Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Rejuvenating the brain: More stem cells improve learning and memory of old mice
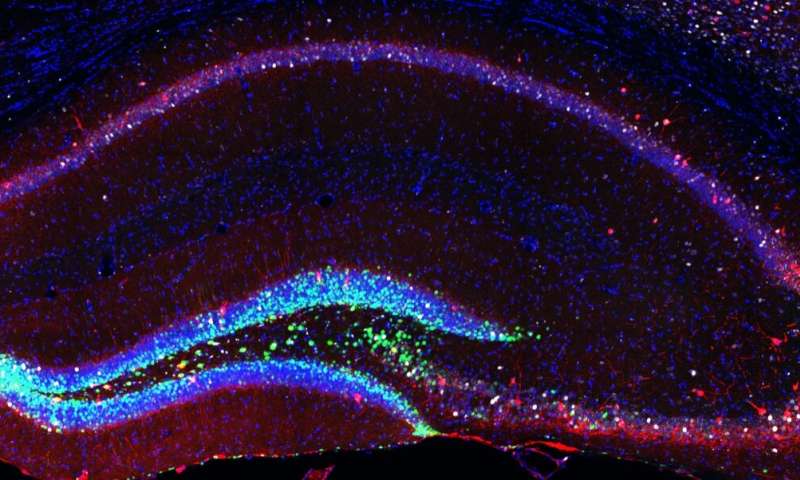
Neural stem cells and newborn neurons (green) artificially generated in the hippocampus and contacting mature cells (red) of the mouse brain. Credit: CRTD The older we get the more our brains will find it difficult to learn and remember new things. The research group led by Professor Federico Calegari used a method to stimulate the small pool of neural stem cells that reside in the brain in order to increase their number and the number of neurons generated by those stem cells. Additional neurons could survive and form new contacts with neighboring cells in the brain of old mice.
We all will experience it at some point, unfortunately: The older we get the more our brains will find it difficult to learn and remember new things. What the reasons underlying these impairments are is yet unclear but scientists at the Center for Regenerative Therapies of TU Dresden (CRTD) wanted to investigate if increasing the number of stem cells in the brain would help in recovering cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, that are lost during ageing.
To investigate this, the research group led by Prof. Federico Calegari used a method developed in his lab to stimulate the small pool of neural stem cells that reside in the brain in order to increase their number and, as a result, to also increase the number of neurons generated by those stem cells. Surprisingly, additional neurons could survive and form new contacts with neighbouring cells in the brain of old mice. Next, the scientists examined a key cognitive ability that is lost, similarly in mice and in humans, during ageing: navigation.
It is well known that individuals learn to navigate in a new environment in a different way depending on whether they are young or old. When young, the brain can build and remember a cognitive map of the environment but this ability fades away in older brains. As an alternative solution to the problem, older brains without a cognitive map of the environment need to learn the fixed series of turns and twists that are needed to reach a certain destination. While the two strategies may superficially appear similar, only a cognitive map can allow individuals to navigate efficiently when starting from a new location or when in need of reaching a new destination.
Would boosting the number of neurons be sufficient to counteract the decreasing performance of the brain in navigation and slow down this ageing process? The teams of Prof. Calegari (CRTD) together with Prof. Gerd Kempermann (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases DZNE/CRTD) and Dr. Kentaroh Takagaki (Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg) found the answer to this challenging question and published it this week in the scientific journal Nature Communications .
The answer is “Yes”: Old mice with more stem cells and neurons recovered their lost ability to build a map of the environment and remembered it for longer times making them more similar to young mice. Even better, when neural stem cells were stimulated in the brain of young mice, cognitive impairments were delayed and memory was better preserved over the entire course of the animal natural life.
In young individuals, a brain area called the hippocampus is crucial for remembering places and events, and is also responsible for creating maps of new environments. However, old individuals use other structures that are more related to the development of habits. It was very interesting to see that adding more neurons in the hippocampus of old mice allowed them to use strategies typical of young animals. It was not only about how fast they were learning but rather, how different the learning process itself was,” explains Gabriel Berdugo-Vega, first author of the study.
“Also humans have a few stem cells in the brain and these stem cells are known to severely reduce in numbers over the course of life. Identifying the causes underlying cognitive deficits in ageing and rescuing them is crucial for our rapidly ageing societies. Our work demonstrates that age-related impairments can be rescued by hijacking the endogenous neurogenic potential of the brain , thus, rejuvenating its function. Being a human myself with my own stem cells and being the senior author of this study, I felt that I had a personal interest in this topic,” says Prof. Federico Calegari, senior author of this study.
Provided by Dresden University of Technology
Boosting the number of neurons improves learning and memory of old mice
We all will experience it at some point, unfortunately: The older we get the more our brains will find it difficult to learn and remember new things. What the reasons underlying these impairments are is yet unclear but scientists at the Center for Regenerative Therapies of TU Dresden (CRTD) wanted to investigate if increasing the number of stem cells in the brain would help in recovering cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, that are lost during aging.
To investigate this, the research group led by Prof. Federico Calegari used a method developed in his lab to stimulate the small pool of neural stem cells that reside in the brain in order to increase their number and, as a result, to also increase the number of neurons generated by those stem cells. Surprisingly, additional neurons could survive and form new contacts with neighboring cells in the brain of old mice. Next, the scientists examined a key cognitive ability that is lost, similarly in mice and in humans, during aging: navigation.
It is well known that individuals learn to navigate in a new environment in a different way depending on whether they are young or old. When young, the brain can build and remember a cognitive map of the environment but this ability fades away in older brains. As an alternative solution to the problem, older brains without a cognitive map of the environment need to learn the fixed series of turns and twists that are needed to reach a certain destination. While the two strategies may superficially appear similar, only a cognitive map can allow individuals to navigate efficiently when starting from a new location or when in need of reaching a new destination.
Would boosting the number of neurons be sufficient to counteract the decreasing performance of the brain in navigation and slow down this aging process? The teams of Prof. Calegari (CRTD) together with Prof. Gerd Kempermann (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases DZNE / CRTD) and Dr. Kentaroh Takagaki (Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg) found the answer to this challenging question and published it this week in the scientific journal Nature Communications .
The answer is “Yes”: Old mice with more stem cells and neurons recovered their lost ability to build a map of the environment and remembered it for longer times making them more similar to young mice. Even better, when neural stem cells were stimulated in the brain of young mice, cognitive impairments were delayed and memory was better preserved over the entire course of the animal natural life.
In young individuals, a brain area called the hippocampus is crucial for remembering places and events, and is also responsible for creating maps of new environments. However, old individuals use other structures that are more related to the development of habits. It was very interesting to see that adding more neurons in the hippocampus of old mice allowed them to use strategies typical of young animals. It was not only about how fast they were learning but, rather, how different the learning process itself was “, explains Gabriel Berdugo-Vega, first author of the study. Also humans have a few stem cells in the brain and these stem cells are known to severely reduce in numbers over the course of life. Identifying the causes underlying cognitive deficits in aging and rescuing them is crucial for our rapidly aging societies. Our work demonstrates that age-related impairments can be rescued by hijacking the endogenous neurogenic potential of the brain, thus, rejuvenating its function. Being a human myself with my own stem cells and being the senior author of this study, I felt that I had a personal interest in this topic.” Prof. Federico Calegari, senior author of this study The research group of Prof. Federico Calegari focuses on mammalian neural stem cells in the context of development, evolution and cognitive function at the CRTD. The institute is the academic home for scientists from more than 30 nations. Their mission is to discover the principles of cell and tissue regeneration and leveraging this for recognition, treatment and reversal of diseases. The CRTD links the bench to the clinic, scientists to clinicians to pool expertise in stem cells, developmental biology, gene-editing and regeneration towards innovative therapies for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, hematological diseases such as leukemia, metabolic diseases such as diabetes, retina and bone diseases.
Putting a face to a name: Research shows women are better than men at recalling verbal information and faces

( Natural News ) Sorry, gentlemen, but women are better than you at remembering certain things , including conversations and people’s faces.
According to the Encyclopedia of Neuroscience , such types of memories are called “episodic memories” – consciously recollected memories related to personally experienced events. Remembering these is a dynamic process that draws upon both mnemonic and non-mnemonic cognitive abilities to mentally reconstruct past experiences from retrieval cues.
And it seems that women are much better at this than men, according to a recent study.
In an article published in Psychological Bulletin , researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden reported that women are better than men at remembering certain types of episodic memories , specifically those related to remembering speech, such as where they left an object and what happened in a movie. According to the researchers, women are also more apt at remembering faces and sensory images compared to men, who, on the other hand, seem to be better at recalling abstract information and navigational data.
Lead researcher Agneta Herlitz and her team conducted a meta-analysis of 617 studies that took place between 1973 and 2013 – with more than 1.2 million participants overall – before they arrived at their study’s conclusion.
Martin Asperholm, a doctoral student at KI, added that the initial results of their study showed that this advantage on episodic remembering is hinged on the type of memory and material to be remembered. (Related: Improve memory and mood with curcumin: Study finds it boosts cognitive function in those with mild, age-related memory loss .)
Sponsored: NEW Biostructured Silver First Aid Gel created by the Health Ranger combines three types of silver (ionic silver, colloidal silver, biostructured silver) with seven potent botanicals (rosemary, oregano, cinnamon and more) to create a breakthrough first aid silver gel . Over 50 ppm silver, verified via ICP-MS lab analysis. Made from 100% Texas rain water and 70% solar power. Zero chemical preservatives, fragrances or emulsifiers. See full details here .
The results of their research corroborate the findings of earlier works, which pointed to subtle differences in memory processing between men and women, including a previous paper by Herlitz herself. In that particular study, published in a 1997 issue of Memory and Cognition , Herlitz stated that during episodic memory tests, women consistently performed at a higher level than men — a finding that researchers Paul Loprinzi and Emily Frith soon built upon in their 2008 study which explored the role of biological sex in memory functions . ABCs of Memory Boosting
Some do’s and don’t’s for improving your memory include:
Added sugar is a no-no
Aside from being a contributor to illnesses such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, excess ingestion of added sugars has been linked to cognitive decline, as shown by a study published in Behavioural Brain Research , which concluded that even short-term exposure to a diet high in fat and sugar can selectively impair hippocampal-dependent memory .
Try organic, natural sweeteners if you want to indulge your sweet tooth.
Boost your omega-3 intake
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), better known as omega-3 fatty acids, are important for overall health according to medical experts and have been shown to lower the risk of heart disease, reduce inflammation, relieve stress and anxiety and even slow down mental decline. According to medical experts, these fatty acids are able to do the latter by preserving cell membrane health and by facilitating communication between brain cells.
To boost your omega-3 intake, the American Heart Association recommends eating 2 servings of fatty fish such as wild-caught salmon , mackerel, herring, lake trout, sardines and albacore tuna per week.
Calm down and meditate
Meditation does a lot more for the mind than just relaxing it. According to a study published in the Neuroimage journal, researchers noted that meditation appeared to increase gray matter , the mass which contains neuron cell bodies, in the brain.
Not only that, another study, published in the Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine , showed that college students who engaged in meditation practices like mindfulness had significantly better spatial working memory or the ability to hold and process information in your mind about the positions of objects in space than students who did not practice meditation.
For more news and stories about how to improve brain health, visit BrainHealthBoost.com .
Sources include:
ScienceDirect.com 1
Heart.org
ScienceDirect.com 2
2020 Wellness trends

As early as October of last year, some of the biggest online publication around the globe had already released their forecast about the biggest trends in the health and wellness industry. This $200 billion industry is cautiously monitored by its stakeholders. Being able to know what is happening in the business and where it is going in the years to come gives the players an advantage to get a bigger slice of the pie.
The Health&Fitness gathered the reports of the three reputable online sites, which they think would give a big impact on the wellness trade this 2020. The biggest wellness trends for 2020 according to wottwellness.com
• Embrace bedtime stories
We all know that our reliance on screens is doing us no favors when it comes to falling asleep, with countless books and apps devoted to improving our “sleep hygiene” or reducing the impact of blue light. But what if the best way to ensure some shut-eye were to revert to the childhood practice of bedtime stories? A host of apps and podcasts make it simple to get your story fix (should your partner not be up for reading to you), from Calm’s Blue Gold, read by Stephen Fry, to Sleep With Me, in which host Drew Ackerman chats away in a soothing fashion that makes staying awake really quite tricky. Get into the mood with a restorative pre-bed bath using the new De Mamiel Altitude Bath Soak, which has been created as an antidote to the hectic nature of modern life.
Sleep tracking apps could be causing “orthosomnia” and actually making you more tired than ever • Make the most of the great outdoors
In the Pinterest 100 Report, which rounds up the top trends to try in 2020 based on search terms, spending time in the big outdoors emerged as a key pursuit for the new year. “Nature is the perfect antidote to digital fatigue, artificial lighting and sitting culture,” the report said, flagging “bushcraft camping,” “nature travel” and “rockhounding” as terms which have seen a big boost in search. Call it eco therapy, call it forest bathing—just get outside and reconnect with nature. In fact, a 2019 study led by the University of Exeter Medical School found that a two-hour “dose” of nature per week boosts health and well-being, so treat it like your five-a-day.
Rewilding is the exciting new wellness trend you need to know • Drink smart
With more and more of us going alcohol-free, the drinks industry has done itself proud in terms of the great offering of nonalcoholic options on sale now. Seedlip’s distilled “spirits” mean that you’re no longer left with only a Shirley Temple for company when you fancy a mocktail, while Fortnum & Mason’s Sparkling Tea makes a good dupe for bubbly, with its delicate blend of jasmine, darjeeling and mint, and the added bonus of a poppable cork. If you’re still drinking alcohol but trying to find healthier options, swap sugary mixers for good-for-your-gut kombucha. London-based brand Momo Kombucha makes an elderflower version that tastes great with gin.
Why we’re all going semi-sober and embracing a wellness trend called “healthy hedonism.” • Get to know nootropics
Do you know what nootropics are? Well, you’re about to: already a big deal in the US, nootropics are just starting to make wave here and are set to go stratospheric in 2020. While research on their effects is relatively scant so far, nootropics are substances believed to improve cognitive function and energy. Perhaps, the most famous of them all is caffeine, but you might find more luck with a supplement than you will by doubling your latte intake. Glow Bar sells powdered herb products which can be added to smoothies and hot drinks, including the nootropics Ashwagandha and Cordyceps. • Pins and needles
Since cosmetic acupuncturist Sarah Bradden started offering her Signature Facial and Body Balancing Treatment at Harvey Nichols, just about everyone in the beauty industry has paid a visit. We predict a rise in popularity of this clever approach to needles, which combines the cosmetic (increased collagen growth, reduced redness and improved definition) and the holistic (many clients report improved sleep and relaxation, as well as an improvement in skin issues, such as dermatitis). The only downside is that you’ll have to move fast for an appointment…
Acupuncture completely helped me de-stress: Here’s everything you need to know about how it can help you, too • And breathe…
Despite breathing being something we do all day without thinking about it, breathing mindfully can actually make a big difference to our well-being. What’s more, it’s something you can do on the go—in waiting rooms, on the bus, and even in the Topshop changing rooms when the January sales crowds get too much. For 2020, make it your resolution to take a few moments to focus on your breathing every day. Glamour loves The Breathing App, founded by Deepak Chopra and yoga teacher Eddie Stern, which aims to recreate the same rate of breathing that Buddhist monks and yogis enter into while meditating. • Expand your CBD repertoire
Our fascination with CBD-based products is going nowhere. As well as CBD oils and CBD skin care, companies like The Chillery stock products ranging from CBD chocolates to bath bombs, lip glosses to tampons. Predicting the path that the substance will take in 2020, The Chillery’s Co-founder and Managing Director, Marisa Schwab says “we will see a spotlight on addressing mental health through CBD and other powerful natural remedies,” as well as flagging CBD-infused bath bombs, pillow mists, candles and face masks as “revamped ways to intentionally take out time for ourselves and create powerful self-care rituals, all while experiencing the therapeutic benefits of CBD.”
Cannabis oil is the latest ingredient taking the beauty world by storm, but is it worth the hype? Byrdie.com’s 9 wellness trends we’ll be seeing everywhere in 2020
• Active Recovery
After years of pushing ourselves to the max in workouts, it […]
What is Quercetin? Food Sources + Dosage & Side Effects

Quercetin, an antioxidant flavonoid, is found in many plant-based foods from apples to nuts to capers. What are the best sources, how does it work, and are there any side effects to its use? Read on to find out.
Most people have heard of flavonoids, plant-based antioxidant pigments that are being touted for many alleged health benefits. Flavonoids give plants their color and belong to the class of polyphenols. Polyphenols became a hot topic recently when some studies suggested their benefits in preventing heart disease, cancer, and other chronic diseases [ 1 , 2 ].
Many vegetables, fruits, nuts, honey , and medicinal herbs are rich in quercetin. Raw capers have the highest amount of quercetin, while apples are the most common food source. Quercetin makes about 75% of all flavonoids consumed through diet [ 3 ].
Quercetin is also relatively better researched than most other flavonoids. Thus, quercetin has earned the nickname “master flavonoid” [ 3 ].
However, this doesn’t mean its potential health benefits are clear. In fact, most of the alleged health benefits of quercetin have not been verified by proper clinical trials. Quercetin has not been shown to treat or prevent cancer or other diseases.
Although quercetin supplements are widely available, they have not been approved by the FDA for medical use. Supplements generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing.
The FDA has issued warning letters to several manufacturers advertising unauthorized health claims. Their quercetin product labels and websites listed claims such as treating diseases, for which quercetin has never been approved. Making such claims places these products in the “unapproved drugs” category by the FDA.
On the other hand, quercetin has cultural and historical significance. Ever since antiquity, people put great value on quercetin-rich foods. For example, people consumed pomegranate as an elixir for good health and longevity .
Quercetin is an antioxidant flavonoid. Limited studies suggest it may scavenge free radicals and reduce tissue and DNA damage. It seems to boost antioxidant defense, which might be helpful for health conditions linked to oxidative stress . According to some theories, most chronic health problems in the modern world have been linked with excessive oxidative stress and free radicals [ 4 , 5 , 2 ].
A PubMed search returns almost 17k studies about Quercetin. However, clinical trials are rare, small, and of questionable quality. About 200 clinical trials involving quercetin have been carried out so far. So is there anything special about it and how weak is the evidence? Reduce oxidative damage to fats
Increase the blood’s overall antioxidant power
Be active against some bacteria and viruses
The dosage in clinical trials varied between ~100-1,000 mg/day. The most common dose was 500-1,000 mg/day [ 3 ].
The main problem with Quercetin is its poor bioavailability . Quercetin bioavailability in typical oral supplements is ~2% .
It’s important to remember that Quercetin is available in many forms: free quercetin (the aglycone) or quercetin bound to various sugar molecules. Rutin from apples, for example, is sugar-bound quercetin. Not all of these types of quercetin have the same bioavailability. For example, Quercetin from onion powder is better absorbed than quercetin from apple peel powder [ 8 ]
Once quercetin is ingested through food, the sugar bound forms are degraded and free quercetin is released. Free quercetin is metabolized very quickly in the small intestine, the kidneys, the large intestine, and the liver, giving rise to numerous metabolites that are probably not active [ 6 ].
Once quercetin is in the gut, its bioavailability also depends on how well it’s modified to be made more soluble [ 6+ ].
Quercetin is sometimes added to commercially-available dog food. Similar to humans, dogs metabolize quercetin very quickly. Its bioavailability in dogs is also low. Unlike for humans, dogs absorb the rutin form of Quercetin found in apples better than humans [ 9 ].
Some people use Quercetin to reduce allergies in dogs. In one study, dogs fed antioxidant- and Quercetin-rich diets had better metabolism and less free radicals [ 10 ].
The human dosage could be adapted to dogs if using Quercetin supplements, although the bioavailability remains uncertain.
Based on the dog size, the dosage may need to be reduced. For example, very small dogs would need only 1/10 of a typical human dose (if the dog is 1/10 the size and weight of an average person).
Talk with your vet before giving quercetin to your dog.
The following may increase quercetin absorption and bioavailability: Taking it with fats or oils. The oils stimulate bile production, which can make quercetin soluble in the gut and easier to absorb [ 11 ]
Combining it with bromelain, which increases both its bioavailability and anti-inflammatory effects [ 16 ]
The combination of quercetin and resveratrol , a polyphenol from grapes may have added health benefits. In rats, only the combination of both reduced fat deposits, while each resveratrol or quercetin alone did not have any effects [ 17 ].
Flavonoids may act in synergy to increase antioxidant defense. Quercetin increases the bioavailability of EGCG and other antioxidant flavonoids [ 6+ ]. Quercetin Side Effects & Safety Quercetin is generally considered to be safe. However, proper safety trials are lacking [ 18 ].The side effects mentioned below were observed in animal or cellular studies. More clinical studies would need to determine the side effects of quercetin in different formulations and doses. Brain cells Quercetin was toxic to rat brain cells. Higher concentrations caused more brain cells to die [ 19 ].It’s uncertain how cellular effects and doses could translate to humans. Homocysteine Levels In human liver cancer cells, quercetin significantly increased homocysteine levels [ 20 ].The same effect has not been observed in clinical trials. Thyroid Function High doses of quercetin and other flavonoids acted as thyroid disruptors in animal studies. People with thyroid problems should use caution [ 21 ].Quercetin is likely safe if taken through a diet of healthy quercetin-rich foods in small amounts during pregnancy and childhood. Children […]
NAC for Mental Health, OCD, Anxiety & Depression
NAC is an antioxidant compound that has recently been found to benefit depression and other mental health issues. Read on to learn more.
Your body uses N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) to make its own antioxidants. Medically, it is used to treat acetaminophen toxicity; it is almost 100% effective as long as it’s given within the first eight hours after overdose [ 1 , 2 ].
For all other purposes, NAC is an unapproved supplement. Preliminary evidence may look promising (and in some cases, very promising!), but future studies may find that NAC is actually ineffective for some of these purposes.
It’s important to talk to your doctor before adding NAC to your health strategies, as it may have unexpected interactions. Proponents:
Some good evidence for a benefit in depression
May help with obsessive-compulsive symptoms and addiction
Promising early research in many mental health concerns
Generally considered very safe
CONs
Doesn’t taste good and can cause nausea
May affect bleeding
Many purported benefits are unproven
Potential Mental Health Benefits of NAC
NAC supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use. Supplements generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing. 1) Depression
Balancing brain glutamate levels
Reducing inflammation
Boosting the growth of new brain cells
In a review of studies including 574 people, NAC improved symptoms of depression and overall day-to-day functioning after 3-6 months [ 5 ].
Additionally, it improved the mood of people with depression after 3-4 months [ 6 , 4 ].
It may also balance mood by reducing oxidative stress in the brain. In a study of 76 depressed patients, those who took NAC had higher brain antioxidant levels [ 7 ].
NAC improved mood in depressed patients, possibly by balancing brain glutamate and reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of NAC for any of the below-listed uses. Remember to speak with a doctor before taking NAC, and never use it in place of something your doctor recommends or prescribes. 2) Bipolar Disorder and Mania
NAC is under investigation for its potential to improve chronic health issues, such as heart disease and hormonal imbalance, in people with bipolar disorder. It had an indirect effect on overall health, antioxidant status, and inflammation [ 8 ].
In another study with 17 bipolar patients, NAC improved low mood and overall symptoms after 6 months [ 9 ].
Larger studies are currently underway to investigate the potential benefits of NAC for Bipolar Disorder [ 10 ].
NAC could also improve mania symptoms in a small study of 15 people after 6 months. The NAC group experienced less severe mania, while the placebo group experienced mood worsening [ 11 ].People with bipolar disorder have benefited from NAC supplementation in small studies, but larger clinical trials will be needed to confirm this. 3) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) NAC may help with OCD by balancing glutamate and increasing antioxidants in the brain. In a study of 44 OCD patients, NAC as an add-on to standard medications improved symptoms, even in severe cases [ 12 ].In a study of 48 OCD patients who previously didn’t respond to drugs, NAC could safely improve the symptoms after 3 months [ 13 ].Some studies, however, didn’t find any benefits of NAC for OCD [ 14 ].Although the evidence is mixed, NAC may be useful for obsessive-compulsive disorders, according to a large review. Overall, it shows promising benefits and has few side-effects [ 15 ]. 4) Autism NAC reduced irritability in a study of 33 children with autism after 3 months [ 16 ].In two studies of 80 autistic children, those who got NAC as an add-on to an antipsychotic (risperidone) experienced less irritability and hyperactivity after two months [ 17 , 18 ].But NAC had no benefits in children with autism in a different study [ 19 ].It boosted glutathione in 31 children with autism but had no effect on their social functioning [ 20 ].NAC reduced irritability and hyperactivity in children with autism, but clinical evidence is still considered insufficient. 5) Schizophrenia NAC may help improve symptoms of schizophrenia and psychosis by balancing the brain’s glutamate levels and fighting oxidative stress and inflammation.NAC improved cognition and working memory in 58 people with psychosis, taken at a higher dose of 2 g/day. It also reduced symptoms like mania and hallucinations and improved response to standard treatment in another study of 121 people [ 21 ].Combined with antipsychotics, NAC improved overall symptoms in 42 people with schizophrenia with no side effects. It especially helped with low mood and apathy [ 22 ].NAC reduced manic and psychotic symptoms in some patients with schizophrenia and improved their cognition. 6) Cognition Combinations of NAC with other antioxidants improved cognition in healthy older people and those with mild cognitive impairment [ 23 , 24 ].Scientists have been researching NAC for boosting cognitive function in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, schizophrenia, and anesthesia recovery [ 25 ]. 7) Compulsions in Children NAC safely reduced obsessive skin picking in a study of 66 children with the disorder [ 26 ].It could also reduce compulsive nail biting in 42 children [ 27 ].It seems to help only with obsessive or compulsive behaviors as it did not improve tic symptoms in 31 children with Tourette Syndrome [ 28 ]. 8) Addiction Some researchers believe that NAC has the potential to help combat various types of addiction, based on the model of binge eating in animals [ 29 ].Cysteine from NAC may normalize brain levels of the neurotransmitter glutamate , which affects reward pathways involved in addiction [ 30 , 31 ].A large review of 165 patients and 9 studies found NAC especially useful for cannabis and cocaine addiction. NAC could also help with nicotine dependence, methamphetamine addiction, and pathological gambling [ 32 ].It seems to help some odd types of impulsive behaviors, such as hair pulling. NAC could reduce uncontrolled […]
Aerobic exercise helps your brain too, says study
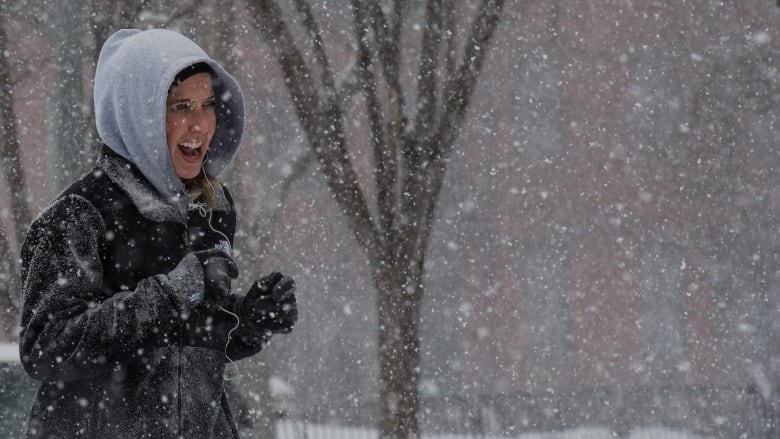

Parts of the brain most affected by exercise in a recent study were those engaged in cognition or thinking. (Nicholas Kamm/AFP/Getty) I run 10 kilometres three times a week. I do it as much to keep my mind sharp as to strengthen my heart and my body.
The beneficial effect on your heart of jogging, cycling or swimming is well-known. A study published last week in the journal Mayo Clinic Proceedings concludes that regular exercise is also good for your brain.
Katharina Wittfeld and colleagues from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Disease studied 2,103 adults ages 21 to 84 years between 2008 and 2012. They evaluated aerobic fitness by measuring the peak oxygen uptake . They also tested the research subjects’ maximal power output while exercising on a bicycle ergometer. Those measures were designed to test that participants were doing enough aerobic exercise to make certain it was having a beneficial effect on the heart.
The researchers did MRI scans to assess the impact on the brain. The researchers found that increases in peak oxygen uptake were associated with increased volume of grey matter (brain tissue) as seen on MRI scans.
The most striking finding is that the parts of the brain most affected by exercise were those engaged in cognition or thinking rather than, say, movement. The other good thing about the findings is that exercise benefited research subjects of all ages, especially those over the age of 45.
The researchers say there are several potential mechanisms that might explain the findings. Studies have shown that physical activity increases the release of natural anti-inflammatory factors. Scientists have long believed that inflammation of brain tissue causes memory loss. Exercise also increases blood flow in the brain. Studies also show that aerobic exercise may also boost the body’s production of chemicals such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor. That might help the brain grow new cells and make new connections following injury and slow cognitive decline associated with aging.
Maximum power output, which was measured in the study, refers to exhausting activities that require intense working of the muscles. As the study by Wittfeld suggested, intense physical activities release chemicals from the muscles that in turn get the liver and other vital organs to produce chemicals that increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the brain.
Another possible explanation is that exercise doesn’t increase higher brain function but that higher brain function motivates people to exercise more. Several of the regions of the brain that were apparently affected by exercise may be relevant for cognitive changes in seniors. (Cathy Alex/CBC ) Other studies have concluded in general terms that exercise is good for brain health. At more than 2,100 participants, this study is one of the largest ever done looking at the benefits of exercise. This study is important because until now, few if any studies have indicated precisely what kinds of exercise might be of benefit. As well, this is the first study to show that cardio-respiratory fitness increases grey matter in the parts of the brain that are needed for memory, executive function and the ability to navigate.
Currently, more than half a million Canadians have dementia, and current trends show the number is rising sharply. That makes me wonder just how much hope this study provides to people with dementia. Several of the regions of the brain that were apparently affected by exercise may be relevant for cognitive changes in seniors. These include the hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus, temporal gyrus, fusiform gyrus, cingulate, and orbitofrontal cortices.
These findings correlate with some of the regions of the brain that researchers believe are affected in older people with cognitive impairment. Some of the regions of the brain with increased grey matter as described in this study line up with similar areas that are depleted in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Start moving
Still, the authors of an editorial that was published alongside the study said one must be careful not to suggest at this point that exercise will have any impact on people with Alzheimer’s disease. They did, however, say the research is “interesting.”
The take-home message is that moderate and regular exercise is good for your heart and likely good for your brain.
The standard recommendation is half an hour of moderate physical activity most days of the week, or 150 minutes a week. If you don’t already do that much, start with a few minutes a day, and increase gradually until you reach 30 minutes per session.
The best and most accessible activity is walking, but other moderate-intensity exercises like swimming, dancing, or racquet sports will do nicely. Household chores like raking leaves and shoveling snow are good provided they make you sweat and provided you do them in a way that does not put extra strain on the heart.
Other things you can do include eating healthy, losing weight as well as getting blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar under control.
The study gives me lots of encouragement to keep on running. There is no better time than a new year to start moving. About the Author
Dr. Brian Goldman is a veteran ER physician and an award-winning medical reporter. As host of CBC Radio’s White Coat, Black Art, he uses his proven knack for making sense of medical bafflegab to show listeners what really goes on at hospitals and clinics. He is the author of The Night Shift and The Power of Kindness: Why Empathy is Essential in Everyday Life.
The Top 10 Benefits of Regular Exercise

Exercise is defined as any movement that makes your muscles work and requires your body to burn calories.
There are many types of physical activity, including swimming, running, jogging, walking and dancing, to name a few.
Being active has been shown to have many health benefits, both physically and mentally. It may even help you live longer (1Trusted Source).
Here are the top 10 ways regular exercise benefits your body and brain.
1. It Can Make You Feel Happier
Exercise has been shown to improve your mood and decrease feelings of depression, anxiety and stress (2Trusted Source).
It produces changes in the parts of the brain that regulate stress and anxiety. It can also increase brain sensitivity for the hormones serotonin and norepinephrine, which relieve feelings of depression (1Trusted Source).
Additionally, exercise can increase the production of endorphins, which are known to help produce positive feelings and reduce the perception of pain (1Trusted Source).
Furthermore, exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms in people suffering from anxiety. It can also help them be more aware of their mental state and practice distraction from their fears (1Trusted Source).
Interestingly, it doesn’t matter how intense your workout is. It seems that your mood can benefit from exercise no matter the intensity of the physical activity.
In fact, a study in 24 women who had been diagnosed with depression showed that exercise of any intensity significantly decreased feelings of depression (3Trusted Source).
The effects of exercise on mood are so powerful that choosing to exercise (or not) even makes a difference over short periods.
One study asked 26 healthy men and women who normally exercised regularly to either continue exercising or stop exercising for two weeks. Those who stopped exercising experienced increases in negative mood (4Trusted Source).
Summary:
Exercising regularly can improve your mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression.
2. It Can Help With Weight Loss
Some studies have shown that inactivity is a major factor in weight gain and obesity (5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source).
To understand the effect of exercise on weight reduction, it is important to understand the relationship between exercise and energy expenditure.
Your body spends energy in three ways: digesting food, exercising and maintaining body functions like your heartbeat and breathing.
While dieting, a reduced calorie intake will lower your metabolic rate, which will delay weight loss. On the contrary, regular exercise has been shown to increase your metabolic rate, which will burn more calories and help you lose weight (5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source, 7Trusted Source, 8Trusted Source).
Additionally, studies have shown that combining aerobic exercise with resistance training can maximize fat loss and muscle mass maintenance, which is essential for keeping the weight off (6Trusted Source, 8Trusted Source, 9Trusted Source, 10, 11Trusted Source).
Summary:
Exercise is crucial to supporting a fast metabolism and burning more calories per day. It also helps you maintain your muscle mass and weight loss.
3. It Is Good for Your Muscles and Bones
Exercise plays a vital role in building and maintaining strong muscles and bones.
Physical activity like weight lifting can stimulate muscle building when paired with adequate protein intake.
This is because exercise helps release hormones that promote the ability of your muscles to absorb amino acids. This helps them grow and reduces their breakdown (12Trusted Source, 13Trusted Source).
As people age, they tend to lose muscle mass and function, which can lead to injuries and disabilities. Practicing regular physical activity is essential to reducing muscle loss and maintaining strength as you age (14Trusted Source).Also, exercise helps build bone density when you’re younger, in addition to helping prevent osteoporosis later in life (15Trusted Source).Interestingly, high-impact exercise, such as gymnastics or running, or odd-impact sports, such as soccer and basketball, have been shown to promote a higher bone density than non-impact sports like swimming and cycling (16Trusted Source).Summary: Physical activity helps you build muscles and strong bones. It may also help prevent osteoporosis.4. It Can Increase Your Energy LevelsExercise can be a real energy booster for healthy people, as well as those suffering from various medical conditions (17Trusted Source, 18Trusted Source).One study found that six weeks of regular exercise reduced feelings of fatigue for 36 healthy people who had reported persistent fatigue (19Trusted Source).Furthermore, exercise can significantly increase energy levels for people suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) and other serious illnesses (20Trusted Source, 21Trusted Source).In fact, exercise seems to be more effective at combating CFS than other treatments, including passive therapies like relaxation and stretching, or no treatment at all (20Trusted Source).Additionally, exercise has been shown to increase energy levels in people suffering from progressive illnesses, such as cancer, HIV/AIDS and multiple sclerosis (21Trusted Source).Summary: Engaging in regular physical activity can increase your energy levels. This is true even in people with persistent fatigue and those suffering from serious illnesses.5. It Can Reduce Your Risk of Chronic DiseaseLack of regular physical activity is a primary cause of chronic disease (22Trusted Source).Regular exercise has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular fitness and body composition, yet decrease blood pressure and blood fat levels (23Trusted Source, 24Trusted Source, 25Trusted Source, 26Trusted Source).In contrast, a lack of regular exercise — even in the short term — can lead to significant increases in belly fat, which increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease and early death (23Trusted Source).Therefore, daily physical activity is recommended to reduce belly fat and decrease the risk of developing these diseases (27Trusted Source, 28Trusted Source).Summary: Daily physical activity is essential to maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of chronic disease.6. It Can Help Skin HealthYour skin can be affected by the amount of oxidative stress in your body.Oxidative stress occurs when the body’s antioxidant defenses cannot completely repair the damage that free radicals cause to cells. This can damage their internal structures and deteriorate your skin.Even though intense and exhaustive physical activity can contribute to oxidative damage, regular moderate exercise can increase your body’s production of natural antioxidants, which help protect cells (29Trusted Source, 30Trusted Source).In the same way, exercise can stimulate blood flow and induce skin cell adaptations that can help delay the appearance of skin aging […]
14 Best Adaptogens Your Body Will Love

Sometimes it seems like the rush of everyday life is overwhelming, creating anxiety and overstimulation from busy schedules and endless to-do lists. Various alternative medicine traditions, from Ayurveda to Chinese medicine, emphasize precisely this modern-day malady as the culprit of most diseases.
In order to prevent chronic stress from building up in the body and throwing us off balance, we need to deal with the sources of the problem, which is usually the communication between the brain and the immune system. Adaptogens, which are ancient mushrooms, herbs, and roots from all over the globe, have special and diverse abilities to mitigate this mind-body connection, and to help the body recover and adapt to various stressors.
If you’re looking for non-chemical ways to help your body deal with stress and to recharge your system’s natural defenses, adaptogens are an incredible resource of vitality. We found some of the best adaptogens that can help with various problems—from lifting brain fog and increasing energy and endurance, to reducing anxiety and helping your sex life. Shutterstock Moringa is the vitamin boost that you’ve been lacking. With more Vitamin C than oranges, more Vitamin A than carrots, and more calcium than milk, this little leafed plant is like a botanical multi-vitamin. It’s also chock-full of iron, protein, and potassium. Moringa can sometimes be found fresh, but is more commonly stocked as a powdered supplement and is used in alternative medicine as a good antioxidant source, treating headaches and boosting a mother’s milk production.
Read more about moringa and its uses here. Shutterstock When it comes to best adaptogens to try, you can’t beat this ‘mushroom of immortality’. It boosts immunity and supports the body’s ability to heal. The antioxidants in reishi can help build strength and vitality and the beta-glucans in the fungus may help fight cancer. Also naturally calming, reishi can be found in bedtime teas to help foster relaxation for better sleep. While capsules are available, it’s best to take it in a liquid or powder form to allow quick absorption in the body.
Read more about reishi and its uses here. Shutterstock Whether you use this ancient Ayurvedic herb for reducing stress and anxiety, assisting your immune system, helping athletic performance or adding a little zing to your sex life, it’s been a studied and proven benefit for a diet for over 4,000 years. It’s also a help to regulate thyroid function, especially in women.
Read more about ashwagndha and its uses here. Shutterstock Full of vitamins and minerals, Chaga mushrooms are referred to in European and Asian folk medicines as a ‘Gift from God’. As an adaptogen, Chaga fights stress, reduces anxiety and regulates hormones. It’s been shown to fight cancer, reduce cholesterol and regulate the cardiovascular system.
Read more about chaga and its uses here. Shutterstock Maca root is another libido booster, helping with mild erectile disfunction and stimulating feelings of desire in both sexes. At the same time maca root is tackling common difficulties in the bedroom, it boosts fertility by raising sperm count for men. It also tackles PMS and menopause symptoms by balancing hormones. Taking maca before a workout may help with a natural, no caffeine energy boost and it’s been found to bring down anxiety levels.
Read more about maca root and its uses here.
The unique appearance of this white, fuzzy mushroom hides a powerhouse of nutritional value. High in protein and full of antioxidants, this fungus contains hericenones and erinacines, two compounds that help protect brain tissue and stimulate new growth. A help with mild cognitive impairment and a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s, this super mushroom is sure to be found in many future clinical trials. Shutterstock In science class, we all learned about the value of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a key component in the transfer of energy in our body. Cordyceps stimulates production of ATP, giving a push to our energy levels. It behaves like insulin, regulating hormones. Cordyceps also is a powerful antioxidant, reducing the effects of aging on skin, hair and nails. Shutterstock A go-to supplement to help with a good night’s rest, valerian’s long-term use is to treat insomnia. It relaxes the central nervous system, helping the user drift off and conquer mild sleep problems. Studies suggest that valerian also helps with PMS, reducing muscle spasms and cramps.
Read more about valerian root and its uses here. Shutterstock Triphala helps ease the digestive system, reducing gas, diarrhea or constipation. It’s a blend of three fruits, amla, haritaki, and bibhitaki, that work together to help good bacteria thrive in the gut and eliminate bad bacteria.
Read more about triphala and its uses here. Shutterstock The gotu kola herb might appear like parsley, but that’s where the comparison ends. This Ayurvedic herb helps with memory and lessens anxiety and depression. The high amount of antioxidants can get rid of the free radicals that constantly bombard our bodies and administered topically, may even help with the appearance of stretch marks and cellulite.
Read more about gotu kola and its uses here. Shutterstock A potential cancer busting, cholesterol-lowering and immune boosting plant, astragalus was used in ancient Chinese culture to regulate the appetite and encourage energy. It’s a great anti-inflammatory and has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, making it a good choice for cold, flu or allergies. Astragalus also strengthens blood vessels and helps blood flow. Shutterstock The endocrine system is fortified by using this flowering herb, resulting in balanced thyroid and adrenal levels. Like other adaptogens, it fights anxiety and exhaustion, but it also balances the production of cortisol which allows the body to properly burn fat, leading to a rise in metabolism. Shutterstock An interesting mugwort treatment is moxibustion. In combination with acupuncture, mugwort is burned over an expectant mother’s body to stimulate breech-position babies to turn. Mugwort also relaxes muscles in the uterus, helping nudge a late period or help with cramps. That makes mugwort unsuitable for a woman in her early stages of pregnancy. There is a risk of miscarriage.
Read more […]
Eggs Are One of the Best Things You Can Eat

Believe it or not, eggs have been a topic of great debate among health specialists lately, namely due to concerns over their cholesterol content. While the United States’ Department of Agriculture’s current Dietary Guidelines for Americans maintain that eggs are an outstanding source of dietary protein, recent research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2019 established a link between eggs and an increased risk of heart disease and a shorter lifespan. Are eggs actually worthy of their health halo, you may ask? Many concerned breakfast lovers are not aware, however, that this newfound link between eggs and cardiovascular disease hinges on someone eating upwards of a dozen eggs in a single week; so unless you’re consuming three or four eggs every day, don’t go throwing out your cartons just yet.
One of the best sources of protein available in your kitchen, eggs are chock-full of essential nutrients such as vitamins A, D, B12, and an under-the-radar essential known as choline. They’re also an inexpensive and versatile staple, so don’t let misconceptions about cholesterol or saturated fats stop you from making them for breakfast, brunch, or Brinner! We’re highlighting the best health benefits associated with eggs below. Plus, we’re tackling all of the chatter around eggs with a list of FAQs — including what you really need to know about egg whites.
More on MSN Health:
Running marathons could help you live longer – but how do you start?
Sore muscles? Here are some home remedies to try
Exercising for people who hate exercise Eggs Nutrition Stats
A large egg contains the following, according to the USDA: 72 calories
0g carbohydrates
6g protein
5g total fat
1.5g saturated fat (8% DV)
0g fiber
0g sugar
69mg potassium (1% DV)
6mg magnesium (1% DV)
28mg calcium
0.8mg iron (3% DV)
99mg phosphorus
0.08mg vitamin B6 (5% DV)
0.45 mcg vitamin B12 (10% DV)
270 IU vitamin A
41 IU vitamin D (11% DV)
What are the health benefits of eating eggs?
They boost brain health. Eggs are chock full of choline, an essential nutrient crucial for healthy memory, mood, and muscle control, says Michelle Hoeing Bauche, MS, RDN, a clinical dietitian in the bariatric services division of the University of Missouri Health Care system. “Choline is in the B vitamin family…and is fairly ‘new’ compared to other nutrients that have been studied and researched,” she says. “Consuming choline through foods like eggs may actually help to prevent things like cardiovascular disease, early brain dysfunction such as dementia, and fatty liver disease.”
But you won’t get choline’s health edge by simply taking supplements; Bauche says that some research shows that choline on it’s own doesn’t have much of an effect on preventing these conditions, most likely “because most nutrients act synergistically with one another and rarely alone.” Your best bet is to incorporate choline-rich foods into regular rotation in the kitchen. Eggs and other dairy items are the best source, Bauche says, followed by beef liver, shiitake mushrooms, fatty-rich salmon, and beans, legumes, and cruciferous vegetables on a smaller scale.
They safeguard pregnant women. During pregnancy, choline intake is critical for fetal brain development and can help prevent birth defects. “Research suggests that as many as 90 percent of pregnant women may not be consuming adequate amounts of choline,” Bauche says, adding that clinical studies have found that pregnant women who eat upwards of 900mg of choline (double the recommended daily intake) may boost cognitive development in their children later on. “While most people are aware that folate plays a role in preventing neural tube defects, choline actually plays an equally important role, since it also aids in the synthesis of cell membranes and neurotransmission.” Two large eggs contain more than 50% of the recommended choline intake for pregnant women. Vitamin B12 is another essential nutrient required for red blood cell formation, neurological function, and DNA synthesis. B12 is almost exclusively found naturally in animal products, so if you’re vegetarian, eggs can help meet your B12 needs. They can help manage weight loss over time. Research has linked meals higher in protein to keeping you fuller, longer. Published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition , a 2004 review suggests that protein-rich foods (including eggs!) is the most filling option available at mealtime, even with smaller portions compared to other nutrients. Plus, lean protein like eggs are lower in calories than higher-fat cuts of meat and poultry. They can preserve vision and eye health. Eggs also contain a crucial chemical compound known as carotenoids that are normally found in fruits and vegetables — and these nutrients can help boost the immune system over time, according to Anne-Marie Gloster, Ph.D., R.D., a lecturer in the nutritional sciences program at the University of Washington. “Carotenoids are the chemical compounds which produce the yellow, orange, and red colors in fruits and vegetables,” she shares, adding that eggs contain a class of carotenoids known as xanthophylls. “The two xanthophyll compounds found in these carotenoid rich foods are lutein and zeaxanthin; they are more of the yellow pigments in our foods. Egg yolks contain these xanthophylls… And the color of [the] yolk is dependent on the feed of the chicken and whether their diet included carotene-rich foods.”The lutein and zeaxanthin found in eggs play a role in maintaining eye health; research published in 2019 shows that lutein in particular may impact cognition in both children and adults. Gloster shares that these pigments allow our eyes to naturally filter blue-light emissions from computers and televisions; research has suggested that these compounds may even help prevent declining vision into old age and cataracts themselves. And while eating a balanced diet usually provides more than enough of these chemical compounds for your body to absorb, Gloster says eggs provide far more immediate benefit than most leafy vegetables. ” Because eggs also contain fatty acids, the lutein and zeaxanthin is more bioavailable, more easily absorbed, than the richer vegetable sources of carotenoids.” They […]
Alzheimer’s May Be Reversed By Shining Light Directly Into The Brain
Currently there is no known cure for Alzheimer’s disease, this Neuro RX Gamma headset developed by Vielight may offer hope to the millions who suffer from the brain wasting disease around the globe: early testing provided positive results of patients regaining memory as well as improvements in reading and writing skills in three months which has paved the way to a 12 week trial into its effectiveness.
To undergo treatment for 20 minutes a day the patient has to wear the device and a separate nasal clip that also channels light through the nostrils; the light is believed to boost photobiomodulation, this then stimulates the brain to activate microglia immune cells which fight the disease.
In Alzheimer’s disease these cells can become inactive and plaques build up stopping the brain from functioning normally. Amyloid plaque is a common hallmark of the disease, the sticky build up is thought to lead to the progressive destruction of brain cells.
“Photobiomodulation introduces the therapeutic effect of light into our brain. It triggers the body to restore its natural balance or homeostasis. When we do that, we call upon the body’s innate ability to heal. Based on early data, we are confident of seeing some measure of recovery in the symptoms not just a slowdown in the rate of decline, even in moderate to severe cases,” said inventor Dr. Lew Lim to The Telegraph.
The trail involves 228 subjects across eight sites within Canada and America and is being led by the University of Toronto; half of the subjects will receive a placebo six days a week for 20 minutes over the course of 12 weeks while the other half will be receiving light therapy.
The safety trial involved 5 subjects with mild to moderately severe dementia showed the condition of all subject’s conditions improve, and reports improved cognitive function, better sleep, fewer angry outbursts, less anxiety, and less wandering as well as better memory. Brain scans revealed visible improvements in connectivity between brain regions as well as better blood flow. However, once therapy stopped the subjects began to decline.
Currently light therapy is used to treat seasonal affective disorder patterns and traumatic brain injuries; it is believed to trigger the release of the happy hormone serotonin to promote better sleep and stimulate areas of the brain that shut down after damage.
The American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine (A4M) is also Shining New Light on Dementia with another trial:
“Treatment for neurodegenerative disorders using noninvasive, non-drug methods has reached a new level of efficacy with the introduction of transcranial and intraocular photobiomodulation (PBM) and brainwave biofeedback training (NFB). Evidence continues to mount supporting the use 1065-1075nm, pulsed infrared light to significantly improve both motor and behavioral symptoms of subjects with both Parkinson’s and probably Alzheimer’s disease. PBM’s proposed mechanism of action is in the mitochondrial functions, microvascular flexibility/perfusion, increased production of ATP and reduction of phosphorylated Tau and Ab42. Cell line studies within a CD-1 mouse model on memory and performance (Michalikova,2007) demonstrated PBM’s beneficial effects and (Duggett & Chazot, 2014) demonstrated PBM reducing amyloid-induced cell death. It is proposed that the PBM confers a tissue-level therapeutic effect while NFB training can remediate the neural network connectivity deficits caused by neuronal dysfunction and death. The synergistic effect of a PBM and NFB treatment strategy should result in enhanced electrophysiological connectivity, CNS health and resistance to further tissue damage. (Nichols & Berman, 2019)”
“Human trials were conducted employing 28 daily, in-office, 6-minute treatments (Berman, 2017) and (Huang, 2018 unpublished) delivering 28, twice daily, home-based, self-administered, 6-minute, transcranial and intraocular treatments (N=12) safely produced marked cognitive and motor behavior improvements. Improvements were associated with frequency of treatment given other relevant variables were invariant.”
“With safety and pilot trials completed, a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled version (N=100) has begun at Baylor Research Institute affiliated with Texas A&M School of Medicine, Dept. of Neurosurgery in Temple, TX and Quietmind Foundation in Elkins Park, PA. Recruitment of subjects from the New York and Philadelphia metropolitan regions and Austin and Temple, TX began in March 2018. Subjects will be evaluated 3 times over 60 days using Quantitative EEG and ADNI (ADAS-cog) neurocognitive testing and caregiver evaluations of subject functioning. Subjects and caregivers will be trained to use the study device they will be self-administering twice daily over 28 days and they’ll return for an interim evaluation and then another 28 days before final assessments are conducted. Subjects are compensated $75/evaluation session attended and a portion of travel expenses may be reimbursed.”
For more information about the A4M shining light, or referrals direct inquiries to Dr. Marvin Berman PhD (610) 940-0488 or www.quietmindfdn.org/trials Materials provided by: Note: Content may be edited for style and length. This article is not intended to provide medical diagnosis, advice, treatment, or endorsement.
Toxicity and effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on cognitive performances in rats.
Abstract
There is increasing scientific evidences that the physical and chemical properties of manufactured nanoparticles lead to an increase in their bioavailability and toxicity. Among them Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) are widely used in different fields. However their potential adverse effects namely on brain functions are still discussed. Thus, the present study aimed to investigate the subacute oral toxicity and effects of CuO-NPs on cognitive performances in rats. Rats were randomly divided into three groups of 8 animals each, a control group received a dose 9‰ sodium chloride and the other groups received a suspension of CuO-NPs at doses of 250 and 500 mg/kg through oral gavage for 14 consecutive days. Multiple behavioral tests showed that CuO-NPs caused little changes in memory and learning performances as well as the locomotors activity, while the anxiety index increased. Copper NPs exposure increased also the liver and stomach relative weights and altered some blood biochemical parameters.
Your guide to the menopause

Challenges await at every life-stage, and in midlife, menopause can be a biggie. Although some women will sail through it symptom-free, others will struggle.
It doesn’t help that it’s an information minefield: type ‘menopause’ into Google and you’ll be confronted with about 115,000,000 results on topics ranging from dwindling sex drives to treatment scares.
But here’s the thing: being involved in your journey by dispelling the myths and getting to grips with the latest developments will help to keep you in the driving seat.
Of course, no advice can be one-size-fits-all because the process of oestrogen and progesterone withdrawal affects each of us in different ways, but we hope we can help you make positive and informed choices. But first – what you need to know about the menopause
What is the menopause?
It’s a normal biological stage that happens when you stop menstruating and reach the end of your natural reproductive life. It’s defined as when you haven’t had a period for 12 consecutive months. After this time, you’re considered to be postmenopausal, but you might experience symptoms for many more years to come.
What age does it start?
Normally between 45 and 55, when your oestrogen levels decline; the average age in the UK is 51. But symptoms such as changes in cycle length, worsening PMS, hot flushes, night sweats and changes in sex drive can happen years beforehand: this is known as the perimenopause. The age your mother went through the menopause may offer clues, as it’s partly influenced by genetics, but smoking, ethnicity and having ovarian surgery or chemotherapy also have an impact.
What’s an early menopause?
About one in 100 women experience a premature menopause before the age of 40. If you’re experiencing symptoms before the age of 45, see your GP as you may have an increased risk of osteoporosis and heart disease.
What are the symptoms?
Periods stopping is just one of many. Hot flushes, night sweats and insomnia are common complaints, but it’s estimated there are more than 40 symptoms, which can include vaginal dryness, low mood or anxiety, reduced libido, palpitations, joint stiffness, UTIs and problems with memory and concentration.
How is menopause diagnosed?
According to NICE guidelines, all GPs should treat women aged over 45 based on their symptoms, with no need for blood tests (which can show false readings due to regular hormone fluctuations). 5 steps for a better change
The menopause is a brilliant time to take control of your health, to help you feel happier and healthier now and in future.
1. Keep moving
Research shows that exercising regularly can help to reduce menopause symptoms, including hot flushes and insomnia, because it helps to stabilise your thermoregulatory system, lowering your core body temperature and improving how your body distributes heat. “We’re only now beginning to understand the true power that exercise has to manage menopause,” says Dr Juliet McGrattan, author of Sorted: The Active Woman’s Guide To Health . “It can also counteract the fall in muscle and bone mass, plus lower the risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer that increase at the menopause.”
TOP TIP Add weight-bearing or resistance exercises to your routine to help boost muscle and bone mass. These can include lifting weights, working with resistance bands, hill walking, push-ups, sit-ups or squats.
2. Make over your bedtime
Hot flushes and night sweats occur because falling levels of oestrogen and progesterone cause blood vessels to dilate. This allows more blood through the body, bringing more heat with it: hello, uncomfortable nights! “Wear fabrics that wick moisture away from the skin to avoid drenching sweats disturbing your sleep,” says Dr Alanna Hare, a specialist in sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital in London. Dr Hare suggests trying CBTI (cognitive behavioural therapy, but specialised for insomnia), which has been found to improve sleep in women with hot flushes. “It works on sleep behaviours as well as helping you to develop coping techniques,” she says. Your GP may be able to refer you, but you can also find CBTI online packages and smartphone apps.
3. Try the menopause diet
This is not about faddy eating; it’s about choosing nutrient-rich foods to help support your body.
Look after your gut: There’s a real buzz around gut health right now. “The emerging research into the gut microbiome and how it relates to hormonal health may place nutritional interventions more centre stage in the future,” says Dr Hannah Short, a specialist in menopausal and premenstrual disorders. “Eating a fibre-rich diet improves gut health and evidence indicates that women who eat a wide variety of plant-based foods suffer fewer menopausal symptoms.”
Eat happy-hormone foods: Studies show that symptoms are also reduced in women who eat a lot of phytoestrogens (naturally occurring plant compounds that are structurally similar to oestrogen). “Phytoestrogens can cushion the effect of the hormone rollercoaster,” says Dr Marilyn Glenville, a nutritionist specialising in women’s health. “Don’t base everything around soya: also include chickpeas, oats, lentils, flaxseeds (linseeds) and kidney beans, and aim for variety.”
Get your calcium quota: We lose up to 20% of our bone density in the five to seven years after the menopause. Good sources of calcium include green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, tinned fish (with bones) and dairy products. You also need vitamin D from sunlight, so take a supplement from October to March.
Eat little, but often: ” Don’t go for more than three hours without eating,” says Dr Glenville. “If you wait longer, your blood sugar will drop and adrenaline and cortisol will be released, giving rise to anxiety-related symptoms.”
Rethink drinks: Now is a great time to cut back on unhealthy habits, like drinking too much caffeine or alcohol, which can stimulate your body and make symptoms worse. Try decaf coffee and having alcohol-free days to see if it helps. 10% of women have considered giving up work due to their menopausal symptoms 4. Mind your mental health
We have numerous oestrogen receptors in the brain, so it’s […]
Alpha GPC Benefits

Originally Posted On: https://mindzymes.com/alpha-gpc/ Recent research indicates that alpha GPC, also known as A-GPC, works to deliver choline to the brain. This, in turn, stimulates a neurotransmitter which helps promote cognitive health.
Interestingly, studies suggest that it is one of the most effective nootropic brain supplements available. What’s more, it’s both well-tolerated by aging people and it’s safe. That makes it ideal for patients with dementia. But what’s interesting is that it also helps young athletes boost their physical capabilities.
Table of Contents What is Alpha GPC?
It is a molecule that is the source of choline. It is referred to as Alpha GPC, alpha glyceryl phosphorylcholine, choline Alfoscerate, choline-glycerophosphate, and Glycerophosphocholine. However, please take caution not to confuse these with CDP-choline, choline, or DMAE.
Again, alpha GPC is a molecule that is a source of choline in the body. However, it’s also found in soy lecithin and other plants as a fatty acid. Additionally, it helps the body produce the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which improves learning and memory. It’s also highly effective as a neurotransmitter for muscles which is why it’s popular with athletes.
Another detail that makes it more effective than other supplements is that A-GPC crosses the blood-brain barrier quickly. In fact, patients with dementia disorders or Alzheimer’s take this supplement because of its promising effects. How Alpha GPC Benefits You
Athletic Performance Improvements
Because of its ergogenic properties, alpha GPC is fast becoming a favorite of athletes because it improves power output, muscle strength, and stamina. Epilepsy Patient Benefits
For patients with epilepsy, a 2017 study using rats evaluates alpha GPC effects on cognitive functions following an epileptic seizure. Findings suggest that alpha GPC has neuroprotective effects and therefore is useful for epileptic patients. Focus and Learning Improvements
Studies on young, healthy adults also show that alpha GPC boosts focus, learning, and memory for them as well.
Another study finds that alpha GPC benefits young adults that include increases in physical and mental outcome scores. Memory Improvements
Alpha GPC improves cognitive functions in the brain. That’s because when alpha GPC goes to work, it increases acetylcholine into the brain. As a result, improvements occur in cognitive brain functions including learning, thinking, and memory. In fact, one study suggests that alpha GPC is promising for the treatment of Alzheimer’s and dementia. Serotonin and Dopamine Levels Increase
Serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitters levels increase which helps increase energy, mood, and motivation. Stroke Recovery Time Improvements
Alpha GPC benefits also apply to patients who recently experienced strokes. Because alpha GPC works as a neuroprotective agent, it supports neuroplasticity through nerve receptors and helps in recovery from stroke or mini-stroke.
Additionally, a study performed in Italy in 1994 also found a low percentage of adverse occurrences following a stroke or mini-stroke. Choline and Alpha GPC
Again, alpha GPC is a molecule that is a source of choline in the body. Choline is important because as a micronutrient it performs as an anti-aging neurotransmitter while it improves nerve communication. However, even though our bodies make small amounts of choline, we must also get this from food sources.
Foods high in choline include: Beef liver
Chicken breast
Chickpeas
Eggs
Salmon
Unfortunately, people often suffer from choline deficiency because their body doesn’t absorb choline from food effectively. That’s why experts recommend alpha GPC supplements to help boost brain functions.
The unique function of alpha GPC to cross the blood-brain barrier after taking the supplement helps convert the choline into the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which is highly important for cognitive function improvements. Alpha GPC vs. CDP Choline
CDP choline helps transport dopamine in the brain. Interestingly, it is a compound made from choline and cytidine. Alpha GPC comprises 40% choline while CDP choline has 18%. However, CDP choline also contains cytidine which helps increase cognitive abilities. Alpha GPC Dosages
Most manufacturers recommend between 200mg to 600mg daily. Reportedly, the benefits you wish to achieve will dictate the dosage you take. A study with healthy athletes who want to improve their physical endurance and stamina shows the best results from 600mg taken 90 minutes before the athletic activity begins.
However, patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease benefit from 1,200mg per day taken in three doses throughout the day. Alpha GPC Side Effects First, check the manufacturer’s labels and check for alpha GPC supplements derived from soy lecithin. That’s because some people experience negative side effects when they use soy products. Those symptoms might include skin rashes, bloating or upset stomach, and nausea.Next, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommended dosages and avoid taking high doses of alpha GPC.Although alpha GPC is safe and well-tolerated in healthy adults, side effects sometimes occur that include nervousness, heartburn, diarrhea, upset stomach, nausea and fatigue.Due to the lack of substantial research, this supplement is one to avoid for pregnant or nursing women. Alpha GPC Stacking Interestingly, alpha GPC stacks well with other nootropics, especially racetams .Here is a recipe for stacking with alpha GPC that includes the racetam, aniracetam , and the nootropic Noopept.Take the following 1 2 times per day: 20mg Noopept 750mg Aniracetam 300mg Alpha GPC Alpha GPC Benefits Conclusion Alpha GPC supplements are available as a supplement taken by mouth. Moreover, it’s available online and in health stores. For convenience, it comes in both capsule and powder form.As a water-soluble oral supplement, alpha GPC is fast-acting because of its excellent bioavailability. In fact, users usually feel the effects within an hour after taking it.This supplement is effective in improvements to cognitive functions and memory, but is also in use to boost athletic ability and strength endurance.If you are soy intolerant, you’ll want to check the manufacturer’s label to determine the source before taking it.Additionally, alpha GPC is hygroscopic. That means it pulls moisture from the air so you must store this supplement in an air-tight container. Also, take care not to expose it to the air any longer than is necessary.Furthermore, alpha GPC is available as an over-the-counter supplement in the United States and Canada. However, in some European countries, alpha GPC is sold only as […]
Health benefits of honey
Olufunke Faluyi
A visit to the wound care section of one of the nation’s teaching hospitals recently encouraged me to write about honey. I saw that they used it in dressing the wounds of patients.
Honey is a natural product made by bees from nectar which is a secretion of flowers of plants. The bees particularly of the genus Apis are known for honey production. Commercial honey production exploits bees through the perfection of bee keeping. Honey is, in effect, a natural product even at the industrial scale.
Honey has a long medicinal history; the ancient Egyptians not only made offerings of honey to their gods, they also used it as an embalming fluid and a dressing for wounds.
Today, many people use honey because of its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Holistic practitioners consider it one of nature’s best all-around remedies.
In addition to important roles of natural honey in traditional medicine during the past few decades, it has been subjected to laboratory and clinical investigations by several research groups and it found a place in modern medicine. Honey has been reported to have an inhibitory effect on around 60 species of bacteria, some species of fungi and viruses
The benefits are explained below:
Healthy sweetener: It can be used as a substitute for sugar in many foods and drinks. It contains about 69 per cent glucose and fructose, enabling it to be used as a sweetener which is far better for one’s overall health than normal white sugar.
Weight loss: Though it has more calories than sugar, honey helps in digesting the fat stored in one’s body. Similarly, honey with lemon juice or cinnamon helps in reducing weight.
Provides relief for cough: In 2012, a research was conducted on 300 children of age one to five years to find out the effect of honey on nocturnal cough and sleep quality. The results published in the Pediatrics Journals showed that honey could be a preferable treatment for a cough and sleep difficulty associated with childhood upper respiratory tract infections.
Boosts energy : According to the USDA, honey contains about 64 calories per tablespoon ; therefore, it is used by many people as a source of energy. Furthermore, the carbohydrates in it can be easily converted into glucose since it is simple for the body to digest this pure and natural substance.
Improves performance: Research has shown that honey is effective in boosting an athlete’s performance. It is a great way to maintain blood sugar levels, recuperate muscles, and restore glycogen after a workout.
Improves memory: Honey contains polyphenols that can significantly improve the memory-related functions of the brain. It counters deficits in recall functions and induces memory formation at the molecular level.
It is this modulation of neural circuitry that helps in improving memory. Research on Tualang honey, multi-floral honey found in Malaysia, showed that its intake improves the brain morphology to improve various learning and memory functions.
Rich in vitamins and minerals: It contains a variety of vitamins and minerals. The type of vitamins, minerals and their quantity depend on the type of flowers used for apiculture. Commonly, honey contains vitamin C, calcium, and iron.
Antiseptic property: It has anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties, so it is often used as a natural antiseptic in traditional medicines. In-vitro tests on different medical-grade honeys showed potent bactericidal activity even in the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria that cause life-threatening infections in humans. However, the antimicrobial activity depends on the source of nectar.
Antioxidant properties: It contains nutraceuticals highly effective for the removal of free radicals from the body. As a result, one’s body immunity is improved against many chronic health conditions. A study on the antioxidant properties of honey, published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, attributed these qualities to the presence of a wide range of compounds, which include phenolics, peptides, Maillard reaction products, organic acids, enzymes, and other minor components.
Anticancer properties: A review published in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that there is growing evidence of honey’s anticancer potential. This is displayed by its antiproliferative, apoptosis, antimutagenic and anti-inflammatory properties. However, the floral source also decides its properties. Another article published in the same journal pointed out that as a natural substance, honey is a sustainable and low-cost option in cancer care in developing nations.
Skin and hair care: Milk and honey are often served together since both of these ingredients help in creating smooth, beautiful skin. Consuming this combination every morning is a common practice in many countries for this reason. A study published in the European Journal of Medical Research investigated and confirmed the use of honey for dandruff and dermatitis. It said that crude honey could markedly improve seborrheic dermatitis, its associated hair loss and prevent relapse when applied weekly.
Speeds wound healing: Significant research is being carried out to study its benefits in the treatment of wounds. These have been listed below: honey possesses antimicrobial properties, helps in promoting autolytic debridement and deodorises malodorous wounds.
It also speeds up the healing process by stimulating wound tissues and helps in initiating the healing process in dormant wounds.
These healing powers are not overstated. The Waikato Honey Research Unit provides details about the worldwide research being carried out on the benefits of honey in medicine.
According to a British Broadcasting Corporation report ; doctors at the Christie Hospital in Didsbury, Manchester are planning to use it for faster recovery of cancer patients after surgery. Such research will provide scientific evidence for the beliefs held by honey lovers all over the world and will help in propagating the benefits to more people.
The Russians used honey in World War I to prevent wound infection and to accelerate wound healing. The Germans combined cod liver oil and honey to treat ulcers, burns, fistulas and boils .
Nearly all types of wounds like abrasion, abscess, amputation, bed sores /decubitus ulcers, burns, chill blains, burst abdominal wound, cracked nipples, fistulas, diabetic, malignant, leprosy, traumatic, cervical, varicose and sickle cell ulcers, septic wounds, surgical wound or wounds of abdominal wall and perineum are found to […]
Is omega-3 supplementation an effective alternative treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS)?

( Natural News ) Omega-3 fatty acids may offer a natural approach to treat the symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS). The nutrients may come from either health supplements or foods rich in fatty acids. Multiple sclerosis is a severe neurodegenerative disease. There is no cure, and no one knows what triggers the autoimmune response. Each patient with multiple sclerosis experiences different symptoms. Also, the disease progresses differently in individual patients, making it hard to pick out a general pattern to it.
Researchers sought out alternative methods of treating multiple sclerosis. They found exciting results with omega-3 fatty acids, and they believe that supplementing with omega-3s may become standard practice for treating patients with the neurodegenerative disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that naturally appear in certain types of foods. Whereas saturated and trans fats harm health, these healthy fats support the normal functions of the body. The three main types of omega-3s are ALA, DHA, and EPA. They are popular over-the-counter health supplements.
Plant-based foods that contain large amounts of omega-3 fatty acids include flaxseed and soybeans. The animal-based sources are certain fish such as herring, mackerel, salmon and sardines. (Related: Research suggests cannabis can relieve symptoms, pain associated with MS .) Omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the harmful effects of multiple sclerosis on the patient’s health
Omega-3 fatty acids benefit the body in many ways. It enhances vision, regulates inflammation, and helps people sleep better.
Let the Health Ranger Store help you achieve your New Year’s resolutions. Enjoy up to 40% OFF during the Health Ranger Store’s New Year’s Resolution Sale with over sixty different lab-verified products for health and more. This limited-time sale is going on now and runs through Jan. 6 at NOON CST, or while supplies last. Learn more here .
The health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids may directly alleviate the symptoms caused by multiple sclerosis. Taking the fatty acids may improve the conditions of patients with progressive MS or during a relapse of the disease. Supports eye health — Patients with multiple sclerosis often suffer from poor vision, such as blindness, blurred vision, double vision, and painful eyes. Omega-3 fatty acids improve the sight organ’s health and vision, which suggests that they may help protect the eyes of MS patients.
Fights inflammation — Multiple sclerosis causes inflammation in the brain and spinal cord that damages the nerve cells there. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that reduce the immune response, making them good candidates for controlling the symptoms of a relapse.
Improves sleep — Patients with multiple sclerosis may find it hard to fall asleep, and the ensuing tiredness makes the other symptoms worse. By helping people sleep better and rest more fully, omega-3 health supplements help reduce or prevent MS-related fatigue.
The immunomodulating effects of omega-3s may rein in autoimmune diseases like MS
Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids are also immunomodulators that regulate the immune system. They may help control multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune disease caused by an overactive immune system. The immune system produces a type of white blood cell called a macrophage. The cells release substances that regulate cell function. Upon detecting internal damage or pathogens, the macrophages also trigger inflammation to fight off infection. If a macrophage finds improperly-functioning or extraneous matter inside itself or in other cells, it breaks down those parts via autophagy. However, a malfunctioning macrophage may not perform the critical process. Eventually, the problems cause excess inflammation .
A Norwegian study ran tests on mice and the cells of healthy human donors. The researchers gave omega-3 fatty acid supplements to the animals and administered the fatty acids to the human cells. The results showed that taking omega-3 fatty acid supplements increases the autophagy process in macrophages. By boosting the efficiency of immune cells, the supplements reduce inflammation levels. Further, omega-3 fatty acids throttled down the response of type 1 interferon, a molecule that triggers inflammation.
The study indicates that patients with multiple sclerosis may consider omega-3 supplements an effective and natural way of improving their lives and health.
Sources include:
This Austin Man Takes Up to 150 Vitamins a Day

Photo Courtesy Melanie Applegate. Wellness The local real estate developer says he does it all in the name of health.
While working in finance in New York City, Ari Rastegar had a raucous lifestyle filled with late nights, steak dinners, and heavy drinking. Consequently, his health and marriage suffered. Motivated to clean up his life after the birth of his first child in 2012, he enlisted the help of a doctor, who tested his blood and gave him a bespoke regimen of up to 150 vitamins and supplements a day. Now 37, the biohacker (a person who uses science and technology to make their body function more efficiently) has a diet mostly free of gluten, sugar, and dairy, and regularly climbs into hyperbaric chambers and infrared light beds. Though he spends $1,500 a month on vitamins, Rastegar says they pay for themselves by boosting his productivity. Here’s a breakdown of his daily pill regimen: Morning/Daytime
MARINE FISH OIL: Marine Fish Oil is a concentrated product supplying 50% EPA/DHA content and is a very affordable option for daily omega-3 supplementation. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish can improve cardiovascular health and lower triglycerides, as well as possibly increase dopamine production and reduce the risk for depression.
MD ULTRA-MULTIVITAMIN: Contains 48 vitamins, minerals, and nutraceuticals that help slow cellular aging, support a healthy lifespan, promote energy production, provide nutrients lost during stress, and reduce fine lines and wrinkles.
VITAMIN D3: Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium. Vitamin D3 is used as a dietary supplement in people who do not get enough vitamin D in their diets to maintain adequate health.
ERGO KIDNEY HEALTH : Developed after years of research by medical doctors, Ergo4health™ Kidney contains all-natural L-ergothioneine (Ergo) and Vitamin D2 and is clinically tested and proven to help support and maintain healthy kidney function. The primary ingredient, Ergothioneine, is a master antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress.
HOMOCYSTEINE CAPSULE: Used to help growth and good health. It is used to treat or prevent low vitamin B6 and B12.
ADRENAL SUPPORT CAP: Supports healthy functioning of the adrenal glands to allow for adequate quantities of hormones, primarily cortisol
ALPHA LIPOIC ACID 100MG CAP: Used in the body to break down carbohydrates and to make energy for the other organs in the body. Alpha-lipoic acid seems to work as an antioxidant, which means that it might provide protection to the brain under conditions of damage or injury.
ANASTROZOLE 1MG TAB: Anastrozole tablets work by cutting down the amount of estrogen produced by the body.
ANTIOXIDANT FORMULA: Antioxidant supplements prevent the damage caused by free radicals to the body’s cells, thereby promoting longevity and warding off disease.
BERBERINE 500MG CAP: Preliminary studies show that berberine may have benefits against depression, cancer, infections, fatty liver and heart failure. It also has potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
BIOTAGEN CAP: BiotaGen ® is recommended to nutritionally support optimal gastrointestinal function, promote populations of healthful colonic bacteria, and enhance gastrointestinal and systemic immune function.
CERAMIDES LIPOWHEAT CAP: Plant-sourced ceramides such as Lipowheat, can help hold skin together by forming a protective layer that limits moisture loss and protects against visible damage from pollution and other environmental stressors.
COENZYME Q10 100MG CAP: CoQ10 has been shown to help improve heart health and blood sugar regulation, assist in the prevention and treatment of cancer and reduce the frequency of migraines. It could also reduce the oxidative damage that leads to muscle fatigue, skin damage and brain and lung diseases.
DHEA 25MG CAP: DHEA is believed to slow up the aging process, improve sports performance, enhance libido, promote weight loss, and bolster the immune system. In addition, DHEA supplements are frequently marketed as testosterone-boosting agents and used for such purposes as increasing muscle mass and reducing fat mass.
IODORAL 12.5MG TAB: Iodoral offers energizing and nourishing support for the thyroid.
KREALKALYN PRO 900MG CAP: Buffered creatine monohydrate that helps with gaining strength, building muscle and enhancing athletic performance.
L-METHYLFOLATE 1MG TAB: A folic acid supplement that is used to support the formation of healthy cells, especially red blood cells. They are used to treat or prevent low folate levels, which can lead to certain types of anemia.
OSTEO PLUS TAB: A dietary supplement that promotes joint comfort and improves their functioning.
PAN-OX-5 (DIGESTIVE ENZYME) TAB: A comprehensive dietary enzyme supplement that is specially formulated for complete digestive support for the entire gastrointestinal system.
PHOSPHATIDYLSERINE 100MG CAP: Phosphatidylserine supplements are believed to preserve memory, promote healthy sleep, improve mood, and enhance exercise performance.
PREGNENOLONE 100MG CAP #100: Pregnenolone is used for fatigue and increasing energy; Alzheimer’s disease and enhancing memory; trauma and injuries; as well as stress and improving immunity.
PYRIDOXAL-5-PHOSPHATE CAP #100: P5P plays an important role in various functions in the body such as metabolism at the cellular level, muscle growth and repair, mood regulation, sleep regulation, and other executive functions.
TESTOSTERONE CYPIONATE 200MG/ML INJ: Testosterone cypionate is used to treat symptoms of hypogonadism in males. In this condition, males don’t produce enough of the sex hormone testosterone.
THER-BIOTIC COMPLETE CAP: Unique combination of colonizing and transient strains providing broad coverage to support a healthy balance of microflora across the entire gastrointestinal tract. VITAMIN K2 50MCG CAP: Vitamin K activates proteins that play a role in blood clotting, calcium metabolism and heart health. One of its most important functions is to regulate calcium deposition. NUTRAFOL HAIR: Nutrafol has been shown to increase growth rate and thickness. SHROOM TECH: Energy and Endurance: Taken before workout to boost energy. TERRAFLORA Broad Spectrum Synbiotic: Formulated with a combination of spore form probiotics, and ancient food-based prebiotics, for robust support of gastrointestinal and immune health. Terraflora’s advanced formula of beneficial probiotic strains and prebiotic fibers are designed to support the gut biodiversity reflected in our ancestral diets. LITHIA WORKS Lithia Basic: A nutritional bioavailable supplement designed to support healthy aging, mood, behavior, and memory, and resist the effects of stress, by combining extremely low doses of bioavailable lithium with […]
Getting Forgetful? 7 Easy Ways to Improve Your Memory Naturally

Growing up, I had to munch on four almonds before eating anything else. “Almonds improve your memory,” my mum would say, and that was that.
And of course, my excellent exam results were the best proof of her unshakeable belief in the superpower of the oval-shaped edible seed.
Well, she wasn’t entirely wrong. Almonds are one of the world’s most nutritious and versatile nuts and are known to improve your brain function and memory.
But they cannot do it alone. So, here are 7 ways to improve your memory naturally and be at the top of your game. 1. Almonds – Surprise, surprise!
Packed with vitamins and proteins, almonds are one of the complete sources of energy. And if you find them too chewy, try soaking them overnight.
But how do they help your memory?
In an interview with NDTV , Shilpa Arora, a Macrobiotic Health Coach elaborates on the benefits of the tiny nut.
“Almonds elevate the levels of ACh acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter in the brain that helps enhance memory and help fight conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. You don’t need a lot of almonds to help improve memory; about eight to 10 almonds soaked in water overnight and consumed in the day works effectively. We soak almonds for the nutrients to be easily absorbed by the body.” 2. Sleep, to keep your memories around for as long as possible
Memory is the faculty of the brain which retains information overtime to influence future action.
The brain creates certain patterns and sends them as signals between our neurons. This process is called synapses. If the memory is not consolidated, it does not get connected to long-term memory and dies out within a matter of seconds. A good night’s sleep helps our brain consolidate memory better, which helps to remember and retain information more accurately. One of the best sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), flax seeds need to be added to your breakfast, stat!
ALA is known to boost our cerebral cortex. This thin layer of the brain is responsible for processing most information that we receive and is also in charge of our cognitive activities like thinking and producing and understanding language.
So, if you have found yourself thinking too hard for a word but failing, or if you cannot keep up in that foreign language class, start having flax seeds regularly.
Don’t have the nutritious seeds at home? Click here to get a pack now! 4. Green is the answer for good memory
Our parents were right all along—green vegetables are excellent not just for our body but also our brainpower. Now, we are not claiming that the greens will make you Sheldon Cooper, but studies say regular consumption will certainly help your brain grow stronger, and by that, we mean, better memory and better recalling skills!
Leafy vegetables that contain antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B are known to have a positive impact on memory consolidation and recall. Include spinach, broccoli, beetroots and kale in your diet as much as possible.
In fact, grow these leafy greens at home! Grow them yourself, so you never forget to eat them. Click here to get grow-kits for your garden. 5. Never miss that cup of tea or coffee
Yes, you need that brew before you start your work. And we recommend you never give up that habit. Not only does it help you jumpstart your assignments early in the morning, but it also helps your mental functions.
Research has indicated that the caffeine contents in tea and coffee are also connected to solidifying new memories. One more reason to justify your love for tea (or coffee, we don’t judge). 6. Exercise!
Regular exercise and a good fitness regime are associated with better memory recall. A fit body will also result in a healthy brain that consolidates memories better.
While research has shown that spatial memory—the information about one’s surroundings and space orientation—has the most advantages, jogging or walking regularly will go a long way in keeping you fit otherwise too. 7. Keep challenging yourself
How do you challenge your brain to stay fit? Play games! Fun, right? Get in a group or choose memory games alone; both work equally well when it comes to keeping your brain active and your memory sharp.
The more you challenge your brain, the better it will function in any circumstances. Make sure these games are related to memory, though.
Click here for a range of such ancient games that will not just keep you away from the screens (which are known to make our attention span shorter) but also help your brain stay young, active and with better memory!
You may also like: 13 Reasons Why a Little Nutmeg Will Improve Your Health, Skin and Hair!
(Edited by Gayatri Mishra) Like this story? Or have something to share? Write to us: contact@thebetterindia.com, or connect with us on Facebook and Twitter .
Adaptogens: What Are They, and Why Do I Want Them in My Drink?

Most of our medicines are derived from or inspired by plants and fungi. We get aspirin from willow bark, opioids from breadseed poppies, antibiotics from bread mold, valium from valerian roots. Western pharmacology is great at isolating, extracting and synthesizing compounds from plants, but it’s unwise to discount the health-protective and performance-enhancing benefits of whole foods.
If you’re like me, your social media feeds are filled with an increasingly aggressive scroll of ads for groups, life coaches, random bloggers and, not insignificantly, products inspired by the radical concept of not centering your social life on alcohol. (OK, it’s possible that is just me-occupational hazard. I digress.) More and more, words like “adaptogen” and “nootropic” enter the food and beverage (and supplement) marketing landscape. Although there are all kinds of debates to be had on what is and is not a reasonable claim to make on a given food-plant, constituent nutrient, tincture, extract or infusion, I’m the first to concede there are some inherently “adaptogenic” qualities to sobriety itself, so whatever you’re replacing some or all of your beer and bourbon allotment with, whether it’s lemon water, tea, or one of the rapidly proliferating apothecary-inspired mocktail brands-anything that isn’t booze is probably going to help Monday morning seem a little friendlier.
An adaptogen, simply put, is a substance with a broad spectrum of compounds proven to (or anecdotally associated with) help combat stress, by which I mean both physical and emotional stress. They often pull this off by lowering cortisol levels, which in turn has a beneficial effect on blood sugar, weight, digestion and overall energy levels. The term also covers many substances that improve cognition, decrease inflammation, boost immunity or help us to not feel fatigue. They’re complicated and in many cases we don’t fully understand what they do or how they do it; we just know there’s a statistically meaningful correlation between consuming them and feeling good (lookin’ at you, CBD). The category encompasses both plants (schizandra, astragalus, moringa, maca, rhodiola and holy basil are all easy to find in a health food store) and fungi (reishi, lion’s mane, chaga and cordyceps are the ones you’re most likely to find). They all have different effects, mechanisms, and flavors, but generally all of them help your body cope gracefully with physiological and emotional stress.
A “Nootropic,” meanwhile, is a substance that improves cognitive function, mood, or both-so there’s definitely overlap. You could say a nootropic improves brain function, while an adaptogen tones the endocrine system, but plants are complicated creatures and so are humans; affect one of these things and you almost by definition affect all of them. Some nootropics are whole plant extracts. Others include “smart drugs” and even things like Adderal, which is pretty much amphetamine salts. However, this category also includes caffeine, green tea, ginkgo biloba and ginseng.
Kin Euphorics makes a handful of non-alcoholic grownup drinks that harness a range of adaptogens and nootropics. Their “Hi Rhode” contains Rhodiola rosea, an adaptogen known for lowering blood cortisol (a catabolic steroid hormone partly responsible for “fight or flight” response and implicated in unmanageable weight gain), and licorice root (a natural sweetener in addition to its digestive system and blood pressure benefits). It also contains neurotransmitters and precursors like GABA and 5-HTP. The flavor is warm, bittersweet and slightly spicy. It’s great with sparkling water, or mixed with any number of bitters, syrups, juices, sodas or whatever else you’re into.
Proposition Cocktail Co recently sent me a taste of their RTD mocktails; a smoky Margarita flavor and a Turmeric Ginger Mule. The vibe with Proposition is definitely more booze-substitute than Whole Other Thing-the mocktails are packaged in flask-oid bottles and the names and flavors evoke dealcoholized cocktails rather than “body-mind enhancing potion,” but adaptogens are still a focal point. Turmeric, and especially the compound curcumin, is a potent anti-inflammatory. Ginger and mint benefit the stomach and gut, and there’s a hemp extract in both flavors. Both flavors are pleasingly savory, with grownup-tasting bitter, salty, smoky and herbaceous flavors-the lime in the margarita version is bracingly pithy too. As it happens, hemp extracts can be hard on my stomach, especially if they are in MCT oil-and these mocktails did provoke a little transient discomfort. If you don’t have this reaction to MCT, you’re probably never going to feel it. If you’re like me, take it slowly to gauge your tolerance.
As more people trade binge-drinking for “biohacking” there will be no shortage of new alternative beverages, ranging from the ultra-simple to concoctions whose ingredient lists read like something out of Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince . The products above are two very solid choices. It’s impossible to guarantee they will make you smarter, faster, calmer, or thinner, but they’re definitely poised to make you less hung over, and they’re sophisticated and interesting enough to short-circuit your urge to feel deprived when others are tying one on.
