Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
LOCKDOWN LUNACY: Social isolation harms brain health and increases dementia risk, warn researchers

( Natural News ) During the Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, governments across the globe enforced many draconian measures like lockdowns and vaccine passports to curb the spread of coronavirus. However, studies show that lockdowns may have done more harm than good, especially to the mental health of people of all ages who have had to spend time in social isolation.
Social isolation, or “the absence or near absence of social connections or relationships,” and loneliness are bad for your well-being. Research points to a connection between living in social isolation and health problems like anxiety, depression, decreased immunity and various physical stress responses.
According to a study published in the journal Neurology , social isolation can even harm the brain and increase dementia risk . People who are socially isolated have a greater risk of developing “later dementia”
For the study, researchers used data gathered from 30,000 participants at the U.K. Biobank .
After examining the data, they discovered that people who were socially isolated had a 26 percent greater probability of developing dementia than socially active individuals. People older than 60 are the hardest hit.
Social isolation itself is a risk factor for dementia and negatively affects brain health.
Barbara J. Sahakian, a professor at the University of Cambridge Department of Psychiatry, advised that since social isolation is a risk to brain health and is linked to dementia, the government and communities must take immediate action “to ensure that older individuals have communication and interactions with others on a regular basis.” The results of a 2021 study also concluded that the forced social isolation that affected many individuals during the pandemic caused a domino effect of repercussions regarding mental health. Scientists examined patients and their caregivers, along with the impact of social isolation and found that: Over 50 percent of patients with dementia experienced a decline in memory function.
Over 30 percent of the patients felt sadder.
At least 40 percent experienced an increase in their anxiety symptoms.
The increase in anxiety symptoms caused an increase in dementia symptoms , such as agitation, hallucinations and difficulty in daily life activities. CDC pushed lockdowns despite their known health risks
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) referenced several studies that highlight the health risks linked to social isolation in adults older than 50.
Studies revealed that social isolation can increase the risk of: Anxiety, depression and suicide
Stroke by 32 percent
Dementia by about 50 percent
Heart disease by 29 percent
Premature death from all causes
Heart failure patients who were socially isolated had: A four-fold increase in the risk of death
Increased risk of hospitalization by 68 percent
Increased risk of emergency room visits by 57 percent
Despite these dangers, during the coronavirus pandemic the CDC advised people to quarantine and isolate themselves . Tips for reducing dementia risk
Here are some tips that can help reduce your risk of dementia :
Monitor your blood pressure and keep systolic blood pressure at 130 mm Hg or lower, especially if you are 40 or older.
Reduce exposure to secondhand smoke and air pollution.
Be careful and prevent falls to avoid head injury . Make sure your home is fall-proof and wear shoes with non-skid soles that fully support your feet. Join fall prevention programs online or in your city. When riding in a car, always wear seatbelts and helmets to help protect you from concussions and other brain injuries.
Maintain good physical health and a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese may increase your risk of related health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
Eat a nutritious diet consisting of different organic fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean meats and seafood, unsaturated fats like olive oil and low-fat or nonfat dairy products. Limit your intake of other fats and sugars. (Related: Study: Choline helps improve cognitive performance in the elderly .) Limit or avoid alcohol consumption altogether. Drinking too much alcohol can cause falls and worsen health conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, memory loss, mood disorders and stroke. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), men should only have two drinks a day and women only one. Don’t smoke or quit smoking. Whether you’re young or old, quitting smoking can improve your health and lower your risk of heart attack, lung disease and stroke. Keep your brain active with brain games, puzzles, lessons and discussions. You can also read more books, start a new craft or take up a new hobby. Another option is to work or volunteer. Keeping your sugar intake very low . Higher than normal levels of blood sugar (glucose) can cause diabetes and may increase your risk of cognitive impairment, dementia, heart disease and stroke. Improve your eating habits, exercise regularly, quit smoking and monitor your glucose levels to manage your blood sugar. Get at least seven to eight hours of good quality sleep . Restful sleep is important for both your mind and body. Talk to your doctor if you are not getting enough sleep or having trouble sleeping. Have regular social interaction with your family and friends . Connecting with people and engaging in social activities can help prevent social isolation and loneliness, which are linked to higher risks for cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s.If you are caring for an older family member, senior centers or senior daycare facilities can be a good way to help them get some social interaction. Plan ahead for older adults who may suffer greatly from loneliness and isolation so you’re ready for another pandemic.Regardless of age, people are social creatures. It’s important to interact with others.Visit BrainHealthBoost.com for more tips on how to boost brain health and prevent dementia.Watch the video below to find out how magnesium can boost your brain health . No compatible source was found for this media.This video is from the Natural News channel on Brighteon.com . More related stories: Toxic foods that may cause dementia . Sources include: NaturalHealth365.com CDC.gov
Healthy human brains are hotter than previously thought, research finds
New research has shown that normal human brain temperature varies much more than we thought, and this could be a sign of healthy brain function. In healthy men and women, where oral temperature is typically less than 37°C, average brain temperature is 38.5°C, with deeper brain regions often exceeding 40°C, particularly in women during the daytime.
Previously, human brain temperature studies have relied upon data capture from brain-injured patients in intensive care, where direct brain monitoring is often needed. More recently, a brain scanning technique, called magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), has enabled researchers to measure brain temperature non-invasively in healthy people. Until now, however, MRS had not been used to explore how brain temperature varies throughout the day, or to consider how an individual’s ‘body clock’ influences this.
The new study, led by researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory for Molecular Biology, in Cambridge, UK, has produced the first 4D map of healthy human brain temperature. This map overturns several previous assumptions and shows the remarkable extent to which brain temperature varies by brain region, age, sex, and time of day. Importantly, these findings also challenge a widely held belief that human brain and body temperature are the same.
The research, published in the journal Brain , also included analysis of data from patients with traumatic brain injury, showing that the presence of daily brain temperature cycles strongly correlates with survival. These findings could be used to improve understanding, prognosis, and treatment of brain injury.
Striking brain temperature variation in health
To study the healthy brain, the researchers recruited 40 volunteers, aged 20-40 years, to be scanned in the morning, afternoon, and late evening over one day, at the Edinburgh Imaging Facility, Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh.
Crucially, they also gave the participants a wrist-worn activity monitor, allowing genetic and lifestyle differences in the timing of each person’s body clock, or circadian rhythm, to be taken into account. For both ‘night owls’ or ‘morning larks’, knowing the biological time-of-day that each brain temperature measurement was taken at allowed differences between each volunteer’s body clock to be factored into the analysis.
In healthy participants, the average brain temperature was 38.5°C, more than two degrees warmer than that measured under the tongue. The study also found that brain temperature varied depending on: time of day,
brain region,
sex and menstrual cycle,
and age.
While the brain surface was generally cooler, deeper brain structures were frequently warmer than 40°C; with the highest observed brain temperature being 40.9°C. Across all individuals, brain temperature showed consistent time-of-day variation by nearly 1°C, with highest brain temperatures observed in the afternoon, and the lowest at night.
On average, female brains were around 0.4°C warmer than male brains. This sex difference was most likely driven by the menstrual cycle, since most females were scanned in the post-ovulation phase of their cycle, and their brain temperature was around 0.4°C warmer than that of females scanned in their pre-ovulation phase.
The results also showed that brain temperature increased with age over the 20-year range of the participants, most notably in deep brain regions, where the average increase was 0.6°C. The researchers propose that the brain’s capacity to cool down may deteriorate with age and further work is needed to investigate whether there is linked with the development of age-related brain disorders.
Dr John O’Neill, Group Leader at the MRC Laboratory for Molecular Biology, said:
“To me, the most surprising finding from our study is that the healthy human brain can reach temperatures that would be diagnosed as fever anywhere else in the body. Such high temperatures have been measured in people with brain injuries in the past, but had been assumed to result from the injury.”
“We found that brain temperature drops at night before you go to sleep and rises during the day. There is good reason to believe this daily variation is associated with long-term brain health — something we hope to investigate next.”
Temperature rhythms in injured brains
To explore the clinical implications of data obtained from healthy volunteers, the researchers analysed temperature data collected continuously from the brain in 114 patients who had suffered from moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI). The patients’ average brain temperature was 38.5°C, but it varied even more widely, from 32.6 to 42.3°C.
Of 100 patients for whom there was enough data to test for daily rhythms, only a quarter had a daily rhythm in brain temperature. Focusing on predictors of survival in intensive care, the researchers found that absolute brain temperature measurements were of limited use, but daily brain temperature variation was strongly linked with survival — indeed, of TBI patients with a daily brain temperature rhythm only 4% died in intensive care, versus 27% who had no such rhythm.
The researchers caution that larger studies are needed to validate this association, and that the link between brain temperature and survival is correlative only, meaning that daily brain temperature rhythms cannot be assumed to directly increase survival. However, the observed link means that monitoring daily brain temperature cycles in TBI patients might be a promising tool to predict survival and would benefit from further research.
Together with the data from healthy people, the findings of this work raise important questions about the use of interventions to modify or control patient temperature in the clinic.
Dr Nina Rzechorzek, MRC Clinician Scientist Fellow from the MRC Laboratory for Molecular Biology who led the study, said:
“Using the most comprehensive exploration to date of normal human brain temperature, we’ve established ‘ HEATWAVE ‘ — a 4D temperature map of the brain. This map provides an urgently-needed reference resource against which patient data can be compared, and could transform our understanding of how the brain works. That a daily brain temperature rhythm correlates so strongly with survival after TBI suggests that round-the-clock brain temperature measurement holds great clinical value.”
“Our work also opens a door for future research into whether disruption of daily brain temperature rhythms can be used as an early biomarker for several chronic brain disorders, including dementia.”
Story Source: […]
Consumption of citrus fruits linked to lower stroke risk

( Natural News ) Citrus fruits are known for being full of vitamin C and having immune system-boosting properties. According to a study, regular consumption of nutritious citrus fruits may also help reduce stroke risk .
The study was conducted by researchers from the University of East Anglia (UEA) in Norwich, United Kingdom. The study findings showed that eating citrus fruit, especially oranges, “lowers the risk of ischemic stroke significantly.”
For the study, the research team compared the health of adult female volunteers who ate both oranges and grapefruit regularly versus those who did not. The researchers also analyzed the flavonoid content of citrus fruits and how they affected blood vessel health.
Data from earlier studies have revealed that specific orange phytochemicals had protective benefits against intracerebral hemorrhage and significantly improved blood flow in the brain.
In the UEA study, researchers reviewed around 14 years of the Nurse’s Health Study data tracking the health and diets of at least 70,000 women. They assessed correlations between six flavonoid sub-classes from citrus fruits related to risks of hemorrhagic, ischemic or complete stroke .
Based on the findings, the female volunteers who consumed the highest amounts of orange and grapefruit along with juices from these fruits had much better blood circulation. The women also had a 19 percent lowered risk of stroke related to blood clotting compared with the women who didn’t consume as much citrus fruits. Citrus consumption and reduced stroke risk
The women who ate more citrus fruits showed a substantially reduced risk of stroke and associated risks, reported the researchers. Other studies of flavonoids in fruits support these results about a reduction in stroke risk. Data suggest that a higher intake of all kinds of fruit has a positive impact on stroke risk and other areas of health.
For example, a 2011 study conducted by researchers from Western University in London, Ontario, revealed that flavonoid intake also helped prevent weight gain.
The study found that nobiletin, a tangerine flavonoid, helped reduce the risk of both Type 2 diabetes and obesity in mice. The mice given the nobiletin flavonoid didn’t develop these health problems while the mice that did not become obese developed Type 2 diabetes and had atherosclerosis and fatty liver issues. Other health benefits of citrus fruits
According to a 2012 Japanese study, the pulp and juice from satsuma mandarin oranges inhibited tumor growth in colon, lung and tongue cancers.
This is important because vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that can help inhibit free radical damage in the cells. The nobiletin in citrus fruit has also been linked with apoptosis or the programmed cell death of cancer cells.
In another study, scientists from Oregon Health & Science University discovered that there is a link between eye health and the vitamin C found in citrus fruits. According to their data, retinal nerve cells benefited from the compound.
The research team believes that there is a chance that both brain and nervous system health are also positively impacted by vitamin C.
While natural fruit juice is nutritious, consuming whole oranges, grapefruits and other fruits offer amazing health benefits. Whole fruits usually contain more vitamins and nutrients and are lower in sugar and higher in dietary fiber. Follow a balanced diet to prevent stroke
Making small changes to your eating habits can have a significant difference in your overall health, especially if you are at risk of having a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
A transient ischemic attack is a stroke that lasts for only several minutes. It happens when the blood supply to part of your brain is briefly blocked .
Symptoms of a TIA are like other stroke symptoms, but it doesn’t last as long. They happen suddenly and may include: Confusion and trouble speaking or understanding speech
Difficulty walking
Dizziness
Loss of balance or coordination
Numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
Eating a healthy, balanced diet will also help lower your blood pressure and control diabetes.
Cholesterol is a fatty substance produced in your body. You can also absorb cholesterol from fatty foods.
If there’s too much cholesterol in your blood, it can cause fatty deposits to build up in your arteries and restrict blood flow. Fortunately, improving your eating habits can help reduce your cholesterol level.
Manage your fat, salt and sugar intake and eat more whole foods like citrus fruits to lower your stroke risk .Watch the video below to know about nine good reasons to add oranges in your regular diet .This video is from the Groovy Bee channel on Brighteon.com . No compatible source was found for this media. More related stories: Compounds in citrus fruits and orange juice found to improve gut health . 5 Creative ways to use citrus peels . Nine reasons to eat an orange (plus a recipe for orange salad dressing) . Sources include: NaturalHealth365.com
Compounds in ginger and chili peppers found to prevent cancer

( Natural News ) On their own, both ginger and chili are delicious spices with well-known health benefits.
Ginger is used in traditional medicine to relieve common health complaints like digestive issues and nausea. On the other hand, chili peppers help boost your mood, metabolism and immune system.
Both ginger and chili peppers can also improve blood circulation.
According to an animal study, combining certain compounds from both ginger and chili pepper can help prevent cancer . Researchers discovered that the likelihood of developing lung cancer was significantly reduced when animal subjects were given these compounds together.
The study was published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . Preventing tumor growth with ginger and chili pepper compounds
Study findings showed that 6-gingerol in ginger and capsaicin, a chili pepper compound, work well together to effectively prevent cancer .
This is because 6-gingerol binds to capsaicin to create a new, extremely strong compound that can help inhibit tumor-growing cell receptors in the body.
For the study, researchers fed mice prone to lung cancer either 6-gingerol or capsaicin alone or in combination for several weeks. All of the mice given only the capsaicin developed tumors in their lungs while only half of the 6-gingerol-only mice did.
Meanwhile, only 20 percent of the mice that received the combination of both capsaicin and 6-gingerol developed cancer.
The study shows that when it comes to fighting cancer, combining 6-gingerol and capsaicin is more effective than taking only ginger or chili pepper. Combining the two forms a powerful compound that binds to cell receptors that would otherwise trigger tumor growth. Health benefits of ginger and chili pepper
It’s amazing that combining two already beneficial spices like ginger and chili pepper can help prevent cancer .
When cooking at home, you can give dishes a nutritious flavor boost by using either fresh or dried ginger and chili peppers.
But that’s not all. Detailed below are more health benefits of ginger and chili pepper. Ginger health benefits
In traditional and alternative medicine, ginger is used to aid digestion , reduce nausea and help fight the flu and common cold.
Ginger’s unique fragrance and flavor are due to its natural oils, the most important of which is gingerol. As the main bioactive compound in ginger, gingerol is responsible for many of ginger’s medicinal properties.
Data suggest that gingerol has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. It can help reduce oxidative stress, which is often caused by having an excess amount of free radicals in the body.
Ginger helps treat many forms of nausea
The data have proven that ginger is very effective against nausea.
Ginger can help ease nausea and vomiting in people undergoing certain types of surgery. It may also help with chemotherapy-related nausea.
According to research, ginger is most effective when treating pregnancy-related nausea, such as morning sickness. According to a review of 12 studies that included a total of 1,278 pregnant women, taking 1.1 to 1.5 grams of ginger can significantly reduce symptoms of nausea.
While ginger is considered safe to consume, consult your doctor before taking large amounts of ginger when pregnant. Take note that pregnant women who are close to labor or who have had miscarriages should avoid ginger since it is contraindicated with a history of vaginal bleeding and clotting disorders.
Ginger helps promote weight loss
Data from studies conducted on both humans and animals suggest that ginger can help promote weight loss.
In a 2016 study involving 80 women with obesity, findings showed that ginger could help reduce body mass index (BMI) and blood insulin levels. High blood insulin levels are often linked to obesity. The volunteers were given relatively high daily doses of two grams of ginger powder for 12 weeks.
According to a 2019 literature review, ginger supplementation can significantly reduce body weight, the waist-hip ratio and the hip ratio of overweight or obese individuals.
In a 2019 literature review of functional foods, researchers reported that ginger had a very positive effect on obesity and weight loss.The evidence supporting ginger’s role in helping prevent obesity is stronger in animal studies.According to one study, rats and mice given ginger water or ginger extract consistently saw decreases in their body weight, even when they were also fed high-fat diets.Experts believe that ginger’s ability to influence weight loss may be related to certain mechanisms, like its potential to help increase the number of calories burned or reduce inflammation. Ginger helps with osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is a common health problem that involves degeneration of the joints in the body. It can result in debilitating symptoms like joint pain and stiffness.According to a literature review, individuals who used ginger to treat their osteoarthritis saw significant reductions in pain and disability. Mild side effects, like dissatisfaction with the taste of ginger, were reported.The volunteers received between 500 milligrams (mg) and one gram of ginger each day between three to 12 weeks. A majority of the volunteers had been diagnosed with osteoarthritis of the knee.Another 2011 study revealed that a combination of topical ginger, mastic, cinnamon and sesame oil can help reduce pain and stiffness in people with osteoarthritis of the knee. Ginger helps improve brain function and prevent Alzheimer’s disease Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation can accelerate the aging process. These two factors are also believed to be among the key drivers of Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline.Data from some animal studies suggest that the antioxidants and bioactive compounds in ginger can help curb inflammatory responses that occur in the brain.Research also suggests that ginger can help enhance brain function directly. According to a 2012 study of healthy middle-aged women, taking ginger extract daily can help improve reaction time and working memory.Additionally, several animal studies have found that ginger can help fight age-related decline in brain function. Chili pepper health benefits Chili peppers have a burning taste, but consuming this fiery spice also offers several health benefits. Chili peppers are full of vitamins and minerals such as: Copper – Copper is an essential trace element. You need copper for strong bones and healthy neurons. Potassium – Potassium is an […]
Regular olive oil consumption found to reduce mortality risk

( Natural News ) Olive oil is a popular cooking oil because it contains antioxidants and healthy fats. According to a study conducted by researchers from the American College of Cardiology , consuming olive oil regularly is also linked to a lower risk of some severe medical conditions , such as heart disease and cancer.
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
During the study, the research team found that respiratory disease mortality and neurodegenerative disease mortality are also less common in individuals who consume over seven grams of olive oil per day.
Additionally, replacing 10 grams of butter, mayonnaise and dairy fat daily with the same quantity of olive oil helped significantly reduce mortality risk .
Dr. Marta Guasch-Ferre, the study’s first author, said the results support current dietary recommendations to “increase the intake of olive oil and other unsaturated vegetable oils.”
She added that clinicians should advise patients to replace certain fats, like butter and margarine , with olive oil to improve their well-being. The study findings can be used to make more specific recommendations that will be easier for patients to understand and implement into their regular diets. (Related: Study links olive oil intake to reduced heart disease and Alzheimer’s risk .) Olive oil consumption and lower disease risk
For the study, the scientists analyzed the diets of more than 30,000 men and over 60,000 women. All the volunteers were disease-free when the trial began in 1990. The volunteers filled in surveys every four years to track their average fat and oil consumption. For the surveys, olive oil intake was measured on how often a volunteer used it: On salads
While baking
While cooking
When adding it to other meals and bread
In the study, one tablespoon equaled more than 13 grams of olive oil.
The scientists discovered that volunteers who consumed the most olive oil daily were 19 percent less likely to die from cardiovascular disease and 17 percent less likely to die from cancer. Results also showed that they were more protected from neurodegenerative mortality and respiratory mortality.
Guasch-Ferre explained that it is possible that higher olive oil consumption could be considered “a marker of an overall healthier diet and higher socioeconomic status.” After adjusting for these and other social-economic status factors, the study results remained largely the same.
She noted that the study cohort was made up mainly of a non-Hispanic white population of health professionals, which should minimize potential confounding socioeconomic factors. However, the study cohort may also limit generalizability as this population “may be more likely to lead a healthy lifestyle.”
The results showed that people with a higher olive oil intake were more likely to have an active lifestyle, follow a healthy diet and more likely to be non-smokers. Tips for incorporating olive oil into a balanced diet
Olive oil is the natural oil extracted from olives that come from olive trees. It is made up of 14 percent saturated fat and 11 percent polyunsaturated fat, like omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids.
The predominant fatty acid in olive oil is oleic acid, a monounsaturated fat that makes up a whopping 73 percent of its total oil content.
Research suggests that oleic acid helps minimize inflammation. It may also have beneficial effects on genes linked to cancer .
Since monounsaturated fats are very resistant to high heat, extra virgin olive oil is a healthy choice for cooking.
Here are some suggestions on how to use more olive oil : Use olive oil in sauces. Whisk to emulsify or blend the watery ingredients with the oil in the sauce.
Use olive oil instead of butter or margarine as a healthy dip for bread. Pour a little olive oil into a small side dish, then add a bit of balsamic vinegar.
Drizzle olive oil in a salad or add it to salad dressing.
Use olive oil in marinades or sauces for meat, fish , poultry and veggies.
Add olive oil at the end of cooking for a healthy flavor boost.
Drizzle olive oil over cooked pasta or vegetables before serving.
Follow a balanced diet and replace butter or dairy fat with olive oil to boost your overall health .Watch the video below to know more about the amazing health benefits of olive oil . No compatible source was found for this media.This video is from the Holistic Herbalist channel on Brighteon.com . More related stories: 5 Reasons to use cold pressed olive oil, a cooking oil full of healthy fats . 4 Amazing health benefits of antioxidant-rich olive oil . The brain-boosting benefits of high-quality olive oil . Sources include:
Changing the Brain’s Immune Environment May Help Stroke Recovery
A therapeutic method for harnessing the body’s immune system to protect against brain damage is published today by researchers from the Babraham Institute’s Immunology research programme . The collaboration between Prof. Adrian Liston (Babraham Institute) and Prof. Matthew Holt (VIB and KU Leuven; i3S-University of Porto) has produced a targeted delivery system for boosting the numbers of specialised anti-inflammatory immune cells specifically within the brain to restrict brain inflammation and damage. Their brain-specific delivery system protected against brain cell death following brain injury, stroke and in a model of multiple sclerosis. The research is published today in the journal Nature Immunology .
Traumatic brain injury, like that caused during a car accident or a fall, is a significant cause of death worldwide and can cause long-lasting cognitive impairment and dementia in people who survive. A leading cause of this cognitive impairment is the inflammatory response to the injury, with swelling of the brain causing permanent damage. While inflammation in other parts of the body can be addressed therapeutically, but in the brain it problematic due to the presence of the blood-brain barrier, which prevents common anti-inflammatory molecules from getting to the site of trauma.
Prof. Liston, a senior group leader in the Institute’s Immunology programme, explained their approach: “Our bodies have their own anti-inflammatory response, regulatory T cells, which have the ability to sense inflammation and produce a cocktail of natural anti-inflammatories. Unfortunately there are very few of these regulatory T cells in the brain, so they are overwhelmed by the inflammation following an injury. We sought to design a new therapeutic to boost the population of regulatory T cells in the brain, so that they could manage inflammation and reduce the damage caused by traumatic injury.”
The research team found that regulatory T cell numbers were low in the brain because of a limited supply of the crucial survival molecule interleukin 2, also known as IL2. Levels of IL2 are low in the brain compared to the rest of the body as it can’t pass the blood-brain barrier.
Together the team devised a new therapeutic approach that allows more IL2 to be made by brain cells, thereby creating the conditions needed by regulatory T cells to survive. A ‘gene delivery’ system based on an engineered adeno-associated viral vector (AAV) was used: this system can actually cross an intact blood brain barrier and deliver the DNA needed for the brain to produce more IL2 production. Left : The top image shows an untreated mouse brain after a controlled impact, the site of damage can be seen by the dark circular impact site. The bottom brain is from a treated mouse 14 days after the impact, the absence of a visible impact site shows the success of the treatment in preventing brain tissue loss. Middle : These immunofluorescence staining images show how the treatment has reduced the amount of damage after traumatic brain injury when mice were pre-treated with the IL2 treatment. The top layer of brain tissue is visibly thicker in the bottom right image compared to top right. Each row shows the uninjured brain hemisphere (left) and the injured hemisphere (right). The top row shows an untreated brain while the bottom row shows a treated brain, with less damage occurring in the injured hemisphere. Right : A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the brains of two mice after a controlled impact to create a traumatic brain injury. The arrow shows there the impact was made, the grey area below the arrow shows the size of the lesion. The amount of brain swelling is visibly reduced in the brain of the treated mouse (bottom).
Commenting on the work, Prof. Holt said: “For years, the blood-brain barrier has seemed like an insurmountable hurdle to the efficient delivery of biologics to the brain. Our work, using the latest in viral vector technology, proves that this is no longer the case; in fact, it is possible that under certain circumstances, the blood-brain barrier may actually prove to be therapeutically beneficial, serving to prevent ‘leak’ of therapeutics into the rest of the body.”
The new therapeutic designed by the research teams was able to boost the levels of the survival molecule IL2 in the brain, up to the same levels found in the blood. This allowed the number of regulatory T cells to build up in the brain, up to 10-fold higher than normal. To test the efficacy of the treatment in a mouse model that closely resembles traumatic brain injury accidents, mice were given carefully controlled brain impacts and then treated with the IL-2 gene delivery system. The scientists found that the treatment was effective at reducing the amount of brain damage following the injury, assessed by comparing both the loss of brain tissue and the ability of the mice to perform in cognitive tests.
Lead author, Dr Lidia Yshii, Assistant Professor at KU Leuven, explained: “Seeing the brains of the mice after the first experiment was a ‘eureka moment’ – we could immediately see that the treatment reduced the size of the injury lesion.”
Recognising the wider potential of a drug capable of controlling brain inflammation, the researchers also tested the effectiveness of the approach in experimental mouse models of multiple sclerosis and stroke. In the model of multiple sclerosis, treating mice during the early symptoms prevented severe paralysis and allowed the mice to recover faster. In a model of stroke, mice treated with the IL2 gene delivery system after a primary stroke were partially protected from secondary strokes occurring two weeks later. In a follow-up study, still undergoing peer review, the research team also demonstrated that the treatment was effective at preventing cognitive decline in ageing mice.
“By understanding and manipulating the immune response in the brain, we were able to develop a gene delivery system for IL2 as a potential treatment for neuroinflammation. With tens of millions of people affected every year, and few treatment options, this has real potential to help people in need. We hope that this system will soon enter clinical trials, […]
Scientists Find Brain Mechanism Responsible For Age-Related Memory Loss
3D male medical figure holding head in pain Research suggests that the hippocampus, an area in the brain responsible for memory, performs two complementary processes: pattern separation and pattern completion.
Pattern completion could be described as the ability to remember visiting a place when you return there a month later, even if some details have changed. On the other hand, pattern separation is remembering which conversations happened during each visit and not confusing them with each other.
As humans and rodents age, their pattern separation abilities decline . Studies have shown that this may be linked to an overactive CA3 network in the dentate gyrus in the hippocampus. Drugs that reduce this hyperactivity have increased memory performance in aged rats.
A direct study of the CA3 network’s effect on memory could help researchers develop treatments to improve age-related memory issues. Most recently, researchers studied how this CA3 network influenced the memory abilities of young and aged rats.
The researchers found that some aged rats could perform similarly to young rats in memory tasks, even though their brains showed deficits in pattern separation.
For the study, the researchers obtained four young rats (aged between 3 and 6 months) and 14 older rats (aged between 22 and 26 months). To begin, the rats underwent behavioral testing in a water maze.
They then underwent hyperdrive implant surgery so that researchers could monitor the lateral edge of their CA3 brain region.
Thereafter, they were trained for eight days to locate a submerged escape platform in a water maze tank. Every sixth time in the maze was considered a ‘probe trial’, and included no escape platform for the first 30 seconds.
The researchers used the rats’ average search proximity scores during these probe trials to calculate a learning index. The mice with a score above 240 were categorized as “aged memory-impaired”, whereas those with a learning index of less than 240 were “aged memory-unimpaired”.
The researchers then further analyzed the rats’ cognitive abilities during foraging sessions, circular track training, and further water maze tests.
As expected, they found that aged memory-impaired older rats performed worse in various tasks than younger rats and that this corresponded with hyperactivity in certain parts of the CA3 area of the hippocampus.
They also found, however, that some of the aged memory-unimpaired rats performed similarly to young rats, even though they showed signs of the same changes in their CA3 regions. Underlying mechanisms
To explain the findings, the researchers noted that in neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, there is little behavioral deficit until a threshold is crossed.
They said this may explain why some older rats performed similarly to younger rats, given their maze scores occurred on a continuum between the scores of the younger rats and those of the most impaired older ones.
When asked about the underlying mechanisms, Heekyung Lee , from the Knierim Lab at John Hopkins University and the primary author of the study, told Medical News Today that inhibitory neurons may play a role.
“The number of inhibitory neurons declines with age in the hippocampus. Prior work […] has shown that while inhibitory neurons in multiple subregions of the hippocampus decrease both in memory unimpaired (AU) and memory-impaired (AI) aged rats, inhibitory neurons specifically in the hilus of the dentate gyrus subregion decrease in AI, but not AU rats,” Lee explained.
“It is noteworthy that there are complex feedforward and feedback connections between the dentate gyrus and proximal CA3, two subregions that support pattern separation computations. The balance of excitation and inhibition plays an essential role in network dynamics,” she added. “One possible compensation mechanism in [aged] rats [with unimpaired memory] can be that the preservation of inhibitory neurons exclusively in the [brain’s] hilus region may be enough to overcome the age-related excitation-inhibition imbalance to favor pattern separation.” — Heekyung Lee, study author Dr. Tara Swart Bieber , neuroscientist and professor at MIT Sloan School of Management, told MNT that neuroplasticity might also play a role.
“Neuroplasticity—the ability to re-wire our brains throughout life—is likely to be the mechanism that underpins this compensation. Although harder in later life, it is possible to make new connections that can bypass pathways that have become weak. […] Also, people can fully recover after a stroke or brain surgery,” she said. The next steps
The researchers concluded that further research is warranted to understand the compensatory mechanisms in aged memory-unimpaired rats to understand how they prevent age-related cognitive decline.
When asked about future research directions, Lee said that determining different subtypes of neurons would be key for targeted therapies. “Future research to understand why inhibitory neurons are vulnerable to aging can help discover therapeutic strategies to increase inhibition in the hippocampus to help improve age-related memory issues.” — Heekyung Lee, study author “Furthermore, there are different subtypes of inhibitory neurons, and understanding the functional specificity of each subtype can allow for targeted intervention,” she added.
Dr. Bieber also said that research into lifestyle habits that may help older people manage age more efficiently could also improve understanding of these compensatory mechanisms.
When asked more generally about preventing age-related memory decline, Dr. Bieber said:
“Taking on new learning throughout your life, that is attention intense enough to change your brain, e.g., learn a new language, sport, musical instrument, etc. is the best thing you can do for your brain in adulthood.”
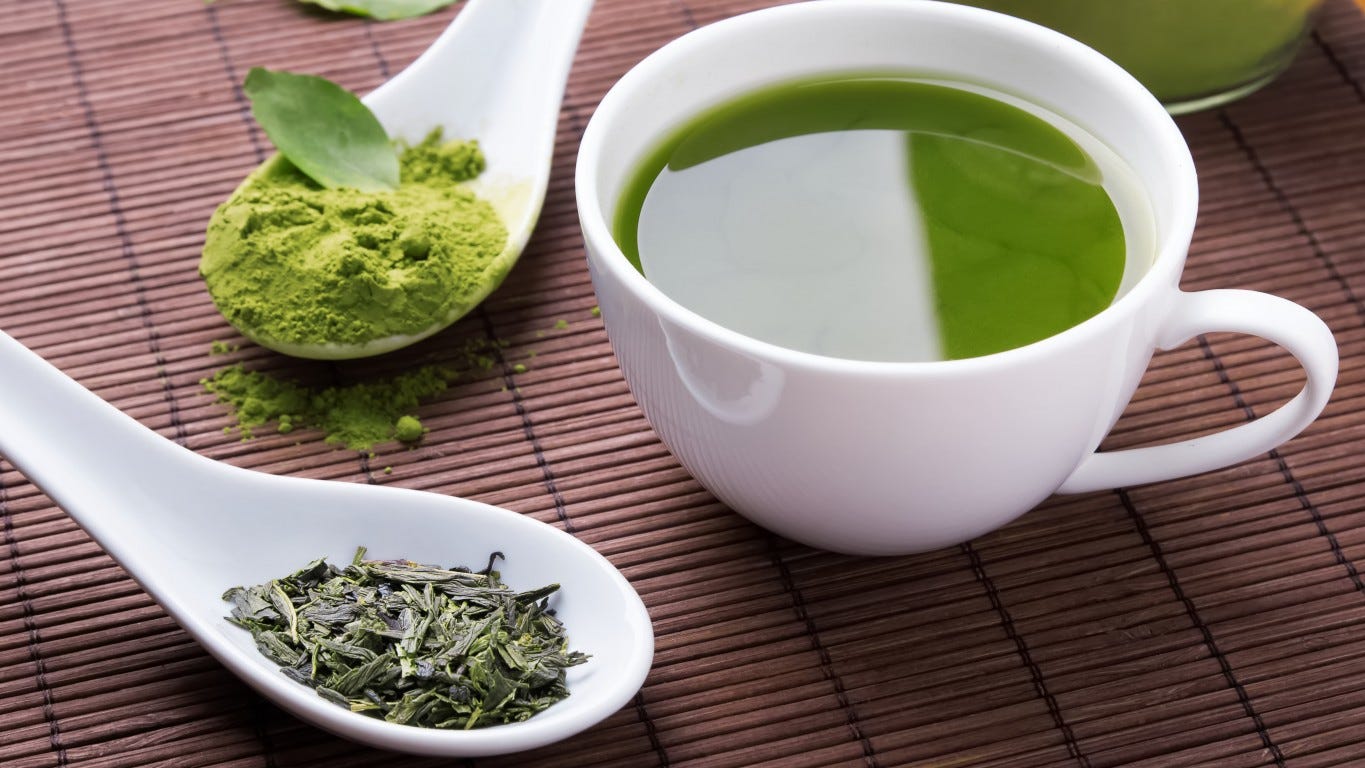
6 Scientifically proven benefits of green tea

( Natural News ) If you drink tea often, especially green tea, you have new reasons to keep drinking it.
Green tea has been the focus of many studies and findings show that drinking green tea regularly offers various health benefits , such as reducing bad breath and promoting weight loss. Where does green tea come from?
For many years, tea has been used for therapeutic purposes in China and Japan.
The black, green and oolong teas all come from the Camellia sinensis plant. The difference between the teas lies in their preparation methods.
Green tea is made by steaming the leaves, pan-frying then drying them.
Since brewed green tea is primarily water-based, it’s free of the usual macronutrients found in other foods and drinks. Green tea doesn’t contain any fat , carbohydrates or protein. Unsweetened green tea is also calorie-free.
Green tea’s many health benefits are often accredited to compounds called catechins, specifically epicatechin , epicatechin-3-gallate, epigallocatechin and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Experts think that these catechins are responsible for green tea’s potential “cancer-fighting, antioxidant, probiotic and metabolism-boosting benefits.”
It also contains trace amounts of potassium and moderate levels of caffeine. A cup of green tea contains 25 to 29 milligrams (mg) of caffeine.
Green tea is a popular beverage and it is often enjoyed in many countries worldwide.
Read on to learn more about the six evidence-based benefits of green tea. Green tea has neuroprotective properties
According to research published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease , amyloid-beta protein has been shown to have a causal relationship with the development of dementia . Modulating amyloid-beta protein is a potential therapeutic modality that should be considered for further study. Green tea has neuroprotective properties, particularly its reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activity that can prevent oxidative stress.
The tea also contains EGCG, which suppresses the neurotoxicity induced by amyloid-beta protein. Scientists suggest that EGCG can help trigger glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3 beta) and also inhibits c-Abl/FE65 or the cytoplasmic nonreceptor tyrosine kinase with a role in nervous system development and nuclear translocation.
According to findings published in the journal Pharmacology & Therapeutics , when stimulated, many proteins translocate into the nucleus to regulate many different cellular processes that are crucial for brain health. These factors make green tea a potential agent to address neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease. Green tea has anticancer properties
Drinking green tea can also help prevent bladder, breast, esophagus, intestinal, lung, pancreatic and stomach cancers .
According to a 2020 article published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, EGCG has the best anti-inflammatory and anticancer potential because it triggers apoptosis or cell death.
Researchers indicate that the control of catechins under an intracellular pool of nitro-oxidative stress is the primary reason for the potential anticancer properties. Additionally, catechins also scavenge harmful free radicals that are linked to chronic diseases. (Related: Drinking tea regularly linked to reduced cardiovascular disease risk .) Green tea helps reduce fat and promote weight loss
Many fat-burning supplements contain green tea extract because this ingredient helps boost your metabolic rate.
Data from an older study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition has shown that green tea extract helped increased the number of calories burned by four percent in 10 healthy male participants. The extract can also help improve physical performance due to the increase in available energy because of the stimulation of caffeine and other compounds.
In a 2017 systematic review published in the journal Nutrición Hospitalaria , researchers examined the effects of green tea and its EGCG content on human fat mass and body weight. Findings showed that the daily consumption of green tea with EGCG doses between 100 and 460 milligrams per day effectively reduced body fat and weight in intervention periods of at least 12 weeks. Green tea improves focus and boosts energy
If you have trouble concentrating but don’t like drinking too much coffee, you can improve your focus with green tea. An eight-ounce cup of brewed green tea contains 28 milligrams of caffeine, which is enough to stimulate both your body and brain without the jittery effects caused by overconsumption.
Green tea boosts your focus and energy because it contains caffeine that blocks adenosine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Additionally, caffeine boosts dopamine and norepinephrine signaling in the brain. This then helps improve your reaction time, memory and mood. Green tea helps fight bad breath
Green tea catechins benefit your oral health by suppressing the growth of harmful bacteria.
Streptococcus mutans is a type of bacterium that often causes plaque and contributes to tooth decay and cavities. While there is no research on whether or not green tea can eliminate this bacteria, data suggests that green tea can help reduce bad breath (halitosis).
In a 2008 study published in the Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology , scientists analyzed the effects of green tea powder on volatile sulfur compounds in the mouth.
Findings showed that polyphenols in green tea had deodorizing and antimicrobial effects. Green tea extract presented the largest reduction in these bad breath compounds by significantly decreasing oral malodor temporarily. Green tea helps improve skin health The protective polyphenols in green tea can help increase collagen, improve elastic content and prevent wrinkles. A 2017 review published in the journal Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition suggests that these compounds may also have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.In a 2021 meta-analysis published in Phytotherapy Research , scientists analyzed the effects of green tea extract on acne vulgaris across five randomized clinical trials.Review findings showed that topical green tea extract application benefits acne treatment without significant adverse events. On the other hand, oral GTE intake presents limited effects.Topical green tea extract offered benefits for both inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions in the studies examined by the research team.If you’re still on the fence about trying green tea, take this as a sign to start drinking this beneficial beverage. Consuming green tea regularly can offer many benefits, such as improving your skin health and lowering your risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases and certain cancers.Visit Superfoods.news for more articles about foods that offer […]
Why Your Gut Could Be the Key to Preventing Anxiety, Alzheimer’s, and More

If you’ve ever experienced butterflies in your stomach before a speech, you knew the sensation didn’t result from a lost monarch. But this common experience—your gut seeming to act out your brain’s anxiety—is an everyday example of fascinating new research into the interconnected worlds inside us.
While your stomach doesn’t contain butterflies, there are tiny organisms in there that are engaged in a conversation with your brain about that stress you’re experiencing. These organisms and their home could be far more powerful than we’ve realized, according to a burst of new studies. Many of the tens of trillions of organisms in your gut, or gastrointestinal tract, can help maintain good digestion and health . But some of them are not so cooperative: When they take over, they wreak havoc. That might mean you get food poisoning or make more bathroom trips than you’d like—but some might have bigger implications. These nasty bugs could be sending the brain signals connected to brain-related disorders including anxiety and Alzheimer’s disease .
So, is your gut the key to a healthy brain? Here’s what you need to know about the gut-brain connection. What is the gut microbiome?
With the help of everyday people, University of California San Diego researchers have uncovered new facets of the worlds within us. As part of the American Gut Project , more than 10,000 people from around the world mailed in their poop (yep). Scientists analyzed it to understand how organisms inside us—our microbiomes—interact with diet, lifestyle, and disease.
Learn more about the powerful gut-brain connection in a free webinar on June 9 , moderated by Joan Lunden and hosted by Prevention , HealthyWomen , and the Women’s Alzheimer’s Movement at Cleveland Clinic .
You may remember the word “biome” from biology class—a habitat such as desert or grassland, designated based on local climate and plant life. Our bodies contain their own worlds, unique habitats of trillions of wee beasties—viruses, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms living on us and inside us. In humans, microbes gather in these worlds on the skin, in the nose , and in the gastrointestinal tract (a.k.a. the gut). Over the past 20 years, experts have refined techniques to “fingerprint” the gut’s cast of microbes through sequencing DNA, says Ami Bhatt, M.D., Ph.D. , an associate professor of medicine and genetics at Stanford University.
You’ve had a microbiome since the day you were born, and it’s been evolving and growing with you. On your ride through the birth canal, your gut filled with a wide cast of microorganisms passed along by your mom. Then skin-to-skin contact, first foods, infections (and antibiotics), and all those germy toys changed your microbiome. Each new interaction, from childhood on, brings in guest stars, removes old standbys, and casts long-term recurring roles— your gut’s world is constantly in flux.
Animal and human research has found that the gut microbiome can be influenced by environmental factors such as chronic stress, artificial sweeteners, pesticides, disinfection, and ultrafine particles in polluted air. You can pick up new gut bacteria from your pet or a bad meal, Dr. Bhatt notes. Ultimately, microbial worlds wholly unique to you inhabit your body.
Helpful gut microorganisms have processes for breaking down foods and turning them into ingredients our bodies use. They develop the immune system, block pathogens, synthesize vitamins , and more. How the gut talks to the brain
In the past, you’ve probably lost your appetite because of stress or sadness—or falling in love. Maybe you’ve “followed your gut” or made a “gut decision.” These familiar terms and experiences clue us in to why some researchers are now calling the gut our “second brain” and saying bacteria may be the “master puppeteers” of our brains.
Scientists aren’t sure yet how the gut’s microbiome influences the brain—but it seems to be a fascinating two-way relationship. For example, among middle-aged adults, a more diverse microbiome was associated with better performance on cognitive tests . Various theories posit that the gut produces molecules that signal the brain via the bloodstream or the enteric nervous system . For example, specific gut bacteria can detect and increase the production of serotonin, which is associated with feelings of contentment. In fact, 90% of the body’s serotonin is made right in the gut . Another kind of bacteria commonly found in the human gut, Lactobacillus rhamnosus , actually contains a neurotransmitter that can help calm anxiety . Other bacteria may influence our social behavior and interactions and our responses to stress.
“It’s a two-way street of feedback loops” between the gut and the brain, says researcher Laura Cox, Ph.D. , a Harvard assistant professor seeking to understand how the microbiome can affect the brain in aging. What happens in the brain when gut bugs go bad
Sometimes unhelpful critters stage a takeover of the gut. This overpopulation can lead to gut dysbiosis , a negative imbalance that seems to cause static in the body’s communication lines and influence the brain’s everyday work. For example, gut dysbiosis is associated with depressive-like behaviors. In an animal study, transferring a mood-disordered animal’s gut bacteria into a healthy animal led to depressive symptoms for the formerly well animal, says Smita Patel, D.O., a neurologist and sleep specialist at iNeuro Institute . Other research is investigating the links between the gut microbiome and ADHD , autism spectrum disorders , anxiety , and stress . Unhelpful gut microbes may create irritants to the immune system that travel through the bloodstream and influence the brain’s immune cells. For example, the guts of Alzheimer’s disease patients show a lack of diversity compared with those of similar adults and are often overpopulated with a specific microbe. This microbe may impair immune functions related to clearing a plaque built upon the brain’s structures that is related to Alzheimer’s symptoms . Sex-based differences come into play as well, says Cox. The gut microbiota can regulate levels of hormones, including estrogen. When gut dysbiosis sets in, estrogen levels can change, possibly influencing cognitive decline.
Fascinating research is now being done by the Alzheimer Gut […]
More for You
A new study has revealed an important way in which sleep helps the brain process emotions for the next day, and while the findings were discovered in mice, they could also help us solve some of the mysteries of human sleep.
The role of sleep in brain function is still very much an enigma, but there is overwhelming evidence that rapid eye movement (REM) sleep helps humans consolidate their emotional memories.
But how that actually plays out in the brain is something scientists are still investigating.
The prefrontal cortex is a part of the brain that is heavily involved in emotional processing, and yet during REM sleep, some of its neurons, known as pyramidal neurons, are strangely quiet .
That might sound paradoxical at first. After all, how is this part of the brain helping us control our emotions during sleep if it’s not being active when we’re actually getting some shut-eye?
As it turns out, silence is also a powerful tool. Research on sleeping and awake mice suggests the quieting of the prefrontal cortex during REM sleep helps the whole system reset.
The findings are consistent with other recent studies that suggest sleep keeps neuronal activity under control.
Without proper REM sleep, networks in the brain can become ‘oversaturated’ with emotional messages, like fear, making it harder to determine important signals from background noise. When awake, this can lead a mouse to act overly fearful or not fearful enough.
When active and awake, neurons in the brain receive messages from their ‘arms’ (aka their dendrites). These messages are then conveyed to the body of the neuron (aka the soma), which is responsible for propagating messages to other neurons.
During REM sleep, however, neurons in the prefrontal cortex of mice appear to behave differently. The dendrites show increased activity, but the soma shows decreased activity.
“This means a decoupling of the two cellular compartments, in other words soma wide asleep and dendrites wide awake,” explains neurologist Antoine Adamantidis from the University of Bern in Switzerland.
In simple terms, this decoupling means that neurons are processing information they have already received, but not sending messages on.
With the body of the neuron no longer sending off as many messages, the arms of the neuron have time to consolidate the information they have already received, essentially ‘learning’ which incoming messages should be sent off and which should not.
This allows the brain to better respond to environmental changes the next day, allowing animals to discriminate between danger and safety with greater effect.
When the activity of dendrites were inhibited during REM sleep, mice in the study lost their ability to discriminate between audio cues associated with danger and safety.
Meanwhile, when the soma was not effectively silenced during REM sleep, mice became more attuned to danger signals overall.
“This may result in overconsolidation of emotional memories observed in post-traumatic stress disorders and other affective psychiatric and mood disorders often associated with REM sleep disturbances,” the authors suggest .
The mechanism has not yet been observed in human neurons, but the findings could help scientists better understand why conditions like post traumatic stress disorder and sleep disturbance are so closely linked .
The study was published in Science .
Study: Turmeric offers mental health benefits for overweight individuals

( Natural News ) A 12-week randomized controlled trial published in Nutrition Journal found significant improvements in the mental health scores of participants who took turmeric capsules.
For the study, the researchers invited 90 men and women between ages 50 to 69 years old, who are considered overweight based on their body mass index (BMI). The participants were divided into two groups.
The turmeric extract group took two capsules daily for 12 weeks. Prepared by the House of Wellness Foods, the capsules contained a mixture of hot water and supercritical carbon dioxide extract with turmeric as well as gelatin, glycerin, soybean-derived emulsifier and beeswax . The other group took two placebo capsules containing carob and tartrazine as coloring agents to match the color of the turmeric capsules.
The participants reported to the institute on the fourth, eighth and 12th week to have their weight, BMI and C-reactive protein measured. They also answered questionnaires on their mood states and quality of life.
“Compared with the placebo group, body weight, body mass index and serum levels of C-reactive protein and the complement component were significantly lower in the group that took the turmeric capsules. In addition, the turmeric extract group showed a significant improvement in the SF-36 (the 36-item short-form health survey) subscale score for mental health and the profile of mode state score for anger and hostility,” the researchers involved in the study wrote.
The researchers concluded that turmeric extract may improve mental health by reducing low-grade inflammation and alleviating undesirable symptoms related to inflammation. Low-grade inflammation is related to aging, obesity and an unhealthy lifestyle. This can also be associated with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, Alzheimer’s disease , mood disturbance, cancer and mortality. “Results suggest that daily intake of a mixture of a hot water extract and supercritical carbon dioxide extract of turmeric may have the potential to improve mental health and negative mood state by reducing chronic low-grade inflammation,” the researchers wrote.
The study was conducted in Japan by the House of Wellness Foods Corporation’s Research & Development Institute. Turmeric: One of the most studied spices in the world
Turmeric is a golden spice that comes from the root of the Curcuma longa plant and one of the most studied spices in the world. Dozens of research have long established that turmeric has some amazing medicinal properties , with major benefits to the heart and brain.
It is anti-inflammatory and recommended by many herbalists and naturopaths for people suffering from conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn’s disease. (Related: The six health benefits of turmeric .)
Turmeric also has natural antibiotic and antiviral properties . Consuming foods or beverages with turmeric is a good way to go if someone is suffering from the flu or an infection. Turmeric has compounds that can naturally help kill off both bacteria and viruses and help the body recover more quickly from microbial attacks.
Curcumin , one of the main active ingredients in turmeric, has been shown in several studies to help prevent or treat different types of cancer, including melanoma ands cancers of the breast or prostate gland.
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body, helping with digestion, blood sugar balance and the removal of waste products before they can harm the body. Turmeric helps detoxify the liver before it becomes compromised.
This golden spice can be easily incorporated into any diet and be added to a lot of recipes. With just a pinch of the powder, one can enjoy the difference it makes to the taste of curries, stir-fries, casseroles and even smoothies.
Visit Turmeric.news to know more about the health benefits of turmeric.
Watch the video below to learn how to create ground turmeric from fresh turmeric roots . No compatible source was found for this media.
This video is from the Natural News channel on Brighteon.com . More related stories:
Why turmeric is truly a gold superfood .
How to unlock the healing potential of turmeric .
Protect your heart with Turmeric . Sources include:
WhFoods.com
Studies suggest boron has potent cancer-fighting properties

( Natural News ) Following a balanced diet is important for your overall well-being. And according to several studies, consuming foods rich in the trace element boron can help protect you from certain types of cancer . How does boron protect you from cancer?
Boron is a trace mineral that naturally occurs in different plant foods. It is a structural component of plant cell walls and has a role in seed formation, pollination and plant growth.
Several studies have shown that boron acts as a potent cancer-fighting agent.
Cervical cancer
Many studies have been conducted in Turkey due to the country’s unusually low incidence of cervical cancer . Researchers believe that is partly due to Turkey’s boron-rich soil.
According to studies on women living in boron-rich and boron-poor areas, there is a lower incidence of cervical cancer among the former compared to the latter.
Data suggests that boron affects the life cycle of the human papillomavirus (HPV). This is important because HPV is a primary factor in 95 percent of cervical cancer cases.
Lung cancer
In a study conducted by researchers from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center from 1995 through 2005, findings revealed that postmenopausal women undergoing hormone replacement therapy enjoyed a reduced risk of lung cancer after increasing their boron intake.
Prostate cancer
Data from various studies have identified boron as a crucial component in reducing the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells.
One study revealed that mice with prostate cancer tumors experienced up to 38 percent shrinkage of their tumors when exposed to boron . The trace mineral is also associated with a lower risk of prostate cancer. Other health benefits of boron
Calcium loss is an issue that plagues women, especially as they age. Studies in humans and animals have revealed an important link between bone health and boron.
These studies have shown that boron benefits bones in many ways: Boron can help prevents bone demineralization.
Boron relieves bone problems linked with vitamin D and magnesium deficiency.
Boron helps prevent calcium loss.
Boron improves and maintains bone density.
Boron helps boost bone strength.
Studies have also shown that boron offers these amazing health benefits: Boron boosts magnesium absorption.
Boron helps improve your body’s use of estrogen, testosterone and vitamin D.
Boron helps improve wound healing.
Boron may help decrease the adverse side effects caused by chemotherapy.
Boron raises levels of catalyst, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and other antioxidant enzymes.
Boron can help lower levels of C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a) and other inflammatory biomarkers.
Boron aids in the activity and formation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), S-adenosyl methionine (SAM-e) and other key biomolecules.
Boron helps improve the electrical activity within your brain, which may benefit improved short-term memory among elderly patients. The trace element can also help boost cognitive performance. Boron offers protective benefits against heavy metal toxicity and oxidative stress caused by pesticides. Incorporating boron into a balanced diet Some plants contain boron. You can also boost your intake by taking boron supplements. (Related: Research shows fish oil supplements boost the effectiveness of cancer treatments .)Fruits, legumes, tubers and other plant foods are full of important trace minerals like boron.Below are the top ten sources of boron: 1 cup prune juice – 1.43 mg 1/2 cup avocado – 1.07 mg 1.5 oz. raisins – .95 mg 1 medium peach – .80 mg 1 cup grape juice – 0 .76 mg 1 medium apple – .66 mg 1 medium pear – .50 mg 1 oz. roasted and salted peanuts – .48 mg 1/2 cup refried beans – .48 mg 2 tablespoons peanut butter – .46 mg Drinking prune juice can help boost your digestive health . Meanwhile, avocados are full of healthy fats and dietary fiber. Additionally, avocados are rich in nutrients like copper, folate and vitamin K.There is still not enough data available for the Food and Nutrition Board to determine a recommended daily allowance for boron. But according to the World Health Organization , adults can safely take one to 13 mg of boron daily.Visit Superfoods.news to learn more about other foods that contain cancer-fighting agents.Watch the video below to know more about the health benefits of supplementing with boron . No compatible source was found for this media.This video is from the Holistic Herbalist channel on Brighteon.com . More related stories: Jingfukang: The TCM herbal medicine that stops lung cancer in its tracks . TCM herbal formula makes resistant cancer cells susceptible to effective treatments . Animal drug fenbendazole shows promise in treating parasites, cancer in humans . Sources include: NaturalHealth365.com
These natural substances NEUTRALIZE covid vaccine spike proteins

( Natural News ) It is estimated that more than 4.5 billion people worldwide have now been “vaccinated” for the Wuhan coronavirus (Covid-19). Many of them now suffer from “long” covid, however, which could be due to the persistent damage caused by the spike proteins contained in (viral vector) and produced by (mRNA) the jabs.
Also known as the S protein, covid jab spike proteins do a whole lot more harm than just bind to the body’s ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) receptors, allowing the virus to invade cells. It turns out that covid jab spike proteins interact with many other cellular tissues, including in the lungs, mitochondria and cardiovascular system.
This assault causes all kinds of health damage to the many intricate and complex systems of the body. And in the case of messenger RNA injections (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna), the spike proteins continue to be manufactured inside the body long after the initial jabs.
We now know for a fact that jab spike proteins:
• Damage the lung cells (including the pulmonary alveoli and pulmonary endothelial cells)
• Damage the mitochondria and DNA structures
• Damage cardiovascular cells
• Increase the risk of blood clots
• Damage brain cells
• Promote inflammation
• Suppress immunity
• Increase the risk of cancer
A 2021 paper published in the bioRxiv preprint repository found that spike proteins cause the Type 1 catalytic receptors in the kidneys to increase in kidney cell tissue, making the kidneys more susceptible to the Fauci Flu.
Spike proteins also cause cells in the small intestine to stimulate large amounts of L-SIGN (liver / lymph node-specific intracellular adhesion molecules-3 grabbing non-integrin) receptors, which defend against pathogens. The problem with this is that after a large number of adhesions occur, the small intestine becomes more susceptible to viral infection. Similarly, spike proteins trigger an increase in DC-SIGN (Dendritic Cell-Specific Intercellular adhesion molecule-3-Grabbing Non-integrin) receptors in the lungs, which can trigger inflammatory symptoms in the lungs.
“In addition, spike proteins can cause different degrees of oxidation of the organs, leading to more cells’ premature deaths and putting the body in a hyperoxidized state, which may further increase the risk of cancer,” reports The Epoch Times .
Another study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA) found that spike proteins negatively impact lung functionality by causing the pulmonary alveolar cell walls to thicken and solidify. They also inhibit the pulmonary cell mitochondria, which is where energy is produced.
Prolonged covid symptoms could actually be the spike proteins damaging mitochondria and blocking their energy production. The result is a cascade of abnormalities and health problems that vary from person to person.
Perhaps the biggest fear is cardiovascular damage, the risk of which is greatly increased by the presence of spike proteins. The risk of blood clots increases massively following exposure to them, hence why many “fully vaccinated” people are developing conditions like myocarditis and pericarditis. Here’s how to protect yourself against spike protein damage
If you or someone you know got “vaccinated” for the Wuhan coronavirus (Covid-19) and now regret it, all hope is not lost. The following vitamins and herbs have been scientifically shown to help neutralize spike proteins and the damage they inflict on the body.
The World Council for Health (WCH) recommends the following immune-boosting compounds, which may help to expel vaccine spike proteins while improving the symptoms they cause:
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
Omega 3 fatty acids
Quercetin
Melatonin
Zinc
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is a powerful anti-inflammatory that further helps protect the body against spike protein damage.
Consuming a low-histamine diet will also help to prevent the immune system from overreacting and harming the body more, a situation known as a cytokine storm.
Common medications that can help improve symptoms include:
Aspirin
Antihistamines
Steroids
Colchicine
Mast cell stabilizers IvermectinAspirin helps to thin the blood, reducing the risk of thrombus and the ever-dreaded Fauci Flu shot blood clots that many people are suffering.Antihistamines, in a similar way to NAC, prevent over-activation of the immune system while the others help to minimize inflammation.Ivermectin, by the way, is a powerful remedy for a variety of health conditions, including cancer. For many, it also rids the body of the Fauci Flu.In the plant kingdom, the following substances are spike protein inhibitors:Selfheal extract Pine needle extract Dandelion leaf extract Rheum emodimNeem is another spike protein inhibitor, as is ivermectin.As for spike protein neutralizers , the following herbs and substances show incredible promise in remediating the damage caused by the injections:NAC Glutathione Fennel tea Anise tea Pine needle tea St. John’s Wort Lithospermum Vitamin C“Some of these ingredients, such as the shikimic acid contained in pine needles, have antioxidant properties that can reduce oxidized free radicals in the body and provide a detoxifying effect,” reports The Epoch Times .More of the latest news about the Wuhan coronavirus (Covid-19) can be found at Pandemic.news . Sources for this article include: TheEpochTimes.com
Top 6 anti-aging superfoods you can add to your diet

( Natural News ) Eating a balanced diet is key to maintaining optimal health. According to David Sinclair, a longevity expert and Harvard geneticist, superfoods like avocados and blueberries can increase your life expectancy.
Aside from exercising regularly and supporting your mental health, incorporating nutritious foods into your regular diet can help you stay healthy and live longer.
Below are six items at the top of Sinclair’s “ longevity-minded grocery list .” Avocados
Avocados rank number one because they are full of healthy monounsaturated fat and dietary fiber, which can help you feel full for longer.
Avocados are also rich in other nutrients like carotenoids, minerals, omega-3s, phytosterols, polyphenols, protein, soluble fiber and vitamins B-complex, C, E and K. These benefits work together to support your brain, eye and heart health by balancing your cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Here are some suggestions on how to eat more avocado : Make scrambled eggs with diced avocados.
Season avocados with a pinch of salt and pepper along with other seasonings like cayenne pepper or paprika.
Serve avocadoes stuffed with eggs, herbs and spices.
Eat avocados with your breakfast toast.
Make homemade guacamole with avocados, herbs and seasonings.
Olive oil
Olive oil is second on Sinclair’s list because it is a natural source of healthy fats. You can enjoy high-quality olive oil as a dip for bread or gluten-free bread.
Olive oil is rich in beneficial antioxidants, phytosterols and vitamins that can help boost skin and brain health. It also helps optimize cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
According to a recent study, there is a link between olive oil intake and increased longevity. Brussels sprouts
Third on Sinclair’s list are Brussels sprouts , especially when roasted and pan-fried with some garlic, salt and pepper.
Brussels sprouts are cruciferous vegetables full of vitamins A, C and K and folate. The vegetable also contains minerals like potassium and fiber that promotes feelings of satiety.
Brussels sprouts support cell and immune health because it contains antioxidants like kaempferol and quercetin, respectively. (Related: Broccoli is a powerful anti-aging food that you should be eating every day .) Cantaloupe
Cantaloupes rank fourth on the list, and according to Sinclair, they are one of the most nutritious fruits on the planet.
Their orange color comes from the carotenoid beta-carotene, which your body converts to vitamin A. The vitamin offers many benefits, such as promoting eye, skin and reproductive health. Blueberries
Blueberries rank fifth on Sinclair’s list of must-have superfoods.
Blueberries are full of beneficial antioxidants that promote healthy skin and collagen production thanks to their vitamin C content. They are also full of dietary fiber, which helps maintain healthy blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Blueberries are rich in anthocyanins that give them their blue-purple pigment and play a crucial role in brain and overall health. According to studies, there is a link between anthocyanins and healthy aging. Nuts
Nuts like cashews and Brazil nuts are sixth on the list. They contain high amounts of protein, with 5.1 grams per ounce of cashews and four grams per ounce of Brazil nuts.
Cashews also contain copper and magnesium, while Brazil nuts are rich in selenium. However, you should limit your consumption of Brazil nuts to one to three pieces per day to avoid consuming too much of the mineral.
Nuts are also full of “good” fats like omega-3s and omega-6s.
Follow a balanced diet and support longevity by eating tasty superfoods like avocados and blueberries. You can find more articles about other anti-aging superfoods at Superfoods.news .Watch the video below to know how to curb your appetite with avocado . No compatible source was found for this media. More related stories: Top 10 anti-aging foods to nourish your skin from the inside . From kimchi to kefir, these are the best anti-aging foods you’ll find anywhere . Could a simple vitamin be an anti-aging tool ? Sources include:
Phytochemical in apple peels found to boost brain health

( Natural News ) A study found that a phytochemical in apple peels promotes the growth of new neurons . This is an important finding because the human brain becomes more susceptible to various health problems with age.
The elderly are susceptible to Alzheimer’s disease , a debilitating condition that can eventually turn a loved one into a stranger. Alzheimer’s can make you forgetful, and it can drastically change your personality to the point where it negatively affects your quality of life.
Fortunately, researchers are learning more about the factors that put people at risk of Alzheimer’s, as well as the healthy habits that can promote brain health. Quercetin and neurogenesis
According to the results of a collaborative study between researchers from the University of Queensland and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (GCND), a phytochemical in apple peels called quercetin can promote neurogenesis, or the growth of new neurons. The study was published in Stem Cell Reports.
The researchers reported that while the compound didn’t make the brain grow neurons at high concentrations, it was pro-neurogenic at low concentrations . This means supplementation with quercetin led to the creation of new neurons, specifically in the hippocampus.
The hippocampus is part of the limbic system where behavioral and emotional responses are generated. These responses are essential for survival and include feeding, the fight-or-flight response, reproduction and caring for babies. Other parts of the limbic system include the amygdala, basal ganglia, hypothalamus and thalamus. The hippocampus has an important role in memory consolidation, coding and learning. It also helps form a cognitive map, which is related to your ability to acquire new knowledge, store it and recall it later.
The hippocampus is also the area of the brain first damaged by the plaques and tangled fibers associated with Alzheimer’s. In 2020, there were an estimated 5.8 million Americans diagnosed with Alzheimer’s, and almost two-thirds were women.
According to health experts, the population of people older than 65 continues to grow. At the same time, the number of people with Alzheimer’s is also rapidly increasing. By 2050, experts estimate that at least 13.8 million Americans will have Alzheimer’s. How quercetin stimulates neurogenic growth
In the study, researchers analyzed how quercetin, a flavonol found in apple peels, can trigger neuron growth. Flavonols are plant pigments that give fruit and vegetables their bright colors.
The researchers reported that some plant compounds are vital for maintaining cognitive function because they help grow new neurons. Through neurogenesis, the brain can reshape and grow itself, which is essential for optimal cognitive agility. The researchers said they chose apples because they are widely available.
For the study, the researchers first analyzed quercetin, the most abundant flavonoid in apple peel. In the second half of the study, the researchers conducted an in vivo study using an animal model.
Data analysis revealed that apple peels contained compounds that help promote neurogenesis. Quercetin from the peel and another active compound from apple flesh, 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHBA), were found to increase precursor cell proliferation and neurogenesis.
The researchers measured the effect of these compounds on neural precursor cells or stem cells that can generate neural cell types within the brain. Results showed that the compounds had similar effects to those observed in earlier studies for other plant compounds like resveratrol and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which is found in green tea .
The researchers also found that the stem cells generated in the brain of mice were protected and exhibited more neurogenesis when quercetin and DHBA were added to the cell cultures. In addition, they found that structures in the brain associated with learning and memory had more neurons when the mice were given either quercetin or DHBA. (Related: Making healthy lifestyle choices can prevent the onset of dementia .) Other ways to boost brain health
While researchers continue to study the benefits of quercetin on neurogenesis , here are other ways to boost your brain health.
Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a potent antioxidant and a naturally occurring carotenoid. It is responsible for the pink or red color found in seafood like lobster, salmon and trout.
Often called the “king of antioxidants,” astaxanthin is derived from the microscopic algae haematococcus that produce it as a protective mechanism to shield it from ultraviolet (UV) light. Once consumed, it helps protect you from reactive oxygen species and oxidation that are linked to aging like Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease and Parkinson’s disease.
In a review of scientific literature, researchers identified several pathways astaxanthin may take to help slow brain aging. Findings also suggest that astaxanthin can boost BDNF levels and reduce oxidative damage to DNA, lipids and proteins.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are healthy fats found in fatty fish that help protect the brain. Omega-3s are long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids that include EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
These nutrients are crucial for cell membrane health and have an anti-inflammatory role in the body. DHA is needed for brain health because it is an important structural component found in high levels in neurons.
Low levels of DHA were associated with both memory loss and Alzheimer’s. Research also found that brain diseases may potentially be reversible when sufficient DHA is provided.
To optimize brain health, eat wild-caught Alaskan salmon , krill oil or other safe fish like sardines, to meet these nutritional requirements.
Avoid processed food
Following a balanced diet and avoiding processed foods and sugar can also help boost brain health.Eating high-sugar foods regularly was found to increase your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes, which is linked to a 60 percent higher risk for any type of dementia.According to a study, even without a diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes volunteers with higher blood sugar levels had lower hippocampal volume and people with higher hemoglobin A1c and glucose measurements had significantly lower scores on memory testing. Avoid drinking alcohol Managing your alcohol intake or avoiding alcohol altogether can also help boost brain health since chronic excessive alcohol consumption is often linked to dysfunction of neuronal dysfunction and brain damage.Even moderate alcohol consumption can reduce brain volume.In a […]
Top 8 tasty and nutritious vegetables for juicing

( Natural News ) Juicing is a great way to improve your overall health, especially if you’re looking for a quick and convenient way to boost your nutrient intake. But if you’re new to juicing, it can be rather difficult to choose which vegetables to use when making a green juice.
Below are eight of the most nutritious vegetables that you can use to make a refreshing green juice. Beets
The most common beets are royal maroon, but you can also find white or yellow beets. The beetroot is the taproot of the beet plant, and it offers many health benefits when juiced.
Beets are full of nutrients like folate and manganese. They’re also rich in nitrates that can help boost brain health, athletic performance and blood pressure.
In a 2019 randomized controlled trial published in the journal Nutrients , researchers observed the results of acute supplementation with nitrate-rich beet juice in 13 younger and 11 older adults. The volunteers consumed 150 milliliters of beetroot juice before walking for 30 minutes on a treadmill.
According to the results, both groups showed improvements. However, there were significant reductions in diastolic blood pressure among older adults.
These findings suggest that acute beetroot supplementation could help boost cardiovascular health in older adults .
Aside from the taproot of beets, you can also juice the leafy greens or beet greens, which are also full of many beneficial nutrients. Broccoli
Broccoli is a superfood powerhouse. This cruciferous vegetable is full of antioxidants and various nutrients, such as potassium and vitamins A, B6 and C. Additionally, broccoli contains kaempferol, a flavonoid antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals and prevent diseases linked to inflammation. Data from a study published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology revealed that kaempferol has neuroprotective properties that can help combat conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety disorders, glioblastoma, neuropathic pain and Parkinson’s disease. The flavonoid promotes a beneficial anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect.
Reap these neuroprotective benefits by adding broccoli to your green juice. (Related: Quench your thirst in the healthiest way possible by juicing these 9 vegetables .) Cabbage
Cabbage is a hydrating vegetable and it contains many essential nutrients like folate, manganese, and vitamins B6, C and K.
Classified as a cruciferous vegetable, a 2020 study published in Frontiers in Nutrition has found that cabbage can help reduce the risk of inflammation, diabetes and heart disease. Carrots
Carrots are low-calorie and naturally sweet. They’re also full of nutrients like biotin, potassium and vitamin A.
Carrots are popular for their high carotenoid content, which includes alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, lycopene and lutein. Data from a 2021 review published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry revealed that these compounds act as antioxidants in your body and help reduce oxidative stress.
Carotenoids in carrots also help reduce your risk of certain cancers , diabetes, eye disease and heart disease.
Add carrots if you prefer veggie juice that’s naturally sweet and not too saccharine. Carrot also complements other juiced fruits and vegetables like beets, citrus and ginger. Kale
Kale is low-calorie but nutritious and it contains vitamins A, B6, C and K, along with calcium and potassium. Another cruciferous vegetable, kale is also a good source of the minerals copper and manganese.
But keep in mind that kale also contains goitrogens, which are naturally occurring substances. These “anti-nutrients” can block iodine from entering the thyroid gland. Iodine is a trace mineral that helps your body make thyroid hormones that promote normal metabolism.
A deficiency of iodine can cause goiter or the enlargement of the thyroid.
Raw kale contains the important antioxidant beta-carotene, which helps neutralize harmful free radicals that increase your risk of developing chronic conditions like heart disease. Spinach
Spinach is a leafy green vegetable full of beneficial antioxidants like kaempferol, lutein and quercetin. It’s also rich in vitamins A and C, along with nitrates that help boost your heart health.
In a 2015 randomized controlled trial, researchers studied the effect of spinach, a source rich in nitrates, on arterial stiffness and related hemodynamic measures in 27 healthy adult participants.
The volunteers consumed spinach for seven days. Findings revealed that there was a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The study was published in the journal Clinical Nutrition Research . Tomatoes
Often used as a vegetable, tomatoes are scientifically considered the fruit of the tomato plant.
Tomatoes are a kitchen staple and they’re often used to make hearty sauces and soups. Tomatoes are also full of nutrients such as folate, potassium and vitamin C. Wheatgrass
Grass doesn’t sound appetizing, but adding wheatgrass to green juice gives your beverage an amazing nutrient boost. Wheatgrass is a nutrient-dense edible grass that’s also considered a vegetable.This superfood contains nutrients like copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and 17 different amino acids.According to a 2014 study published in the journal Natural Product Research , methyl phophorbide a (MPa) presents antioxidative and anticancer activity when isolated from the ethanol extract of the wheatgrass plant. Researchers reported that their findings prove that wheatgrass can be used to treat cancers, iron-overloaded disorders and oxidative stress.For a nutritional boost, replace espresso with a shot of wheatgrass. You can also add wheatgrass to almost any juice recipe. Delicious fruit and vegetable juice pairings to try Here are some thirst-quenching, nutritious and tasty fruit and veggie pairing suggestions for your next glass of green juice: Apple, bitter gourd and lemon Avocado, celery, cucumber and lemon Avocado and papaya Carrot and sugarcane Cherry, dragonfruit and mango Cucumber, kale and pear Lemon, papaya and pineapple Starfruit and strawberries How does juicing improve your diet? According to a review published in the journal Nutrients , regular consumption of at least 500 milliliters of fruit juices daily can help improve vascular function and reduce blood pressure, as revealed in short- to medium-term studies.In another 2021 study published in ACS Food and Technology , researchers discovered that juicing techniques could influence the antioxidant and phytochemical content of vegetable juices. Compared to high speeds, juicing at low speed helps preserve more of these beneficial compounds in the vegetable juice due to less introduction of heat.Low speeds also […]
Cause of the Massive Drop in Testosterone in Men: Estrogens in Water Supply and Food Packaging

Testosterone levels in men have dropped by 50% in the last 2 decades.
Xeno-estrogens are in the water supplies of many cities and cannot be filtered out.
Also in plastic packaging.
Women on birth control urinate estrogen into the water systems. Current water treatment technology does not filtered the estrogen out.
Best way to counteract is working out, eating healthy and taking testosterone suppliment and estrogen blocker.
Testosterone supplements below.


CDC warns against too much fluoride in kids’ toothpaste, ignores harms from fluoridated water

Tags: absurd , badhealth , badmedicine , badscience , brain damage , brain health , CDC , children’s health , clean water , Dangerous , Dental fluorosis , dental health , dentistry , Flouride , Fluoridated Water , harmful chemicals , insanity , poison , products , tap water , toothpaste , toxic ingredients
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
( Natural News ) According to the CDC, 40% of children between the ages of 3 and 6 use potentially dangerous amounts of toothpaste .
(Article republished from ChildrensHealthDefense.org )
The CDC and ADA recommend using no more than a pea-sized amount for children in this age group, and those younger than 3 should use no more than the size of a rice grain on their toothbrush.
The problem with using excessive amounts of toothpaste has to do with the fluoride it contains. If you look closely, you’ll find fluoride-containing toothpastes have a warning on their label stating that “If you accidentally swallow more than used for brushing, seek professional help or contact a poison control center immediately.” This warning was made mandatory for fluoride-containing dental products by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in April 1997.
Ironically, while swallowing toothpaste is recognized as a cause for concern, we’re supposed to believe that drinking fluoridated water in any quantity is not only safe but beneficial for our teeth.
Too much fluoride causes dental fluorosis
The fact of the matter is that fluoride is a toxic substance with no known biological imperative. Researchers have even questioned its efficacy as a topical anticaries prophylactic .
Dental caries are caused by the demineralization of your teeth by the acids formed during the bacterial fermentation of dietary sugars. Demineralization is countered by the deposit of minerals from your saliva. However, the remineralization process is a slow one, and fluoride is said to prevent dental caries by enhancing this remineralization.
The problem is that your teeth do not actually rely on fluoride for remineralization. What’s more, research has concluded that the protective shield fluoride forms on teeth is up to 100 times thinner than previously believed.
It has long been believed that fluoride changes the main mineral in tooth enamel, hydroxyapatite, into a more-decay resistant material called fluorapatite.
However, the researchers found that the fluorapatite layer formed in this way is only 6 nanometers thick — meaning it would take almost 10,000 such layers to span the width of a human hair.
As noted by the authors, “it has to be asked whether such narrow … layers really can act as protective layers for the enamel.”
Meanwhile, fluoride has been shown to cause significant systemic harm when ingested, which is part and parcel of the CDC’s 2019 warning against using too much toothpaste. As reported by the Chicago Sun-Times:
“Brushing with too much toothpaste can damage enamel, as children could swallow too much fluoride while their teeth are developing, the CDC says. This can cause dental fluorosis, white marks and discoloration of teeth.”
However, dental fluorosis is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to fluoride damage. For example, evidence shows fluoride is an endocrine disruptor that can affect your bones, brain, thyroid gland, pineal gland and even your blood sugar level. Importantly, it’s a known neurotoxin, shown to lower IQ in children.
Over half of U.S. kids have fluoride-damaged teeth
According to research presented at the April 2017 National Oral Health Conference in Albuquerque, New Mexico, 57% of youth between the ages of 6 and 19 years have dental fluorosis, a condition in which your tooth enamel becomes progressively discolored and mottled.
When Fluoride Action Network (FAN) researchers analyzed the same set of data, they found over 21% of adolescents had moderate fluorosis and 2% had severe fluorosis .
According to FAN, “The data suggests that up to 24 million adolescents now have some form of dental fluorosis, with over 8 million adolescents having moderate fluorosis, and 840,000 having severe fluorosis.”
Incredibly, the situation is still worsening. According to the most recent data, which has yet to be published, the dental fluorosis rate in the U.S. may now be a staggering 65%.
In stark contrast, when water fluoridation was first started in the U.S. in 1945, it was promised that only 10% of people would suffer from mild dental fluorosis at the then-recommended levels. Clearly, they were wrong.
In 2011, concerns over escalating fluorosis rates prompted the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to lower the recommended level of fluoride in drinking water, from a previously recommended range of 0.7 to 1.2 mg/L to 0.7 mg/L.
However, adverse effects, including reduced IQ, behavioral alterations, neurochemical changes, hypothyroidism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have been demonstrated even at that lower level, so while it reduced exposure for many, the most serious risks remain.
What’s more, reduced IQ has been seen in study participants with higher urinary fluoride concentrations even when no dental fluorosis was present, which suggests the doses of fluoride that impair cognitive ability are far lower than those that cause severe dental fluorosis. Fluoridated water is likely a far greater concern Unfortunately, public health officials often brush off fluorosis as a purely aesthetic issue, one they believe is an okay trade-off for the supposed benefits of fluoride. In reality, dental fluorosis is an outward sign that fluoride is damaging the body in other ways as well.Research has found impairment in cognitive abilities among children with fluorosis (even mild fluorosis) compared to children with no fluorosis, for example. Studies have also found that children with higher levels of fluorosis have increased rates of cavities — a finding that suggests more is definitely not better, not even when it comes to protecting against cavities. Importantly, the CDC completely ignores the role fluoridated water plays in this epidemic, as toothpaste is by far not the only source of fluoride for young children, and probably isn’t the most significant source either.In a January 2019 study in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, the prevalence of dental fluorosis among 10- to […]
5 Reasons to use cold pressed olive oil, a cooking oil full of healthy fats

( Natural News ) If you’re a health-conscious person, it’s normal to think about the different ingredients you can cook your meals with. But are you using a healthy cooking oil?
If you want to switch to a healthier cooking oil, try cold pressed olive oil . Olive oil is a versatile superfood that’s packed with essential nutrients.
Olive oil originated from the Mediterranean region and has been used for centuries as both food and medicine.
Different types of olive oil differ in quality depending on how the oil is extracted. The oil processing method used also influences the quality of the final product.
Compared to other kinds of cooking oil, cold pressed olive oil stands out as one of the best types of olive oil that you can cook with or add directly to your meals.
Olives are a nutrient-rich stone fruit. Olive oil contains oleic acid, a beneficial monounsaturated fat.
Olive oil is a natural source of vitamins E and K. Cold pressing olive oil helps the extracted oil retain its healthy fats and antioxidants.
Here are five amazing reasons to switch to cold pressed olive oil. Olive oil is full of healthy fats
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) recommends that adults limit their calories from fat to 30 percent, with a focus on unsaturated fat.
If you use olive oil, you can rest easy because it contains oleic acid, a healthy unsaturated fat. According to a 2013 review published in Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry , oleic acid has a beneficial modulatory effect on autoimmune diseases, cancer and inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Oleic acid also helps promote wound healing.
According to another study published in the journal Medical Science Monitor , supplementing with olive oil, which contains healthy fat, may help lower LDL cholesterol or “bad” cholesterol.
An article from Harvard Health suggests that olive oil contains omega-six and omega-three fatty acids, which have roles in blood clotting, blood pressure regulation and immune system response . Olive oil is an antioxidant-rich cooking oil
Because cold pressed olive oil isn’t treated with heat, it’s more likely to retain a higher portion of its antioxidant content.
Antioxidants are important because they can help prevent oxidative stress by protecting you against harmful free radicals. Oxidative stress is one of the major causes of inflammatory diseases such as cardiovascular disease. (Related: Olive oil vs. avocado oil: Both are green and healthy, but which one’s better for you? )
A 2018 peer-reviewed study published in IntechOpen’s Functional Foods has found that oleocanthal, oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol are the phenolic compounds mainly responsible for the antioxidant activity in olive oil.
Olive oil also contains vitamin E , a powerful antioxidant. You can find vitamin E in other superfoods like nuts, seeds, some vegetables and some fortified products.
Vitamin E plays many roles in your body. It can also help protect your cells from oxidative damage, and it has a role in proper immune function and cellular signaling . Olive oil helps protect against inflammation
The IntechOpen study also suggests that olive oil contains anti-inflammatory properties.
Oleocanthal, a compound in olive oil, is a natural anti-inflammatory agent. When combined with the antioxidant properties and healthy fats in olive oil, dietary supplementation may naturally help reduce inflammation.
Additionally, olive oil can help reduce the risk of certain chronic conditions linked with inflammation, such as arthritis , diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Olive oil helps boost brain health
Experts have also found that supplementing with cold pressed olive oil can support brain health.
The Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet is a specific diet that focuses on the use of olive oil and is backed by scientific research. The MIND diet is a combination of the traditional Mediterranean diet and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet , as recommended by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.
According to data, volunteers following the MIND diet have shown reduced rates of declines in mental sharpness and memory with age in population studies. The finding has also shown reduced rates of declines following a stroke.
In a 2015 study published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia , scientists worked with 923 participants. According to data from the 4.5-year study, there was a 53 percent percent rate reduction of Alzheimer’s disease in volunteers who adhered to the diet.
The MIND diet also included other brain health-boosting superfoods like berries, fish, nuts and whole grains. If you want to try the MIND diet, you should also reduce your sodium intake. Olive oil helps prevent heart disease Want to boost your heart health naturally ? Switch to olive oil now.According to the American Heart Association, a person dies of cardiovascular disease every 36.1 seconds in the United States. Based on 2019 data, there is an average of 2,396 deaths daily resulting from cardiovascular disease.Earlier research has proven that olive oil contains important compounds that can help fight inflammation and reduce LDL cholesterol.Data from a 2015 study on 84,000 women revealed that there was a 15 percent risk reduction of heart disease after replacing five percent of saturated fats with foods high in monounsaturated fats, such as olive oil. The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .Follow the Mediterranean diet , which relies on olive oil as a healthy fat source, to boost your heart health and reduce heart health risk factors. How to incorporate cold pressed olive oil into a balanced diet You can replace cooking oil for baking, roasting, or sauteing with cold pressed olive oil. The most straightforward way to include cold pressed olive oil in your diet is by substituting it for saturated fats.Here are some food swap suggestions for cold pressed olive oil: Replace bacon grease, butter or lard with cold pressed olive oil when cooking. Dip bread in olive oil instead of using butter. Make an olive oil dressing or purchase olive oil dressings instead of creamy salad dressings. Buy or make olive oil-based baba ganoush or hummus over cheesy or creamy dips. While cold-pressed olive oil is a healthy cooking oil, remember that it […]


