Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Relaxation-Induced Anxiety Is a Thing

Roughly 14 percent of Americans meditate — a number that’s nearly triple the mere 4 percent in 2012, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. And its popularity is only going up: The meditation market value is set to double from $1.2 billion in 2017 to $2 billion by 2022.
None of this is surprising when you consider mindfulness can improve pretty much every aspect of your life. For starters, people who practice mindfulness are better able to regulate their emotions. Because of this, studies show that mindfulness can help reduce anxiety, prevent depressive episodes, control stress, and increase self-compassion and body satisfaction. Mindfulness also helps boost your brain, improving focus and information retention and reducing the power of distractions.
Mindfulness also encourages healthy behaviors , like getting regular health check-ups, exercising, eating healthy, and cutting back on nicotine and alcohol. It can also help lower blood pressure (probably thanks to stress control) and improve cardiovascular health (mostly from helping people quit smoking).
But, as everyone who has ever tried to sit on the floor, quiet their anxiety, and clear their mind knows, meditation is really effing hard to get into.
Chances are, you’re overthinking it — for starters, you’re not supposed to clear your mind, but instead just allowing thoughts to come through judgement-free. But there’s another potential roadblock: Some people actually feel more anxious when they’re supposed to be relaxing. Here’s how to know if you have relaxation-induced anxiety (yep, it’s a real thing) — plus how to be mindful even if you’re anxious. WTF Is Relaxation-Induced Anxiety?
It’s worth noting that a lot of people for whom meditation will eventually help, initially feel uncomfortable and antsy in their early sessions. Often, that’s because people are under the impression their swirling thoughts should stop when they meditate. When they don’t, the spiral of questions and thinking continues, which can exacerbate the anxiety over “not doing it right,” explains Jasmin Terrany , a Miami- and New York-based psychotherapist and mindfulness and meditation coach.
“Whatever thoughts and emotions arise within, that’s what is inside you at that time. The challenge people experience is that they are actually dealing with those things directly during mindful practices instead of distracting or self-medicating not to feel it, which can make it all feel more overwhelming and challenging,” says Terrany.
But a recent study in the Journal of Affective Disorders found people who are more sensitive to shifts in negative emotions — that is, those who have a hard time calming after a stressful meeting, or coming down from being scared — feel more anxious when they’re lead through relaxation exercises like mindfulness and meditation.
It’s called relaxation-induced anxiety and anywhere from 17 to 53 percent of adults experience it, according to an older study out of the University of Cincinnati.
It’s similar to what happens when you’re wired or experiencing insomnia and try to force yourself to fall asleep — the harder you try and relax, the more frazzled you get, says mindfulness expert Beverly Conyers, author of Find Your Light: Practicing Mindfulness to Recover from Anything .
If you’ve read every beginner’s guide to meditation and still can’t seem to get the hang of it, you may simply be neurologically predisposed to prefer more adrenaline-fueled relaxation activities (more on that later) than tranquil ones, says Manhattan-based psychologist and elite performance coach Ben Michaelis, Ph.D.
It likely has something to do with dopamine, the neurotransmitter involved in reward, motivation, memory, and attention, he explains. “Although we are all driven by it, some people, often high performers, may have more of this neurotransmitter or may be more sensitive to its effects,” Michaelis says. “If you are one of these people, then trying to ‘chill’ will only make you more anxious because you are fighting your natural brain chemistry.” How to be Mindful When You’re Anxious AF
“Ironically, many of the people who are most in need of some calming relief are the ones whose anxiety spikes when they try to relax,” Conyers says. For our purposes, it doesn’t much matter whether you have official relaxation-induced anxiety or just standard trouble sitting with the uncomfortable feelings when you sit down to meditate — either way, slowly wading into mindfulness and meditation, rather than jumping in deep, can help you build a practice over time. Here’s how:
Start being more mindful. Simple acts of mindfulness are the most approachable way to begin to sync your intentions with your mind. It then has a snowball effect — if you intentionally practice mindfulness on the reg, you’ll naturally become more mindful in all areas of your life which will help you control your anxiety more, all our experts agree. Learning to master your breath, for example, can help calm your nervous system when you’re supposed to be tranquilly enjoying savasana but you’re actually spiraling out about your post-yoga to do list.
Do a full-body scan . The goal of mindfulness is to control and focus your attention to the present moment. Practice micro-moments to help build to bigger ones: While sitting or standing, do a body scan from your head to your feet, Conyers suggests. Release tension by unclenching your jaw, lowering your shoulders, and relaxing your hands. Gently straighten your spine. Soften your gaze as you look forward. Breathe evenly and feel the stress leave your body.
Practice smiling . “Not only does smiling make you feel good, but it actually changes your mental and physical biology, increasing happiness , relieving stress , boosting your immune system , and lowering your blood pressure,” says Kathleen Hall, Atlanta-based stress expert and founder of The Mindful Living Network . Plus, smiling is contagious so you’re also changing the mood of those around you, which inherently will benefit you. Try smiling at every person you say “hi” to — the coffee barista, the office security guard, your boss. It’ll help to reduce anxiety and allow you to move into mindfulness and meditation more readily.
Sweat it out. If you have trouble with tranquility, try a repetitive, […]
Brain-Boosting Chocolate Bites
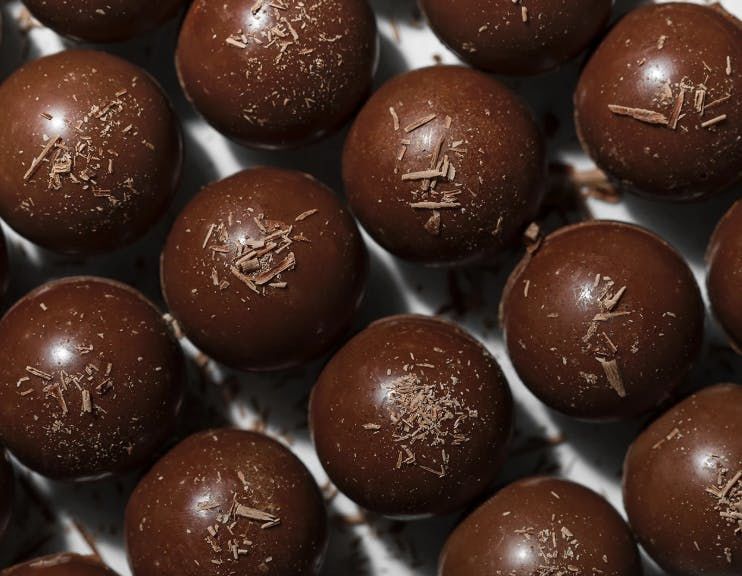

Nyrvana is a “Smart Chocolate” Enriched with Nootropics
Nyrvana is introducing the world’s first “smart chocolate” as a functional treat that’s packed with brain-boosting benefits. The product is made with dark chocolate, which is nutritious and antioxidant-rich on its own, but Nyrvana doesn’t stop there and enhances its recipe with nootropics like Alpha-GPC and L-Theanine to boost brain function.
The all-natural, soy- and lactose-free dark chocolate also sets itself apart as a better-for-you treat that’s free of additives and enhanced with THrē, a blend of all-natural sweeteners stevia, erythritol and allulose. The Chocolate or Peanut Butter Ganache Truffles are guilt-free and energy-boosting, offering a satisfying way to beat a sweet tooth. Unlike many sugar-free confections, Nyrvana’s smart chocolate is rich, decadent and won’t leave people feeling as if they’re missing out on something.
Image Credit: Nyrvana
Researchers examine the anti-cancer properties of carnosine
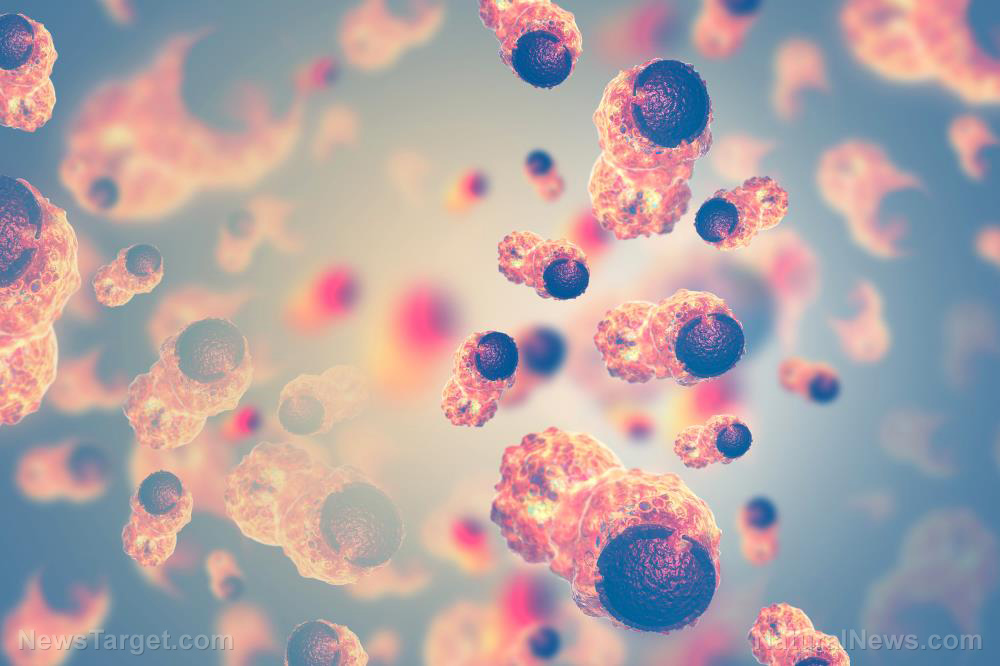
( Natural News ) Cancer development is often linked to a high consumption of red meat and processed meat. While processed foods are scientifically proven to be bad for your health, eating moderate amounts of animal meat, fish and poultry may be helpful for cancer patients. In a new study published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine , researchers from different universities in Taiwan showed that carnosine, a dipeptide found primarily in meat, is capable of inhibiting the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells . Both of these processes are vital for cancer metastasis, the development of secondary malignant growths. The researchers believe that this fusion of two amino acids not only reduces inflammation, it also exerts a regulatory effect on epithelial-mesencymal transition (EMT) — an event involved in both developmental and pathological processes such as cancer progression. Carnosine can suppress cancer cell migration and intravasation
The first step in tumor metastasis is the invasion or migration of cancer cells into surrounding tissue. This movement is triggered by chemical signals from their environment and facilitated by the activity of the cell membrane and its attachment to the extracellular matrix — a three-dimensional network of large molecules that gives structural support to cells. Another way by which cancer spreads is via the blood vessels. Called intravasation, this process involves the entry of cancer cells into the blood or lymph vessels . This allows cancer cells to reach tissue located far away from their site of origin. Intravasation is considered a relatively late event in tumor development .
The power of the elements : Discover Colloidal Silver Mouthwash with quality, natural ingredients like Sangre de Drago sap, black walnut hulls, menthol crystals and more. Zero artificial sweeteners, colors or alcohol. Learn more at the Health Ranger Store and help support this news site.
According to previous studies, carnosine has the ability to regulate the migration and invasion of human colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. However, the mechanism by which it achieves this is still unknown. To address this, the researchers treated cultured HCT-116 cells (human colon cancer cell line) with carnosine, then examined their migratory and intravasive abilities. The researchers also looked at the expression of EMT-associated molecules and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) after carnosine treatment. MMPs are enzymes that promote cancer progression by increasing cancer cell growth, migration, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis — the development of new blood vessels.
The researchers reported that carnosine treatment inhibited both migration and invasion of treated cells. It also significantly decreased the expression of Twist-1, a protein that promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis . Meanwhile, carnosine increased the expression of E-cadherin, a cell adhesion molecule and known tumor suppressor. Loss of E-cadherin-mediated adhesion turns benign cells into invasive, metastatic cancer cells. The researchers also detected increases in the mRNA and protein levels of TIMP-1 after carnosine treatment. TIMP-1 is a tissue inhibitor of MMPs.
Besides suppressing pro-metastatic components, treatment with carnosine also reduced the levels of phosphorylated I k B and NF- k B DNA-binding activity in HCT-116 cells. I k B is a protein involved in the activation of NF- k B, a transcription factor that plays an important role in inflammation , immunity, cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that carnosine inhibits the migration and intravasation of CRC cells by suppressing NF- k B activity and modulating MMP and EMT-related gene expression. Carnosine: health benefits and sources
The body naturally produces the dipeptide carnosine. It is formed by the linking of two amino acids, namely, alanine and histidine . An endogenous molecule with antioxidant properties, carnosine is mainly found in skeletal muscles and in the brain. Humans also obtain it from dietary sources like beef, fish and chicken meat or by taking carnosine supplements. (Related: Carnosine provides broad-range cellular protection to fight vascular injury and extend lifespan .)
According to research, carnosine can boost the immune system , support eye health and improve a person’s mood and brain function. Carnosine supplements are said to be a great remedy for a variety of conditions, such as autism, cataracts , diabetic complications, high blood pressure and kidney problems. Clinical evidence also suggests that carnosine can prevent cognitive decline, slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, protect against diabetes and help fight cancer.
Read more stories about carnitine and other anti-cancer supplements at SupplementsReport.com .
Sources include:
Cell.com 1
Cell.com 2
10 Dos and Don’ts for Surviving Finals

In Warren Towers, Prasida Unni (CAS’22) (left) and Indra Alagar (CAS’22) prepare for an upcoming chemistry test. Photo by Cydney Scott Wednesday is the final day of classes for the semester, followed by study days Thursday and Friday and final exams next week. In other words, we’ve hit crunch time, marked by too much caffeine, too little sleep, and a whole lot of stress. To help you navigate the end of the semester, we reached out to a team of experts, including folks at the Educational Resource Center, the Center for Career Development, and Wellness & Prevention, and asked them for some tips. 1. Pace yourself during this period and take breaks
Make time to eat, sleep, and exercise. When you study, do it in 30-to-45-minute increments, and then take a short break. Doing so will improve your cognition. 2. Cramming doesn’t work—the best way to study is what’s called distributed practice
Experts say that most of what you learn during cramming doesn’t stay in your memory long-term. Better to follow a distributed practice model, where you space your studying out over several days and weeks. This allows your brain to learn the information more deeply and retain it better. Of course, if you’ve got an exam tomorrow and you haven’t been studying all along, you’ve got no choice but to cram. 3. Healthfully hydrate
Consider water or low-caffeine or no-caffeine beverages to stay hydrated during finals. If you do need a caffeine pick-me-up, BU Dining Services has special late night hours , with free coffee, soda, and hot chocolate. 4. Snack smart
Chances are, you’ll be snacking a lot over the next couple of weeks. Take a look at the Sargent Choice Build You Own Snack chart for healthy snacking. The list includes whole-grain Goldfish crackers, fruit, hummus, and nuts. 5. Change up your study environment
Check back on BU Today tomorrow for our updated list of the best study spots around campus. Mixing up the places you study improves retention, according to a New York Times story on study habits . 6. Procrastination is a slippery slope
Procrastination happens because a task is giving you anxiety, but it makes the underlying problem worse. If you find yourself procrastinating (by reading this BU Today story about Baby Yoda or weighing in on the Peloton commercial debacle ), take a few deep breaths, acknowledge the underlying feeling of anxiety, and steer yourself back to the assignment at hand. 7. Reme m ber these study strategies
Predict questions that might be on the exam.
After you create your questions, quiz yourself.
If possible, review past quizzes/exams to see how your professor framed questions. It’s also helpful to ask yourself: did I have trouble remembering material I studied? Did I misunderstand a question? Did I forget to review certain material? 8. It’s go time
When you first get the exam, read it through completely, including the directions. Then budget your time according to the weight of each question. For example, if you have an essay question that’s worth 30 points, spend more time on it than on a multiple-choice question that’s worth only 2 points. 9. Breathe
If you find yourself feeling anxious, focus on your breathing: breathe in through your nose, hold it, breathe out through your mouth. Start incorporating breathing exercises into your routine now so that it feels more natural on test day. 10. Be kind to yourself
Finals period is a long, exhausting week. Try to incorporate “self-talk” that’s kind and supportive, like: “You are studying so hard! You’ve got this.”
Why Dietary Supplements are Essential for Healthy Routine
The dietary supplement is defined as a drug taken orally as a capsule, powder, gelcap, liquid or in tablet form. It includes desired ingredients such as fiber, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids to fuels the brain and enhances the mental concentration. Reason Why Everyone Should Take Dietary Supplement For Brain Health
It doesn’t matter how strenuous exercise you perform in your gym until you do not eat healthily. After doing too much workout you still have craved for eating fast food, then you are surely in the risk of dementia. Even not fruits, vegetables, and dairy products that we eat regularly are not vegan completely. These are injected with chemicals to look better and helps in retaining the authentic taste. In clear words, we can say that the food which we eat is poisonous and may become the major reason for memory loss. One of the effective capsules is a neurogain memory booster that has a blend of herbal extracts, vitamins, and minerals that helps in elevating the focus and memory. The use of potent nootropics popping up several ideas energizes the mental ability to keep your mind in working condition for the whole day. People with mild cognitive impairment may add a supplement in the regular diet to bring health benefits. You may also consult with a doctor before taking the prescription that will help you a lot to know whether the capsule should be taken before or after the meal. Additional Benefits of Nutritional Supplements
Bulk of ingredients
The most commonly used ingredients using in food supplements are vitamin D & E, amino acids, calcium & iron, fish oil, garlic, and echinacea. These components fill the nutritional gap and provide a well-balanced diet to track you in progress.
Improves energy levels
It improves the cognitive functions and leaves a positive impact to make you more energized than ever. Whether you are an athlete or trying to enhance your skills, it will aid you in generating more ideas and improve the quality of life.
Enhances the mental clarity
The daily intake of junk food leads to poor memory, drives more stress and keep the body inactive. Thus, it is essential for increasing mental stamina to feel an instant spark while performing outdoors.
Boosts logical processing
The natural concoction in brain booster enhances alertness to solving the high level of math problems. It speeds up brain activity and makes the mind more active to stay in the right state. For instance — as per the report from the centers of disease control & prevention, more than half of Americans take a multivitamin along with the dietary supplements to stay healthy forever.
100% GMO-free
The neuro-based pills are completely tested under the laboratory to ensure that the pills are extremely safe and don’t pose any side effects. It doesn’t include flavored additives and other toxic elements that are prone to danger. Do you want to improve your IQ & Creativity? Discover the Myochem that supplies neuro gain products to maximize the brainpower and lift your mood to keep you fit and healthy.
Not just for the eyes: Lutein also boosts memory, says study

( Natural News ) Lutein is known for its ability to support eye health. But a recent study from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign revealed that the carotenoid can also help in boosting memory, especially for people suffering from obesity.
For the study, the team collected dietary data from the participants — all of whom were either obese or overweight. In addition, they were also screened for their medical history and subjected to adiposity tests during the initial appointment. On their second appointment, the researchers asked the participants to complete a spatial reconstruction test and collected fasting blood levels. The latter, in particular, helped determine the participants’ regular carotenoid intake.
After analysis, the researchers found that lutein seemed to enhance memory function in the participants. They noted a direct relationship between higher lutein blood levels and improved accuracy in object binding – the ability of a person to recall various features of an object as a logical whole. They also found an inverse link between lutein and misplacement error, which was not seen in other carotenoids. (Related: Study shows lutein can boost heart health .)
“Our results revealed that serum lutein was significantly related to two metrics of relational memory performance even after adjusting for significant covariates,” the research team concluded in their report. “While this study was correlational, it lays the groundwork for subsequent research in this area.” Get more lutein for better brain health
Lutein is a carotenoid, that is, a pigment that gives plants their bright colors. It’s found in many vegetables – spinach smoothies are great sources.
Sponsored: NEW Biostructured Silver First Aid Gel created by the Health Ranger combines three types of silver (ionic silver, colloidal silver, biostructured silver) with seven potent botanicals (rosemary, oregano, cinnamon and more) to create a breakthrough first aid silver gel . Over 50 ppm silver, verified via ICP-MS lab analysis. Made from 100% Texas rain water and 70% solar power. Zero chemical preservatives, fragrances or emulsifiers. See full details here .
While many studies have linked lutein to better eyesight, an increasing pool of literature has showed its ability to contribute to brain health. Scientists have shown that lutein is present in brain tissue, comprising around 60 percent of total carotenoids. However, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey reveals that lutein makes up only 12 percent of dietary carotenoids. This shows an apparent preference for lutein in the brain.
An earlier study on rhesus macaques also showed how adding lutein to infant formula positively impacted brain development. The team reported selective increases in the brain’s carotenoid levels, with the highest concentrations seen in the occipital cortex, which processed visual information. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of lutein improves memory
For the current study, the team looked at the participants’ carotenoid intake by measuring it in blood samples. Additionally, the participants took tests on relational memory – their ability to store and remember associations and relationships between two different objects.
The research team found that serum lutein, in particular, positively affected memory function. They theorized that the carotenoid achieved its beneficial effects through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
“Participants with overweight or obesity are more susceptible to oxidative and inflammatory stress due to the higher levels of chronic inflammation associated with excess adipose tissue,” the researchers reported. “Inflammation and oxidative stress can be mitigated by fruit and vegetable intake, foods that are often rich in carotenoids.”
Inflammation disrupts the proper function of the hippocampus. It prevents the process of long-term potentiation, the molecular means by which the brain forms memories. Lutein helps prevent age-related macular degeneration in the retina. By scavenging harmful molecules, the antioxidant decreases the oxidative stress that harms the eyes.
The researchers concluded that lutein performed the same antioxidant role in the hippocampus. They recommended that future studies check carotenoid levels in the macula and blood.
They published their findings in the scientific journal Nutrients.
Sources include:
MDPI.com
Lion’s Mane: How the Mushroom Can Boost Brain Health
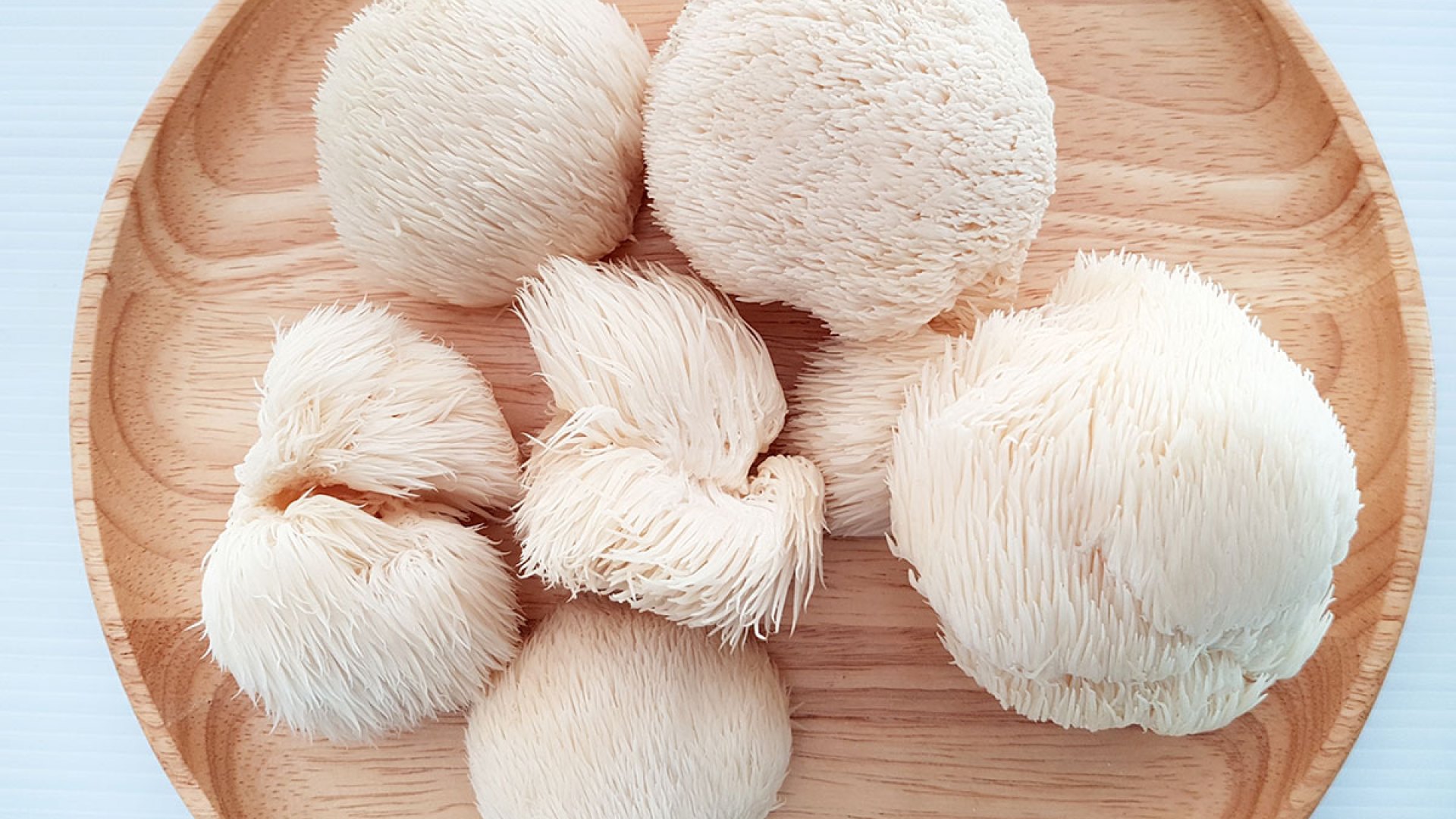

If you’re lucky enough to come across the lion’s mane mushroom while wandering through the woods, it may be time to gather some of this powerhouse fungi, the world’s first “smart” mushroom, and even consider colonizing your very own log for future generations. Fortunately for the rest of us, lion’s mane powders and capsules can be found at many health stores and even beauty retailers. But what makes this trendy mushroom special? What is lion’s mane?
It’s not your average mushroom. No other mushroom species looks like it, but it’s a lot more than just a handsome fungus. It’s obvious where it gets its name from because it has white, cascading tendrils or spines and looks like a lion’s big head of hair (or like a cluster of icicles, or like a landbound sea anemone). Other names for the fungi species include ‘old man’s beard,’ ‘pom pom,’ and ‘hedgehog.’
Lion’s Mane is native to North America, Europe, China, and Japan. In the United States, it is most abundant in the Southern regions. It’s fairly common and easy to spot—most frequently found on logs or stumps and growing on dead or dying hardwood trees. But it can also be cultivated indoors on sawdust (a popular spawning method among mycologists and mycophiles). What are the health benefits of lion’s mane?
Holistic doctors and nutritionists affirm there are potential healing capabilities of lion’s mane mushroom. It’s a great nutritional source of antioxidants and high in protein. Functional medicine expert Dr. Will Cole, FMCP, DC , regards lion’s mane as “king of neuroprotective mushrooms” and believes anyone struggling with brain fog or memory impairment can benefit from using it. But the benefits to brain health don’t stop there. It may have nerve-protective and regenerative properties
Renowned mycologist, Paul Stamets, refers to it as the “smart mushroom” because of its nerve-regenerative properties. It contains two important medicinal compounds, hericenones and erinacines, that can stimulate the growth of brain cells and help protect brain tissue.
In a small clinical study from 2009, Japanese patients with mild cognitive impairment increased their cognitive function significantly after taking 750 milligrams of lion’s mane powder a day for 16 weeks. The results of this study suggest that lion’s mane is effective in improving mild cognitive impairment in humans. Considering the fact that as many as 5.8 million people are expected to be suffering from Alzheimer’s in 2020 , lion’s mane may be a valuable health supplement in the future.
While there are few research studies focused on human subjects, lion’s mane proves to be a valuable antidote in numerous studies conducted on mice. In a 2011 study lion’s mane has been shown to reduce symptoms of memory loss in mice, and in a 2016 study , it was shown to prevent neuronal damage caused by Alzheimer’s. It may help relieve anxiety and depression
In addition to its brain-boosting capabilities, lion’s mane has also been found to have anti-inflammatory effects that can reduce anxiety and depression . And in a promising clinical study on humans , it has been shown to decrease anxiety and depression in menopausal women. Lion’s mane may help boost mood and boost memory, for those with cognitive impairments and healthy neural functioning alike. It may support GI health
Lion’s mane has also been studied for its benefits to human gastrointestinal health. It’s been shown to inhibit the growth of H. Pylori bacteria , a gastrointestinal condition that could lead to the development of stomach ulcers.
Other research suggests that lion’s mane can potentially reduce the risk of heart disease, may improve fat metabolism, could lower triglyceride levels, and help manage diabetes symptoms. Its anti-inflammatory effects may help to reduce heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. While more studies on humans are needed, Stamets believes the data from studies thus far suggest a number of positive outcomes for more widespread use in the future. Cooking with lion’s mane
This mushroom is a wonderful culinary ingredient, and some compare its flavor to that of lobster or shrimp. For vegans and culinary adventurists, it makes a great fish substitute or a vegan lobster roll.
Stamets recommends lion’s mane caramelized in olive oil, and finished with butter to taste, first frying this mushroom covered over high heat until the fingerlike teeth are singed brown and become crispy. You can add tamari or chopped onions, but wait until the end to add the butter, allowing the mushroom’s seafood-like flavor to blossom.
Ari Rockland-Miller , writer, lecturer, and co-founder of The Mushroom Forager, recommends wringing the extremely absorbent mushrooms after washing as you would a sponge because sautéing wet lion’s mane spoils its impressive texture. Lion’s mane health supplements
Los Angeles-based clinical herbalist and founder of Zizia Botanicals , Abbe Findley, loves using the nootropic mushroom for its numerous benefits. She recommends first trying it as a tea, powder, capsule or tincture and playing with what works for you.
Years in the making, Zizia’s Focus Tincture combines lion’s mane with another adaoptogen, gotu kola , and rosemary, and was created for cognitive function and memory support. Findley swears by daily use to not only promote nerve cell regeneration and immune health, but also to get in the zone, especially during a long day at the office or just before taking on a big project.
In addition to Zizia products, Findley regards Host Defense Mushrooms Lion’s Mane capsules as another great lion’s mane supplement. In her practice, she also uses Gaia Herbs, which makes a couple of formulas where lion’s mane is a star ingredient and can be found at many health food stores. Bottom line: Should you try lion’s mane?
Its numerous benefits prove it’s definitely worth a test ride. One final note: I purchased Zizia’s Focus Tincture and used one drop two times a day over the course of one week. In just a few days, I cut my coffee consumption down by more than half (and trust me, I drink a lot of coffee) and my ability to focus for extended periods of time has sharpened. […]
Suggestions for some healthy holiday indulgences: Dr. Nina Radcliff

This time of the year has a reputation for dishing out some “bah-humbug” moments with added stress, more demands than time can manage, deadline pressures, budget considerations, relationship dynamics, long lines and slow check-outs at stores, crowded places and even more temptations of tables full of sugary, unhealthy treats.
But actually, the holidays present some great opportunities to nourish your body, mind and spirit — even in the face of added demands. And while the dose of what makes you happy and content may look different from others — here are some ways you can indulge during the season and reap huge health benefits.
• Catch up with old friends or enjoy a special holiday event. Humans are social creatures and research shows that people with good social support generally live longer and healthier than those who are isolated. Social engagement improves feelings of well-being while combating those of depression. And it is key to improving your memory, cognitive skills and overall brain health — decreasing the risk of developing dementia. And, too, it strengthens your immune system (which during flu season is critical). LOADING…
• Combine your holiday shopping with physical activity at the store or mall. Walking is linked to a myriad of health benefits including a decreased risk of heart disease, stroke, certain cancers and diabetes. And it helps you to maintain an optimal weight. The weather is climate-controlled and you can walk comfortably, without suffering from the cold, rain, sleet, hail or snow. And, there are some beautiful sights, sounds and holiday smells, as well as security and bathrooms — all can be beneficial while getting your shopping done.
• Listen to seasonal music, or any type of music that you love and inspires you . Music treats your senses, your emotions and connection with your body in a very healthy manner. Listening to tunes you like have been shown to help lower stress levels (which in itself has a ton of health benefits), pain, and anxiety and improve mood, memory, learning, concentration and physical performance.
• Be active in your self-care and mindful that you don’t deprive yourself time to refuel. Experts agree that self-care needs to be something you actively plan, rather than something that just happens. It is an active choice and you must treat it as such for your mental, physical and emotional well-being. Add certain activities to your calendar, announce your plans to others to increase your commitment, and actively look for opportunities to practice self-care. You must plan to indulge in things that truly feed you in a healthy way. Instead of lamenting all the holiday foods you shouldn’t eat, focusing on the delicacies you can enjoy that are truly nutritive.
• Avoid “Holiday Perfectionism.” It’s natural to want the best for your loved ones. However, imposing impossible standards when it comes to decorating, attending or throwing too many holiday parties, cooking of meals, gift giving (or receiving), or traveling — that can seldomly be achieved by normal human beings — often results in greater stress and disappointment. This is a time of sharing and celebrating, and the goals should be to create memories and have fun in the process. Create a “to-do” list and calendar. Help decrease circuit overload by setting realistic goals, maintaining balance and creating boundaries. Be discriminating and rank to-do’s as “need to do” or “nice to do.” You can eliminate some “nice to do’s output.” Remember, “a must” is to set some time to enjoy relaxing to “take in” this holiday.
• Don’t cheat yourself — enjoy an occasional treat. They are called treats for a reason. Save “that favorite treat” for a “once-in-a-while” reward. Try to remain organic and fresh, but if it is Auntie’s cake you have longed for — have one slice. As long as you eat a nutritious diet most of the time, that’s what matters. Or, maybe for you it’s going out by yourself to shop, alone. Or, to buy that little something special you know, no one else knows you want. Maybe it’s a slower morning or having coffee in bed instead of racing off to accomplish all your “to do’s.” Or, maybe even someone else makes the coffee and serves it. Figure out what that treat is for you and those you love — and treat yourself (and them) every once in a while!
Dr. Nina Radcliff, of Galloway Township, is a physician anesthesiologist, television medical contributor and textbook author. Email questions for Dr. Nina to editor@pressofac.com with “Dr. Nina” in the subject line. This article is for general information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions and cannot substitute for the advice from your medical professional. Dr. Nina Radcliff
Cancer prevention: 6 Ways nature helps you fight cancer

( Natural News ) Cancer has been on the rise in recent years, with statistics from the American Cancer Society (ACS) estimating a grand total of more than 1.7 million new cancer cases in the US. Researchers from the ACS found that at least 42 percent of these newly diagnosed cancer cases – about 740,000 – are avoidable. This includes the 19 percent of cancers caused by smoking and the 18 percent caused by a combination of excess body weight, high alcohol intake, poor nutrition and lack of physical activity. Certain lifestyle changes help reduce the risk of cancer, but nature can also bring some surprising cancer-fighting benefits that will help you stay healthy and cancer-free . Natural ways to prevent cancer
One way to reduce your risk of cancer is through your diet. In fact, maintaining an overall healthy diet is a good line of defense against many health problems, including obesity and cardiovascular disease. Here are some reasons why a healthy diet is a good way to curb cancer:
> Decreases inflammation . Recent studies have shown that there is a link between inflammation and cancer progression. According to a study in the journal Nature, many of these cancers can start from a point of infection , chronic irritation and inflammation. Cox -2, for instance, is an enzyme responsible for both increasing inflammation and promoting cancer. This calls for increased awareness of anti-inflammatory foods and supplements to reduce the harmful effects of such compounds. For example, curcumin, the active ingredient of the spice turmeric, is widely known for its potent anti-inflammatory effects used in traditional medicine for hundreds of years. You can also include fatty fish like salmon and tuna in your diet, which are chock-full of healthy omega-3 fatty acids that also possess anti-inflammatory properties .
Prevents DNA damage . Many cancers begin with some sort of DNA damage that triggers the cells to become cancerous. One of the main suspects of DNA damage is oxidative stress caused by the accumulation of harmful molecules known as free radicals. Oxidative stress not only leaves you more vulnerable to cancer, but also increases the risk of heart disease and diabetes. You can prevent this by eating foods that are rich in antioxidants , compounds that can combat oxidative stress. These foods include blueberries, pecans and kale.
Triggers apoptosis. When a healthy cell reaches the end of its existence, it undergoes a process called apoptosis or cell death. Cancer cells, however, work differently. They ignore the signals that trigger this process and keep replicating. Nutrients like curcumin and those found in cruciferous vegetables – namely DIM I3C – can destroy cancer cells and promote their self-destruction.
Prevents metastasis. Cancers, like breast cancer, are often characterized by metastasis or the spread to nearby organs like the lungs, liver and even the brain. Certain nutrients like sulforaphane – found in cruciferous vegetables — can help inhibit the tumor’s ability to spread.
Stops blood vessels from feeding tumors. Once a tumor develops, it needs a steady supply of blood to keep growing. To do so, the body develops new blood vessels. This process is called angiogenesis. There are anti-angiogenic foods that can help inhibit this process. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which is found in abundance in green tea, is especially effective against angiogenesis.
Blocks abnormal estrogen production. Inhibitors can block the production of estrogen in the body and can lead to some serious side effects. Fortunately, there are plenty of natural ways to regulate your hormones . For example, lignans from flax seeds can bind excess aggressive estrogens present in the body and expel them. The hormone melatonin – found in cherries – can put breast cancer cells to “sleep.”
Sponsored: NEW Biostructured Silver First Aid Gel created by the Health Ranger combines three types of silver (ionic silver, colloidal silver, biostructured silver) with seven potent botanicals (rosemary, oregano, cinnamon and more) to create a breakthrough first aid silver gel . Over 50 ppm silver, verified via ICP-MS lab analysis. Made from 100% Texas rain water and 70% solar power. Zero chemical preservatives, fragrances or emulsifiers. See full details here .
Stay cancer-free by adopting a healthy, balanced diet full of organic and fresh foods to help you live a much longer and healthier life.
Sources include:
NaturalHealth365.com
Factors that Increase/Decrease Melatonin Levels + Synergies
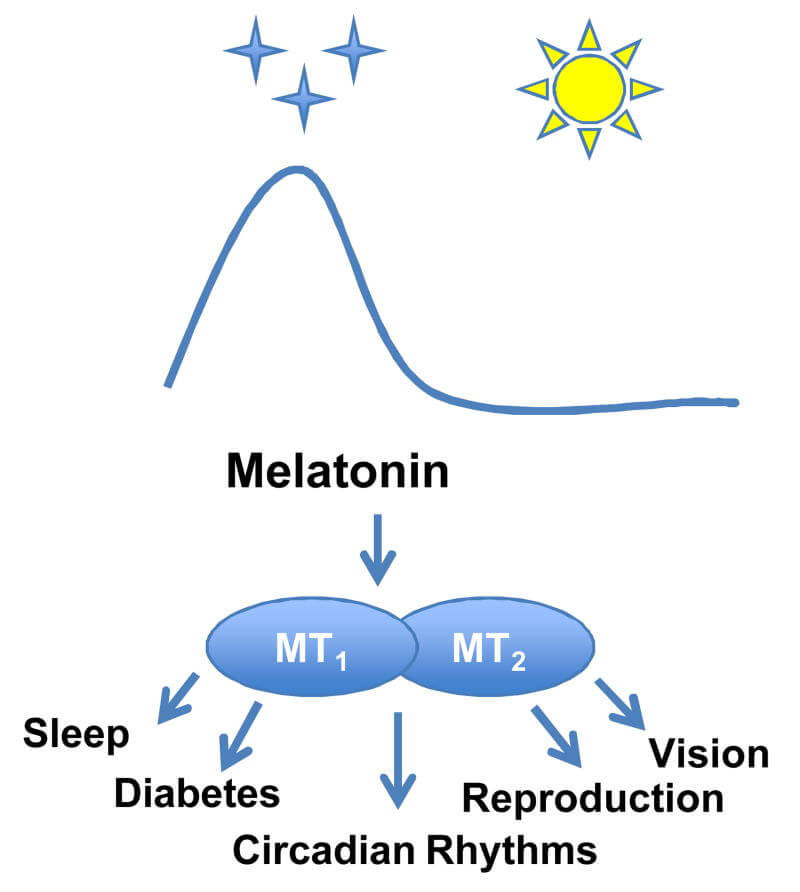
Melatonin is known for its role in sleep control, but it has a range of other roles and potential benefits. Optimal levels will ensure proper sleep quality, brain and gut health, reduced inflammation, and more. Read on to learn the factors that increase or decrease melatonin levels and discover potential synergies. Factors That Increase Melatonin Levels
Melatonin levels are a marker of sleep quality and overall health. Low or high levels don’t necessarily indicate a problem if there are no symptoms or if your doctor tells you not to worry about it. Improving your melatonin levels won’t necessarily cause improvement in sleep quality.
The following is a list of factors that may balance low melatonin levels. Though studies suggest various dietary and lifestyle factors may increase melatonin, additional large-scale studies are needed. Remember to talk to your doctor before making any major changes to your day-to-day routine. 1) Melatonin Supplements
In a review of 35 studies, researchers found that melatonin supplementation slightly improves sleep quality [ 1 ].
Melatonin shows promise in improving insomnia and reducing jet lag. It also does not have any serious side effects [ 1 ].
Although the optimal dosage is not yet determined, researchers recommend a lower dosage range. Even at low dosages, there is already a significant increase in melatonin levels after administration [ 2 ].
The recommended dosage range for elderly adults is 0.3 – 2 mg, around 1 hour before bedtime [ 2 ]. 2) Vitamins and Minerals
Folate and vitamin B6 boost the formation of serotonin , which is the precursor of melatonin [ 3 ].
In rats, vitamin B6 injections enhance melatonin production. After two months of B6 injections, the blood level of melatonin increased by 35.95% [ 4 ].
Additionally, zinc and magnesium increase the formation of melatonin from serotonin. They bind and activate the AANAT enzyme. This increases the affinity of serotonin for binding to AANAT [ 3 ].
Zinc supplementation increases melatonin levels in rats [ 5 ]. 3) Food and Drinks
4) Traditional Chinese Herbs
Factors That Increase/Activate Melatonin Receptor Activity
Agonists (activators) are agents, usually drugs, which bind and increase the activity of a receptor. The following are melatonin activators. Ramelteon is a selective MT1 and MT2 activator. Its binding affinity to melatonin receptors is higher than melatonin itself. It is used to treat insomnia [ 14 , 15 ].
Factors that Decrease Melatonin Levels
1) Drugs
Beta blockers: Beta blockers are drugs that help lower blood pressure. Beta blockers decrease melatonin release. They do this by inhibiting specific receptors [ 17 ].
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) : NSAIDs, including aspirin and several other over the counter painkiller drugs, suppress nighttime melatonin levels [ 18 ].
2) Blue Light Exposure At Night
Blue light exposure at night can reduce melatonin levels and narrow the time window of melatonin secretion [ 19 ]. 3) Other Factors
Aging : The pineal gland, which produces melatonin, contains cells called pinealocytes. The number of pinealocytes decreases with age. This then decreases melatonin production [ 3 ].
Fasting : Fasting reduces the nighttime secretion of melatonin. Short-term fasting from 2 to 7 days reduces blood melatonin levels by 20% [ 3 ].
Nutrient deficiencies : Folate, magnesium, and zinc deficiencies are linked with lower melatonin levels in rats [ 3 ].
Factors That Decrease/Block Melatonin Receptor Activity
During aging and Alzheimer’s disease, MT1 receptor expression in the SCN and cortex decreases. MT2 receptor expression is also reduced during Alzheimer’s disease [ 16 ].
Luzindole is a competitive MT2 melatonin receptor antagonist. This means it blocks receptor function [ 16 ]. Melatonin Potential Synergies Vitamin C , Vitamin D 3 , and Vitamin E are important antioxidants. Melatonin also has antioxidant activity. It can synergize with each vitamin individually to make a more powerful effect [ 21 , 22 , 23 ].In animals, alpha-lipoic acid works to scavenge free radicals. This means that it stops oxidative damage and has antioxidant activity [ 21 ].When used in combination with melatonin, alpha-lipoic acid stopped DNA damage 3 times more effectively than when it was used alone. Melatonin and alpha-lipoic acid worked together to protect calf DNA from oxidative stress [ 21 ]. Glutathione is a potent antioxidant that decreases lipid (fat) breakdown [ 22 ].Melatonin and glutathione combined had a greater antioxidant effect than when either was given individually. Their antioxidant activity combined to have a greater effect in rat livers [ 22 ].Melatonin also helps stimulate glutathione activity in rat brains. They work together to eliminate peroxides and free radicals that cause oxidative damage [ 24 ]. Selenium has free radical scavenger effects. It protects nerve cells and restores the activity of antioxidant enzymes [ 25 ].Melatonin and selenium work together to improve the treatment of brain ischemia and consequent damage in male rats. This combination helped reduce injury and prevented brain inflammation [ 25 ]. EGCG is responsible for most of the antioxidant effects of green tea . It prevents oxidative damage and protects cellular DNA [ 21 ].However, high doses of EGCG or green tea extracts can cause hepatotoxicity (liver damage). Melatonin reduces toxicity due to EGCG overdose [ 21 ].In one study, researchers gave mice toxic and lethal doses of EGCG. Melatonin extended the survival time of mice given toxic doses of EGCG. Meanwhile, it also helped reduce liver injury caused by a nonlethal toxic dose of EGCG [ 26 ]. Resveratrol has both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, it can also exhibit pro-oxidant action and contribute to oxidative damage in excessive amounts [ 27 ].Resveratrol, in the presence of other antioxidants, loses its pro-oxidant action and acts as an antioxidant. Melatonin was highly effective in reversing resveratrol’s pro-oxidant DNA damage in calf DNA. However, they do not combine to make a greater (synergistic) antioxidant effect [ 21 ]. Learn More
Health Benefits of Niacin (Vitamin B3) + Sources & Dosage
Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, is found in a variety of foods. This nutrient is essential for the skin, heart, brain, gut, and more. As a supplement, it can improve blood lipids and skin complexion, while the effects on heart health are mixed. Read on to learn the benefits, food sources, dosage, and side effects of niacin. What is Niacin?
Vitamin B3 exists in two different forms: nicotinamide and nicotinic acid – sometimes collectively termed “niacin”. This vitamin is essential for the nervous system, digestion, skin health, and more [ 1 ].
A variety of whole and processed, fortified foods contain significant amounts of niacin. Deficiency is rare in the western world and usually limited to chronic health conditions. On the other hand, people from poor regions may lack this vitamin due to general malnutrition [ 2 ]. Health Benefits of Niacin
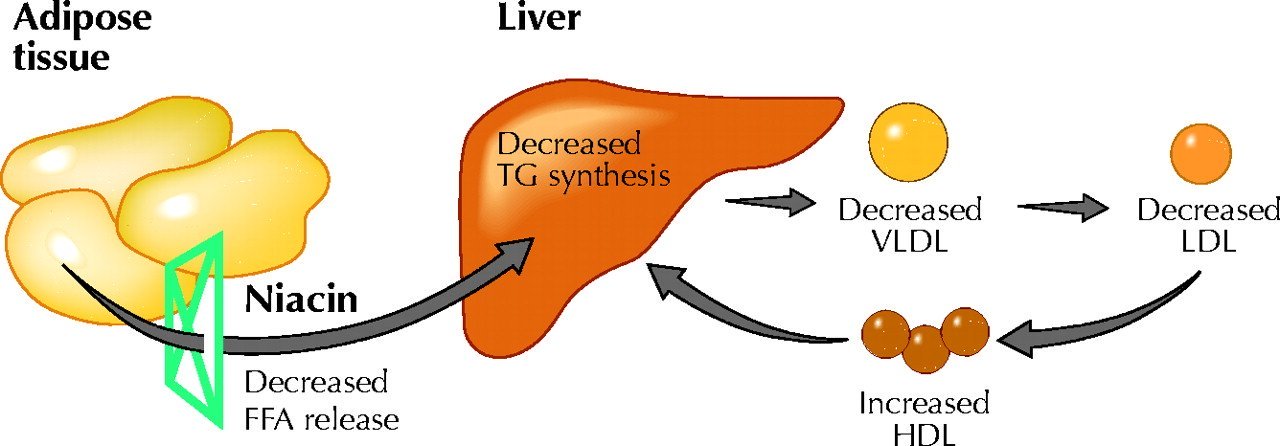
1) Blood Lipids
Niacin can improve blood lipids in multiple ways. A solid body of clinical evidence confirmed its potential to:
Based on these results, the FDA approved prescription niacin products for irregular blood lipids (dyslipidemia). These products typically come in doses of 500 mg or higher. On the other hand, dietary supplements contain 250 mg or less and thus may not have significant effects [ 8 ].
Niacin can improve blood lipids in patients with metabolic syndrome and also HIV/AIDS-related dyslipidemia [ 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Despite its potential to improve blood lipids, niacin doesn’t seem to prevent heart disease or reduce mortality (more details to follow) [ 12 , 13 ]. 2) Niacin Deficiency/Pellagra
Symptoms of a mild niacin deficiency include [ 14 ]: Indigestion
Fatigue
Canker sores
Nausea
Severe niacin deficiency causes pellagra, which manifests with dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia (known as the “three Ds”) [ 15 ].
Niacin (500-1000 mg daily) can resolve the symptoms within one week; it’s FDA-approved for the prevention and treatment of pellagra. Nicotinamide may be preferred over nicotinic acid because it doesn’t dilate the blood vessels [ 16 , 17 ]. 3) Skin Health
When applied topically to the skin (5%), niacin reduced fine lines, wrinkles, redness, and skin yellowing in 50 women after 12 weeks. It also improved skin elasticity [ 18 ].
In 196 women, a regiment of different skincare products with niacin was better tolerated more effective in reducing facial wrinkles than a prescription (tretinoin) treatment [ 19 ].
A 4% niacin formulation significantly reduced wrinkles in the eye area in 30 Japanese women [ 20 ]. 4) Cholera
Severe cholera can be lethal due to rapid fluid loss. In a study of 62 adults with cholera, 2 grams of niacin daily significantly reduced diarrhea and fluid loss [ 21 ].
No valid clinical evidence supports the use of niacin for any of the conditions in this section. Below is a summary of up-to-date animal studies, cell-based research, or low-quality clinical trials which should spark further investigation. However, you shouldn’t interpret them as supportive of any health benefit.
Despite the promising initial results, there’s insufficient clinical evidence to rate the effectiveness of niacin for:
Multiple older studies have indicated the potential of niacin – alone or in combination with other treatment options – to prevent heart disease and reduce related mortality [ 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ].
However, more recent trials and comprehensive clinical reviews (over 39,000 patients included) failed to confirm these findings [ 12 , 13 , 31 , 32 ]. Important Mechanisms
Niacin Side Effects
When taken in recommended daily amounts, niacin is likely safe for healthy adults and pregnant women [ 36 ].
Flushing of the face is the most common side effect. It can result in burning, tingling, itching, and redness of the face, as well as headaches . It can occur because niacin dilates blood vessels [ 37 ].
An overdose of niacin can cause thrombocytopenia or low blood platelet count. This can cause bruising and excessive bleeding [ 37 ].Although there is no evidence that taking large doses of niacin can let you pass drug tests, there have been people who tried doing so. Niacin toxicity from extreme doses caused organ damage, fever, skin problems, and other health issues [ 38 ]. Niacin Sources You can meet daily vitamin B3 needs through diet. It is most abundant in [ 1 ]: Meat Eggs Fish Dairy products Vegetables Whole grains The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of niacin is 16 mg daily in adult men and 14 mg daily in adult women, which can easily be obtained from a normal diet since vitamin B3 is present in all animal, plant, and fungal food sources [ 1 ].For supplementation, studies safely used up to 1,000 mg daily, divided into multiple doses with meals [ 27 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 16 , 17 ].However, niacin can be toxic at high doses. You should not take doses higher than the RDA except under your doctor’s supervision [ 39 ].
Top 7+ Borage Oil Benefits + Side Effects & Precautions

Borage is a flowering herb full of fatty acids and antioxidants. Its oil has shown promise for premature infant growth, heart health, arthritis, and skin health. Read on to learn more. What is Borage?
Borage ( Borago officinalis ), also known as the Star Flower, is an herb native to parts of Asia, North Africa, and Europe [ 1 ].
Borage has been used since ancient times in Iranian traditional medicine as a tranquilizer. In the modern day, its oil is being researched as a potential aid in arthritis and respiratory distress [ 2 ]. Components
Polyunsaturated fatty acids make up a large portion of borage oil [ 2 ].
The herb is an excellent source of Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA), the compound responsible for many of the healing powers of borage. GLA helps maintain animal cell membranes’ structure and function. It is the precursor to many vital active compounds and hormones ( prostaglandins , thromboxanes, and leukotrienes ) [ 2 ].
Borage contains another fatty acid called stearidonic acid. Both stearidonic acid and GLA help treat conditions where people’s bodies lack these fatty acids, such as blood clotting, inflammation, and cancer [ 3 , 4 ]. Intermedin: a protein that aids in the normal function of the gut, heart, and other processes [ 8 ]
Saponins: a group of plant compounds, many of which have the potential to lower cholesterol [ 9 , 10 ]
Rosmarinic acid: an antioxidant fatty acid with potential activity against bacteria, inflammation, diabetes, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease [ 13 ]
Polyphenols: a group of antioxidant plant compounds which are considered by some to be vital nutrients [ 15 , 16 ]
Antioxidant Activity
Borage leaves had high antioxidant activity when in hot water. Borage had high levels of tannins, flavonoids, and phenols. These compounds increase antioxidant capacity, which may protect against DNA damage and harmful mutations [ 7 ].
In one study of 38 participants, the subjects drank borage twice daily for 2 weeks. The total amount of antioxidants in their blood samples increased . This study attributed the herb’s ability to combat oxidative stress largely in its key antioxidants [ 17 ]. Potential Benefits of Borage
Borage oil supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use and generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing. 1) Infant Growth
In a study of 238 premature infants, the infants were given borage and fish oil supplements for 9 months after birth. They had benefits in overall growth and development . However, there was no significant difference between the 2 groups in regards to brain development [ 18 ]. 2) Heart Health
In an 8-week study of 59 subjects, a combination of oils from borage and echium reduced total and LDL (bad) cholesterol . The oil also increased HDL (good) cholesterol levels and lessened the severity of type 2 diabetes in the short term [ 19 ].
In a 28-day study of 30 men, the participants had their heart response to stress tested. Those given borage oil supplement experienced lower blood pressure and heart rate and better performance under stress [ 20 ].
In mice, borage oil treatment protected against heart failure and heart attacks. Unlike other drugs and anti-inflammatory medicine, borage oil did not leave deformations or scars in heart tissue [ 21 ].
A borage oil diet in mice also reduced plaque buildup in the arteries that lead to coronary heart disease. The high amount of fatty acids in the oil reinforce cell membranes and blood, which is associated with improved heart health [ 22 ]. 3) Arthritis
In an 18-month study of 150 participants, the participants who took borage seed oil capsules had fewer rheumatoid arthritis symptoms [ 23 ].
Also, several studies demonstrated that borage seed oil reduced inflammation in the lining of joints (synovitis). Thus, the need for anti-inflammatory drugs was also reduced [ 24 , 25 , 26 ].
A GLA-rich diet reduced acute and chronic (long-term) inflammation in rats with arthritis [ 27 ]. 4) Skin Health
Borage oil contains high levels of omega-6 fats that are vital to the proper structure and function of the skin barrier [ 28 ].
Borage oil promotes a healthy skin barrier. In one study of 37 children, 3 to 4 weeks of topical borage oil treatment cleared skin symptoms of infantile seborrhoeic dermatitis [ 29 ].
In another study of 32 children with eczema, wearing undershirts coated with borage oil for 2 weeks improved their skin barriers. They also had relief from itch [ 30 ].
About 2 g of borage oil supplements a day increased skin hydration and reduced skin roughness and scaling in a study of 45 healthy women with sensitive and dry skin [ 31 ].
However, another study of borage oil supplements found no improvement to atopic dermatitis in 160 patients [ 32 ].Overall, the results have been more promising in trials of topical borage oil than in trials of oral borage supplements.The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of borage oil for any of the below-listed uses. Remember to speak with a doctor before taking borage supplements or using topical borage creams, and never use them in place of something your doctor recommends or prescribes. 5) Mental Health Borage extract capsules significantly reduced depression in 19 patients in a 6-week study. The borage oil contained flavonoids that contributed to antidepressant actions [ 33, 6, 34 ].In a similar, 6-week study of 24 people, borage extract capsules significantly reduced OCD symptoms and anxiety [ 35 ].In mice with an induced-brain decline, borage extract treatment helped maintain their brain function. Borage constituents reduced oxidative stress in the brain and therefore may be used for the treatment of memory impairment and Alzheimer’s disease [ 36 ].Borage extract also reduced anxiety in rats [ 37 ]. 6) Asthma Ingesting 5 mL of borage extract 3 times daily for […]
Does Glucuronolactone Boost Energy? Benefits vs. Dangers

Even if you have never heard of it before, chances are you drank it. Glucuronolactone is a naturally-occurring substance and a lesser-known ingredient in energy drinks like Red Bull. It is also added to pre-workout supplements touted to increase physical performance, stamina, endurance, and detox. Find out if the popular claims about its benefits are valid and learn the potential dangers. What Is Glucuronolactone?
Glucuronolactone is a normal product of glucose breakdown in the liver. All connective tissues contain it, as well as many plant gums. The amounts found in food and those produced in the body, though, are negligible compared to the dosage in energy drinks and supplements [ 1 ].
Glucuronolactone is an ingredient in certain energy and sports drinks, such as Red Bull. As a supplement, it’s available in the powder/capsule form.
It is advertised as a supplement to enhance athletic performance, detoxify the liver, and reduce mental fatigue. However, clinical research about the specific effects of this compound is scant. Snapshot
PROs
Naturally occurring substance
No reported side effects and toxicity
Might have heart- and liver-protecting benefits
Might aid in cancer prevention
CONS:
Combined with potentially harmful ingredients into energy drinks
Lack of clinical trials
Very few animal studies
Animal studies only examined its breakdown products
What Does Glucuronolactone Do?
Glucuronolactone converts to glucuronic acid in the body. This conversion occurs back and forth; there are equal amounts of each molecule in the body [ 2 ].
Glucuronic acid is involved in detox and the breakdown of glucose, as part of a specific pathway crucial for creating fatty acids, amino acids, and DNA components (known as the Pentose Phosphate Pathway) [ 3 ].
Upon glucuronolactone ingestion, glucuronic acid levels (in both blood and urine) will rapidly increase [ 4 ].
Glucuronic acid plays a key role in a detox pathway known as glucuronidation . It binds to chemical and environmental toxins, pharmaceutical drugs, and cancer-causing molecules. By joining with glucuronic acid, these toxins become [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]: More soluble
Transported faster in the body
Less toxic
Eliminated through urine or feces
Beta-Glucuronidase
Another product of glucuronolactone breakdown is called D-glucaro-1,4-lactone. About 25% of glucuronolactone is quickly converted to it. This compound is a potent inhibitor of beta-glucuronidase , an enzyme dominantly produced by your gut bacteria . Various tissues can also make it in lower amounts (the liver, spleen, kidney, gut, endocrine glands and sexual organs) [ 1 , 8 +].
Gut bacteria that make beta-glucuronidase can break down complex carbohydrates. However, this enzyme reverses the glucuronidation process, which slows down detox. Its levels rise with exposure to chemical and environmental pollutants, such as tobacco smoke and heavy metals [ 9 , 10 ].
High levels of beta-glucuronidase may point to [ 11 ]: Liver inflammation and cirrhosis Liver inflammation Tuberculosis Cancers: brain, colon, pancreatic, breast and prostate Potential Benefits of Glucuronolactone No valid clinical evidence supports the use of glucuronolactone for any of the conditions in this section. Below is a summary of up-to-date animal studies, cell-based research, or low-quality clinical trials which should spark further investigation. However, you shouldn’t interpret them as supportive of any health benefit. 1) Exercise Performance The effects of glucuronolactone on exercise performance and endurance have been studied in humans, but only as an ingredient in functional energy drinks.Taking a pre-workout energy supplement (mix of caffeine, taurine, glucuronolactone, beta-alanine , creatine , and amino acids) 10 minutes before resistance exercises significantly increased workout performance in eight resistance-trained men [ 12 ].In a clinical trial of 12 trained cyclists, consumption of Red Bull energy drink 40 minutes prior to exercise increased endurance and overall physical performance [ 13 ].That said, energy drinks contain numerous ingredients aside from glucuronolactone, including caffeine , taurine , glucose, and B-vitamins. Therefore, the observed benefits cannot be attributed to glucuronolactone alone. In a rat study, high doses of glucuronolactone enhanced physical performance and increased stamina given shortly before swimming exercises [ 14 ]. 2) Cognition (Nootropic Effects) In a study of 36 participants, drinking Red Bull (composed of sugar, taurine, glucuronolactone, and caffeine) led to significant improvements in attention, concentration, and memory [ 15 ].Drinking Red Bull improved driving quality, reduced variation in speed, and lowered mental strain from prolonged driving in 24 healthy volunteers [ 16 ].In an observational study of 10 graduate students, drinking Red Bull led to faster motor reaction time, improved attention and decision making when compared to the control group [ 17 ].Once again, Red Bull contains caffeine and other active ingredients that likely contributed to these results. In the lack of clinical research, we can’t estimate the nootropic effects of pure glucuronolactone. No clinical evidence supports the use of glucuronolactone for any of the conditions listed in this section. Below is a summary of the existing animal and cell-based studies; they should guide further investigational efforts but should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit. 1) Blood Clotting and Antioxidant Protection In a study on human plasma, a product of glucuronolactone breakdown (D-glucaro 1,4-lactone) decreased damage to the blood proteins caused by free radicals. It reduced the excessive clumping of platelets that can lead to heart disease and stroke. This effect is amplified in combination with the antioxidant resveratrol , found in red wine [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. 2) Liver Detox Glucuronolactone might protect the liver by enhancing the glucuronidation detoxification pathway.In rats with liver disease, D-glucuronolactone lowered liver inflammation ( IL-6 , NF-κB ) and tissue injury markers. In addition, it increased antioxidant liver enzyme activity ( SOD , glutathione , and glutathione peroxidase ) [ 21 ]. 4) Cancer Prevention Supplementation with a glucuronolactone breakdown product (D-glucaro 1,4-lactone) inhibited breast tumor growth in rats [ 22 ].In rats with liver cancer, the same compound increased survival rates from 45% to 70%. It also reduced the levels of a cancer marker, alpha-fetoprotein [ 23 ].Glucuronolactone plays a role in detoxifying the body from […]
Factors that May “Grow” the Brain: Hope for Brain Injury?
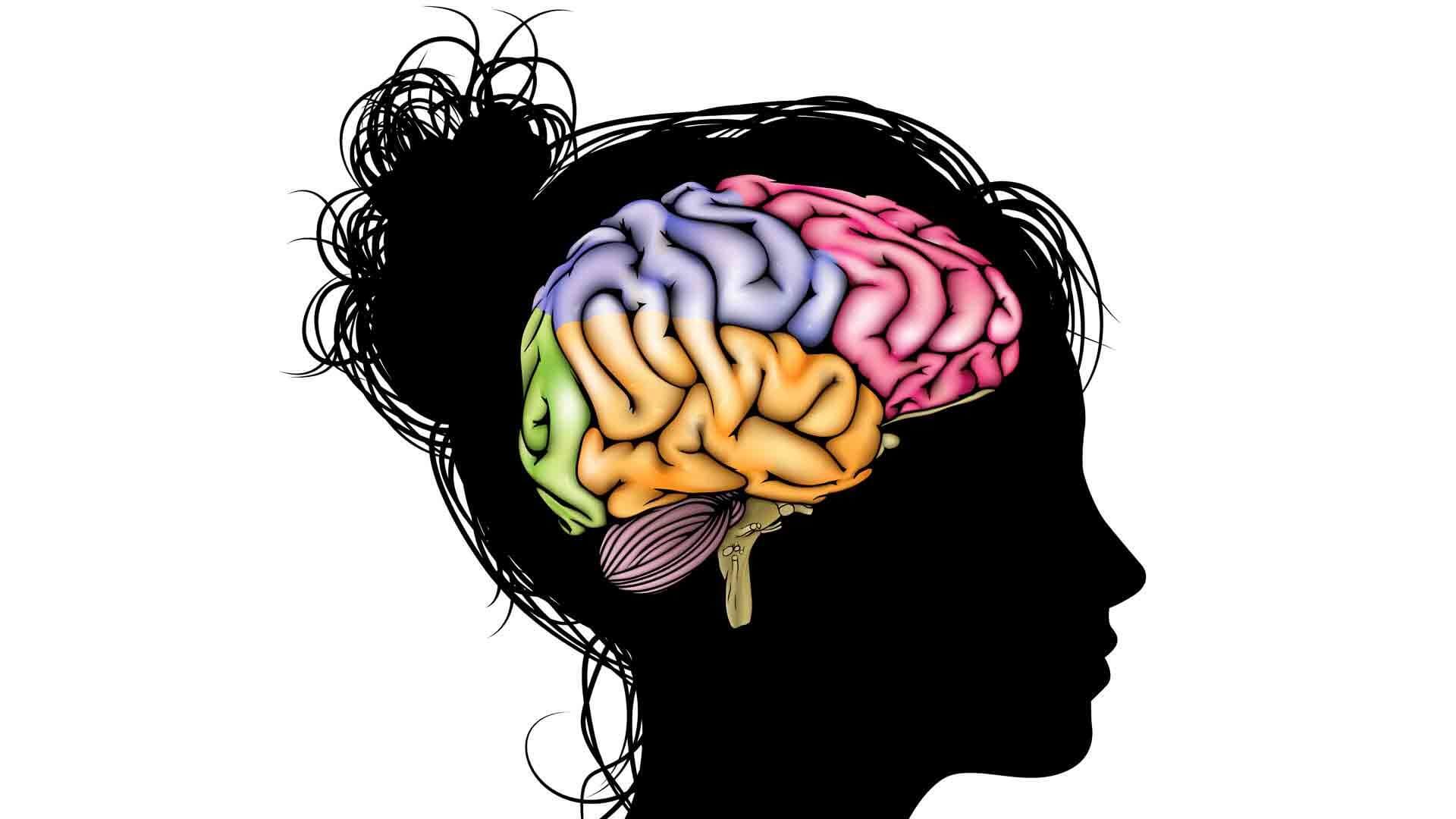

For a long time, scientists believed that no part of the human brain could regenerate. What have we learned since our technology improved? This article explores whether new research offers hope for brain injury and goes over various factors that may either shrink or grow the brain.
“Once again, a flurry of new research is suggesting neurogenesis may be more common than previously thought.”
Comb jellyfish can regrow their rudimentary brains [ 1 ]. But in most mammals (including humans), neurogenesis largely ceases in adulthood. It has been observed in a few places, including the hippocampus, a relatively ancient part of the brain many animals share. In comparison, only humans have a developed neocortex [ 2 ].
The party line in neuroscience has been observational. First, we believed no part of the human brain could regenerate. And we’ve added exceptions as our technology has improved.
Who’s to say we won’t find more exceptions?
Nothing in neuroscience is absolute because the brain is still a black box.
When we sleep, the hippocampus reactivates and connects with various brain regions, including the cortex – the brain’s “crust” or outer layer – all the while emitting delta brainwaves. Scientists think that this may explain, in part, how our memories stabilize while we’re asleep. A study published in Science in 2019 suggests just this [ 3 ].
One part of the cortex is called the occipital cortex is smaller than a speck of dust and it revealed cell types we had never seen before. Nor do we know exactly how memories are stored, though various scientific theories have been proposed [ 3 ].
An older but widely accepted working theory stands on long-term potentiation ( LTP ): neurons that fire together wire together. But that’s more a description than an explanation. We don’t know what induces LTP. When scientists temporarily block certain kinases to prevent neuronal connection (reconsolidation), it often reverts back [ 4 ].
So, researchers emphasize that the brain is more than its connectome (set of neuronal connections). But exactly what–that’s a focus of ongoing research.
Does new research give hope to people struggling with brain injury? Perhaps, but it’s still too early to say. Research findings are mostly limited to animal experiments.
Further studies need to clarify the relevance of neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury in humans. Until then, people with brain injury shouldn’t keep their hopes too high.
For example, induction of adult neurogenesis has been observed in normally non-neurogenic regions of the brain in response to injury and death of neurons – in animals [ 5 ].
Scientists say that upon injury in the non-neurogenic regions, there have been reports of local precursor cells generating new neurons and migrating from the neurogenic to the non-neurogenic region [ 5 ].
This has been suggested to occur in the neocortex [ 6 ], striatum, and hippocampus as a result of ischemic brain injury in rats [ 7 , 8 ].
Neurons that were being generated in the subventricular zone were able to migrate to the injured striatum and differentiate into mature neurons in these animal experiments. Scientists have hypothesized that these migrated and matured cells may help repair neurological deficits, but this remains unproven [ 9 ].
Another study suggested that mice, in response to cortical lesions, may produce new neurons in the ventricular areas. The new neurons then migrated and populated to the cortical areas [ 10 ].
The authors mention that the migration and differentiation of neurons to nonneurogenic regions suggests the brain might have much more potent regenerative capabilities than previously imagined. How and whether this is relevant in humans is still highly uncertain [ 10 ].
Further studies need to clarify the relevance of neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury in humans.
This post explores associations between neurogenesis and aspects of health.
The majority of studies we discuss deal with associations only, which means that a cause-and-effect relationship hasn’t been established.
For example, just because memory and learning have been linked with neurogenesis doesn’t mean that increasing neurogenesis will improve these processes, unless clinical data about a direct link are available. However, data are lacking to make such claims.
Additionally, even if a study did find that neurogenesis contributes to brain recovery after TBI, neurogenesis is unlikely to be the only contributing factor. Complex processes like post-stroke or post-TBI recovery always involve multiple possible factors – including symptom severity, therapeutic modalities, brain chemistry, environment, health status, and genetics – that may vary from one person to another.
If your goal is to increase neurogenesis to improve your neurological issues – including those of traumatic brain injury – it’s important to talk to your doctor, especially your symptoms are significantly impacting your daily life.
Your doctor should diagnose and treat the condition causing your symptoms.
The existing evidence does not suggest that reduced neurogenesis causes any disease.Additionally, changes in brain chemistry are not something that people can change on their own with the approaches listed below. Instead, the factors listed here are meant to reduce daily stress and support overall mental health and well-being. Therefore, you may try the additional strategies listed below if you and your doctor determine that they could be appropriate . None of these strategies should ever be done in place of what your doctor recommends or prescribes.We’re providing a summary of the existing research below, which should guide further investigational efforts.The studies listed in the sections below were mostly done in animals and should not be interpreted as supportive of health benefits in humans. Factors to Avoid that May “Shrink” the Brain It’s always a good idea to avoid unhealthy habits – such as smoking, fast food, overeating, being under a lot of stress, and drinking too much – that can bring your body and mind out of balance. Look to get regular exercise , enough nutrients, sleep, and keep a healthy circadian rhythm . Alcohol Avoid in excess. Drinking 3-4 drinks a day (rather, having an alcohol percentage of .08%) could reduce the number of cells produced in the hippocampus by 40% in one human study [ 11 ]. Stress […]
9 Benefits of Thiamine (Vitamin B1) + Sources, Dosage

Thiamine, or Vitamin B1, is an essential nutrient required by the body. It has many health benefits, from protecting the brain and heart to boosting the immune system. What is Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)?
Thiamine, also known as Vitamin B1, is essential for every tissue in the body. It is a cofactor for enzymatic reactions in the skeletal muscles, heart, liver, kidney, and brain [ 1 ].
Ingested Vitamin B1 from food and dietary supplements is absorbed by the small intestine through active transport at nutritional doses and by passive diffusion at pharmacological doses [ 1 ].
Most dietary Vitamin B1 is in phosphorylated forms, and intestinal phosphatases hydrolyze them to free thiamine before the vitamin is absorbed. Humans store thiamine primarily in the liver, but in very small amounts [ 2 ]. Snapshot
Vital for metabolism
Boosts the Immune system
Supports brain function
Helps digestion
Protects the heart
Functions & Benefits of Thiamine
1) Metabolism
The body needs Vitamin B1 to make ATP, the body’s main energy-carrying molecule.
Thiamine helps in the conversion of carbohydrates into glucose , which is the preferred source of energy that the body runs off of to keep your metabolism running smoothly. It also helps break down proteins and fats [ 3 ].
Thiamine is specifically needed for a system of enzyme reactions called pyruvate dehydrogenase, which works to metabolize sugars that we eat [ 4 ]. Sugar Metabolism
Thiamine (as thiamine diphosphate, the main active form of the vitamin) is essential to glucose metabolism [ 5 ].
The proportion of people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who have low thiamine ranges from 17% to 79%. Studies have found that increasing Vitamin B1 intake decreases the severity of symptoms associated with early-stage diabetes [ 6 ]. 2) Immunity
Like other B-complex vitamins, Vitamin B1 is sometimes called an “anti-stress” vitamin because it may strengthen the immune system and improve the body’s ability to withstand stressful conditions [ 7 ].
Giving rats a Vitamin B1 blocker caused a significant decrease in immune system function [ 7 ]. 3) Brain
Previous studies have reported low levels of thiamine and pyruvate dehydrogenase dysfunction in patients with ataxia, a condition that causes loss of movement. Long-term treatment showed significant improvements [ 8 ].
Vitamin B1 appears to help with the development of the myelin sheath , a coat that wraps around nerves to protect them from damage and death [ 9 ].
In the brain, it is required both by the nerve cells and by other supporting cells in the nervous system [ 10 ].
Autopsy studies have shown that thiamine-dependent enzymes have decreased activity in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease [ 11 ]. Supplemental Thiamine & the Brain
High-dose thiamine improved fatigue in patients after stroke [ 12 ].
Some researchers suspect that vitamin B1 therapy might have a favorable impact on neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s disease [ 13 ].
Further research needs to be done before any conclusions can be made about whether it can help people with neurodegenerative conditions. 4) Cardiovascular Health
Thiamine is vital to the function of the cardiovascular system, and thiamine deficiency can cause congestive heart failure [ 5 ]. Supplemental Thiamine & the Heart In a review of 20 clinical studies, supplementation with thiamine improved cardiac function in people with heart failure [ 14 ].Compared against placebo, thiamine supplementation in 2 randomized, double-blind trials resulted in a significant improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction [ 15 ]. 5) Cataracts Recent studies suggest that thiamin may lower the risk of developing cataracts . These studies show that people who ingest plenty of protein along with vitamins A, B1, B2 , and B3 (or niacin ) in their diet are less likely to develop cataracts. Getting enough vitamins C, E, and B-complex vitamins further protect the lens of the eye ( 16 ). 6) Digestion Thiamine is also necessary for the proper functioning of the digestive system . Vitamin B1 helps to regulate the production of hydrochloric acid, which is needed for maintaining proper digestive function [ 17 ]. Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome Thiamine deficiency is the established cause of Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome (WKS), an alcohol-linked neurological disorder. Alcohol consumption can damage the brain through numerous mechanisms; one of these mechanisms involves the reduced availability of Vitamin B1 to the brain as a consequence of continued alcohol consumption [ 10 ].Thiamine deficiency causes beriberi. Some of the symptoms include swelling, tingling, or burning in the hands and feet as well as trouble breathing because of fluid in the lungs [ 18 ].People in developed countries do not usually get beriberi because staple foods such as cereals and bread are fortified with vitamin B1 [ 5 ]. Sources of Thiamine Food Serving Thiamin (mg) Lentils (cooked, boiled) ½ cup 0.17 Green peas (cooked, boiled) ½ cup 0.21 Long-grain, brown rice (cooked) 1 cup 0.19 Long-grain, white rice, enriched (cooked) 1 cup 0.26 Long-grain, white rice, unenriched (cooked) 1 cup 0.04 Whole-wheat bread 1 slice 0.10 White bread (enriched) 1 slice 0.23 Fortified breakfast cereal (wheat, puffed) 1 cup 0.31 Wheat germ breakfast cereal (toasted, plain) 1 cup 1.88 Pork, lean (loin, tenderloin, cooked, roasted) 3 ounces* 0.81 Pecans 1 ounce 0.19 Spinach (cooked, boiled) ½ cup 0.09 Orange 1 fruit 0.11 Cantaloupe ½ fruit 0.11 Egg (cooked, hard-boiled) 1 large 0.03 Dosage (RDA) Heating foods can reduce their thiamine content . For example, pasteurization reduces thiamine content by 20% in milk [ 2 ].
19 Factors that May Increase Neurogenesis Naturally

Some scientists think that neurogenesis may improve memory and help with anxiety and depression , though this is still uncertain. One thing’s for sure: the brain continues to birth new neurons throughout life. Read on to learn what may increase neurogenesis. Can Certain Factors Increase Neurogenesis?
If your goal is to increase neurogenesis to improve your brain- or mood-related issues – including those of depression, anxiety, or traumatic brain injury – it’s important to talk to your doctor, especially your mood is significantly impacting your daily life.
Your doctor should diagnose and treat the condition causing your symptoms.
The existing evidence does not suggest that reduced neurogenesis causes any disease.
Additionally, changes in brain chemistry are not something that people can change on their own with the approaches listed below. Instead, the factors listed here are meant to reduce daily stress and support overall mental health and well-being.
Therefore, you may try the additional strategies listed below if you and your doctor determine that they could be appropriate . None of these strategies should ever be done in place of what your doctor recommends or prescribes.
We’re providing a summary of the existing research below, which should guide further investigational efforts.
The studies listed in this section were mostly done in animals and should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit in humans. 1) Exercise
Research suggests that aerobic exercise increases the number of new neurons in the hippocampus and increases hippocampal volume [ 1 , 2 ].
Running doubled the number of new cells in the hippocampus of mice [ 3 ].
One study found that aerobic exercise increased hippocampal volume in 120 elderly adults with dementia [ 4 ]. 2) Mental Activity
Learning new skills (particularly challenging ones) increases the survival of new neurons in the hippocampus, according to some recent studies [ 5 ].
Scientists think that the hippocampus shrinks with age, and engaging in a complex mental activity is associated with less shrinkage [ 6 , 7 ]. 3) Sleep
Short-term sleep deprivation (less than one day) has little effect on neurogenesis [ 8 ].
However, chronic sleep deprivation seems to reduce neurogenesis by increasing levels of stress hormones [ 9 ].
Researchers consider that adequate sleep increases neurogenesis by lowering TNF-α and stress hormones [ 9 ]. 4) Meditation
Stress is thought to be one of the main factors that decrease neurogenesis in the adult brain [ 10 , 11 , 12 ].
Both physical and social stresses appear to decrease hippocampal neurogenesis [ 13 , 14 ].
According to limited research, meditation may increase the size of the hippocampus. Scientists think that stress reduction may underlie neurogenesis [ 15 , 16 ]. 5) Sexual Activity
Sexual activity can also help relieve stress, but animal studies suggest it may also increase neurogenesis. Scientists found this with both acute and chronic sexual activity in rats [ 17 ].
Sex prevented a decrease in neurogenesis and improved memory in chronically-stressed mice [ 18 ]. 6) Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a group of compounds found in most fruits and vegetables.
Cocoa flavonoids seemed to build up in the hippocampus and protect the brain in animal models of aging, dementia, and stroke. Human evidence is lacking [ 19 ].
Blueberries and oolong and green teas are rich in flavonoids; they also increase neurogenesis in the hippocampus in animal experiments [ 20 , 21 ].
Based on animal and cellular studies, researchers hypothesize that several flavonoids may support brain health by [ 22 , 23 ]:
However, human data are lacking to back these mechanisms up. 7) The LMN Diet The LMN diet is a patented Medittarenean-like diet rich in polyphenols, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and soluble fiber [ 27 ].The LMN diet increased neurogenesis in mice, presumably by increasing precursor cells and mature neurons [ 28 ].This diet also appeared to increase neurogenesis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s. The researchers claimed it delayed the formation of amyloid plaques in the hippocampus and improved cognitive function [ 29 ].Nonetheless, human studies are lacking. Plus, the main author of the studies hold the patent for the LMN diet, opening room for bias [ 27 ]. 8) Omega-3 Fatty Acids The omega-3 fatty acid DHA increased the formation of new connections in the hippocampus in gerbils [ 30 ].Increased hippocampal neurogenesis via omega-3 fatty acids has been proposed as a way to prevent PTSD , but this hasn’t been proven in humans. More research is needed [ 31 ]. 9) Coffee and Tea (Chlorogenic acid) Chlorogenic acid is found in coffee and black tea . Scientists are investigating whether it promotes hippocampal neurogenesis in cells, along with its by-product m-coumaric acid [ 32 ].Chlorogenic acid also seems to help protect the hippocampus and improve memory in animals, yet clinical trials have not explored this compound [ 33 , 34 ]. 10) Ketogenic Diets? Ketogenic diets are low-carb and high-fat, and they are claimed to induce the body to burn fat as its primary fuel source.One group of researchers found that a ketogenic diet increased neurogenesis in mice with epilepsy [ 35 ].However, another study reported that a ketogenic diet had no effect on neurogenesis in adult rats [ 36 ].Therefore, additional research is needed to determine whether–and what type of–ketogenic diets affect neurogenesis, particularly in humans. Herbs and Supplements that May Increase Neurogenesis Speak with your doctor before taking any supplements. Make sure to let them know about any prescription or over-the-counter medication you may be taking, including vitamins and herbal supplements. Remember that dietary supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use. Supplements generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. 11) Resveratrol In animals and cells, resveratrol appeared to increase the birth of new neurons [ 37 ].Scientists hypothesize it might increase angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) and levels of growth factors that are associated with neurogenesis. Theoretically, these changes may lead […]
Benefits of Branched Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplements

BCAAs are essential amino acids that bodybuilders and athletes use to increase power output, reduce fatigue, and improve fat loss. However, excessive BCAA usage can have negative side effects, such as increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes and other conditions. Read on for further details on the potential effects of BCAA and their correct dosage. What Are BCAAs?
There are three BCAAs: leucine , isoleucine, and valine, which are all essential amino acids – not produced by the body but needed for survival [ 1 , 2 ].
BCAAs are the largest collection of amino acids in the body, accounting for up to 35% of muscle proteins . These amino acids (especially leucine) stimulate protein production in the muscles, possibly helping with muscle building and recover [ 1 , 3 , 4 ].
They also seem to promote sugar storage in the muscles. In animal studies, BCAAs (especially isoleucine) promoted blood glucose uptake into the muscles while blocking muscle carbohydrate (glycogen) breakdown [ 5 , 6 ].
Normally, BCAAs are excreted rapidly. BCAA intermediates can be toxic at high concentrations, so functional BCAA breakdown is vital. Because BCAAs are broken down in the muscle rather than in the liver, they are thought to help produce energy during exercise [ 1 , 2 , 7 ].
BCAA formulas have been on the market since 1996, mainly for treating liver diseases such as cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia [ 8 ].
Nowadays, BCAAs are mainly used by bodybuilders for exercise purposes, to increase energy, and boost protein synthesis (especially leucine) [ 1 ]. Snapshot
Proponents
Essential amino acids
Approved for nitrogen loss
May help recover from exercise and increase body lean mass
May help with liver cirrhosis and its complications
Skeptics
Unclear effects on exercise performance
Excessive supplementation may trigger type 2 diabetes and ALS
May cause high ammonia levels
May interfere with the uptake of other essential amino acids
Not recommended in people with insulin resistance, McArdle’s disease, and maple syrup urine disease
Health Benefits
Effective for:
Nitrogen Loss
An injectable 4% BCAA formulation (BranchAmin) is approved by the FDA as a nitrogen source in people with severe nitrogen loss due to poor protein absorption or septic shock [ 9 ]. Possibly Effective for:
1) Exercise Recovery
Muscle Soreness
BCAA supplements taken before and after exercise reduced exercise-induced muscle soreness and damage in 8 clinical trials on 134 people. This may speed up exercise recovery while preventing injuries [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ].
However, they were of little or no effectiveness in trials on 21 older volunteers performing a 2-day trail in the mountains and 30 well-trained men recovering from intense weight training [ 18 , 19 ].Supplementing with BCAAs seems to preserve muscle proteins by both preventing their breakdown and stimulating their production [ 20 , 21 , 22 ].A meta-analysis of 8 clinical trials concluded that BCAA supplementation was better than rest alone for recovery after exercise due to its ability to reduce muscle soreness and function decline [ 23 ]. Physical Performance Decline In 2 clinical trials on 21 athletes, BCAA supplementation reduced central fatigue after intense exercise [ 24 , 25 ].In 2 clinical trials on 27 well-trained people, BCAAs prevented the decline in power output after exercise [ 26 , 15 ]. Cognitive Performance Decline The reduced central fatigue caused by BCAA supplementation preserved the ability to couple movement and spatial perception (perceptual-motor skills) after exercise in a clinical trial on 9 tennis players [ 25 ].In a trial of 12 volunteers, BCAA supplementation prevented the decline in short-term memory caused by exercise [ 27 ].In another trial on 10 soccer players, BCAA supplements reduced the decline in reaction time by 10% [ 28 ].Taken together, the evidence suggests that BCAAs may help with exercise recovery, especially by reducing muscle soreness and preserving its function. You may discuss with your doctor if you may add them to your training routine. 2) Increasing Lean Mass In a clinical trial on 36 body-builders, BCAA supplements increased lean mass better than other supplements like carbohydrates and whey protein [ 29 ].In another trial on 40 men, both low (6.25 g) and high (25 g) BCAA doses were similarly effective at promoting muscle building after exercise when supplemented with high levels (5 g) of leucine [ 30 ].In 17 resistance-trained men on a low-calorie diet, BCAA supplementation maintained weight loss while preserving muscle mass . Similarly, elite wrestlers on a low-calorie diet l ost more weight when supplemented with BCAAs in a clinical trial on 25 people [ 31 , 32 ].A high dietary consumption of BCAAs was associated with a reduced incidence of obesity in 2 observational studies on over 5,500 people [ 33 , 34 ].Supplementing with BCAAs and vitamin B6 failed to promote weight loss but reduced waist-to-hip ratio and preserved legs lean in a clinical trial on 42 overweight women [ 35 ].BCAAs may also help prevent muscle loss in people at risk. In a study on 73 functionally-limited elderly people, high BCAA levels were associated with increased lean mass (both increased muscle section and reduced fat). Supplementation improved muscle mass and strength in 2 trials on 73 people with rheumatoid arthritis and 68 people with sarcopenia [ 36 , 37 , 38 ].Although limited, the evidence suggests that BCAA supplementation may help both build muscle and lose fat. However, doing more exercise and improving your diet may be safer and more effective ways to obtain these benefits. You may discuss with your doctor if BCAAs may help as a complementary strategy. 3) Liver Damage and Complications In 3 clinical trials on almost 700 people with liver cirrhosis, supplementation with BCAA granules increased survival and quality of life . The treatment was more effective when given during the night, probably because it helped spare proteins [ 39 , 40 , 41 ].The survival rate without any detrimental event was […]
Top 14 Health Benefits of Exercise + Safety Tips

For much of history, high levels of intense daily exercise was probably a necessary requirement for human survival. However, in most industrialized countries the necessity for physical activity to sustain life is declining. As a result, we are seeing a decline in physical fitness in many of these populations.
The purpose of this article is to explore the scientific literature and uncover the role that physical activity plays in the maintenance of good health and the avoidance of chronic disease. We will also discuss different types of exercise and why, for some people, exercise may not be a great option. What is Exercise?
Physical exercise refers to any bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness, health, and wellbeing [ 1 ].
The idea that physical activity is important for health and disease prevention is not a new concept but has been appreciated for millennia. Indeed, Hippocrates (∼450 BC) stated that the body falls sick when exercise is deficient.
The Global Burden of Disease Study carried out by the World Health Organization included physical inactivity as one of the most important risk factors threatening global health [ 2 ].
In fact, research from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has attributed 23.3% of US deaths to the lack of regular exercise. Health Benefits of Exercise
1) Enhances Cognition
Exercise boosts BDNF , which increases neuronal survival, enhances learning, and protects against cognitive decline [ 3 ].
One study found that three 60 minute sessions of moderate physical activity per week increased memory. This was possibly due to increased blood flow to certain parts of the brain (hippocampus) [ 4 ].
Even in old people, aerobic exercise can increase cognition, brain size, and power [ 5 ].
Studies have shown that without a regular exercise regime the brain deteriorates and loses cognitive power much faster [ 6 ].
In fact, one study found that elderly people who engage in aerobic exercise had bigger brains. Non-aerobic yoga or toning exercises did not produce the same effect [ 7 ].
In obese children, physical activity improved executive function and mathematics test scores [ 8 ].
By supporting nerve growth, metabolism, and vascular function, exercise promotes brain plasticity [ 9 ].
Moderate physical activity increases neurotrophins, proteins that support brain plasticity (ability to change). As such, exercise is probably even more important for the young (<25), developing brain [ 10 ].
Recent studies have shown that the beneficial effects of exercise on the brain can be increased by the consumption of natural products like omega-3 fatty acids or plant polyphenols [ 11 ]. 2) Supports Heart Health
Many studies have shown that regular physical activity is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease [ 12 ].
One long-term study looked at the effects of regular exercise on men and women over the age of 73. It found that total exercise, exercise intensity, and leisure time intensity were all associated with a l ower risk of heart attack [ 13 ].
For women, the beneficial effects of exercise on the heart requires just 1 hour of walking per week [ 14 ].
Energy expenditure of 1600-2200 calories per week via exercise is needed for mild heart disease [ 15 , 16 ].
Low-intensity exercise (<45% of max intensity) improves the health of people with heart disease [ 17 ].
A recent study confirmed that regular walking is the best form of physical activity for heart health [ 18 ].
Exercise improves heart health by reducing “bad” cholesterol ( LDL ) and increasing “good” cholesterol ( HDL ) [ 19 , 20 ]. 3) Helps With Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Aerobic and anaerobic training decrease the risk of developing type 2 diabetes [ 21 , 22 , 23 ].
In one study, every extra 500kcal burned per week through exercise decreased the risk of diabetes by 6% [ 24 ].
40 minutes of intense exercise per week reduced the risk of diabetes in middle-aged men [ 26 ]. Weight loss via exercise can reduce the risk of diabetes by 40-60% among overweight individuals [ 27 ].Moderate physical activity for >150 minutes per week was found to be more effective than the drug metformin [ 27 ].One study showed that diabetics who walked at least two hours per week had 39-54% lower mortality [ 28 ].Inactive men with diabetes were found to be 1.7 times more likely to die than physically active diabetics. This relationship also applies to those with metabolic syndrome [ 29 , 30 ].Resistance training (e.g. weightlifting) might help regulate blood sugar more than aerobic exercise [ 31 ]. 4) Improves Mental Health People who engage in regular physical activity experience fewer depressive and anxious symptoms [ 32 ].Both aerobic (e.g swimming) and anaerobic (e.g. weight training) exercise effectively lower depression and enhance mood [ 33 ].Individuals who maintain a reasonable level of aerobic fitness are less likely to relapse into depression [ 34 ].People with chronic anxiety often have a dysregulated HPA axis . Studies have shown that exercise improves the way the HPA axis modulates stress reactivity and anxiety [ 35 , 36 ].High levels of physical activity are associated with improved heart rate variability scores (stress resilience marker) [ 37 ].One study found that college students who exercised regularly experienced less stress and hassle than those who didn’t [ 38 ].Another study found that regular physical activity buffered the stressful effects of widowhood in elderly subjects [ 39 ].Exercise increases norepinephrine , which helps the brain deal with stress more effectively [ 40 ].In one study, both African dance (rigorous exercise) and yoga caused significant improvements in stress levels [ 41 ].As well as reducing mental stress, some forms of exercise are very effective at reducing cellular stress. For example, yoga has been shown to improve antioxidant status and limit oxidative damage [ 42 ]. 5) Boosts Sleep Quality The idea that exercise helps sleep has existed for thousands of years [ 43 ].Disturbed sleep is a common symptom of anxiety. Thus, exercise’s positive effect on sleep may be […]

