acids that are hypothesized to have beneficial effects on liver lipid metabolism, fatty tissue function, and inflammation [ 4 ].
Omega-3s may also decrease liver fat according to one study [ 5 ].
A meta-analysis indicates that eating plenty of white meat or fish might reduce the risk of liver cell carcinoma (HCC), but far more research is needed [ 6 ]. 2) Eggs
Egg yolks abound in choline , which is thought to enhance the liver’s detoxification of fats and cholesterol . Hence, eating more eggs is hypothesized to prevent Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), but large-scale human data is needed to confirm this link [ 7 ].
On the other hand, the consequences of choline deficiency on the liver are well known. According to one study, 77% of men and 80% of postmenopausal women deprived of dietary choline developed fatty liver or muscle damage. Once they were given choline, their liver function recovered [ 8 ].
Intravenous choline improved hepatic steatosis associated with parenteral nutrition in one study, but larger trials are needed [ 9 ]. 3) Liver
Animal liver contains uridine and choline, which are often seen as essential for a healthy liver. Beef liver is the richest source of choline (333 mg in 100 gms of food) [ 10 ]. 4) Chicken
Chicken contains carnosine , which is hypothesized to protect against toxin-induced liver injury in rats due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory properties [ 11 ].
According to one limited cohort, white meat (like chicken) intake was associated with reduced risk of chronic liver disease and liver cancer in both men and women. Better-designed trials are needed to determine the impact of white meat intake on liver cancer risk [ 12 ]. 5) Blueberries & Probiotics
This one seems like an unlikely combination. But scientists think that both blueberries and probiotics may protect animals from acute liver injury. They are hypothesized to reduce liver cell injury, inflammation, and pro-inflammatory cytokines and improve antioxidant activity. Human data are lacking [ 13 ].
Blueberries are rich in antioxidants, while probiotics have many potential benefits on overall gut and liver (and brain) health. Read more about probiotics here.
Also, proanthocyanidins from blueberry leaves are being investigated for suppressing the replication of the hepatitis C virus in test tubes – though it’s far too early to draw any conclusions [ 14 ]. 6) Beets
Beets contain a pigment called betalain, which may protect the liver from oxidative stress and chronic inflammation based on animal experiments [ 15 ].
The liver-protective potential of beetroot (table beet) and beetroot extracts (betacyanin) are also being investigated in mice [ 16 , 17 ]. 7) Olive Oil
An olive-oil rich diet decreased the buildup of triglycerides in the liver in limited clinical trials. Scientists think it might be helpful for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) patients who have high triglycerides , but large clinical trials are needed to confirm this [ 18 ].
One small study in patients with NAFLD demonstrated that olive oil has protective effects. The authors said it may improve glucose and lipid metabolism and prevent atherogenesis (hardening of the arteries) [ 19 ]. They also mentioned the Mediterranean diet, in general, as potentially good for people with NAFLD.
In animal experiments, extra virgin olive oil and its extracts had protective effects against oxidative damage of the liver tissue when exposed to toxins (by preventing excessive lipid peroxidation) [ 20 ]. 8) Carrots Biofortified Carrot (carrots with increased bioactive compounds) intake increases liver antioxidant capacity and Vitamin A status in animals [ 21 ].Carrots are also being researched for protecting against liver injury, modifying bile acid excretion, and increasing antioxidant status in animals [ 22 , 23 ].In rats chronically poisoned with alcohol, oral supplementation with β-carotene seemed to reduce oxidative stress, cell death, and inflammation [ 24 ].Human data are lacking. 9) Garlic Garlic is often described as a powerful nutraceutical , but its effects on liver health are still largely unknown.One study suggested that 15-week garlic supplementation may decrease body fat mass among NAFLD patients. The authors hypothesize that garlic may reduce the amount of fat in the liver and prevent or delay the progression of NAFLD, but larger trials are needed to verify these claims [ 25 , 26 ].Some small […]
19 Potential Ways to Stimulate Synaptic Plasticity

“Synaptic plasticity” refers to the brain’s ability to adjust how neurons connect to and “talk” to each other, which in turn affects how the brain processes information. This process is crucial for all forms of learning and memory – but are there ways to “boost” synaptic plasticity in the brain? In this post, we’ll review what the latest science has to say about some dietary compounds and supplements that may potentially affect synaptic plasticity throughout the brain. Read on to learn more! Synaptic Plasticity: A Quick Review
Synaptic plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to adjust how neurons connect to and “talk” to each other, which in turn affects how the brain processes information.
Synaptic plasticity is critical to our ability to learn and store new knowledge and memories, since the brain has to be able to change its structure in order to encode new information and facts!
Deficits and other changes in the cellular processes underlying synaptic plasticity are also believed to be involved in a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders, making it very important for overall brain health and psychological well-being.
P.S: For a more detailed overview of what synaptic plasticity is, how it works, and why it’s important, check out our detailed SelfHacked post all about synaptic plasticity here . Dietary Compounds And Supplements That May Increase Synaptic Plasticity:
According to some preliminary research, there may be a number of foods and dietary compounds that may support or stimulate synaptic plasticity throughout the brain [ 1 , 2 ].
However, whether consuming the foods and supplements below can actually result in noticeable changes in cognitive function is still an open question. While there is some early research with promising results so far, a lot more research will be needed to fully confirm these effects in healthy human users, and so far there is “insufficient evidence” to officially recommend these strategies for enhancing cognitive functions or treating diseases. Therefore, these early findings should be taken with a grain of salt until more extensive research is done to figure out their full effects.
With that in mind, let’s see what some of the latest science has to say about some nutritional compounds and dietary supplements that may potentially help boost synaptic plasticity! INSUFFICIENT EVIDENCE:
1) Polyphenols May Stimulate Synaptic Plasticity
Fruits, vegetables, cereals, and beverages contain natural polyphenols . Grapes, apples, pears, cherries, and berries may contain up to 200-300 mg of polyphenols in each 100-gram serving [ 3 ].
Phenolic acids, flavonoids, phenolic amides, resveratrol , lignans, curcumin , rosmarinic acid/caffeic acid, ellagic/gallic acid, and tannins are all specific types of polyphenols [ 4 ].
According to some early research, polyphenols possess unique molecular properties that have been reported to reduce oxidative stress , and may even stimulate the activation of molecules that aid in synaptic plasticity [ 5 ]. 2) Red Wine and Resveratrol May Enhance Learning Ability
Resveratrol is a polyphenol abundant in grapes, red wine, berry fruits, and some nuts [ 4 ].
According to some preliminary animal studies, resveratrol has been reported to increase AMPAR protein levels, AMPAR synaptic accumulation, and the strength of excitatory synaptic transmission in the neurons of rats [ 6 ].
AMPARs are glutamate-associated receptors that are believed to be particularly important for fast excitatory transmission, and synaptic plasticity in general [ 6 ].
In one animal study, resveratrol was reported to significantly enhance the learning ability of diabetic rats. The authors of this study propose that this may be because resveratrol has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, as well as the ability to facilitate hippocampal structural synaptic plasticity [ 7 ].
In another study, six weeks of resveratrol supplementation resulted in normalization of the expression of genes implicated in hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in diabetic mice [ 8 ].
A few more recent studies have reported that resveratrol may activate the SIRT1 gene , an aging-related gene that is believed to have important anti-inflammatory effects [ 9 , 10 ].
Additionally, mice born without the brain-specific SIRT1 gene have been reported to show decreased overall synaptic plasticity [ 11 ]. 3) Green Tea May Improve Memory
The active compounds in green tea are predominantly polyphenols and caffeine . According to one animal study in mice with impaired long-term memory due to abnormal levels of the DYRK1A gene (believed to be involved in learning), green tea polyphenol treatment partially reduced the resulting cognitive deficits [ 12 ].
According to a recent review, green tea polyphenols (such as EGCG ) may help increase cognitive function and mood , while also protecting against various cognitive and psychiatric disorders [ 5 ].
In one 12-participant study (DB-RCT), green tea extract was reported to increase working memory [ 13 ].
Additionally, green tea extract was reported to increase both working and spatial memory in an animal study in mice [ 14 ].
Flavonoids , a group of major constituents of green tea, have also been reported to inhibit cell death triggered by neurotoxic compounds and an increase in synaptic plasticity, according to another review [ 15 ]. 4) Berries May Have Anti-Aging Properties
Some recent studies have reported that berries may potentially help improve cognitive functions. Natural compounds found in many types of berries have been reported to reduce inflammation as well as potentially increase cell survival, neurotransmission, and overall neuroplasticity [ 16 ].
According to some cell- and animal-based studies, aging animals given a blueberry-enriched diet were reported to show an increase in both long-term potentiation and synaptic strength, up to the levels commonly observed in younger animals [ 17 ]. Resveratrol , a phenolic compound abundant in berries, has been reported to protect neurons against amyloid beta-induced toxicity (involved in Alzheimer’s), and may even reduce memory degeneration (in rats) [ 18 ]. 5) Soy May Improve Spatial-Memory Acquisition Soy contains plant-derived, non-steroidal compounds with estrogen-like effects ( phytoestrogens ) [ 19 ].A few preliminary studies have suggested that estrogens may help stimulate learning and memory – at least in women [ 20 , 21 ].In another early study, […]
3 Potential Uses of Coluracetam + Side Effects & Safety
Coluracetam is a nootropic that proponents believe can help memory and learning, depression, anxiety, as well as to improve vision. However, research is sorely lacking, and the company that was developing coluracetam has since closed. Learn the whole story here.
Note : We recommend strongly against using coluracetam or any other unapproved experimental drug. Some of our readers who were already taking the drug requested that we commission a post on it and we are simply providing information that is available in the clinical and scientific literature. Please discuss your medications with your doctor. What is Coluracetam?
Coluracetam, also known as BCI-540 or MKC-231, is a nootropic of the racetam class.
Coluracetam was originally studied in Japan in the mid-1990s for Alzheimer’s treatment. These studies showed coluracetam’s ability to repair memory and learning in mice with damaged nerve cells. However, none of the research on Alzheimer’s has ever been published [ 1 ].
Coluracetam’s second round of research, by Brain Cells Inc., on more than 100 people with major depression and anxiety , is reported to have shown benefits for major depressive disorder (MDD). However, these trials were never published either . Mechanism of Action
Coluracetam is unique among brain enhancers in that it improves choline uptake in the nerve cells via the choline uptake system (HACU) in cell studies. This choline uptake system could potentially increase the amount of acetylcholine in the brain. According to some researchers, coluracetam could, therefore, restore this choline uptake system after nerve cell damage; this has yet to be confirmed in animal or human trials [ 2 , 3 , 4 ].
Coluracetam also protects the NMDA receptors from glutamate toxicity. Damage to these receptors is involved in stroke, Alzheimer’s, traumatic brain injury, and other brain diseases [ 5 ]. Treatment-Resistant Depression Study
In a study (double-blind randomized controlled trial) of 101 people with depression who had failed treatment with 2 antidepressants and also had anxiety, coluracetam had a positive effect on depression scores at doses of 80 mg 3 times daily [ 6 ].
Unfortunately, this is the only published human study on coluracetam. There is nowhere near enough evidence to support its use, and safety data is also sorely lacking. The risks overwhelm the potential benefits; this is why we strongly recommend against using coluracetam.
No clinical evidence supports the use of coluracetam for any of the conditions listed in this section. Below is a summary of the existing animal and cell-based research, which should guide further investigational efforts. However, the studies listed below should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit.
Furthermore, it’s important to remember that coluracetam has not been approved by the FDA for any medical purpose. It is currently illegal to import and sell coluracetam in the United States [ 7 ].
We therefore strongly recommend avoiding coluracetam. The following animal research is included for educational purposes only. 1) Memory and Learning
Coluracetam improved memory and learning in rats treated with a nerve toxin that damages the choline uptake system in the brain. This improvement surprisingly lasted beyond treatment. However, these benefits in learning and memory were not seen in rats who were not exposed to the nerve toxin [ 2 , 3 , 4 ].
Acetylcholine levels are often lower in those with Alzheimer’s. By boosting acetylcholine in the hippocampus, coluracetam may improve some Alzheimer’s symptoms, such as poor memory and learning [ 8 ].
In rats that were given the recreational drug PCP (which inhibits ChAT , the enzyme that creates acetylcholine), coluracetam repaired the damage to the learning function by increasing ChAT [ 9 ]. 2) Anxiety
In a rat study, dosing 21 days of coluracetam led to a 20% improvement in anxiety , which was greater than the 12% effect valium had in a single dose in the same study [ 10 ]. 3) Schizophrenia
The enzyme that helps make acetylcholine (ChAT) is impaired in schizophrenia [ 11 ].
Coluracetam increased the activity of ChAT in rats with nerve cell damage. More research directly on people with schizophrenia is needed [ 9 ]. Side Effects, Interaction, Supplementation, Dosage
Side Effects
Users report brain fog , low mood , suicidal thoughts, and changes in response to coluracetam based on their sleep levels.
An unpublished study of levels up to 240 mg daily did not report major side effects in humans [ 12 ]. Drug Interactions
Coluracetam may counteract the effects of anticholinergic drugs, such as Benadryl, Parkinson’s medications, and some antipsychotics.
Coluracetam may also increase the effects of cholinergic drugs, such as some medications for glaucoma and Alzheimer’s, and nicotine .
It may also interact with drugs that act on the NMDA receptor, such as cough suppressants and anesthetics.
To avoid adverse effects and unexpected interactions, we recommend talking to your doctor about better-studied and safer alternatives to coluracetam. Forms of Supplementation
Coluracetam can be taken: Orally – capsule or power Under the tongue Proponents of coluracetam believe that its benefits come from an increase in acetylcholine. A better and safer way to increase acetylcholine may be to eat foods rich in choline, the precursor to acetylcholine. Choline can be found in [ 13 ]: Eggs Beef & beef liver Scallops Chicken Salmon Cod Shrimp Broccoli Many people who take coluracetam also take choline as CDP-Choline or Alpha-GPC to enhance coluracetam’s effects and reduce possible side effects. No evidence supports these combinations. Dosage There is no safe and effective dose of coluracetam because no sufficiently powered study has been conducted to find one. Furthermore, safety data is lacking. Limitations and Caveats The only research on coluracetam that has been published is in rats and mice, whereas human research has not made it to publication. As of January 2014, the company BrainCells Inc, the last company to research coluracetam, is closed . With the numerous side effects listed from users and no long-term studies, we strongly recommend against using coluracetam . User Experiences While not being studied extensively, nootropics users say […]
4+ Jicama Benefits + Carbs, Calories & Nutrition Facts

Jicama is a low-fat, low-calorie root vegetable originating from Mexico. It is rich in fiber, nutrients, and antioxidants. According to early studies, it may help digestion, heart health, blood sugar, and metabolism; learn more about its potential benefits here. What Is Jicama?
Jicama (pronounced hee-kah-mah or hick-ah-mah ) is a tuberous root vegetable, with golden-brown skin and a starchy white interior. It is also known as Yam bean , Mexican potato , or bengkoak and belongs to the Pachyrhizus tropical plant family [ 1 , 2 ].
Jicama originates from Mexico but has spread to Central America, Philippines, China, Malaysia and Southeast Asia [ 3 ].
Jicama is a food full of nutrients and low in calories. It contains some immune-stimulating proteins ( albumins , globulins ) but seems to be low in lectins [ 4 , 5 ].
Another major benefit is its low glycemic score. This makes it a great dietary choice for people with diabetes. It is also high in fibers that aid in digestion and promote gut health. Plus, it is packed with essential nutrients – such as vitamin C , potassium and magnesium – that lower oxidative stress and fight inflammation [ 6 , 7 ].
And unlike most tubers, it can be eaten raw. Alternatively, cook it for flavor with your favorite spices. It’s extremely versatile and can be prepared in vegan , paleo, and keto recipes [ 8 , 9 , 10 ].
But beware! Its seeds, stems, leaves, and skin are toxic . Only the white inside flesh is edible [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Snapshot
Here is an overview of the health benefits and risks of jicama [ 1 , 2 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]: Proponents:
Low-calorie
High nutritional value
Rich in antioxidants and fiber
Possible benefits to digestion, immunity, heart function, and blood sugar
Skeptics:
Seeds, stems, leaves, and skin are toxic
Jicama Nutrition
Jicama’s nutrient profile (100gr) and recommended daily intake (RDI) based on a 2000 calories diet [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 7 , 17 ]: Calories
Jicama is composed of around 90% water, so it’s naturally low in calories . A serving cup of jicama (100 gr) contains only 38 calories and has a low glycemic index, making it ideal for weight loss and people with diabetes [ 14 , 18 ]. Carbohydrates
Jicama (100 gr) contains 8.82 g of carbohydrates from which 4.9 g is fiber and 1.8 g sugar, whereas the starch accounts for 2.2 g. This makes jicama a low-carb vegetable, keto- and paleo-friendly [ 7 , 19 ].
Furthermore, a reasonable 200g of jicama makes up for 26% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) for fiber for men and 40% for women (based on a 2,000 calories diet) [ 7 , 19 ]. Fats
Jicama is a low-fat food, providing less than 0.1 gram per 100gr [ 7 , 14 ]. Proteins
The proteins in jicama are low, only 0.72 g in 100 g. This is half the amount in regular potatoes, but double the amount in sweet potatoes. Jicama also contains amino acids, such as alanine, aspartic acid , lysine , histidine , leucine , and glutamine [ 20 , 21 ]. Nutrients
Jicama is a good source of vitamin C . Just 200g would provide you with almost 70% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that lowers the risk of many chronic diseases. Keep in mind that cooking jicama will lower its vitamin C levels, though [ 3 , 22 ].
Other vitamins include folate , riboflavin (V2) , vitamin B6 , vitamin E , niacin , and thiamine . About 200g of jicama would provide you with only up to 6% of your daily needs of these vitamins, which might not be high enough to have a significant health effect [ 3 ].
But 300g of the root will provide you with ~12% of your daily potassium and 9% of your daily magnesium requirements – pretty good for a low-calorie tuber [ 7 , 23 , 24 ]! Antioxidant Activity
Jicama is high in antioxidants, especially vitamin C . As mentioned, 300g of jicama will cover your daily needs – if you eat it raw. Small amounts of other compounds – potassium , magnesium , vitamin E , folate and selenium , flavonoids, and choline – add to its antioxidant effect [ 3 , 25 ].
Altogether, these nutrients lower oxidative stress , prevent cell damage and fight inflammation [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ].Diets rich in antioxidants are associated with lower rates of many diseases, including cancer, obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 ]. Potential Benefits of Jicama The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of jicama for any of the uses discussed below. Jicama is considered safe to eat as food, but it has not been approved by the FDA for medical use, and it should never be used to replace something your doctor recommends or prescribes. 1) Gut Flora Jicama contains significant quantities of a fiber called inulin , which is also responsible for its sweet flavor [ 36 , 7 ]. Inulin acts as a prebiotic that feeds the good gut bacteria (such as Bifidobacteria ). In turn, it may boost gut health and improve IBD and IBS symptoms, such as stomach pain and bloating [ 12 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ].Thanks to its inulin content, jicama could potentially also aid in digestion. In clinical studies with over 300 adults and children with constipation, inulin improved bowel movements and stool consistency [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ].Note that this benefit has only observed with inulin itself; no studies of whole jicama have investigated its effect on gut flora and gut health. 2) […]
12 Benefits of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF) + Side Effects
7,8-DHF is an investigational plant compound and a new nootropic. It has attracted a lot of attention in recent years because it targets a brain receptor that helps grow new neurons. Learn about its potential here. What Is 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone?
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF) is a flavone found in plants. It was discovered while searching for molecules that imitate the function of brain-derived neurotrophic factor ( BDNF ) [ 1 , 2 ].
BDNF promotes the growth of neurons and synapses (synaptogenesis) and is very important for normal brain function. Lower amounts of BDNF are observed in diseases such as depression , Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and schizophrenia [ 1 , 3 , 4 ].
Studies in animals show that 7,8-DHF could potentially help with brain repair, long-term memory, depression, and neurodegenerative diseases. However, studies in humans have not yet begun [ 2 ]. Mechanism of Effect
7,8-DHF mimics the effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor ( BDNF ) in brain cells by activating tropomyosin-related kinase B ( TrkB ) receptors, the typical target of BDNF [ 5 ].
The therapeutic potential of BDNF is restricted due to its short half-life (less than 10 minutes) and its inability to cross the blood-brain barrier because of its large size. Unlike BDNF 7,8-DHF is able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and enter the central nervous system (CNS) [ 1 ].
7,8-DHF also increases the production of Nrf2 . Nrf2 increases antioxidants enzymes such as heme oxygenase 1 ( HO-1 ) and also enzymes that repair DNA (8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1 – OGG1) [ 6 , 7 ]. Antioxidant Activity
7,8-DHF rescues cells from damage and death caused by oxidative stress [ 8 ].
Cells do not need to have the TrkB receptor to be protected [ 8 ].
In this case, 7,8-DHF:
Because of the relatively low apparent bioavailability of 7,8-DHF (about 5% in mice), researchers are currently developing prodrugs that can be converted to 7,8-DHF once inside the body. The most promising of these is currently known as R13, which has eliminated plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease in the brains of living mice [ 12 , 13 ].
R13 has not yet been tested in humans, and we do not recommend using it until such studies are conducted. Animal & Cell Research on 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone
No clinical evidence supports the use of 7,8,-DHP for any health condition , as all research thus far has been preclinical. Below is a summary of the existing animal and cell-based research, which should guide further investigational efforts. However, the studies listed below should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit.
7,8-DHF improved object recognition (a test used to determine learning and memory) in healthy rats when given immediately following and three hours after learning. It also improved memory in mice with dementia [ 14 ].
In rat models of post-traumatic stress disorder ( PTSD ), 7,8-DHF prevented stress-related memory impairment [ 15 , 16 ].
7,8-DHF also improved memory in aging rats [ 17 , 18 ].
7,8-DHF promoted the repair of damaged neurons [ 19 ].
It also increased the production of new neurons in the brains of adult mice after brain injury and promoted neuron growth in aged mice [ 20 , 21 ].
Similarly, 7,8-DHF, along with exercise , improved brain function in rats that experienced traumatic brain injury [ 22 ].
7,8-DHF protected against stroke-related brain damage in mice. The beneficial effect was more pronounced in females [ 11 , 23 ].
7,8-DHF also prevented neuronal damage in mice after traumatic brain injury [ 24 ].
7,8-DHF decreased the release of inflammatory factors in brain cells by blocking NF-κB [ 25 ].
7,8-DHF also reduced the levels of inflammation-causing nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2 ( PGE2 ), TNF-alpha , and IL-6 in macrophages ( white blood cells ) [ 26 ]. Alzheimer’s Disease
Reduced amyloid plaque formation
Reduced oxidative stress
Prevented loss of synapses Prevented memory deficits and preserved cognitive function However, another study found no benefits in treating mice with Alzheimer’s-like brain damage with 7,8-DHF [ 31 ]. Parkinson’s Disease 7,8-DHF improved motor function and prevents the loss of dopamine -related neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [ 32 , 33 , 34 ].It also prevents the death of dopamine-sensitive neurons in monkey models of Parkinson’s disease [ 35 ]. Huntington’s Disease 7,8-DHF delayed the motor and cognitive impairment and prolonged survival in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease [ 36 , 37 ]. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) 7,8-DHF improved motor deficits and neuron survival in a mouse model of ALS [ 38 ]. Multiple Sclerosis 7,8-DHF reduced disease severity in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis [ 39 ]. Schizophrenia 7,8-DHF decreased cognitive deficits and improved learning and memory in rat models of schizophrenia [ 40 ].Infections in pregnancy and subsequent abnormal brain development can increase the risk of schizophrenia in offspring. Early use of 7,8-DHF decreased behavioral abnormalities and psychosis in mice offspring at risk of developing a schizophrenia-like disorder [ 41 , 42 ]. Down Syndrome In a mouse model of down syndrome, early intervention with 7,8-DHF increased the production of new neurons (hippocampus) and improved learning and memory [ 43 ]. Fragile X Syndrome Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition. It causes a range of developmental problems including cognitive impairment and learning disabilities.In a mouse model of fragile X syndrome, 7,8-DHF improved cognitive function and reduced spine abnormalities [ 44 ]. Rett Syndrome Rett Syndrome is a non-inherited genetic brain disorder, mainly affecting girls. Symptoms include unusually slower growth, difficult coordination control, and language issues.7,8-DHF improved symptoms in a mouse model of Rett syndrome [ 45 ].7,8-DHF improved depression in mice that experienced social defeat [ 46 ].It also reduced depressive behaviors in rodents experiencing chronic stress [ 47 , 48 ].7,8-DHF decreased abnormalities in behavior and dopamine transport in mice on METH (methamphetamine) [ 49 , 50 ].7,8-DHF also reduced the rewarding effects of cocaine in mice [ 51 ].7,8-DHF reduced fat production and fat build-up by increasing antioxidant enzymes and neutralizing reactive oxygen […]
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH) Roles & Regulation
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus. It controls thyroid hormone secretion and has important roles in metabolism, cognition, mental health, and more. This post reveals lesser-known roles of TRH, along with 13 factors that increase or decrease its levels. What is Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)?
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus. It stimulates the release of TSH, which then increases thyroid hormones. Thus, TRH controls [ 1 ]: energy balance (homeostasis)
eating patterns
thermogenesis (heat production)
autonomic regulation (the unconscious control of vital bodily functions)
The hypothalamus, pituitary, and the thyroid gland (also called the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid or HPT axis) controls T4 levels [ 2 ].
These three glands release the following hormones: TRH (Hypothalamus) -> TSH (Pituitary) -> T4 (Thyroid).
If there is too little of the thyroid hormones in the bloodstream, the hypothalamus will signal the pituitary gland (via TRH) to produce TSH for the thyroid to release more T4.
Hypothyroidism that is caused by low TRH is called hypothalamic hypothyroidism, or central hypothyroidism. Reference Range
Normal Range of TRH is 5-25 U/ml , but it may depend on the lab. Roles of TRH in Health & Disease
1) Learning and Memory
TRH is widely found in the brains of mammals and is considered a neurotransmitter [ 3 ].
Whether TRH has a positive or neutral effect on cognitive function is still debated.
A rat model of Alzheimer’s showed no beneficial effects of TRH in learning and memory [ 4 ].
However, other studies have found TRH to enhance learning and reduce memory impairment [ 3 ].
In rabbits, chronically high levels of TRH improved learning and memory [ 3 ].
TRH and similar hormones are promising research agents in the treatment of brain degeneration, but the clinical evidence is lacking [ 1 ]. 2) Mental Health
Depressed patients do not produce as much TSH in response to TRH and have decreased TRH gene expression in the hypothalamus. Hypothyroidism is found in many patients with major depression [ 5 , 6 ].
In mice, TRH functions by activating two receptors – TRH-R1 and TRH-R2, the latter of which is not found in humans. Activation of these receptors initiates a number of effects in the brain. Mice lacking TRH receptor type 1 (TRH-R1) are more depressed and anxious. These mice exhibited hypothyroidism [ 7 ].
Mice lacking TRH receptor type 2 (TRH-R2) have no thyroid abnormalities, with regular development and growth. However, female mice were slightly more depressed but less anxious than male mice [ 7 ].
Rats treated with TRH showed less anxiety in stressful situations [ 8 ]. 3) Appetite Control
TRH may suppress appetite. Both fed and food-restricted animals ate less food when injected with TRH [ 9 ].
Generally, the presence of healthy dopamine levels can reduce eating for pleasure, which helps with weight loss . Hungry rats injected with TRH had more dopamine [ 10 , 9 ]. 4) Blood Sugar Control
TRH is also made in the pancreas. It inhibits amylase secretion and increases glucagon secretion from the pancreas [ 11 ].
Genetically modified mice that lack TRH have elevated blood sugar (hyperglycemia) [ 12 ].
Injection of TRH combats elevated blood sugar in hyperglycemic mice, by reducing damage and stimulating regeneration of insulin -producing cells in the pancreas [ 12 ]. 5) Digestion In the brain, TRH acts through the vagus nerve to increase stomach acid, pepsin, and serotonin , blood flow in the gut lining, and contraction [ 13 , 14 ]. 6) Prolactin Secretion The secretion of TRH can also stimulate the release of prolactin , another hormone from the pituitary gland [ 15 ]. Factors that Increase TRH 1) Low Thyroid Hormones If there is too little of the thyroid hormones in the bloodstream, the hypothalamus will signal the pituitary gland (via TRH) to produce TSH for the thyroid to release more T3 and T4 [ 16 ].Once there is enough of these hormones, they signal the hypothalamus and pituitary to stop this cascade of actions and drop T3 and T4 levels. 2) Estrogen (Estradiol) E2 decreases the effects of ghrelin on the hypothalamus, which also reduces the activity of agouti and neuropeptide Y. This increases levels of TRH in rats [ 17 ].In menopausal mice, feeding estrogen (E2) increased TRH and thyroid hormone levels [ 18 ]. 3) Cold Exposure Cold exposure increases TRH, according to preclinical research. In rats, exposure to 4 degrees C or 39 degrees F increased TRH release by twofold in the first 15 minutes [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. 4) Drugs Lithium increases the TRH production and the response of TSH to TRH [ 23 , 24 ].Valproate and lithium increase levels of TRH receptors in the brain [ 25 ].In rats, administration of ketamine (anesthetic) increases TRH levels in most regions of the brain and the body [ 26 ]. 5) Other Inhibiting Sirt1 In diet-induced obese rats, inhibiting Sirt 1 increased TRH level. Read this post to learn about the factors that inhibit Sirt1.This effect is possibly mediated through circadian rhythm , by changing POMC and a-MSH levels [ 27 ]. Electroconvulsive Therapy Electroconvulsive therapy is a treatment for treatment-resistant depression. In rats, electroconvulsive therapy increased TRH levels, which correlated well with the reduction in depressive symptoms [ 28 ]. Factors that Decrease TRH 1) High Thyroid Hormones High Free T4 and Free T3 levels can signal the pituitary and hypothalamus to adjust TSH and TRH levels.T4 increases the production of pyroglutamyl peptidase II , an enzyme that degrades TRH in the hypothalamus [ 29 ]. 2) Stress and High Cortisol Cortisol can inhibit the HPT axis by reducing TRH levels at the hypothalamus [ 30 , 31 ].However, in cell-based experiments, cortisol stimulated TRH production [ 31 ]. 3) Inflammation In rats, injection of LPS (a bacterial toxin) suppresses the production of TRH, TSH, and T3 levels, while increasing CRH and cortisol levels […]
15 Amazing Jujube Fruit Health Benefits (Ziziphus Jujuba)

Jujube has been used to alleviate stress , reduce inflammation, and enhance immune health for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine. Read on to learn more about the health benefits of jujube, as well as its other uses, interactions, and risks.
Ziziphus Jujuba of the Middle East: Source [ 1 ].
Jujube ( Ziziphus jujuba ) is a fruit-bearing plant first domesticated in South Asia around 9000 BCE. Jujube is known by more than 40 names around the world, being “red date” and “Chinese date” the most common. The two most popular varieties are Li and Lang.
Jujube is still used today to treat digestive disorders, high blood pressure, inflammation, fever, insomnia, and skin infections. More recently, jujube has been used in the food industry as a food additive and flavoring [ 2 ].
Jujube is a natural source of active compounds such as flavonoids and triterpenoids [ 2 , 3 ]: Flavonoids
Triterpenoids
Oleanolic acid: Also known as oleanic acid, a compound with antitumor, antiviral, and anti-HIV properties [ 10 , 11 ].
Ursolic acid : A compound with anti-inflammatory and antitumor activities which may heal liver injury [ 10 , 12 ].
Others
Oleic acid: A fatty acid abundant in olive oil that has anti-cancer and pro-heart health properties, but is also linked to metabolic and inflammatory diseases [ 15 , 16 ].
Ziziphin: A compound unique to jujube leaves that blocks human taste receptors for sweetness [ 17 ].
Jujube also contains many essential vitamins and minerals necessary for healthy cells [ 18 , 19 ]: Health Benefits of Jujube
1) Jujube May Improve Heart Health and Decrease the Risk of Heart Disease
Jujube treatment (fruit powder, three times daily for one month) decreased total cholesterol and “bad” cholesterol (LDL) levels in obese patients with elevated fat levels in the blood [ 20 ].
Low levels of “good” cholesterol (HDL) and excess fat in the blood (triglycerides) are heart disease risk factors and are linked to obesity. High levels of HDL cholesterol decrease hardening of the arteries and risk of heart disease [ 21 , 22 , 23 ].
Jujube increased HDL levels in diabetic and insulin-resistant mice [ 24 , 25 ].
Jujube extract reduced oxidative stress and thickening of arterial walls in diabetic rats [ 26 ]. 2) Jujube Improves Gut Health
In one study (DB-RCT) of 37 chronically constipated people, jujube extract reduced constipation and increased quality of life compared to placebo [ 27 ].
Jujube leaf extract protected against castor oil -induced diarrhea in rats [ 28 ].
In rats, jujube stem bark protected against stomach ulcers caused by alcohol [ 29 ].
Jujube extract shortened digestion time and protected against oxidative stress and excess ammonia in the gut in rodents [ 19 , 30 ]. 3) Jujube May Protect Against Brain Damage
Glutamate is an important excitatory (causes neurons to fire) neurotransmitter in the brain. Too much glutamate may cause brain damage in stroke, epilepsy, or Parkinson’s. Jujuboside A, a compound in jujube, reduces glutamate levels [ 31 ].
Amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques are involved in the development of Alzheimer ’s disease. Ziziphus mucronota, a close relative of jujube that contains the same compounds , reduced the toxic effects of Aβ plaques on neurons in human brain cells [ 32 ].
Astrocytes are star-shaped cells found in the brain that protect neurons by releasing growth factors and controlling antioxidant enzyme levels. Decreased neurotrophic factors and increased oxidative stress are linked to brain disease. Jujube extract improves astrocyte function [ 33 ]. 4) Jujube May Improve Cognitive Function
Alcohol disrupts learning and memory. Rats treated with jujube extract before being given alcohol had improved spatial memory and learning capacity [ 34 , 35 ].
The dentate gyrus is one of two known areas in the human brain where new neurons develop (neurogenesis). Jujube extract increased nerve cell growth and development in the dentate gyrus of mice [ 36 , 37 ].Estrogen-deficient rats treated with jujube had improved learning and memory function. Jujube also increased estrogen levels in the blood and increased acetylcholine levels in the brain [ 38 ]. 5) Jujube May Improve Sleep and Treat Insomnia Spinosyn, found in jujube, decreased the time to fall asleep and increased sleep length in mice [ 9 , 8 ]. Jujubosides in jujube fruit increased the duration of REM sleep in rats [ 39 ]. Jujube produced calming (sedative) effects in mice at higher doses [ 40, 9 , 31 ]. Suan Zao Ren Tang is a concoction containing jujube that is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat insomnia, and which improves sleep quality and efficiency [ 41 ]. Suan Zao Ren Tang taken alongside Zhi Zi Chi Tang (another concoction in traditional Chinese medicine) improved sleep quality in people with insomnia and anxiety [ 42 ]. 6) Jujube May Protect Against Seizures Jujube extract protected against seizures, improved brain function, and reduced oxidative stress in epileptic rats [ 43 ]. 7) Jujube May Treat Anxiety and Depression Jujube significantly reduces anxiety in mice. Sanjoinine A, a major compound in Jujube, reduced anxiety comparable to the popular anti-anxiety medication Valium [ 44 , 14 ].Jujube seeds contain saponins like jujuboside A/B, which increase GABA receptor activity. Depression and anxiety are linked to low GABA levels [ 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 ].Inflammation may be involved in the development and progression of depression. A jujube concoction ( Z. jujuba, Crataegus pinnatifida, Triticum aestivum, and Lilium brownii ) decreased depressive symptoms and inflammatory molecules ( TNF-α ) in mice [ 49 ]. 8) Jujube Improves Immunity and Reduces Inflammation Jujube is rich in vitamin C (534.94 mg/100 g), which supports immune function and prevents infections by increasing the production of beneficial inflammatory cytokines [ 50 , 51 ].Doxorubicin, a drug used to combat cancer, causes side effects, including severe inflammation. Betulinic acid found in jujube fruit protected immune cells from doxorubicin-induced inflammation [ 52 ].Allergies are often associated with inflammation due to increased inflammatory […]
12 Surprising Health Benefits of Myricetin

Myricetin is a natural substance found in many vegetables and fruits. It is a good antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and offers many other health benefits at very little risk of side effects. Read on to know why you should make myricetin an important part of your nutrition.
Myricetin, also known as myricetol, is a naturally occurring compound that belongs to the group of chemicals known as flavonoids [ 1 ].
Flavonoids are known for their antioxidant properties. Myricetin, in particular, stands out in this group as it is a better antioxidant compared to other flavonoids.
A variant of myricetin (dihydromyricetin or ampelopsin) gives the oriental raisin tree its “anti-hangover” properties. The oriental raisin tree has been used as a hangover cure, as it reduces the alcohol levels in the blood [ 2 ].
Myricetin is also attached to many sugar storing molecules in plants (glycosides). Glycosides in flowers of Roselle are beneficial for patients with high blood pressure, as they reduce blood pressure.
Myricetin occurs naturally in many vegetables and fruits along with other edible parts of plants. Red wine also contains myricetin [ 3 ].
Some of the commonly available fruits and vegetables that are a good source of myricetin are:
Myricetin works by disrupting cellular pathways. It interacts with enzymes and suppresses their activities (enzyme inhibition).
It inhibits phosphodiesterase enzymes (PDE), which are involved in setting up inflammatory responses against injuries or toxins [ 8 ].
Myricetin also blocks aromatase, an enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen . This blockage has the potential to prevent breast cancer [ 9 , 10 ].
Free radicals and reactive oxygen species that form in our bodies can harm our cells, tissues, and bodies.
Myricetin, like all flavonoids, has antioxidant properties [ 11 , 12 ].
In a test tube study, the antioxidant activity of myricetin increased in the presence of ascorbic acid and iron [ 13 ].
Myricetin prevented human platelets (blood cells) from clotting , which is an important step in the inflammation process [ 14 ].
It also suppressed protein kinases (enzymes that enable the function of other enzymes), many of which act as signaling molecules during inflammation [ 15 ].
Since it is a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory molecule, myricetin is also a possible solution for chronic inflammatory disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and atopic dermatitis [ 16 ].
Myricetin also inhibited snake venom PLA2, which causes inflammation and pain [ 16 ].
DNA in normal cells have special genes called oncogenes, or tumor suppressor genes. These genes control cell division and prevent cancer [ 17 ]. If DNA in normal cells undergoes oxidative damage and mutations in these genes occur, it may lead to cancer.
Since myricetin is a good antioxidant, it protects DNA from oxidative damage [ 18 , 19 ]. The prevention of oxidative damage to DNA reduces the risk of cancer .
Although myricetin is a good antioxidant, it can also act as a pro-oxidant in the presence of certain ions such as copper [ 20 , 21 ]. In this form (myricetin-copper complexes), myricetin is toxic to cancer cells causing cell death (apoptosis). Copper-myricetin complexes produce reactive oxygen species that break DNA in cancer cells [ 20 ].
Cisplatin, in combination with myricetin, increased inhibition of cancer cell growth and increased cell death compared to cisplatin by itself [ 22 ].
Myricetin has a chemopreventive potential for the following types of cancer:
In rats, myricetin treatment decreased high blood sugar by 50% within a couple of days of treatment [ 31 ].
Myricetin also increased glucose uptake by muscles and other cells [ 32 , 33 ].
In a study (RCT) of 42 diabetic patients, Blueberin supplement containing 50 mg of myricetin reduced blood glucose when compared to the control group [ 34 ].
Progression of Alzheimer’s disease has been associated with an increased phosphorylation of tau proteins. Myricetin decreased this phosphorylation, and therefore, may slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease [ 23 ].It also blocks β-amyloid aggregates formation, which is associated with Alzheimer’s disease [ 35 ].Myricetin decreases glutamate . Excessive glutamate has been associated with chronic brain disorders [ 36 ].Myricetin improved spatial learning in mice subjected to stress . This improvement was associated with the ability of myricetin to increase BDNF in the hippocampus [ 37 ].Myricetin also increases the activity of GABAA receptors. GABA improves mood, relieves anxiety , and enhances deep sleep [ 38 , 39 , 40 ].When blood returns to tissues after periods of lack of oxygen, it can cause inflammation and oxidative damage to the tissue. This is known as reperfusion injury [ 41 ].Myricetin protects the heart from reperfusion injury by inhibiting the activation of STAT-1 [ 42 ].In guinea pigs, myricetin treatment also caused a 27% decrease in cholesterol deposition in blood vessels [ 43 ].In rats, myricetin reduced oxidative damage as well as reduced high blood pressure. It also slowed down the heart rate and reduced sodium in the urine [ 44 ].Myricetin also decreased toxicity induced by isoproterenol in rats. This shows a potential of myricetin for the treatment of heart attack [ 45 ].Myricetin inhibits the formation of fat-storing cells [ 46 , 47 ].This can help in controlling fat deposition and obesity caused by diets rich in carbohydrates and fats [ 48 ].Myricetin increases Cl‑ secretions in the tissue of the respiratory (breathing) tract. This thins the mucus in cystic fibrosis patients and helps the movement of cilia (hairs that clean trachea by moving mucus out of trachea). The cleanup of the trachea prevents infections by virus and bacteria in cystic fibrosis patients [ 49 ]. It also suppressed the enzyme reverse transcriptase in HIV, which is crucial for virus replication [ 50 ].Myricetin inhibits Fyn , which causes skin cancer in the presence of UV rays [ 51 ].It also suppresses RAF kinase enzyme, which is responsible for wrinkle formation in the skin [ 52 ].In cells, myricetin-3- O -β-rhamnoside (myricetin with an added rhamnose sugar) increased fibroblast (cells that repair wounds) migration to the wound site. This significantly decreased healing time [ 53 ].Cataracts are one of the most common eyesight problems […]
HEMPAVIDA’s Hemp CBD + Wellness Launches at Art Basel in Miami, FL
DREAM (Ambien-alternative Sleep Aid), CHILL (Anti-Anxiety), FOCUS (Brain Booster), RESTORE (Joint & Mobility).
MIAMI, Dec. 10, 2019 /PRNewswire-PRWeb/ — HEMPAVIDA, a new innovative wellness and skin care lifestyle brand, launches its first CBD Hemp + Wellness collection at Art Basel in Miami, FL. Amidst a surge of trending hemp CBD products flooding the market, HEMPAVIDA has created a series of “symptom-specific” wellness products blended with other powerful natural ingredients to target ailments such as insomnia, anxiety, stress, mood stability, arthritis, joint mobility, pain, attention, memory, sleeplessness, social angst, and overall well-being.
Wellness by HEMPAVIDA’s Hemp CBD interacts with pathways in the body to deliver health benefits, but doesn’t bind with receptors in the brain and nervous system, which is why it doesn’t cause a psychoactive effect (getting high); unlike marijuana with THC that does in fact cause a “high-effect”. There has been increasing demand for pure hemp CBD (without high-effects), for moms who complain of “mommy brain fog”, working professions who get random drug tested, college students who don’t want to buy something questionable from the campus “dealer”, baby boomers who are facing skyrocketing pharma costs, and suburban mainstream who want to try a safe alternative remedy.
“It’s not just the mg dosage that makes a hemp CBD-related product effective,” said Kelly Yocum, CEO HEMPAVIDA “blending the right natural ingredients to target specific symptoms is a highly-effective way to dip your toe into the CBD world and ensure you are using it properly to treat your ailments.”
DREAM by HEMPAVIDA is a powerful “Ambien-alternative” natural sleep aid made from a proprietary blend that helps with sleeplessness, insomnia, and correct irregular sleep patterns. DREAM plays a big part in the sleep-wake cycle related to the circadian processes, working naturally to help insomniacs fall into a deep sleep and wake up well rested.
CHILL by HEMPAVIDA is an effective stress-reliever designed to naturally alleviate anxiety, stabilize mood swings, relax social situations, and promote happiness. CHILL is a natural way to relieve tension and give a sense of well-being so users can be more relaxed, positive, an overall better mood without drowsiness or fatigue side-effects.
FOCUS by HEMPAVIDA is a brain booster to help improve cognitive function, memory, focus, clarity, and attention. People are constantly bombarded by information overload finding it hard to stay on track. FOCUS is a natural blend to maintain a healthy brain, be more productive, stay focused and improve memory.
RESTORE by HEMPAVIDA is a blend of potent natural ingredients designed to improve cartilage health by reducing pain, increasing joint mobility, alleviating inflammation, and is used to ease arthritis symptoms.
Consumers nationwide are seeking hemp-based products; however, many hemp CBD supply companies are supplementing with cheap filler ingredients, or just increase the milligram dosage and have had difficulties keeping up with supply and demand. HEMPAVIDA has 3rd party tested, non-GMO, high quality premium hemp extracted using organic farming practices from hemp plants grown on nationally certified farms, and never tests on animals.
HEMPAVIDA is now available on Amazon, and to celebrate the launch of their new products, use 20% off code: CYBER @ http://www.HEMPAVIDA.com.
HEMPAVIDA is in the process of growing its advisory board and executive team as it transitions into its next stage of growth. Request an invitation to one of our investor meetings in Chicago, San Diego, Park City New York, Miami, or San Francisco by contacting kelly@hempavida.com Interested in trying HEMPVIDA? Visit HEMPAVIDA.com and sign up for your chance to get a free sample. Be sure to follow @HEMPAVIDA on Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
ABOUT HEMPAVIDA
HEMPAVIDA is a pure approach to life with clean ingredients from nature. Our products utilize the hemp plant’s natural medicinal properties, infused with other elements from nature to provide powerful effective benefits from the inside-out. Interested in being a HEMPAVIDA social media influencer? We are looking for active engaging social media influencers for paid opportunities to help us get the word out. For more information contact: kelly@hempavida.com 202-360-5470
[Legal Disclaimer: *These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, care, or prevent disease.]
SOURCE HEMPAVIDA
Dementia: The hot drink shown to lower your risk of developing the degenerative condition

Dementia is an umbrella term for a cluster of symptoms associated with an ongoing decline of brain functioning that tends to affect people as they age, but it is not a natural part of ageing.
Alzheimer’s disease, a neurological disorder characterised by memory loss and cognitive decline, is the most common form of dementia.
While it is not known how to prevent the neurological disorders associated with dementia, such as Alzheimer’s, a report published today adds to the growing body of evidence suggesting that early lifestyle interventions may reduce your risk. Alzheimer’s charity demands £320m spent on research to stop condition
Dementia: New drug has reversed the condition
Dementia: Playing this game may reduce your risk
While research is yet to explain the association, the researchers hope the findings will encourage further studies into coffee.
Dr Rothenberg added: “Neurodegenerative conditions such as AD and PD markedly change life conditions by successively impairing functional capacity, with profound effects on independence and well-being.
“Currently no curative treatment is available, and therefore ways to reduce the risk of developing these conditions or relieve symptoms is laudable.
“At present research has shown promising results regarding the impact of life-style factors including diet. The Mediterranean diet has been of main interest.
DON’T MISS
How to live longer: The diet proven to help you stave off cancer and boost life expectancy [TIPS]
Type 2 diabetes: The popular vegetable shown to lower your blood sugar [TIPS]
How to live longer: This activity has been proven to boost life expectancy [INSIGHT] David Attenborough health: Presenter on his health struggle
Dementia care: The cooking oil shown to prevent the condition
“There are also some interesting studies regarding coffee consumption suggesting that caffeine is potentially beneficial in preventing AD and PD.
“However, it is still too early to draw firm conclusions regarding causal relationship between dietary factors and the risk of developing AD and PD. Further research is required.” Other ways to reduce your risk
According to the Alzheimer’s Society, of all the lifestyle changes that have been studied, taking regular physical exercise appears to be one of the most promising ways to reduce your risk of getting dementia.
Several studies looking at the effect of aerobic exercise in middle-aged or older adults have reported improvements in thinking and memory, and reduced rates of dementia. Monty Python star sill laughing with Palin despite dementia
How to lose visceral fat: Limit intake of this ingredient to reduce the harmful belly fat
Vitamin D deficiency symptoms: Experiencing this feeling is a warning sign
How to live longer: This diet has been proven to help you live longer and stave off cancer
Of the five behaviours that were assessed (regular exercise, not smoking, moderate alcohol intake, healthy body weight and healthy diet), exercise had the greatest effect in terms of reducing dementia risk.
Overall, people who followed four or five of the above behaviours were up to 60 percent less likely to develop dementia.
In the short term, aerobic exercise can also improve the performance of healthy adults on thinking tests.
Aggregating the results of 29 clinical trials revealed that a month or more of regular aerobic exercise resulted in improvements in memory, attention and processing speed when compared with regular non-aerobic exercise such as stretching and toning.

