Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
East Meets West: 22-Year-Old Blends Asian Herbs and Matcha Into Zero Sugar Energy Drink

HONG KONG, Jan. 14, 2020 /PRNewswire/ — The story began like this – a young college student who suffers from mild dyslexia and struggles to spell created an one-of-a-kind tea soda made with organic Japanese matcha and several natural energy-boosting herbs to challenge Redbull’s traditional energy drinks.
The new in town HISE soda is a magical combination to power up your brain functions, especially on concentration and memory, and battle enervation and fatigue by strengthening your physical ability. The tea soda comes in environmental friendly aluminum cans that are infinitely recyclable and made with up to 95% of recycled material to avoid new cans production as green beverage business. The great blend of herbs & matcha provides you a great variety of vitamins (A, B, C, E, K etc.), minerals (ie. potassium, iron, and magnesium) and dietary fiber to improve your diet. Hise also helps you fight and stabilize harmful free radicals with the high antioxidants content from matcha, Rhodiola Rosea , Ginkgo Biloba and Eleuthero Root. “I used to rely on energy drinks to deal with my concentration issue as I hate pills. Sure, they do hype you up for three hours but the side-effects are just too much – blushing my skins, crazy heart pounding and energy crash,” the young innovator explained. “So, I turned to Chinese herbal and mint tea instead that worked like magic. Inspired by the natural drinks, I founded HISE, the powerful future energy soda that come with clean ingredients and zero sugar that are suitable for everyone, even diabetics and persons on a diet!”
To the remedy of many who want to stay energized but also value health, HISE’s new future soda comes with no side-effect but only side-benefits. With the recent super-food trend, matcha has been brought to the spotlight for its rich antioxidant content and free radical fighting properties. Matcha is also high in dietary fiber and fosters metabolism which assists you in weight control and keeping fit. On top of that, the energy soda features three types of top-notch Asian herbs that improve your heart health and help fight age-associated and long-term diseases. One of the three, Rhodiola Rosea, helps in improving mood and easing stress by correcting the chemical imbalances.
“Born in a family that is enthusiastic about teas and herbs, I am always amazed by their nutrition benefits. But we are aware that tea soda is also a soda that needs to taste good. So we studied the popular Western beverages’ taste and came up with this delightful tea lemonade recipe which is actually refreshing and sweet!” The Hong Kong based team pointed out that the sweet taste is from a new innovative natural sweetener extracted from the Eastern traditional favorite sweetener – Monk Fruit.
Excited for the future energy soda? HISE is now available as crowdfunding on Kickstarter https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/hisedrink/hise-organic-matcha-lemonade-soda-zero-sugar and check them out at www.hisedrink.com
SOURCE HISE Drink
25 Ways You’re Damaging Your Health and Don’t Even Know It

Sure, we all know that eating junk food, avoiding exercise, and drinking like Jimmy McNulty isn’t going to do any favors for our health and overall well-being. However, did you know there are many other habits, rituals, and practices most of us engage in that, unbeknownst to us, are also damaging our health—only we have no idea?
The Remedy spoke to some of the top health and medical experts around the country to reveal all the ways that we are inadvertently doing more hurt than harm to ourselves.
You might think you are eating a super-healthy diet, but are in fact consuming dangerous chemicals. “Most grain and soy products in North America are sprayed with Roundup—a.k.a. glyphosate—a known carcinogen and gut microbiome disruptor,” explains Dr. Steven Gundry, MD medical director at The International Heart and Lung Institute Center for Restorative Medicine and the New York Times best-seller The Plant Paradox and The Plant Paradox Cookbook . Basically, we unwittingly eat glyphosate while eating “healthy” whole grain products. He points out that even new plant-based hamburger meat products may have Roundup in them—as well as most of our animal products like chicken, beef or pork, as most are fed with these same tainted grains and/or soy.
The Remedy Rx: In order to avoid eating foods tainted by glyphosate, there are a number of things you can do. Eat organically, eat locally by shopping at your farmer’s market for meat and produce, or grow your own produce.
Dr. Gundry points out that the vast majority of whole grain products are loaded with plant proteins called lectins which are part of the plant’s defense system against being eaten. “As The Plant Paradox series show, lectins are major causes of leaky gut, arthritis, depression, weight gain and brain and heart disease as well as autoimmune diseases,” he explains.
The Remedy Rx: Reduce your gluten consumption. “As I have reported at The American Heart Association, most patients who remove gluten and other lectin-containing foods resolve autoimmune issues and leaky gut within months,” he says.
Artificial sweeteners might be a zero-calorie sugar-free alternative, but they aren’t doing any wonders for your digestive system. “Most people who use artificial sweeteners have no idea that they are destroying and altering their gut bacteria, the microbiome with every packet, the same bacteria that have the potential to keep them lean and happy,” Dr. Gundry says.
The Remedy Rx: Try to avoid artificial sweeteners. If you need a boost of sweet, you can always opt for a natural sweetener such as stevia.
You might not realize it, but certain positions while sleeping can damage your health. “Many people will sleep every night on their sides in the fetal position. While this seems harmless, this sleeping position can actually be detrimental to your health,” points out David Greuner, MD , of NYC Surgical Associates “When you sleep like this, it cuts your diaphragm’s free range down which can cause back pain as well as issues with your lungs.”
The Remedy Rx: Try another sleeping position. According to the National Sleep Foundation , the healthiest way to sleep in on your back.
It can be hard to remember to drink enough fluids. But try and remember it can be hazardous to your health. “Vein insufficiency can be amplified due to dehydration,” explains Dr. Greuner. “When you are hydrated your blood is thinner and flows better. When your blood is thicker, it can make vein insufficiency problems worse.”
The Remedy Rx: Drink lots of fluids! The Institute of Medicine of the National Academies of Sciences recommends 2.7 (11 cups) liters to 3.7 liters (nearly 16 cups) per day . “Make sure to stay hydrated to keep your entire body healthy including your veins!” says Dr. Greuner.
Just because a product is called “organic” doesn’t mean it is good for you. “Many packaged products are highly processed, and may contain many unhealthy ingredients,” points out Talia Segal Fidler , MS, HHC, AADP, nutritionist at The Lodge at Woodloch. For example, they may contain a high sugar content. “Even though it is organic, it is still sugar and still a processed product.”
The Remedy Rx: Remember that processed food is processed food and sugar is sugar—even if it has an organic label on it.
Most of us were raised believing that drinking fruit juice was actually good for you. However, Fidler points out that many fruit juices are loaded with sugar and high fructose corn syrup. “There are hardly any connections between the fruits and that beverage,” she explains. “You are basically only consuming sugar!”
The Remedy Rx: If you are going to drink juice, look for ones that are 100 percent juice and no added sugar. Better yet, eat a piece of fruit, so you get the belly-filling fiber.
Eating yogurt that has added fruits, or giving it to children thinking it is a good thing, is pretty common. Unfortunately, Fidler points out that those “fruits” are loaded with unhealthy sugar which defeats the purpose.
The Remedy Rx: “A better choice is to buy plain organic yogurt and add freshly cut fruits to it,” Fidler suggests. “For extra sweetness you can add a bit of local honey.”
Sure, many fish are high in good fats and can be a great addition to your diet. However, Fidler points out that size matters when it comes to just how healthy a swimmer is. “The larger the fish, the more likely that it may have a high mercury levels and other toxins,” she explains. This is due to the fact that the fish has lived longer and accumulated toxins overtime.
The Remedy Rx: Fidler suggests eating smaller fish, such as sardines, mackerel anchovies etc. Or, opt for a deep-water fish that isn’t exposed to the same toxins.
While farm raised salmon may boast health benefits in the form of omega 3 fatty acids, they can also be contaminated with toxins, explains Fidler. According to one study , it is higher in cancer causing pollutants.
The Remedy Rx: “Salmon needs to be chosen carefully,” says Fidler. “Wild caught […]
The blue magic
Shankupushpam flowers are used as natural colouring agent in many recipes. They are dipped in batter and deep fried like fritters. The flowers are…
Shankupushpam/Butterfly pea flower/Darwin pea flower is a creeper plant. This is usually used as an ornamental plant. The distinct medicinal properties add enormous value to this beautiful vine. The leaves, roots, seeds, and flowers are all used in ayurvedic treatments to cure various diseases.
Shankupushpam is widely used in traditional Indian system of medicine as a brain tonic and is believed to improve memory and intelligence. It helps to relieve throat and eye infections. It also helps in curing skin and urinary diseases.
Butterfly pea flower is a boon to people suffering from anxiety, low energy, less memory, sleeplessness, poor eyesight, hair loss, skin loosening and conceiving problems. These flowers are rich in antioxidants, flavonoids and peptides.
The flowers are used as natural colouring agent in many recipes. They are dipped in batter and deep fried like fritters. The flowers are used to make tea and sherbet too.
It’s time we included this miracle plant in our gardens. Here are a few recipes that one can make to include these flowers into our daily menu.
– Rajeshwari Puthalapattu has done her MBA in marketing and MA in English literature but has chosen to pursue her passion in cooking. She has looked into her family’s heirloom recipes to bring out forgotten and rare recipes as well.
Shankupushpam Chai Ingredients Shankupushpam – 2
Water – 1cup,
Ginger – 1/4 tsp – crushed,
Fennel seeds – 1/4tsp,
Sweetener of your choice (sugar/honey/jaggery),
Lemon grass – 1/4inch.
Method
Heat water in a bowl,
Add crushed ginger, crushed fennel, and lemon grass along with the flowers to the boiling water,
Let the chai simmer for 5-6 on a low flame .
Turn off the flame and cover the chai with a lid, let it rest for 2mins then strain and serve.
Shankupushpam Sherbet
Ingredients
Water – 1 glass – chilled,
Lemon juice -juice of 1/2 lemon,
Basil seeds -soaked -1tsp,
Sweetener of your choice – (sugar/honey/jaggery/palm sugar)
Shankupushpam – 4 flowers.
Method In a bowl add warm water and to it add flowers, cover it with a lid and let it rest, till the flowers decolourise.Now strain the water and to that add lemon juice, basil seeds, and sweetener of your choice and mix well.Serve chilled, garnished with a slice of lemon. Shankupushpam Sheera Ingredients Rava/semolina – 1cup,Sugar – 3/4cup,Cardamom – 2 powdered,Sesame seeds – 1tsp,Ghee – 4tsp,Shankupushpam – 8,Water – 3cups, Method In a kadai dry roast the sesame seeds and keep it aside.Add ghee in the kadai and fry the semolina till golden brown and keep this aside.Now add 3cups of water and let it boil, when the water is boiling add flowers along with fried rava and cook on a low flame till it is done.Now when the rava is completely cooked add sugar and cardamom powder mix well and sprinkle the roasted sesame too.Mix well and turn off the flame and serve garnished with flower.
Slow down, you’re going too fast – how to calm your mind

There is a misconception that a calm mind means an empty mind, a kind of Zen flatline. In fact, it’s the opposite; a calm mind is a productive mind, one where ideas and thoughts linger and percolate long enough to become productive, where creative thinking is favoured and decisions are taken out of an instinctual understanding of what you need.
A calm mind is a pleasant place to dwell, and is resilient when faced with life’s inevitable shocks.
So how to achieve this desirable state of being? Here are some strategies for slowing down, for changing the pace at which you live – perhaps not permanently, but often enough to remind yourself why calming the mind is something to aim for.
These are aimed at the many of us who understand that by being busy all the time we have lost something valuable, are risking our fundamental health and happiness, and who wish to arrive at a state of greater serenity.
Some are short-term strategies, to deploy in a moment of agitation (breathing, for example), others are medium and long-term – physical and psychological changes to incorporate into our daily lives that will bring good results.
1. Pause
Consultant psychologist Dr Jane Louise Clarke, owner and director of The Consulting Clinic (www.theconsultingclinic.ie), recommends as a first step that we “stop, pause and check in with yourself. In the rush of life we often feel we don’t have time to stop and gather our thoughts, but doing so can calm the mind and reduce reactivity.”
So take a moment, and ask yourself the following questions: “What am I feeling right now? Am I reacting rather than responding? Am I getting things out of proportion? Am I predicting the worst? Am I jumping to conclusions? What advice would I give to a friend in this situation?”
All these questions “help us to stand back and get a wide perspective, which then helps to calm the mind”.
2. Breathe
After that, breathe. “Take a few moments to stop and connect with your breath. The breath helps to increase focus, regulate emotions and anchor back into the present moment,” says Dr Clarke.
There are various formulae for breathing yourself calm, but one of the simplest and most effective is the 7-11 breath: Breathe in for seven counts, breathe out for 11. Repeat.
3. Take stock
Dr Clarke also suggests we take stock of our “areas of nourishment and depletion. When we feel stressed we tend to neglect the nourishing activities and get lost within the depleting activities that exhaust us. Nourishing activities lift mood, increase energy and help you feel calm.”
Such activities might be exercise, healthy eating, meditation and connecting with your values. Areas of depletion are too much screen time, working long hours, avoiding socialising and exercise. Make your own personal list of nourishing and depleting activities, with the aim to reduce the depletion activities and increase your nourishing list.”
4. Exercise
Linda Hamilton, cognitive behavioural therapist at Kinsale CBT (www.kinsalecbt.com), says: “Exercise is hugely important for mental as well as physical health, and one of the most effective ways of reducing anxiety or depression (around five minutes of aerobic exercise can stimulate anti-anxiety effects, while as little as one hour of exercise a week reduces the risk of future depression).
“It releases endorphins, which can significantly boost mood and is one of the quickest ways of reducing stress. It reduces fatigue and tension, improves alertness and concentration, and the ability to sleep. Joining a gym or going hill-walking is great, but more modest steps – just getting out and moving when you can – will also help.”
5. Get outdoors
If that exercise can take place in nature, the proven benefits are increased: “A growing body of research confirms nature has the power to rejuvenate,” Hamilton says. “Recent research has found that people who spent at least two hours in contact with nature over the previous week were much more likely to report a greater sense of well-being than people who spent no time outdoors. It didn’t matter how the 120 minutes was achieved (for example, one long visit versus several shorter ones).
“Spending more than five hours was not associated with additional benefits.
“Correlation is not causation, but it’s fair to assume that most of us feel the benefits from accessing green space, whether it be in a leafy park or a walk by the sea. People at risk of anxiety or depression are especially likely to benefit – being near water and trees and birds and animals is a positive distraction that takes you out of your head, calming the mind and bringing you back to the moment.”
6. Do new things
Hamilton also advocates spending time doing whatever it is that your enjoy – “whether it be reading, baking, listening to music” – but equally, highlights the power of the new: “The more novelty in your life, the longer it seems. It’s easy to fall into familiar routines as we get older; as a result, one day can blur into the next.
“That’s why a week holidaying in an unfamiliar location seems longer than a normal week. In novel situations, we pay more attention, taking in the different smells and sights. We can’t be on holidays all the time, but we can shake things up by varying where we walk, drive, cycle, what we eat, and so on. Small injections of newness keep life fresh.”
7. Work out your NATs and tackle them “Life can be stressful,” Hamilton says, “but stress can also be self-generated, with unhelpful thinking patterns making a difficult situation seem like an intolerable one. We often forget that our thoughts are not facts.”This is especially the case when we are stressed or anxious. It’s a good idea to jot down the NATs – Negative Automatic Thoughts – that pop into your head in times of stress and take a look at them later on, when things are calmer. You’ll see that these thoughts can be harsh and self-limiting and characterised by the various cognitive distortions […]
Natural Ways To Boost Serotonin Levels And Become Happier

Here’s how you can be your happier self All thanks to our chaotic and stressful lifestyle, many have turned to antidepressants to boost their serotonin levels. Serotonin is basically a happy hormone that exerts a powerful influence over mood, emotions, memory, cravings (especially for carbohydrates), pain sensation, sleep habits, appetite, digestion, and body temperature regulation. Serotonin levels, let’s face it are often reduced in people who are not exposed to sunlight for months. It is also closely linked to the availability of vitamin B6 and the amino acid tryptophan. If our diet lacks sufficient vitamins, we run a greater risk of serotonin deficiency. Now before you resort to antidepressants, here are some of the natural ways to boost serotonin levels. 1. Workout:
Regular exercise can have an antidepressant effect. 30-minutes of workout or exercise is sufficient to boost serotonin levels in individuals. Go for the gym, swimming, light hiking, Zumba, aerobics, running, cycling, cardio anything that can help regulate serotonin levels. Serotonin via exercise can lower hostility and symptoms of depression. It also encourages agreeableness. 2. Get Serotonin Rich Food:
Feed yourself Serotonin rich foods. Though you can’t directly get serotonin from food, you can get tryptophan, an amino acid that’s converted to serotonin in your brain Since our gut produces almost 90 percent of the serotonin in our bodies, we need to feed it the right things to prevent a chemical imbalance, which will affect depression and anxiety levels. Have foods that include pineapples, eggs, fish, tofu, cheese, spinach, salmon, nuts and seeds. 3. Sunlight:
Did you notice you feel real mood dips during the winter(winter blues anyone?). Yes natural Vitamin D e.g. sunshine is extremely important to improve those mood dips. Light therapy is a common remedy for seasonal depression. studies show a clear relationship between being exposed to bright light and serotonin levels. To get better sleep, or to boost your mood, try to work in a daily lunchtime walk outside in the sun for around 20 minutes. 4. Gratitude/Positivity:
Gratitude is directly proportional to happiness. Scientific research has shown gratitude affects the brain’s reward system. It correlates with the release of dopamine and serotonin. Gratitude has been directly linked to increased happiness. Secondly, happy memories can increase dopamine or serotonin levels like nothing else. People reliving sad memories produced less serotonin in that region. People dwelling on happy memories produced more serotonin. 5. Taking Supplements:
Supplements are a gentler solution than medication since they’re unlikely to have adverse side effects. You can take one specifically designed to boost serotonin, reduce anxiety and stress. Supplements rich in vitamin D helps in improving mood swings and reducing depression.
The bottom line is that there are a ton of benefits to elevating your mood, from increased health to clearer thinking. And fortunately, there are lots of simple things you can do to get that boost quickly. However, don’t hesitate to reach out for help if these tips aren’t cutting it.
For all the latest Bollywood News and gossip, follow us on Twitter & Instagram , like us on Facebook and subscribe to our channel YouTube . New videos up every day!
10 ways to improve your memory at any age

Want to sharpen your memory?
Hot flushes, insomnia, and troubling mood swings. Does that remind you of something? During menopause, women’s ovaries stop making their regular levels of progesterone and oestrogen. As a result, the entire system changes. There’s no age calculator to tell you exactly when you’re going to experience it, although on average it’s age 51.
But there’s one symptom you might not have heard about: brain fog. At first, you assume you’re experiencing mental fatigue because you can’t sleep well. You notice you can’t pay attention, you’re confused, and forget things that are easy to remember.
In my case, it’s the phone. I always forget where I left it. One time, I found it in the fridge. Everyone thought it was a joke, but it was a moment of awareness for me: something is wrong and I need to do something about it. Why do memory issues occur during menopause?
A study from 2013 showed that fluctuations in oestrogen levels during perimenopause significantly affect the memory capacity. Before their oestrogen levels dipped, the women who participated in the study had normal working and semantic memory. When the levels dropped, their performance was affected.
Hold on.
This is not something we should make peace with.
There are ways to prevent the memory decline. In fact, a study from 2014 showed that mind-body medicine had a great potential to improve a woman’s cognitive performance at any age. 10 ways to improve your memory at any age
1. Change your eating habits
Sugar is out. When your brain is foggy, you feel a lack of energy. Carbs give you an instant boost, so you often reach for them. However, you quickly hit a new low after that spike. You need to avoid sugar and shift towards loads of veggies and fruits. 2. Try to get your sleep in order
“Maintain a regular sleeping schedule” is an easy tip to give. Lack of sleep does affect your cognitive performance. But how do you solve this issue when it’s not something you willingly caused?
There are a few things you can do: Quit coffee. If that’s too hard, you can limit your intake to one cup in the morning.
Get a good mattress and a nice pillow.
Try not to use your computer, smartphone, or tablet at least two hours before going to bed.
Learn a relaxation technique and practice it before bed.
3. Exercise
Aerobic exercise and yoga are great for women at any age. Physical activity can contribute towards memory improvement because it gives you energy, it motivates you to eat healthy, and it improves your sleep.
It’s best to exercise in the morning or throughout the day. Avoid doing it in the evening, since the energy boost will disturb your sleep. 4. Read
You have to keep your mind active. Read books, but choose good ones. Don’t opt for mainstream page-turners. Read the books that have been on your list for ages, but you never got to them. 5. Write
Journalling helps a lot! Note down the highlights of the day. This habit will inspire you to pay attention to everything that happens. You’ll want to remember a moment, so you’ll write about it later on. With time, you’ll become more aware of everything you do.
If writing isn’t your thing, you can collaborate with a professional personal statement writing service . A writer will help you find your unique voice, so you’ll like the stuff you put on paper. You can even turn your journal into a blog. 6. Play mind games
Try a brain training app with lots of different games and activities to give yourself a new challenge every day. 7. Take ginkgo biloba supplements
You should consult your doctor before taking any supplements. Ask if you can take ginkgo biloba. It’s generally considered safe as a supplement, but it may interact negatively with some meds you’re taking.
This is a useful natural supplement that prevents memory loss and dementia. 8. Meditate
Meditation is usually recommended as a way to combat stress. However, it has magnificent effects on the mind when practiced regularly. It boosts your awareness for the now , so it naturally leads to memory improvement.
Meditation is hard at first. You sit with your eyes closed, and your mind starts wandering. You’ll have to learn how to control it, and you’ll need to practice every day. 9. Practice mindfulness Being mindful means being aware of the present moment. Meditation gets you in a state of mindfulness. However, you have to maintain it throughout the rest of the day.When you train your mind to be mindful of all thoughts and surroundings, it will stop wandering. You’ll become more attentive and it will be easier for you to remember everything. 10. Test your vitamin D levels and supplement if necessary Low levels of vitamin D may be responsible for the decline in cognitive function. This is a simple blood test to perform, but many doctors forget to recommend it. Test your Vitamin D levels. If you’re deficient, your doctor will prescribe a supplement. You can do this… Don’t get disappointed if you start forgetting things. Your female brain is still powerful and beautiful. You can work with it to make it stronger and more attentive.All tips listed above are pretty easy to implement into your lifestyle. You’ll have to make some effort to start exercising, reading, writing, and eating well on a regular basis. But when you turn these activities into habits, you’ll love yourself for making that effort.
Learning and memory of ageing mice improved with stem cells
It has been discovered that cognitive functions such as memory and learning in old mice are improved with more stem cells and neurons. Scientists have discovered that increasing the number of stem cells in the brain help in recovering cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, that are lost during ageing.
The scientists were from the Center for Regenerative Therapies of TU Dresden (CRTD) and led by Professor Federico Calegari, working with Professor Gerd Kempermann (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases DZNE / CRTD) and Dr Kentaroh Takagaki (Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg).
The researchers used a method developed to stimulate the small pool of neural stem cells that reside in the brain in order to increase their number and as a result, to also increase the number of neurons generated by those stem cells. Surprisingly, additional neurons could survive and form new contacts with neighbouring cells in the brain of old mice.
Next, the scientists examined a key cognitive ability that is lost, similarly in mice and in humans, during ageing: navigation. Image of neural stem cells and newborn neurons (green) artificially generated in the hippocampus and contacting mature cells (red) of the mouse brain (credit: CRTD). The researchers wanted to find out if boosting the number of neurons was sufficient to counteract the decreasing performance of the brain in navigation and slow down this ageing process and they found out that old mice with more stem cells and neurons recovered their lost ability to build a map of the environment and remembered it for longer times making them more similar to young mice.
Furthermore, when neural stem cells were stimulated in the brain of young mice, cognitive impairments were delayed and memory was better preserved over the entire course of the animals’ natural life.
“In young individuals, a brain area called the hippocampus is crucial for remembering places and events and is also responsible for creating maps of new environments,” explained Gabriel Berdugo-Vega, first author of the study. “However, old individuals use other structures that are more related to the development of habits. It was very interesting to see that adding more neurons in the hippocampus of old mice allowed them to use strategies typical of young animals. It was not only about how fast they were learning but, rather, how different the learning process itself was.”
“Also humans have a few stem cells in the brain and these stem cells are known to severely reduce in numbers over the course of life,” added Prof. Federico Calegari, senior author of this study. “Identifying the causes underlying cognitive deficits in ageing and rescuing them is crucial for our rapidly ageing societies. Our work demonstrates that age-related impairments can be rescued by hijacking the endogenous neurogenic potential of the brain, thus, rejuvenating its function.”
The study was published in Nature Communications .
7 Intermittent Fasting Benefits That Aren’t Weight Loss

7 Fasting Benefits That Aren’t Weight Loss PeopleImages But science has also discovered health benefits linked to whole-day, alternate-day, and time-restricted fasting, says Carolyn Williams, Ph.D., the registered dietitian that helped develop the new book The Mens Health Guide to Intermittent Fasting .
Scientists speculate that the benefits of short-term fasts may come from the structured break they provide to around-the-clock eating.
Even if you dont change the content of your diet, by controlling the time period in which your calories are consumed, you give your body a pause from a constant onslaught food, says Williams.
Maybe youre skeptical . But Williams says that, at first, she was too.
She studied the research. She looked at the data. She even tried a time-restricted fast herself. I expected the fast to affect my blood sugar because Im prone to low blood sugar and I know how I get without eating, Williams says. But Williams says she was surprised to find that she had no trouble going 16 hours without eating. Her method: She stopped eating after dinner and fasted from 7 p.m. to 11 a.m., following the popular 16:8 intermittent fasting pattern, which leaves an 8-hour-long window for eating.
I find Im really not hungry; in fact, sometimes I have to remind myself to eat lunch, Williams says.
While more research is needed to determine if fasting is effective for long-term dieting, theres no debate that it works in the short-term.
By refraining from eating for at least 12 hours (ideally 16), your body starts burning through glucose and can begin tapping fat for fuel, explains Williams. Studies show that you can expect to lose between 3 and 8 percent of your bodyweight in as few as three weeks. Compared to calorie-restriction diets, intermittent fasting tends to trigger more belly fat loss, the research suggests. Anecdotally, Williams says she senses greater energy and improved clarity of thought.
Here are some other potential upsides of intermittent fasting, each supported by research. Intermittent fasting may help maintain muscle .
Whenever you restrict calories and lose weight, some of that weight comes from a reduction in muscle mass. That goes for intermittent fasts as well as traditional calorie-restriction diets. However, at least one study conducted by the Department of Kinesiology and Nutrition at the University of Illinois suggests that intermittent fasting may be more effective for retaining muscle mass.
The study compared overweight and obese adults who followed a calorie restriction diet with similar-weight subjects who restricted calories through intermittent fasting. After 12 weeks, the researchers found both diets to be equally effective in trimming body weight and fat mass, but less muscle was lost by the group that fasted. Intermittent fasting may target belly fat.
Overweight people who could choose any 10-hour timeframe to eat as long as they refrained from eating the other 14 hours of the day saw a reduction in waist circumference and visceral abdominal fat after 12 weeks, according to a report in the journal Cell Metabolism. Intermittent fasting may reduce diabetes risk.
The study in Cell Metabolism referenced above also demonstrated the potential of intermittent fasting to reduce risk of metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
All the participants in the study were diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of health conditionsincluding high blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol or triglycerides levelsthat occurring together boost the risk of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and heart disease.
After 12 weeks, every participant experienced improvement in all of the common markers of metabolic syndrome. A similar study in the journal Translational Research found that alternate-day fasting, in which participants restricted calories by 75 percent on a fast day, followed by a feed day without calorie restriction, resulted in clinically significant reductions in blood sugar and insulin resistance. Intermittent fasting may lower high blood pressure.
A study published in Nutrition and Healthy Aging demonstrated that participants who practiced 16:8 intermittent fasting without calorie counting significantly reduced their systolic blood pressure compared to a control group after 12 weeks. Intermittent fasting could fight inflammation.
Inflammation is your bodys natural way of fighting off infection, illness, and injury. But theres another type of inflammation, a chronic inflammation that can silently trigger heart disease and diabetes.
Smoking, mental stress, and a regular diet of fatty, fried, or sugary foods are common causes. Several studies have shown that intermittent fasting may induce an anti-inflammatory effect that reduces risk of those metabolic diseasesand even improve pulmonary function in people with asthma. Whats more, a reduction in inflammation due to short-term fasting appears to protect the brain from memory disorders and depression, according to a study in Obesity. Intermittent fasting may reduce oxidative stress.
Even when you dont lose weight while on an intermittent fasting routine, your cells may benefit from extra protection, according to a study in Cell Metabolism.
The study assigned men with prediabetes to either a 6-hour early eating period, where they could eat only from 8 a.m. until dinner before 2 p.m., fasting the rest of the day, or a 12-hour feeding period.
At the end of five weeks, the researchers found that the men on the early time- restricted fast improved blood pressure and insulin sensitivity (as expected), but also improved resistance to oxidative stress, where unstable molecules called free radicals can damage proteins and DNA. Intermittent fasting may help you live longer.
Rodent studies suggest that intermittent fasting, which is much easier to maintain than extreme calorie cutting, may boost lifespan, too. In one study comparing rats who were given unrestricted access to food to rats who were fed every other day, the rats who fasted lived 83 percent longer than those who gorged themselves.
For a quick primer on how to start a health-boosting fast yourself, plus dozens of delicious recipes for brunch, dinner, and even Keto-diet-friendly meals, check out The Mens Health Guide to Intermittent Fasting here.
Researchers discover a protein in the blood of young mice that improves cognition and lifespan in older mice
( Natural News ) The quest for finding ways to delay aging has led scientists from the Washington University School of Medicine to a protein extracted from the blood of young mice. When injected into older mice, the protein, known as eNAMPT, could delay aging and inhibit age-related diseases in the senior rodents.
The researchers found that eNAMPT extended the lifespan of the older rodents by 16 percent. “We have found a totally new pathway towards healthy aging,” said Shin-ichiro Imai, senior author of the study, which was published in the journal Cell Metabolism. In human terms, this would be the equivalent of a 79-year old living to the age of 91.
“That we can take eNAMPT from the blood of young mice and give it to older mice and see that the older mice show marked improvements in health – including increased physical activity and better sleep – is remarkable.”
In their animal trials, Imai and his team experimented on two groups of lab mice. One group was given an oral dose of eNAMPT, while the control group received a saline solution. According to them, the differences between the groups were “dramatic.”
The mice in the control group all died within around 2.4 years. The mice who were given eNAMPT died within 2.8 years. Furthermore, the mice who were given the enzyme had improved cognitive function on memory tests, better sleep quality, ran more on their running wheels and, according to the authors, grew “thicker, shinier fur.” This suggests that eNAMPT could be directly increasing the lifespan of the mice .
100% organic essential oil sets now available for your home and personal care, including Rosemary, Oregano, Eucalyptus, Tea Tree, Clary Sage and more, all 100% organic and laboratory tested for safety. A multitude of uses, from stress reduction to topical first aid. See the complete listing here , and help support this news site. eNAMPT may be the key
The enzyme eNAMPT plays a crucial role in the process cells use to create NAD, a coenzyme found in all living cells and a crucial component in energy production.
“We think the body has so many redundant systems to maintain proper NAD levels because it is so important,” said Imai on why NAD is such an important molecule for the body. He said that the studies suggest NAD governs how long people live and how healthy people can remain as they grow older.
“Since we know that NAD inevitably declines with age, whether in worms, fruit flies, mice or people, many researchers are interested in finding anti-aging interventions that might maintain NAD levels as we get older.”
In Imai and his team’s research, keeping eNAMPT levels high were able to sustain NAD levels. When both remain high, it’s possible that many of the side effects of aging can be delayed. (Related: Longevity science: Study reveals benefits of nutraceuticals and the Mediterranean diet when it comes to improving lifespan .) Longer life may be within reach
Imai and his team believe that the reason aging speeds up when eNAMPT levels decline has to do with the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that plays an important role in releasing hormones, regulating body temperature and controlling social behavior, among others. Recently, other studies have found that the hypothalamus also has a hand in the body’s aging process. As levels of eNAMPT decrease during aging, researchers believe that the hypothalamus ceases to function at peak efficiency, shortening lifespans.
The research team recommends that future studies look into whether low levels of eNAMPT are associated with the arrival of diseases in older humans and whether this essential protein can be a viable ingredient in anti-aging treatment.
The findings from this study, at the very least, look promising because they open avenues to more research into anti-aging interventions. If eNAMPT could be harnessed safely, longer life may just be one blood transfusion away.
Sources include:
Cell.com
Sales of healthy food trends to go up in 2020

CEBU, Philippines — Any food product that boosts mental and physical health is expected to make a stride in sales this year, as the market is becoming more aware of investing on fighting stress related effects.
Mintel 1, the world’s leading market intelligence agency, in its market intelligence digest released by the Export Management Bureau of the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) recommended that brands should focus on solutions to help consumers relax, meet their stress relief goals, and optimize their mental performance.
“Mental and physical health are becoming equally as important,” stated Mintel’s report.
The report identified five ingredient groups corresponding to the emerging food and nutrition trends that appeal to Asia-Pacific consumers this 2020.
These ingredients include adaptogens and nervines which provide natural stress relief, and nootropics which aim to enhance brain health and performance.
Synbiotics and postbiotics are the new category of ingredients in the gut health and wellness field.
According to Mintel, stress and anxiety are common problems faced by consumers around the world.
These are opportunities for food and drink manufacturers to incorporate adaptogens into products for stressed-out consumers to help them gain control over their stress,” the report noted.
Adaptogens include holy basil, ashwagandha and medicinal mushrooms.
Nervines are another group of stress-fighting herbs related to adaptogens. Sedative nervines include chamomile, lemon balm, valerian and lavender.
Mintel said nootropics are substances that improve cognitive functions like memory, focus, creativity or motivation.
Caffeine is considered the most common nootropic. Other emerging nootropics are B vitamins, choline, L-theanine, MCT oils, omega-3s and ginko biloba.
The report further said synbiotics and postbiotics are the new category of ingredients in the gut health and wellness field, noting digestive health and wellness is increasingly recognized as an integral part of wellbeing.
Synbiotics, which are specific combinations of probiotics and prebiotics that work synergistically within the body, are starting to be added to food and drink products to provide health benefits.
The report added that brands could capitalize on Asian consumers’ growing interest in gut health and in getting more fiber in their diet.
It further cited a recent study published by Trends in Food Science & Technology noting that postbiotic is a newly coined term for metabolic byproducts or “beneficial waste products” of probiotic bacteria, such as organic acids or short-chain fatty acids, peptidoglycans, and polysaccharides.
At present, there are very few products containing postbiotic ingredients have launched; they mostly come from Asia Pacific. Chiefly applied commercially in personal care products, postbiotic potential is now appearing in pharmaceutical and functional food and drink categories. SIGN UP TO RECEIVE OUR EMAIL
The most important news of the day about the Philippines and the world in one email
How to cope with war anxiety over Iran

Joan Cook is an associate professor at Yale University and the 2016 president of the American Psychological Association’s Division of Trauma Psychology. The opinions expressed in this commentary are her own. View more opinion on CNN.
(CNN)Recent tensions between the United States and Iran and the underlying threat of war have many Americans on edge. After a US air strike in Baghdad on January 3 killed Gen. Qasem Soleimani, Iran’s influential military commander and a power broker of terror in the Middle East, the Iranians vowed harsh revenge. They kept their promise by bombing US military bases in Iraq holding US troops.
As a trauma psychologist, I can very well understand public fear and anxiety resulting from this military escalation and the uncertainty it has generated about the future. An important study last year indicated that Americans were already suffering from a rising anxiety epidemic , particularly about health, safety and finances, and these new events will surely get people even more jacked up when our health can least afford it.
Concerns of going to war understandably bring increased tension and fear, whether by awakening past traumas or inviting worry about new trauma, such as concerns of being attacked on our own soil, loss of lives or the reverberating effects that could bring about World War III . Today’s onslaught of video imagery brings war powerfully home, giving an up close feel of the danger and anguish. But there’s something we can all do to cope.
For individuals who have experienced traumatic events, such as combat, sexual assault or natural disasters, fears of future war can act as triggers and negatively mix with or amplify unresolved psychological wounds. Many trauma survivors have reactions to reminders of their traumas. Some of the combat veterans I’ve worked with over the past 20 years will hear a noise, like fireworks, or even a car backfiring, and nearly jump out of their skin. Within a split second, they’ll think they are under attack or that war has broken out in their back yard.
This is not just something we see in clinical settings. Research has documented this phenomenon. For example, in a sample of survivors of the 2011 mass shooting massacre on Utoya Island, Norway, survivors frequently found auditory reminders, such as sudden and sharp noises, as incredibly distressing. Furthermore, studies show that those survivors who had a higher frequency of exposure to such trauma reminders were even more emotionally distressed.
Trauma triggers can also affect survivors’ psychological health by getting under the skin, impacting their bodies and brains. For example, research shows that survivors of war and torture experience a significant increase in cortisol when reminded of their traumatic events.
In a sample of relocated Hurricane Katrina survivors, exposure to trauma reminders resulted in an increased heart rate. In one study , a sample of survivors of recent road traffic accidents underwent functional MRI scans to examine brain activity patterns in response to trauma reminders. These patients showed increased activity in visual-, sensory-, memory- and attention-related areas of the brain in response to trauma-specific stimuli.
But you don’t have to be a trauma survivor to strongly feel the threat of war. Given the rise of social media, the speeding up of the news cycle and the use of Twitter by world leaders (the back and forth of the American and Iranian flags after airstrikes alone, for example), regular folks have more access to information about the possibility of war and violence than they ever did before.
In the case of potential war with Iran, this climate of fear and for many, full-on anxiety, can intrude wherever and whenever there is a screen available. These images make people feel tense, worried about what this may mean for our troops and citizens stationed abroad and leave them wondering if there will be a 9/11 style attack stateside. Some individuals may even feel physical changes such as increased blood pressure.
In situations of heightened tension and fear, people in their everyday lives will feel the stress of our nation’s pain and anxiety. Following the terrorist attacks of 9/11, many among the public experienced a heightened perception of threat . This perception also included feelings of animosity toward our threatening enemy and an increased desire for retaliation. In a longitudinal investigation of the public psyche post 9/11, people’s heightened anxiety regarding potential threats was felt especially keenly during anniversary periods.
This cycle of fear and anxiety in response to a war or terror threat is not unique to our times. Actual or threatened bioterrorism attacks impacted people’s fears in previous eras as well. In fact one study developed and tested a measure of nuclear war anxiety. The authors demonstrated how nuclear war anxiety was primarily made up of feelings of depression, despair and fear of what the future might bring. They talked about the importance of adopting realistic attitudes towards avoiding or preventing war, particularly regarding the tension between US and the then Soviet Union, to reduce stress levels.
It may provide some reassurance to realize that anxiety is normal under these roller-coaster conditions, and that human beings have been experiencing this kind of fear for a long time. A range of other strategies can be helpful in managing the anxiety from war or terror attacks.
One technique we use when working with trauma survivors is to try to limit their exposure to potential trauma triggers. This does not mean you should stay uninformed about world events but making sure our eyes do not stay fixated on a screen or that we don’t instinctively swipe the Twitter feed to help minimize hyperarousal.
I often suggest to veterans with PTSD that they only take in strategic doses of news every day — that they limit exposure to one to two times a day for short periods and that they will be better off reading the news rather than experiencing video depictions of it.
In addition, it is incredibly important that we do not let excessive fears impact our daily lives. A good way to do this is to maintain daily routines and […]
Slow down, you’re going too fast – how to calm your mind

A calm mind is a productive mind There is a misconception that a calm mind means an empty mind, a kind of Zen flatline. In fact, it’s the opposite; a calm mind is a productive mind, one where ideas and thoughts linger and percolate long enough to become productive, where creative thinking is favoured and decisions are taken out of an instinctual understanding of what you need.
A calm mind is a pleasant place to dwell, and is resilient when faced with life’s inevitable shocks.
So how to achieve this desirable state of being? Here are some strategies for slowing down, for changing the pace at which you live – perhaps not permanently, but often enough to remind yourself why calming the mind is something to aim for.
These are aimed at the many of us who understand that by being busy all the time we have lost something valuable, are risking our fundamental health and happiness, and who wish to arrive at a state of greater serenity.
Some are short-term strategies, to deploy in a moment of agitation (breathing, for example), others are medium and long-term – physical and psychological changes to incorporate into our daily lives that will bring good results.
1. Pause
Consultant psychologist Dr Jane Louise Clarke, owner and director of The Consulting Clinic (www.theconsultingclinic.ie), recommends as a first step that we “stop, pause and check in with yourself. In the rush of life we often feel we don’t have time to stop and gather our thoughts, but doing so can calm the mind and reduce reactivity.”
So take a moment, and ask yourself the following questions: “What am I feeling right now? Am I reacting rather than responding? Am I getting things out of proportion? Am I predicting the worst? Am I jumping to conclusions? What advice would I give to a friend in this situation?”
All these questions “help us to stand back and get a wide perspective, which then helps to calm the mind”.
2. Breathe
After that, breathe. “Take a few moments to stop and connect with your breath. The breath helps to increase focus, regulate emotions and anchor back into the present moment,” says Dr Clarke.
There are various formulae for breathing yourself calm, but one of the simplest and most effective is the 7-11 breath: Breathe in for seven counts, breathe out for 11. Repeat.
3. Take stock
Dr Clarke also suggests we take stock of our “areas of nourishment and depletion. When we feel stressed we tend to neglect the nourishing activities and get lost within the depleting activities that exhaust us. Nourishing activities lift mood, increase energy and help you feel calm.”
Such activities might be exercise, healthy eating, meditation and connecting with your values. Areas of depletion are too much screen time, working long hours, avoiding socialising and exercise. Make your own personal list of nourishing and depleting activities, with the aim to reduce the depletion activities and increase your nourishing list.”
4. Exercise
Linda Hamilton, cognitive behavioural therapist at Kinsale CBT (www.kinsalecbt.com), says: “Exercise is hugely important for mental as well as physical health, and one of the most effective ways of reducing anxiety or depression (around five minutes of aerobic exercise can stimulate anti-anxiety effects, while as little as one hour of exercise a week reduces the risk of future depression).
“It releases endorphins, which can significantly boost mood and is one of the quickest ways of reducing stress. It reduces fatigue and tension, improves alertness and concentration, and the ability to sleep. Joining a gym or going hill-walking is great, but more modest steps – just getting out and moving when you can – will also help.”
5. Get outdoors
If that exercise can take place in nature, the proven benefits are increased: “A growing body of research confirms nature has the power to rejuvenate,” Hamilton says. “Recent research has found that people who spent at least two hours in contact with nature over the previous week were much more likely to report a greater sense of well-being than people who spent no time outdoors. It didn’t matter how the 120 minutes was achieved (for example, one long visit versus several shorter ones).
“Spending more than five hours was not associated with additional benefits.
“Correlation is not causation, but it’s fair to assume that most of us feel the benefits from accessing green space, whether it be in a leafy park or a walk by the sea. People at risk of anxiety or depression are especially likely to benefit – being near water and trees and birds and animals is a positive distraction that takes you out of your head, calming the mind and bringing you back to the moment.”
6. Do new things
Hamilton also advocates spending time doing whatever it is that your enjoy – “whether it be reading, baking, listening to music” – but equally, highlights the power of the new: “The more novelty in your life, the longer it seems. It’s easy to fall into familiar routines as we get older; as a result, one day can blur into the next.
“That’s why a week holidaying in an unfamiliar location seems longer than a normal week. In novel situations, we pay more attention, taking in the different smells and sights. We can’t be on holidays all the time, but we can shake things up by varying where we walk, drive, cycle, what we eat, and so on. Small injections of newness keep life fresh.”
7. Work out your NATs and tackle them “Life can be stressful,” Hamilton says, “but stress can also be self-generated, with unhelpful thinking patterns making a difficult situation seem like an intolerable one. We often forget that our thoughts are not facts.”This is especially the case when we are stressed or anxious. It’s a good idea to jot down the NATs – Negative Automatic Thoughts – that pop into your head in times of stress and take a look at them later on, when things are calmer. You’ll see that these thoughts can be harsh and self-limiting […]
Amazing study reveals bees can connect symbols to numbers: Insects COMPUTE

( Natural News ) Research has established that bees understand the concept of zero and are capable of doing basic math. Now, a recent research conducted by scientists from the RMIT University in Australia suggests that bees are also capable of being trained to connect symbols to numbers in order to receive food.
This experiment used a carrot and stick reward system to train the bees. If they learned the correct route through a maze by connecting a symbol to a number, they got a sugary treat. If not, they received a bitter one.
This study, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B , aimed to determine if bees could understand numbers when they are represented symbolically . Two groups of bees were trained using a Y-shaped maze. For the first group, there was a symbol at the entrance of the maze, which was represented by either number 2 or number 3. When the bees came to the fork in the Y, there were signs placed above their two possible routes. The signs contained shapes, two on one side and three on the other. The bees had to choose the route marked by the right number of shapes, and if they did, they were rewarded with nectar. If they failed, they received bitter quinine.
The scientists remarked that after taking several sips of quinine, which is a bitter compound commonly used in tonic water, the bees began learning to take the correct path. The second group of bees were trained in the opposite approach, matching the number of shapes at the entrance of the maze to a symbol at the fork. It produced similar results.
Adrian Dyer, associate professor at RMIT, said that while humans were the only living species to develop systems and symbols to represent numbers, people aren’t the only ones who can grasp this concept. His team’s study on the tiny brains of bees has proved this.
Support our mission to keep you informed : Discover the extraordinary benefits of turmeric gummy bears and organic “turmeric gold” liquid extract , both laboratory tested for heavy metals, microbiology and safety. Naturally high in potent curcuminoids. Delicious formulations. All purchases support this website (as well as your good health). See availability here.
“We take it for granted once we’ve learned our numbers as children, but being able to recognize what ‘4’ represents actually requires a sophisticated level of cognitive ability,” said Dyer. “Studies have shown primates and birds can also learn to link symbols with numbers, but this is the first time we’ve seen this in insects.”
He added that if bees have the capacity to learn “something as complex as a human-made symbolic language,” then that revelation opens up exciting new possibilities for communicating between different species, much in the same way that a person may teach their pet a set of commands that correspond to an action. (Related: Trained bees successfully locate landmines in Croatia .) Bee brains are smarter than you think
Pigeons, parrots and chimpanzees, among other animals, are known to be capable of learning that symbols can represent numbers. This study shows for the first time that this ability is not restricted to vertebrate species .
However, the study has some limitations. For example, the bees were able to grasp their specific training, but could not work out what to do when tested to reverse the association, suggesting that number processing and understanding of symbols is a different process in bee brains . Further research is required to find out how tiny bee brains process information given to them. According to Dyer, learning this can open the path to bio-inspired solutions for better processing systems.
“Our results show honeybees are not at the same level as the animals that have been able to learn symbols as numbers and perform complex tasks,” said Dyer. “But the results have implications for what we know about learning, reversing tasks and how the brain creates connections and associations between concepts.”
“Discovering how such complex numerical skills can be grasped by miniature brains will help us understand how mathematical and cultural thinking evolved in humans, and possibly, other animals.”
Sources include:
Rejuvenating the brain: More stem cells improve learning and memory of old mice
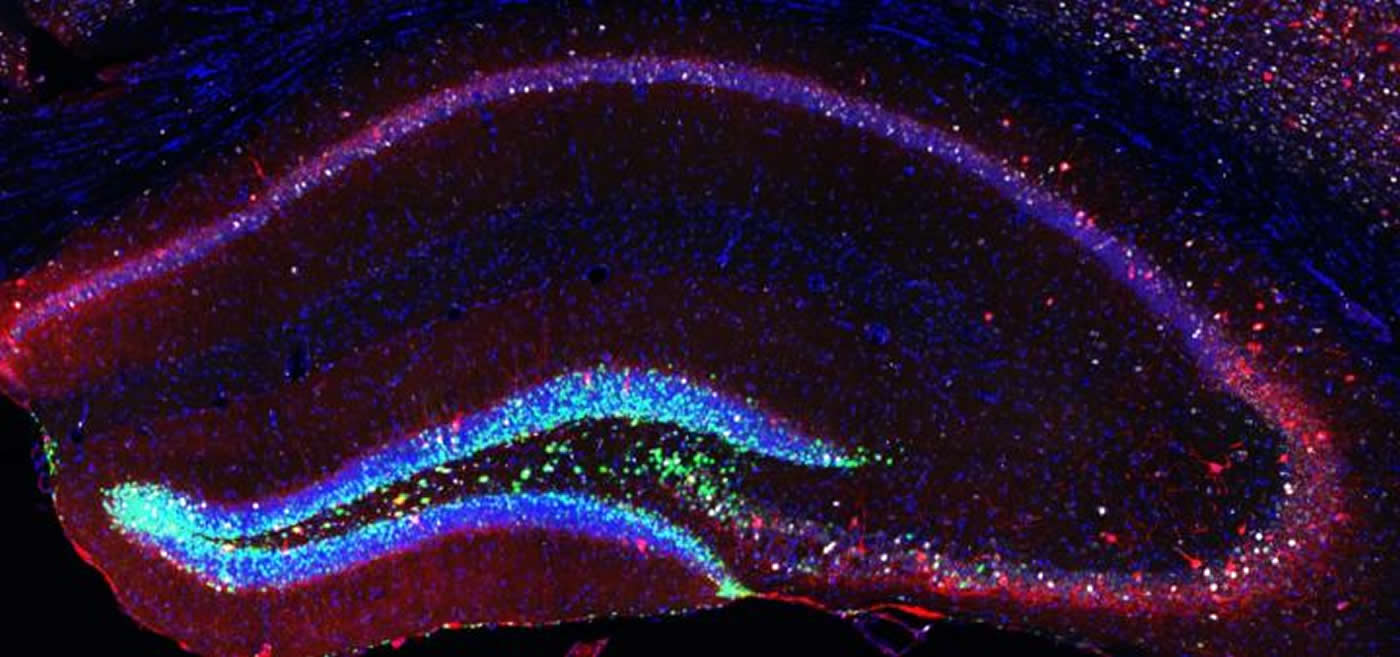
Summary: Critical aspects of hippocampal function can be reversed in old age, or compensated for throughout life, with the help of neural stem cells.
Source: TU Dresden
We all will experience it at some point, unfortunately: The older we get the more our brains will find it difficult to learn and remember new things. What the reasons underlying these impairments are is yet unclear but scientists at the Center for Regenerative Therapies of TU Dresden (CRTD) wanted to investigate if increasing the number of stem cells in the brain would help in recovering cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, that are lost during aging.
To investigate this, the research group led by Prof. Federico Calegari used a method developed in his lab to stimulate the small pool of neural stem cells that reside in the brain in order to increase their number and, as a result, to also increase the number of neurons generated by those stem cells. Surprisingly, additional neurons could survive and form new contacts with neighboring cells in the brain of old mice. Next, the scientists examined a key cognitive ability that is lost, similarly in mice and in humans, during aging: navigation.
It is well known that individuals learn to navigate in a new environment in a different way depending on whether they are young or old. When young, the brain can build and remember a cognitive map of the environment but this ability fades away in older brains. As an alternative solution to the problem, older brains without a cognitive map of the environment need to learn the fixed series of turns and twists that are needed to reach a certain destination. While the two strategies may superficially appear similar, only a cognitive map can allow individuals to navigate efficiently when starting from a new location or when in need of reaching a new destination.
Would boosting the number of neurons be sufficient to counteract the decreasing performance of the brain in navigation and slow down this aging process? The teams of Prof. Calegari (CRTD) together with Prof. Gerd Kempermann (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases DZNE / CRTD) and Dr. Kentaroh Takagaki (Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg) found the answer to this challenging question and published it this week in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The answer is “Yes”: Old mice with more stem cells and neurons recovered their lost ability to build a map of the environment and remembered it for longer times making them more similar to young mice. Even better, when neural stem cells were stimulated in the brain of young mice, cognitive impairments were delayed and memory was better preserved over the entire course of the animal natural life.
In young individuals, a brain area called the hippocampus is crucial for remembering places and events, and is also responsible for creating maps of new environments. However, old individuals use other structures that are more related to the development of habits. It was very interesting to see that adding more neurons in the hippocampus of old mice allowed them to use strategies typical of young animals. It was not only about how fast they were learning but, rather, how different the learning process itself was “, explains Gabriel Berdugo-Vega, first author of the study.
“Also humans have a few stem cells in the brain and these stem cells are known to severely reduce in numbers over the course of life. Identifying the causes underlying cognitive deficits in ageing and rescuing them is crucial for our rapidly ageing societies. Our work demonstrates that age-related impairments can be rescued by hijacking the endogenous neurogenic potential of the brain, thus, rejuvenating its function. Being a human myself with my own stem cells and being the senior author of this study, I felt that I had a personal interest in this topic.” says Prof. Federico Calegari, senior author of this study. Image of neural stem cells and newborn neurons (green) artificially generated in the hippocampus and contacting mature cells (red) of the mouse brain. Image is credited to CRTD. The research group of Prof. Federico Calegari focuses on mammalian neural stem cells in the context of development, evolution and cognitive function at the CRTD. The institute is the academic home for scientists from more than 30 nations. Their mission is to discover the principles of cell and tissue regeneration and leveraging this for recognition, treatment and reversal of diseases. The CRTD links the bench to the clinic, scientists to clinicians to pool expertise in stem cells, developmental biology, gene-editing and regeneration towards innovative therapies for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, haematological diseases such as leukaemia, metabolic diseases such as diabetes, retina and bone diseases.
Funding: This study was funded by TU Dresden / CRTD through the German Excellence Initiative, the German Research Foundation and a European grant from the H2020 programme. In addition, it was supported by the Faculty of Natural Sciences of Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, the Dresden International Graduate School for Biomedicine and Bioengineering (DIGS-BB) and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE).
Source:
Rutgers
Media Contacts:
Gabriel Berdugo-Vega – TU Dresden Image Source:
The image is credited to CRTD.
Original Research: Open access
“Increasing neurogenesis refines hippocampal activity rejuvenating navigational learning strategies and contextual memory throughout life”. Gabriel Berdugo-Vega, Gonzalo Arias-Gil, Adrian López-Fernández, Benedetta Artegiani, Joanna M. Wasielewska, Chi-Chieh Lee, Michael T. Lippert, Gerd Kempermann, Kentaroh Takagaki & Federico Calegari.
Nature Communications doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14026-z .
Abstract
Increasing neurogenesis refines hippocampal activity rejuvenating navigational learning strategies and contextual memory throughout life
Functional plasticity of the brain decreases during ageing causing marked deficits in contextual learning, allocentric navigation and episodic memory. Adult neurogenesis is a prime example of hippocampal plasticity promoting the contextualisation of information and dramatically decreases during ageing. We found that a genetically-driven expansion of neural stem cells by overexpression of the cell cycle regulators Cdk4/cyclinD1 compensated the age-related decline in neurogenesis. This triggered an overall inhibitory effect on the trisynaptic hippocampal circuit resulting in a […]
Best supplements for tiredness: A natural supplement proven to help fight tiredness

Feeling tired most of the day often feels like an unavoidable aspect of modern-day living. Most have not even been able to even catch their breaths from Christmas when it’s right back to next set of demands. For many, entrenched habits get in the way and solutions can seem unrealistic. Opting for that fourth or fifth cup of coffee might help with the tiredness for the interim but many are wanting a more natural stimulant to help them fight the feelings of tiredness. According to leading health experts, taking this supplement could help. What is it?
How to live longer: Engaging in this activity increases life
Vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms: Sign in breath
Eleuthero is a plant and people use the root of the plant to make medicine.
The supplement is sometimes referred to as Siberian ginseng.
Eleuthero is often called an adaptogen which is a non-medical term used to describe substances that can supposedly strengthen the body and increase general resistance to daily stress.
Vitamin D deficiency symptoms: Lack of vitamin could cause pain here
What is eleuthero?
There is evidence that eleuthero was first used as an herbal remedy in China some 2,000 years ago.
The plant is mostly used in traditional medicines as an adaptogen, a compound that helps the body better handle and adapt to stress.
Eleuthero also acts as a stimulant, increasing nervous system function. Tom Hanks health: Actor diagnosed with serious condition
Best supplements for tiredness: The supplement also boosts brain power How does it work?
In traditional and herbal medicines, eleuthero is used to treat dozens of different health conditions.
Eleuthero contains many chemicals that affect the brain, immune system and certain hormones.
It might also contain chemicals that have activity against some bacteria and viruses.
Early research suggests that eleuthero might improve memory and feelings of well-being in middle-aged people.
As a stimulant, eleuthero boosts energy levels and contains compounds known to help overcome exhaustion and prevent its side effects.
Scientists develop home-testing kit that measures stress hormones

( Natural News ) Stress can either be a person’s boon or his bane, depending on the situation. In certain situations, it can motivate people, but those with chronic levels of stress are more likely to develop health problems, including heart disease and even mental disorders. To combat its adverse effects, researchers have developed a simple test to help measure and monitor stress levels.
The test, a brainchild of researchers from the University of Cincinnati , uses a biosensor that measures stress hormones through sweat, blood and urine. In their preliminary paper, which the researchers published in the American Chemical Society Sensors , they highlighted the device’s potential, in particular, for home application. The National Science Foundation and the U.S. Air Force Research Lab sponsored the study.
“I wanted something that’s simple and easy to interpret,” said Andrew Steckl, a co-author of the study and a professor of electrical engineering at UC. “This may not give you all the information, but it tells you whether you need a professional to take over.” Taking control of stress before it controls you
For most people, stress is deeply ingrained in daily life. While healthy levels of stress can help a person perform better in school or work, being subjected to elevated levels of stress can lead to bad habits like sleep deprivation and overeating. Over time, chronic stress can lead to the development of more serious conditions, like atherosclerosis . For UC researcher Prajokta Ray, who is also the study’s first author, the primary motivation behind the study was to develop a test that was cheap, effective, and affordable.
The power of the elements : Discover Colloidal Silver Mouthwash with quality, natural ingredients like Sangre de Drago sap, black walnut hulls, menthol crystals and more. Zero artificial sweeteners, colors or alcohol. Learn more at the Health Ranger Store and help support this news site.
The device, which is currently in its development phase, uses UV spectroscopy to measure stress-related hormones and neurotransmitters. These compounds include cortisol – better known as the stress hormone, serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and neuropeptide. The device detects their concentrations in various bodily fluids.
“You’re not going to replace a full-panel laboratory blood test. That’s not the intent,” Steckl noted. “But if you’re able to do the test at home because you’re not feeling well and want to know where you stand, this will tell whether your condition has changed a little or a lot.” Natural ways to reduce stress levels
Despite the device being in its early stages, people can still make use of other natural methods to manage their stress levels. Here are some ways to naturally reduce stress . (Related: How to Manage Stress and Anxiety Naturally .) Take time to exercise
Getting the body moving is a great way to help relieve mental stress. Exercise, in particular, helps lower cortisol levels in the body and releases endorphins. The latter improves mood and offers pain relief. Additionally, exercising helps a person get better sleep . Control what you can
People who feel stressed out often feel that they cannot manage things. However, making simple behavioral changes can greatly help manage, even avoid, stress. For instance, if the sound of honking cars is exceptionally irritating, try to avoid these areas, or plan a different route to avoid being stressed out. Join a yoga or meditation class
Studies have found that practicing either yoga or meditation can help reduce stress levels as it develops mindfulness and improves mental health. Spend time with family, friends or like-minded communities
Social support, such as talking to others and listening, can go a long way when it comes to stress relief. Both men and women benefit from camaraderie and friendship, so make some time to interact with others.
Learn more about stress relief for maintaining overall health at Health.news .
Sources include:
Curcumin: Prevent Liver Disease And Reduce Liver Fat With This Amazing Natural Plant Compound

Health
45 views
NaturalNews
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a life-threatening condition caused by an abnormal buildup of fat in the liver. While it is usually caused by excessive alcohol drinking, this disease can also stem from non-alcoholic means. This fat buildup could lead to inflammation in the liver, causing damage and creating scarring. Severe cases of fatty liver disease can even lead to liver failure. Reducing this abnormal buildup of liver fat often involves regular exercise and other healthful lifestyle changes like eating a balanced diet and reducing your sugar intake. Now, a recent research suggests that a well-known compound found in turmeric could make a big difference in improving liver health.
A study published in the journal Drug Research found that curcumin has liver health-boosting effects like improving liver blood flow and reducing liver fat.
Take curcumin to improve liver health
Over the years, the list of beneficial health effects of curcumin somehow gets longer and longer. Curcumin is considered the main active ingredient of turmeric (Curcuma longa), a perennial spice closely related to ginger. Turmeric has been used for thousands of years both as a spice and as a staple in Ayurvedic medicine for its powerful medicinal properties, including potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Curcumin is also found to increase a growth hormone called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Increasing this hormone could help delay or even reverse age-related cognition decline and plenty of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Higher levels of BDNF can also improve memory.
In this study, researchers from Iran aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of curcumin as a dietary supplement for subjects afflicted with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). To do so, the researchers recruited 87 patients diagnosed with NAFLD and randomly assigned them into one of two groups. The team tasked one of the groups to take 1,000 mg of curcumin per day for a period of eight weeks while the other group took placebo in the same time frame. Each patient received both dietary and lifestyle advice before the trial began. The researchers analyzed physical measurements, hepatic enzyme levels and liver scans both before the trial and after eight weeks of the follow-up.
At the end of the follow-up period, the researchers found that curcumin supplementation was associated with a significant reduction in body mass index and waist circumference compared to the placebo group. This finding is particularly important because obesity is considered a risk factor for NAFLD.
In addition, the ultrasonographic liver scans revealed that 75 percent of those who took curcumin showed significant improvements in overall liver health, while the improvement rate of those in the control group only hit 4.7 percent. While serum levels of both aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase were elevated in participants in the placebo group, those in the curcumin group showed significantly reduced hepatic enzyme levels.
Lastly, participants who took curcumin supplements daily also found significant improvements in liver volume, liver blood flow, and liver vein diameter; all of which contribute to proper liver function.
The study suggests that short supplementation of curcumin can effectively reduce the amount of liver fat present in patients with NAFLD. The findings also confirm curcumin’s ability to improve body measurements and support proper liver function. The researchers added that their study warrants further research exploring the promising effects of this “miracle compound.”
Source:
courtesy of NATURALNEWS
by Darnel Fernandez
If you have any stories or news that you would like to share with the global online community, please feel free to share it with us by contacting us directly at pr@brudirect.com
EXPLORING SERMORELIN BENEFITS AND HGH RESTORATION

Originally Posted On: https://naturalspro.com/blogs/news/exploring-sermorelin-benefits-and-hgh-restoration?_pos=1&_sid=3a113d400&_ss=r You’ve done your research and are doing everything right to look and feel young, from logging lifting sessions at the gym to eating a diet tailored to your fitness and anti-aging goals.
But if you’re over 40, your hormones are holding you back. Your body isn’t producing repair-boosting human growth hormone, or HGH, like it used to, and your muscles, bones, skin and mood are all feeling — and showing — it.
You’ve reached that challenging time in life known as somatopause.
An age-related decline in HGH is natural, but you don’t have to take this hit to your hormones without a fight. You can supplement with Sermorelin , an amino acid chain. Sermorelin benefits include naturally boosting pituitary gland function to increase your HGH.
How Sermorelin Therapy Works
Your pea-sized pituitary gland, which is attached to the center of your brain, packs more power than its small size suggests. It’s known as the master gland because it controls other glands that produce hormones. Hormones are chemicals that send vital messages throughout your body and brain.
Your pituitary gland produces HGH, which is a master hormone because it controls other hormones and repair processes. HGH production declines to zero as you age, but there’s a solution: Sermorelin, a chain of 29 amino acids (the building blocks of protein).
Sermorelin biologically acts like growth hormone-releasing hormone, which stimulates HGH secretion. In simple terms, Sermorelin works to release the contents of your pituitary gland.
When you supplement with Sermorelin, you are naturally giving your pituitary gland the signal to produce more HGH. And you will feel the difference with increased energy and vitality.
Here are eight Sermorelin benefits that you can enjoy from restoring your HGH to more youthful levels.
> Improved Youthful Skin Integrity and Reduced Wrinkles
When your HGH is low, you’re more likely to have dry, thin, and loose skin — dermatological hallmarks of aging. Getting older causes skin to lose elasticity, making it more fragile and crepe like. Hormone changes also decrease sebum oil production, so skin becomes dry and wrinkled. Indeed, loss of hormones and essential nutrients cause many of the phenomena we call “aging.”
Sermorelin therapy boosts HGH, which tightens and strengthens the skin and restores natural moisture. Supplementing with Sermorelin can even help stave off hair loss and thinning hair, which are other symptoms of low HGH.
start=”2″> Elevated Energy Production
Adults with lower levels of HGH report tiredness, energy loss, exercise intolerance, sensitivity to heat and cold and a reduced sense of wellbeing. They have an increased risk of heart disease, weak heart, high LDL cholesterol and high triglycerides. Scientists report that injecting 0.1 milligrams of HGH daily will boost heart injection fraction by an average of 27%.
By taking Sermorelin to raise your body’s HGH, you can have a stronger heart and experience more energy and improved wellbeing.
Because Sermorelin is an amino acid chain, you are also giving your body more amino acids, which are required for energy production.
start=”3″> Better Tissue Distribution
HGH helps your body better metabolize protein, fat and carbohydrates, through both direct and indirect effects.
It stimulates tissues to use protein in ways that benefit your body, including increasing its ability to absorb and incorporate amino acids, which are essential to body tissue repair.
HGH helps your body use fat by helping it break down fats and other lipids. It’s been shown to regulate the deposit of lipids in adipose tissue, which is where your body stores fat.
Growth hormone also acts an anti-insulin agent and is one of several hormones that can help keep your blood glucose at optimal levels.
start=”4″> Increased Muscle Mass and Improved Lean Muscle
True to its name, HGH helps bodies grow. As an adult, you aren’t going to grow any taller with more HGH, but you can build muscle.
HGH is a body shape influencer. If you have ever wondered why young adults have firm, round and solid muscles, it’s because their bodies produce large quantities of HGH and its downstream sister hormone, IGF-1 or insulin-like growth factor-1. On the other hand, older adults have low or no HGH which causes more fat mass and less lean body mass. Some older adults even experience insulin resistance and struggle with waist-area weight gain even though they exercise often and limit their food intake.
In contrast, higher HGH stimulates muscle formation and reduces fat tissue. Sermorelin’s muscle-boosting benefits work hand-in-hand with healthy habits you control, including your exercise routine and protein intake. start=”5″> Stronger Bones HGH doesn’t just help with muscle development and tissue repair — it also helps to grow bones. HGH stimulates the liver and other tissues to secrete a different growth hormone (IGF-1) that impacts cartilage production, which leads to bone growth.Bones are weaker with lower HGH levels, which are associated with low bone density. In serious cases, low bone density can develop into the condition osteoporosis. start=”6″> Improved Mood HGH declines as you get older with the most drastic drop typically during middle age — the same years when biological depression tends to begin.Your HGH levels can influence your likelihood of developing both anxiety and depression. Low levels are linked with physical depression symptoms, including decreased energy and increased irritability, pain and tiredness. Increasing your HGH can combat the emotional and physical toll mood problems take on your day. This means you will become more resolute in your thinking.HGH impacts cognitive function, too. Fifty percent of eighty year olds have impaired cognitive function. Sermorelin therapy can help boost your concentration and memory. start=”7″> Heightened Sex Drive If your HGH isn’t up to par, you may be struggling with decreased libido and sexual function. Keep in mind that the pituitary gland’s master roles include controlling ovaries and testicles, so if your sex drive is low, you may require pituitary support.You can help ensure your sex glands get youthful hormonal messages by supplementing with Sermorelin. start=”8″> Sermorelin Benefits Include Looking and Feeling Younger What do you get […]
Curcumin: Prevent liver disease and reduce liver fat with this amazing natural plant compound

( Natural News ) Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a life-threatening condition caused by an abnormal buildup of fat in the liver. While it is usually caused by excessive alcohol drinking, this disease can also stem from non-alcoholic means. This fat buildup could lead to inflammation in the liver, causing damage and creating scarring. Severe cases of fatty liver disease can even lead to liver failure. Reducing this abnormal buildup of liver fat often involves regular exercise and other healthful lifestyle changes like eating a balanced diet and reducing your sugar intake. Now, a recent research suggests that a well-known compound found in turmeric could make a big difference in improving liver health .
A study published in the journal Drug Research found that curcumin has liver health-boosting effects like improving liver blood flow and reducing liver fat. Take curcumin to improve liver health
Over the years, the list of beneficial health effects of curcumin somehow gets longer and longer. Curcumin is considered the main active ingredient of turmeric ( Curcuma longa ), a perennial spice closely related to ginger. Turmeric has been used for thousands of years both as a spice and as a staple in Ayurvedic medicine for its powerful medicinal properties, including potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. (Related: Curcumin naturally fights cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and obesity .)
Curcumin is also found to increase a growth hormone called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Increasing this hormone could help delay or even reverse age-related cognition decline and plenty of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Higher levels of BDNF can also improve memory. Discover how to prevent and reverse heart disease (and other cardio related events) with this free ebook : Written by popular Natural News writer Vicki Batt, this book includes everything you need to know about preventing heart disease, reversing hypertension, and nurturing your cardiac health without medication. Learn More. In this study, researchers from Iran aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of curcumin as a dietary supplement for subjects afflicted with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). To do so, the researchers recruited 87 patients diagnosed with NAFLD and randomly assigned them into one of two groups. The team tasked one of the groups to take 1,000 g of curcumin per day for a period of eight weeks while the other group took placebo in the same time frame. Each patient received both dietary and lifestyle advice before the trial began. The researchers analyzed physical measurements, hepatic enzyme levels and liver scans both before the trial and after eight weeks of the follow-up.
At the end of the follow-up period, the researchers found that curcumin supplementation was associated with a significant reduction in body mass index and waist circumference compared to the placebo group. This finding is particularly important because obesity is considered a risk factor for NAFLD.
In addition, the ultrasonographic liver scans revealed that 75 percent of those who took curcumin showed significant improvements in overall liver health, while the improvement rate of those in the control group only hit 4.7 percent. While serum levels of both aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase were elevated in participants in the placebo group, those in the curcumin group showed significantly reduced hepatic enzyme levels.
Lastly, participants who took curcumin supplements daily also found significant improvements in liver volume, liver blood flow, and liver vein diameter; all of which contribute to proper liver function.
The study suggests that short supplementation of curcumin can effectively reduce the amount of liver fat present in patients with NAFLD. The findings also confirm curcumin’s ability to improve body measurements and support proper liver function. The researchers added that their study warrants further research exploring the promising effects of this “miracle compound.”
Sources include:
NaturalHealth365.com
Rejuvenating the brain
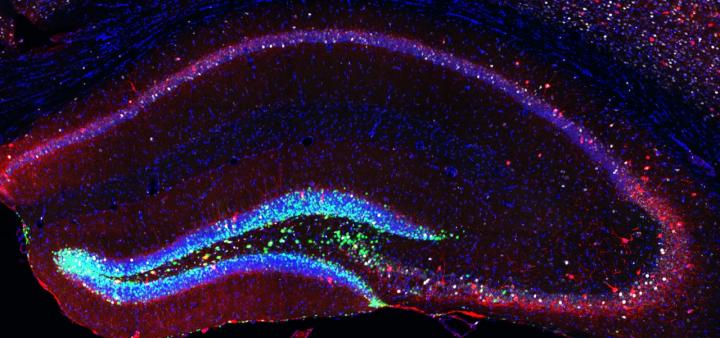
More stem cells improve learning and memory of old mice Credit: CRTD
We all will experience it at some point, unfortunately: The older we get the more our brains will find it difficult to learn and remember new things. What the reasons underlying these impairments are is yet unclear but scientists at the Center for Regenerative Therapies of TU Dresden (CRTD) wanted to investigate if increasing the number of stem cells in the brain would help in recovering cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, that are lost during ageing.
To investigate this, the research group led by Prof. Federico Calegari used a method developed in his lab to stimulate the small pool of neural stem cells that reside in the brain in order to increase their number and, as a result, to also increase the number of neurons generated by those stem cells. Surprisingly, additional neurons could survive and form new contacts with neighbouring cells in the brain of old mice. Next, the scientists examined a key cognitive ability that is lost, similarly in mice and in humans, during ageing: navigation.
It is well known that individuals learn to navigate in a new environment in a different way depending on whether they are young or old. When young, the brain can build and remember a cognitive map of the environment but this ability fades away in older brains. As an alternative solution to the problem, older brains without a cognitive map of the environment need to learn the fixed series of turns and twists that are needed to reach a certain destination. While the two strategies may superficially appear similar, only a cognitive map can allow individuals to navigate efficiently when starting from a new location or when in need of reaching a new destination.
Would boosting the number of neurons be sufficient to counteract the decreasing performance of the brain in navigation and slow down this ageing process? The teams of Prof. Calegari (CRTD) together with Prof. Gerd Kempermann (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases DZNE / CRTD) and Dr. Kentaroh Takagaki (Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg) found the answer to this challenging question and published it this week in the scientific journal Nature Communications .
The answer is “Yes”: Old mice with more stem cells and neurons recovered their lost ability to build a map of the environment and remembered it for longer times making them more similar to young mice. Even better, when neural stem cells were stimulated in the brain of young mice, cognitive impairments were delayed and memory was better preserved over the entire course of the animal natural life.
In young individuals, a brain area called the hippocampus is crucial for remembering places and events, and is also responsible for creating maps of new environments. However, old individuals use other structures that are more related to the development of habits. It was very interesting to see that adding more neurons in the hippocampus of old mice allowed them to use strategies typical of young animals. It was not only about how fast they were learning but, rather, how different the learning process itself was “, explains Gabriel Berdugo-Vega, first author of the study.
“Also humans have a few stem cells in the brain and these stem cells are known to severely reduce in numbers over the course of life. Identifying the causes underlying cognitive deficits in ageing and rescuing them is crucial for our rapidly ageing societies. Our work demonstrates that age-related impairments can be rescued by hijacking the endogenous neurogenic potential of the brain, thus, rejuvenating its function. Being a human myself with my own stem cells and being the senior author of this study, I felt that I had a personal interest in this topic.” says Prof. Federico Calegari, senior author of this study.
The research group of Prof. Federico Calegari focuses on mammalian neural stem cells in the context of development, evolution and cognitive function at the CRTD. The institute is the academic home for scientists from more than 30 nations. Their mission is to discover the principles of cell and tissue regeneration and leveraging this for recognition, treatment and reversal of diseases. The CRTD links the bench to the clinic, scientists to clinicians to pool expertise in stem cells, developmental biology, gene-editing and regeneration towards innovative therapies for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, haematological diseases such as leukaemia, metabolic diseases such as diabetes, retina and bone diseases.
###
This study was funded by TU Dresden / CRTD through the German Excellence Initiative, the German Research Foundation and a European grant from the H2020 programme. In addition, it was supported by the Faculty of Natural Sciences of Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, the Dresden International Graduate School for Biomedicine and Bioengineering (DIGS-BB) and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE).
Media Contact
Gabriel Berdugo-Vega
Gabriel.Berdugo@tu-dresden.de
49-035-145-882-200
