Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Magic of melody: Music therapy can ease anxiety disorders, and speeds up recovery too
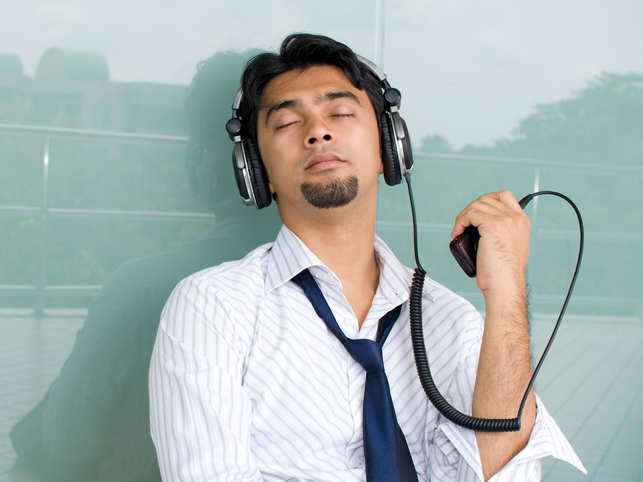

Related By Rashmi Ramesh A nine-year-old, who’d never uttered a word all his life, spoke for the first time during a music session. His first word was “open”. Diagnosed with autism, the boy had been non-verbal until then. The development came as a pleasant surprise to Purvaa Sampath—currently India’s only CBMT (Certification Board for Music Therapists)-certified music therapist and neurologic music therapistwho was an intern at the time. “With that boy, my supervisor and I had developed a song where he would knock on the drum when we prompted him to. I was leading the session and began the song. When I got to the part about knocking, the song went ‘Who’s that knocking on the door?’ and instead of just knocking on the drum, he looked straight at me and said the word ‘open’. That was the first time he’d ever said a word and it was a huge moment for me, my supervisor, his teacher as well as his family. And this word came after months of music therapy ,” Sampath said. With music therapy, consistency, patience and practice are key, according to her. music therapy_GettyImages Akanksha Pandey, consultant clinical psychologist at Fortis Hospital in Bengaluru, said music is an expressive therapeutic tool that helps people improve their physical and mental health — it relaxes the mind and has a functional effect on the brain. “The therapeutic role of music has been recognised since ancient times, through texts such as Raga Chikitsa, and has the support of current research as well, which talks about the physiological benefits of music on the immune system, the benefits of music for relaxation and stress management, the application of music to improve memory and attention, as well as music-induced longterm changes in the behaviour of depressed elderly people,” Pandey said. “Music […]
A cup of tea a day keeps the doctor away: Oolong tea extract can help prevent breast cancer, say researchers

( Natural News ) Drinking tea may not be as fashionable as coffee, but its health benefits simply can’t be beat. There is nothing more comforting than a good cup of tea, especially when you aren’t feeling your best. A wide array of teas have been used for medicinal and healing purposes for eons, and new research continues to build on what many natural health practitioners have long since known: Tea is just as good for the body as it is for the soul. Recently published research shows that oolong tea, in particular, can help fight cancer — and it may even keep death from knocking on your door. Oolong tea is a traditional Chinese tea, made from the same Camellia sinensis plant used for green and black teas. It contains benefits seen in both green and black teas, making it a uniquely potent beverage. Oolong tea tackles cancer Medical News Today reports that scientists at Saint Louis University have discovered oolong tea extract has an extraordinary quality: It kills breast cancer. The team recently published their study in the journal Anticancer Research . Chunfa Huang, Ph.D., and associate research professor in the college’s department of internal medicine, led the investigation. Along with colleagues, Huang examined oolong tea’s effects on six different breast cancer cell lines — including ER-positive, PR-positive, HER2-positive, and triple-negative cancers. Green tea, black tea and dark tea were also studied. After finding that oolong tea was capable of destroying cancer cells, the team concluded it does “play an inhibitory role in breast cancer cell growth, proliferation, and tumorigenesis, and [it has] great potential as a chemopreventive agent against breast cancer.” The power of the elements : Discover Colloidal Silver Mouthwash with quality, natural ingredients like Sangre de Drago sap, black walnut hulls, menthol crystals and […]
Wikipedia: The new inquisition

( Natural News ) Consider: you are given a serious diagnosis – cancer, dementia, multiple sclerosis – and your doctor runs you through the standard treatment protocol. It fails to reverse or cure the condition, leaving you hundreds of thousands of dollars poorer and sicker. It’s time to explore your options, you decide, and seek out others who’ve recovered or improved from your condition. Your doctor tells you you’re already receiving the gold standard of medical treatment – there’s nothing more to do now but try the protocol again, shell out for another round of chemotherapy or do crossword puzzles to “exercise” your brain as you gradually forget the names of your loved ones – but then you read about some natural therapy, administered by board-certified physicians, that seems to show promising results. Surely all doctors read the same literature, so you ask yours. Humoring you – and probably unfamiliar with the therapy, but unwilling to admit anything less than omniscience – your doctor tells you to do some research, certain there’s nothing out there that could possibly be superior to what he learned in medical school. You type the name of the therapy into Wikipedia, which everyone knows contains the sum total of medical knowledge and science, distilled by the experts and perfected through millions of edits. Surely, if there’s something to this therapy, Wikipedia will know. (Article by Helen Buyniski republished from PRN.fm ) But Wikipedia claims this therapy doesn’t work. Worse, it condemns it as quackery, calling its practitioners charlatans and frauds preying on sick people. Not just this therapy, but other holistic modalities are methodically trashed, one by one. Wikipedia says your doctor was right. There’s his way, or the highway. Bewildered, you realize that all the people who think they’ve been healed or helped […]
Tips On How To Increase The Serotonin In Your Brain Naturally
Share Share on Pinterest Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that can influence many things throughout your body like your mood, memory, sleep cycle, and even your sex drive. By increasing the serotonin in your body naturally, you can also enhance your mental state and your motivation. Want to increase serotonin? Here are 11 natural ways to boost your serotonin. 1. Eat Tryptophan. Tryptophan is an amino acid that helps in your body’s production of serotonin. Serotonin is synthesized from tryptophan. It’s believed that tryptophan is associated with mood issues like depression and anxiety. Tryptophan supplements can increase serotonin, but a more natural approach is to eat foods that contain tryptophan. Research has shown that when you follow a low-tryptophan diet, brain serotonin levels drop. Foods that include tryptophan include eggs, turkey, dairy, lean meats, salmon, pineapples, tofu, nuts, and seeds. Keep in mind: High-tryptophan foods won’t increase serotonin on their own. But if you mix high-tryptophan foods with carbs, you’re more likely to boost serotonin. The body releases more insulin when it absorbs carbs, which promotes amino acid absorption and leaves tryptophan in the blood. The tryptophan you find in natural food competes with other amino acids to be absorbed in the brain so that it won’t boost serotonin a huge deal on its own. 2. Get a massage. Share Share on Pinterest Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Getting a massage can boost your mood no matter what, but did you know that it can reduce your cortisol levels? A study found that after massage therapy, cortisol was found to be 31% less on average in saliva or urine tests, and serotonin and dopamine increased by 28% and 31%, respectively. Another study looked at massage therapy on babies of Depressed Mothers. They massaged […]
Electric bikes can boost older people’s mental performance and their well-being
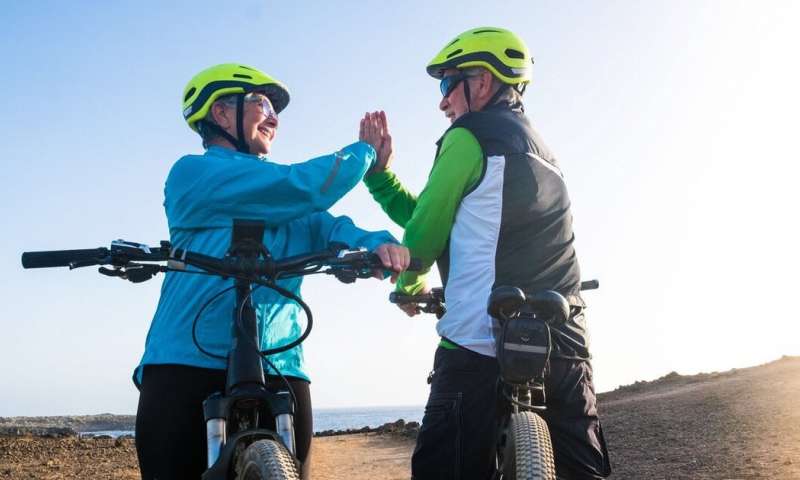

Credit: shutterstock Getting on your bicycle can give you an enormous sense of freedom and enjoyment. It can increase your independence and knowledge of the local area, and improve your access to the natural (or urban) environment. It can also be highly nostalgic – reminding you of your childhood cycle rides and the joy of being young. But beyond the feel-good factor, can cycling actually make any difference to mental abilities and well-being? This was something our new study aimed to investigate – specifically looking at cycling among older adults. While most studies incorporate exercise in a gym situation, our study wanted to examine the impact of cycling in the real world – outside a controlled environment. So older adults, aged 50 and above, were asked to cycle for at least an hour and a half each week for an eight-week period. Participants either cycled on a conventional pedal bike, on an electrically assisted "e-bike" or were instructed to maintain their regular non-cycling exercise routine as a comparison group. Mental abilities, mental health and well-being were measured before and after the eight-week cycling period. Mental boost Exercise is thought to improve mental functioning through increased blood flow to the brain – as well as encouraging regrowth of cells, specifically in the hippocampus . This is known to be an area associated with memory. So it was expected that the greater physical exertion required for pedal cycling, compared to cycling an e-bike with a motor, would result in greater benefits to mental functioning. Having a bike can open up new places of adventure. Credit: Shutterstock One of the tasks we used to measure mental ability is the " Stroop test ". The task involves participants being shown the name of a colour printed on a card in a different colour […]
WTF Are Nootropics and Should You Be Using Them?

Nootropics have been gaining major buzz for being “smart drugs.” If you’re into the health and fitness world, you probably already know about their rumored positive benefits — and they probably have you wondering if they can actually make you a smarty pants. Nootropics are said to increase memory , focus and even motivation while reducing the effects of aging. All of this is accomplished with chemicals that help increase blood circulation in the brain. Nootropics have been found to have certain long-term cognitive benefits, such as increased memory function and focus. They include chemicals that are both naturally occurring, like ginkgo and ginseng, and manmade, like lab-produced piracetam. While both the naturally occurring and manmade nootropics seem to increase blood flow, piracetam specifically has been shown to improve memory function in Alzheimer’s patients. Regardless of their immediate impacts, the supplements are said to protect neural pathways from signs of aging — meaning it keeps the brain young by continually supplying it with blood and oxygen — and perhaps even Alzheimer’s disease. This is because nootropics protect the dopaminergic pathway — the very same pathway affected by many degenerative brain diseases. Sydney Johnson , an ICF certified health coach who specializes in women’s hormonal health, explained how these supplements can be helpful, as well as why she thinks they’ve become so trendy recently. “We are seeing fitness influencers on Instagram not only taking supplements like collagen to help with physical appearance, but now taking nootropics to improve their mental cognition. The introduction of these supplements has allowed people to consider how increased cognitive functioning could help them in their academic and professional pursuits.” According to the National Library of Medicine , another way that nootropics may be able to improve cognitive function is through their ability to decrease inflammation. […]
Centella Asiatica Market : Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, and Threats 2018-2028

Centella asiatica is also known as Gotu Kola and is a small herbaceous plant. It is also a traditional medicinal herb that has been used in India, China, Nepal, Sri Lanka and Madagascar over the last century. Centella asiatica is indigenous to the Asia Pacific region, belongs to the Apiaceae family and has been long known for its faster healing properties for small wounds and scratches. The plant is also known for its ability to cure a number of skin diseases, for which it is being widely used in a number of skin care products. Centella asiatica extracts are widely used for its traditional herbal remedy and culinary uses and has been used in Ayurveda for a very long time. A number of companies including Himalaya, SD Biotechnologies Co.,Ltd. Nutricare Co., Ltd. Pairs of Horses Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Elishacoy are some of the companies using Centella asiatica in their skin and personal care products. In some countries Centella asiatica is also used as a vegetable and in beverages. Get Free Exclusive Sample Copy of This Report @ https://www.factmr.com/connectus/sample?flag=S&rep_id=2200 Global Centella asiatica Market: Dynamics Centella asiatica extract is used to make a number of caffeine-free beverages, which prevent mental fatigue, anxiety and depression. It is also used on wounds as antifungal and antibacterial, which helps in fast healing. Centella asiatica cultivation is spread through a number of tropical and sub-tropical courtiers globally. Though it is known by different names in different cultures, Centella asiatica is used as a raw vegetable in salads, but its medicinal uses actually drive its growth in the market. Centella asiatica extract is used in a number of skin care products in the western countries, for its healing properties. Centella asiatica extracts are among some of the key botanical extracts and some of the key factors […]
TESH: Here is Some Sleepy Intelligence

Here’s a little sleepy intelligence…as in, “good for your sleep!” Pay attention to your sleep window. That’s a 30-45 minute window when your eyes are getting heavy or you yawn frequently, because that’s the time when you’re the most naturally ready to sleep. If you go to bed then, you’ll fall asleep quickly and you’ll sleep soundly. If you wait and you miss that sleep opportunity “window”, your nervous system kicks in and gets you going again. This is according to sleep expert Dr. Michael Bruce. And if you get that second wind, you could be up for another 90 minutes, so try to go to bed during your natural sleep window. Tomorrow morning will be here before you know it, so it’s a fantastic time to test out a new sleep routine. Share this today to friends from The John Tesh Radio Show ! Is rosemary a part of your pantry staples? It should be, because rosemary is basically MAGICAL! Sniff it, make rosemary tea, use it to season food. Thanks to its antioxidant compounds, it increases alertness and energy for hours! That’s because it improves circulation, delivering more oxygen and nutrients throughout your body. Rosemary also has ursolic acid, which has an antidepressant effect. The University of Maryland Medical Center also says rosemary can ease muscle pain and spasm, stimulate hair growth and improve memory, because its scent triggers biochemical changes in the brain. It also reduces the oxidative stress that damages brain cells. That means, long-term, less age-related mental decline. Parsley, sage and thyme? All great. But share the benefits of rosemary with your friends today, and they’ll be back for more from The John Tesh Radio Show ! Happy “make-a-rosemary-infused-pot roast” evening!!!
Electric bikes can boost older people’s mental performance and their well-being
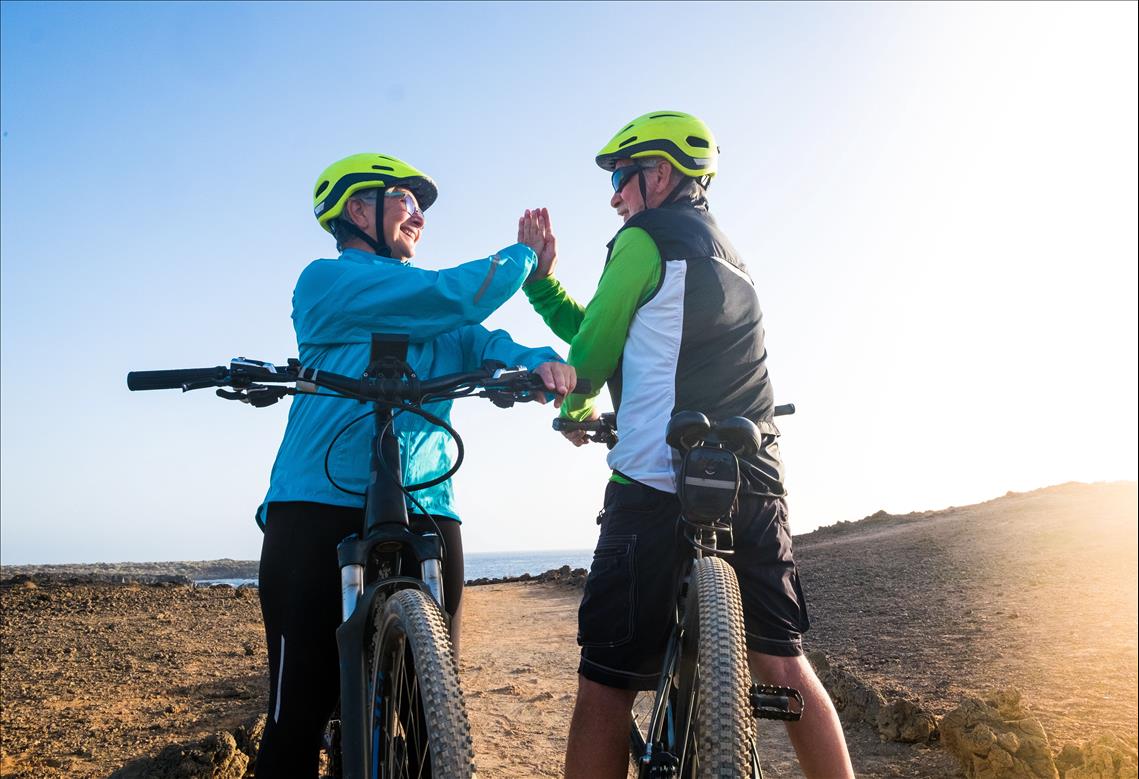

(MENAFN – The Conversation) Getting on your bicycle can give you an enormous sense of freedom and enjoyment. It can increase your independence and knowledge of the local area, and improve your access to the natural (or urban) environment. It can also be highly nostalgic – reminding you of your childhood cycle rides and the joy of being young. But beyond the feel-good factor, can cycling actually make any difference to mental abilities and well-being? This was something our new study aimed to investigate – specifically looking at cycling among older adults. While most studies incorporate exercise in a gym situation, our study wanted to examine the impact of cycling in the real world – outside a controlled environment. So older adults, aged 50 and above, were asked to cycle for at least an hour and a half each week for an eight-week period. Participants either cycled on a conventional pedal bike, on an electrically assisted ‘e-bike’ or were instructed to maintain their regular non-cycling exercise routine as a comparison group. Mental abilities, mental health and well-being were measured before and after the eight-week cycling period. Mental boost Exercise is thought to improve mental functioning through increased blood flow to the brain – as well as encouraging regrowth of cells, specifically in the hippocampus . This is known to be an area associated with memory. So it was expected that the greater physical exertion required for pedal cycling, compared to cycling an e-bike with a motor, would result in greater benefits to mental functioning. One of the tasks we used to measure mental ability is the ‘ Stroop test ‘. The task involves participants being shown the name of a colour printed on a card in a different colour script – imagine the word ‘blue’ printed in red ink. […]
Bill Gates is funding research for more drugs: His father suffers from Alzheimer’s which inspired him to invest $100M

( Natural News ) Bill Gates recently disclosed that his father has Alzheimer’s disease. Gates also announced that his father’s illness inspired him to donate a staggering $100 million towards Alzheimer’s disease research. But, as is typical of Bill Gates, his motives are not as altruistic as they may seem. The billionaire businessman admits that his donations are driven by the fear that he too will one day struggle with Alzheimer’s disease. Of his massive donation, $50 million will reportedly go to the Dementia Discovery Fund. The other half will go to a national patent registry and an international research database. And as the United Kingdom’s Daily Mail reports , both sums will be drawn from Gates’ personal fortune, and are separate from the infamous Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. In an interview with NBC’s Maria Shriver, Gates commented that his 92-year-old father’s diagnosis prompted concerns about his own brain “staying intact as long as possible.” Gates has garnered quite the reputation; to some, he’s a philanthropist who focuses on the poor and underprivileged in developing nations. To others, Gates is a man who funds experimentation on the poor and underprivileged in developing nations. The mainstream propagandist media may do their best to paint Bill Gates in a heroic, shining light — but the truth is that where his money goes, darkness often follows. In 2016, it was revealed that over 30,000 Indian children had been used as test subjects under Bill Gates’ version of philanthropy — wherein the less fortunate people of the world are used as guinea pigs for medical experiments. Mother Nature’s micronutrient secret : Organic Broccoli Sprout Capsules now available, delivering 280mg of high-density nutrition, including the extraordinary "sulforaphane" and "glucosinolate" nutrients found only in cruciferous healing foods. Every lot laboratory tested. See availability here. […]
Why exercise is the safest way for you to reduce your anxiety
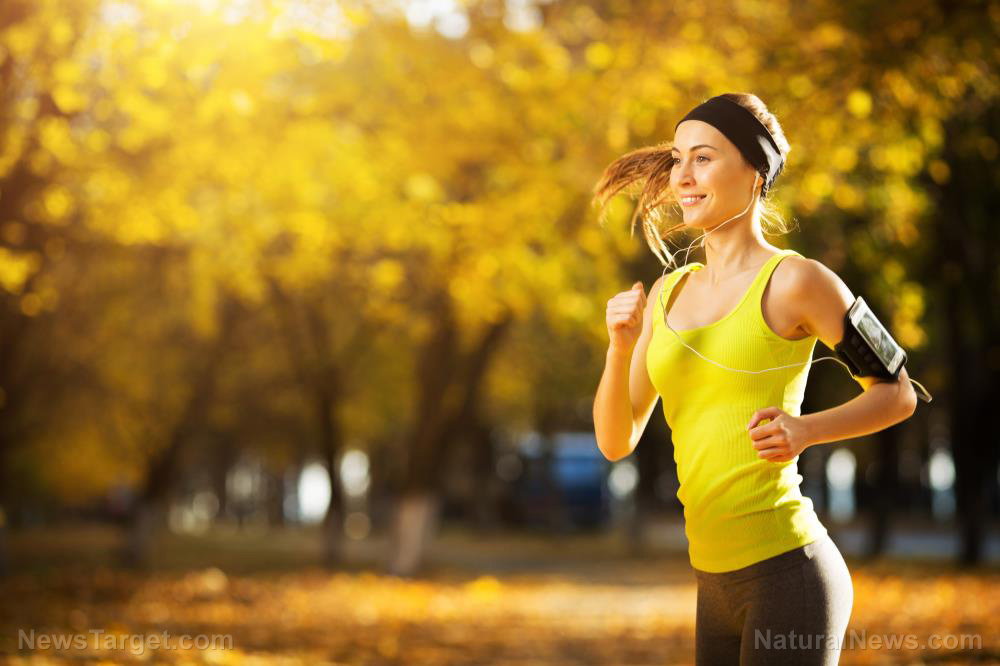

( Natural News ) Feeling anxious about something? Try exercising. Multiple studies have shown a link between the two – from psychological theories suggesting that exercise improves self-efficacy and social interaction to clinical trials that reveal a positive relationship between exercise and anxiety prevention. But why exactly is exercise a great way to reduce feelings of anxiety ? Here are just some of the evidence-backed reasons to explain this benefit. It can greatly reduce a person’s stress levels. The idea of exercising while you’re already stressed out from being anxious might seem counterintuitive, but experts say that exercise can indeed bring about relaxation – if done in a controlled, graded fashion. In particular, it can bring down adrenaline and cortisol levels – dubbed as the body’s stress hormones – and can boost the production of endorphins, natural chemicals that function as the body’s painkillers and mood elevators. A review in American Family Physician noted that aerobic exercise significantly reduced symptoms in people with anxiety and panic disorders. It does take some getting used to: The first steps are usually the hardest, but it gets easier as you begin to tolerate exercise and start getting into shape. It contributes to improvements in behavior. Regular exercise can benefit a person physically, but its behavioral and emotional benefits are things that should also be considered. A person who regularly exercises will see noticeable changes in their appearance, which can improve their self-image. Exercise also instills a sense of discipline, mastery, and self-control, which can help a person achieve other important goals. Studies on how exercise improves a person’s behavior have been promising. In a 2008 study in the journal Depression and Anxiety , researchers found that regularly working out could help a person who’s prone to anxiety to better control their behavior […]
TESH: Here is Some Sleepy Intelligence

Here’s a little sleepy intelligence…as in, “good for your sleep!” Pay attention to your sleep window. That’s a 30-45 minute window when your eyes are getting heavy or you yawn frequently, because that’s the time when you’re the most naturally ready to sleep. If you go to bed then, you’ll fall asleep quickly and you’ll sleep soundly. If you wait and you miss that sleep opportunity “window”, your nervous system kicks in and gets you going again. This is according to sleep expert Dr. Michael Bruce. And if you get that second wind, you could be up for another 90 minutes, so try to go to bed during your natural sleep window. Tomorrow morning will be here before you know it, so it’s a fantastic time to test out a new sleep routine. Share this today to friends from The John Tesh Radio Show ! Is rosemary a part of your pantry staples? It should be, because rosemary is basically MAGICAL! Sniff it, make rosemary tea, use it to season food. Thanks to its antioxidant compounds, it increases alertness and energy for hours! That’s because it improves circulation, delivering more oxygen and nutrients throughout your body. Rosemary also has ursolic acid, which has an antidepressant effect. The University of Maryland Medical Center also says rosemary can ease muscle pain and spasm, stimulate hair growth and improve memory, because its scent triggers biochemical changes in the brain. It also reduces the oxidative stress that damages brain cells. That means, long-term, less age-related mental decline. Parsley, sage and thyme? All great. But share the benefits of rosemary with your friends today, and they’ll be back for more from The John Tesh Radio Show ! Happy “make-a-rosemary-infused-pot roast” evening!!!
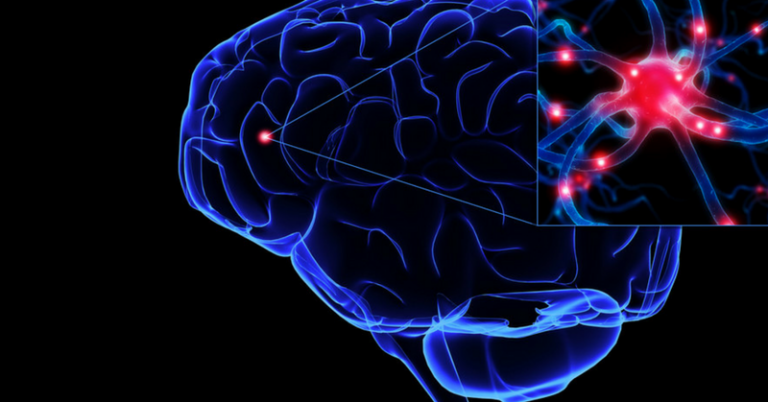
Zapping brain with precise electrical current boosts memory in older adults, BU study finds
Shooting electrical current into the brain for just 25 minutes reversed the decline in working memory that comes with aging, Boston University scientists reported Monday. Although the researchers tested the effects on people for only 50 minutes, the finding offers hope for boosting a mental function that is so crucial for reasoning, everyday problem-solving, and planning that it has been called the foundation of intelligence. By stimulating the brain in precise regions with alternating current, “we can bring back the superior working memory function you had when you were much younger,” psychology researcher Robert Reinhart of BU told reporters. “The negative age-related changes [in working memory] are not unchangeable.” For alternating current, delivered by electrodes embedded in a skull cap, to become a treatment for working memory deficits, however, it would have to overcome a long list of hurdles, starting with proof that it’s safe. But whether or not the findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, result in any practical applications, they provide some of the strongest evidence yet of why older adults aren’t as good at remembering a just-heard phone number or an address in a just-seen text: Brain circuits become functionally disconnected and fall out of synchrony. “This is a well-designed, rigorous study,” said neurophysiologist Michael Nitsche of Germany’s University of Göttingen, who reviewed the paper for the journal. “It adds important information about the causal relevance of alterations of [brainwaves] for age-dependent cognitive decline, and it shows that these alterations are reversible.” Working memory is the sketchpad of the mind, where information is weighed, considered, manipulated, and fed into cognitive tasks, from following a conversation to doing mental math. For their experiments, the BU scientists tested the working memories of 42 younger adults (aged 20 to 29) and 42 older ones (60 to 76). People saw an […]
Common, colorful and really good for your brain

Carotenoids are plant pigments. They make tomatoes red and give carrots their distinctive orange hue. You see them when leaves change colors in the fall. But carotenoids are not just decorative. Among the roughly 600 carotenoids in nature, two in particular, lutein and zeaxanthin, have been found to improve the function of the human brain, according to researchers at the University of Georgia. ”Carotenoids, in general, when we eat them, they are antioxidants, so they do a great job of keeping our bodies healthy and free of oxygenated damage,” says Lisa Renzi-Hammond, one of the researchers looking at the effect of lutein and zeaxanthin. “They are anti-inflammatories, so we see that the more of these molecules we eat, the less inflammation we tend to have,’’ she says. “Our research shows that they are also changing, in many ways, the structure of the brain, and making it a more efficient organ.” Lutein is a lipid, fat-based anti-oxidant that the brain uses to prevent the oxidation of the fat in the brain, says Billy Hammond, who is Renzi-Hammond’s research partner and husband. “It basically kind of links neurons together so they act more efficiently, so it helps cognition and a number of other processing things that the brain does.” In an experiment, Hammond and Renzi-Hammond looked at increased lutein intake in both older adults and people of college age. The study populations were given lutein and zeaxanthin supplements for a year to see how this changed their cognition. The groups taking the supplements were compared to groups taking a placebo. “We found that by improving basic functions, like helping the brain process faster, that all of the cognitive functions were improved as well, so they had better memory, better problem-solving, compared to a placebo,” says Hammond, “The [patients with] placebos didn’t […]
Qatar- Healthy living with Wellness and Spa

(MENAFN – Gulf Times) Health, as defined by the World Health Organization, is a ‘complete state of physical, mental and social well-being, not merely an absence of disease.’ Thus, health does not reside merely in the physical domain, but in the mind and in the spirit as well the holistic approach. Reconnecting body-mind-spirit, one of the objectives of taking a spa and/or wellness day out, can have a profound effect on one’s health. Scientific research says that most of the diseases human beings face are related to stress. Stress can not only affect the mental health of a person but also can damage your physical health. In the ever-changing world and with today’s ultra fast-paced lifestyle, meditation, and yoga with life coaching, is on the rise. We are in a world where there is no slowing down, and mental rejuvenation is what people need to cope with stress. As perceived, stress is reduced or removed at a wellness centre and spa, with meditation, yoga, opening up your chakras or a simple oil massage to relax the muscles, one can actually change the biochemistry of their body. Ultimately, a greater state of balance and a higher state of health can be achieved. Wellness is the hot new word in holistic approach these days. It’s the most powerful argument anyone can make against seeing spas as a mere luxury, but rather a research-backed tool that can improve your health. From the rise of ageing baby boomers to high net worth clients whose stress levels and the need for self-fulfilment have increased, spa and wellness is on the rise. Whether it’s a sweaty workout or an intense day at work that has your muscles in a knot, a wellness treatment like a massage or a trip to the sauna can sound like […]
Can coffee and cannabis be a solid pairing? Taking things slow and easy is likely the best course until that question can be answered

Coffee and weed seem like a pair matched in heaven. Perfect for a wake-and-bake, the idea is that a person will get both the psychoactive effects of cannabis and the energy of coffee. There’s also a mix of pleasant aromas and tastes that offers promise as a fine pairing, similar to wine and cheese. As it stands, however, coffee and weed have not achieved that natural fit. The combination has to be taken with caution, as the science is still coming in with regard to how the two interact. What’s science say about mixing cannabis and coffee? A 2014 study published in the Journal of Neuroscience, for example, investigated the impact of a caffeine-like substance on squirrel monkeys predisposed to THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, the chemical that causes cannabis’ psychoactive effect. The results suggest that caffeine enhances the effects of THC, but also increases the desire for cannabis. One of the study’s authors, Sergio Ferré, a National Health Institutes investigator, has also studied the impact of caffeine and THC on rats. His 2012 report in the British Journal of Pharmacology concluded that “caffeine did not counteract memory deficits induced by THC, but actually exacerbated them.” Both caffeine and cannabis increase dopamine levels in the brain, Ferré explained in an interview with Live Science, so when taken together, caffeine can magnify the effect of dopamine from the cannabis. “Caffeine increases tremendously the effects of a psycho-stimulant, including THC and cocaine,” Dr. Ferre said. “So, any substance that releases dopamine, including THC, its effects are increased by caffeine.” Last year, a study by researchers at Northwestern University also found that, like marijuana, caffeine binds to the neurotransmitters related to the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Unlike cannabis, though, the more coffee subjects drank, the less impact it had on the ECS . While the […]
Electrical Stimulation Makes Old Brains Act Young Again

MORE Credit: Shutterstock A short session of brain zapping can reverse some of the effects of aging in older adults, a new study suggests. The technique isn’t ready for non-experimental use yet, and it’s not clear how long the benefits last. But the study authors said they hope that their findings will set the stage for improving cognition in both healthy adults and in people experiencing Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia . "These findings are important because they not only give us new insights into the brain basis for age-related working-memory decline, but they also show us that the negative age-related changes are not unchangeable," said study leader Robert Reinhart, a neuroscientist at Boston University. [ Why You Forget: 5 Strange Facts About Memory ] The findings were published today (April 8) in the journal Nature Neuroscience . Working memory Reinhart and his co-author, doctoral student John Nguyen, focused their study on an aspect of cognition called working memory. This is the sketch pad of the brain, Reinhart said in a press briefing. It allows people to hold information in active use for a few seconds at a time, facilitating all sorts of important tasks, from performing mental math to reading to having a conversation. Research has shown that working memory is a key part of intelligence, Reinhart told reporters. But working memory declines over adulthood. The decline is not dramatic, but it is significant enough that older adults perform worse , on average, on working-memory tasks than younger adults. Reinhart and Nguyen wanted to see if they could figure out why — and perhaps change that trajectory. The researchers recruited 42 adults ages 20 to 29 and 42 older adults ages 60 to 76; the scientists asked the participants to complete a working-memory task while their brain […]
Why nurses should spend time outdoors every single day

Registered home health nurse Susannah Bonner loves the days when her Monday-Friday job starts at 8 a.m. and ends at 4 p.m. When that happens, she’s able to put on her athletic shoes after work and walk in the great outdoors of small town Canton, Georgia. "I put the music on, and I’m not dwelling about work," she says. "I do all that so that once I go back out and am in a home, it’s all about that person." Along with improved heart rate and other physical benefits of walking, Bonner is tapping into the sheer benefits of breathing fresh air and being around nature. Sure, part of the benefit is the movement. According to the CDC , physical activity helps bump up your brain function, can lower the risk of heart disease, Type 2 Diabetes and some cancers, and boost mood. But if you add what researchers call "forest therapy" or "forest bathing," the health boost is almost designed to combat the stress inherent in nursing work. And it boosts brain power, too. A University of Michigan study , for example, demonstrated that those who walked in areas with lots of trees improved their memory by almost 20 percent. Another study of healthy nurses who went "forest bathing" on a three-day, two-night trip in northwest Japan showed a substantial increase in the immune-boosting "Natural killer" activity, and it lasted at least seven days after the trip was over. Researchers have also determined that heart rate and cortisol levels both plummet when study subjects spend time in the forest. But how do office- and hospital-corridor bound nurses get this nature boost? Try these tips to increase your chances: Get an annual membership to a nature preserve. Places like the Chattahoochee Nature Center in Roswell offer great discounts if […]
Zapping brain with precise electrical current boosts working memory in older adults, study finds
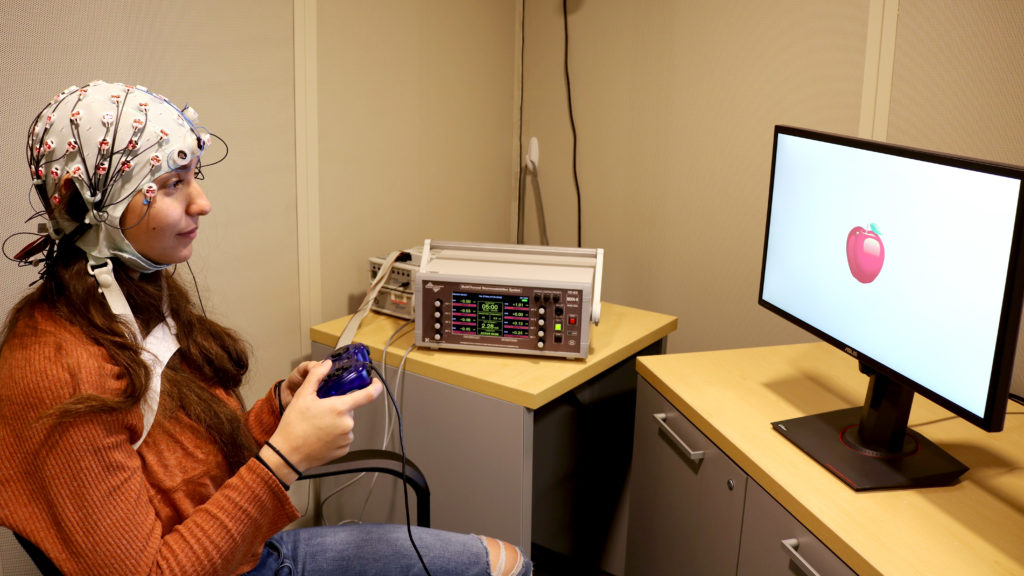

A participant taking a memory test as part of a study testing the use of alternating current to improve working memory in older people. Younger adults were used as controls. hooting electrical current into the brain for just 25 minutes reversed the decline in working memory that comes with aging, scientists reported on Monday. Although the researchers tested the effects on people for only 50 minutes, the finding offers hope for boosting a mental function that is so crucial for reasoning, everyday problem-solving, and planning that it has been called the foundation of intelligence. SBy stimulating the brain in precise regions with alternating current (AC), “we can bring back the superior working memory function you had when you were much younger,” psychology researcher Robert Reinhart of Boston University told reporters. “The negative age-related changes [in working memory] are not unchangeable.” For alternating current, delivered by electrodes embedded in a skull cap, to become a treatment for working memory deficits, however, it would have to overcome a long list of hurdles, starting with proof that it’s safe. But whether or not the findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, result in any practical applications, they provide some of the strongest evidence yet of why older adults aren’t as good at remembering a just-heard phone number or an address in a just-seen text: Brain circuits become functionally disconnected and fall out of synchrony. “This is a well-designed, rigorous study,” said neurophysiologist Michael Nitsche of Germany’s University of Göttingen, who reviewed the paper for the journal. “It adds important information about the causal relevance of alterations of [brainwaves] for age-dependent cognitive decline, and it shows that these alterations are reversible.” Working memory is the sketchpad of the mind, where information — just acquired or hauled up from long-term memory — is weighed, considered, manipulated, […]
expert reaction to brain stimulation to restore working memory in older adults
Tweet Research published in Nature Neuroscience describes a technique of noninvasive brain stimulation that resulted in improvement in working memory of performance in adults aged 60-76. Dr Sven Braeutigam, Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Physicist at the Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, and Senior Researcher, Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, said: “Increasing life expectancy implies, unfortunately, an increasing prevalence of cognitive decline in older adults. The effects of age-related decrease in our ability to think and remember are highly significant both at the individual and societal level, however, neither the biological mechanisms underlying such decrease are fully understood nor are consistent therapeutic approaches available. “Here, the recent work by Reinhardt and Nguyen could be a real advancement in the debate. The authors employed transcranial electric stimulation targeting a specific neuronal mechanism, known as phase-amplitude coupling (PAC), in order to modulate the behavioural response in older adults performing a change-detection memory task. Critically, during and even after stimulation, task performance in older subjects reaches the level of young participants. Importantly, the observed correlation of task performance and PAC provides strong, arguably the best currently available insight into the neurophysiological foundations of human working memory. “There is reason, however, to control ones enthusiasm because the authors applied only sham stimulation (a kind of placebo control) in young people, implying that it is currently not known to exactly what extent the effects observed are age specific. Nevertheless, the work by Reinhardt and Nguyen is important early stage work that may well stimulate fruitful research into effective treatments of age-related decline of human cognitive function.” Dr Sara Imarisio, Head of Research from Alzheimer’s Research UK, said: “To function properly the brain requires both electrical as well as chemical signals and research is beginning to investigate whether electrical stimulation of certain brain regions can help improve […]
