Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Can Mushrooms Help in Managing Alzheimer’s Disease? Here’s What we Know

Can Mushrooms Help in Managing Alzheimer’s Disease? Here’s What we Know. Picture Credits: Pixabay Alzheimer’s disease is a mental health issue that sets in mid ’60s which leads to deterioration the memory and thinking skills. It accounts for 60 to 70% of dementia cases. Having to deal with difficulties relating to thinking, reasoning, remembering, and behaviour, life turns harder with time after the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.Also Read – Alzheimer’s Disease And Dementia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests And Treatment
Although there is no treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, medications help manage symptoms and cope with the disease. With nootropics being widely used in treating patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, the question is could consuming food that are natural nootropics help managing symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Nootropics are substances that have stimulant effects and help boosting brain’s performance which enhances memory. Also Read – World Alzheimer’s Day 2021: From Weight Loss to Anger Issues – Major Symptoms You Should Know About What Types of Mushrooms Are Helpful?
Certain types of mushrooms are natural nootropics that boost the brain’s functions when consumed. Lion’s Mane mushroom, Chaga mushroom and Cordyceps are popular super mushrooms that are widely used among health enthusiasts for strengthening the immune system and improving gut balance. Their nootropic benefits make them apt to be used to help managing symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Also Read – Alzheimer’s Likely Causes Identified Says Australian Researchers Lion’s Mane Mushroom: Lion’s mane grows on the trunks of hardwood trees is rich in nootropic compounds such as hericenones and erinacines that stimulate growth of brain cells and improves cognition. Studies have shown that consuming Lion’s Mane mushroom in small quantities for a period of 4 months improves mental functioning.
Chaga Mushroom: Chaga Mushrooms are rich in antioxidants that are important for brain’s health. Brain is prone to oxidative stress which is associated with decline in cognition and increased risk of suffering Alzheimer’s disease. It helps protecting the brain from neuro degeneration by balancing the antioxidant system and protects the cells.
Cordyceps Mushrooms: Cordyceps are mostly found in mountain regions increases blood flow to damaged brain cells. It reduces the impact of ageing and the risk of age-related cognitive decline. Chronic stress leads to inflammation in the brain which results in memory damage and increases the risk of suffering cognitive disorders. This mushroom has a positive influence on the mood and boosts memory.
How to Add Mushrooms to Your Diet?
The simplest way is to replace your regular coffee with mushroom coffee.
(Authored article by Rajat Bahl, Director at The Forest Superfood)
For breaking news and live news updates, like us on Facebook or follow us on Twitter and Instagram . Read more on Latest Health News on India.com .
Study: Vitamin D levels linked to improved mood and mental health

( Natural News ) Vitamin D is often associated with bone health since the sunshine vitamin is essential for maintaining strong, healthy bones. You also need vitamin D for thyroid health, optimal gut and immune function, healthy brain development and function, and a healthy pregnancy.
According to a recent study, there’s also a crucial link between the sunshine vitamin and your mood and mental well-being . Vitamin D intake and your mental health
Within the last decade or so, researchers have conducted numerous studies to understand the link between vitamin D and the brain. Some studies have identified the presence of vitamin D receptors and metabolites throughout the brain, which suggests that the vitamin plays a role in both cognitive function and mood regulation.
Aside from brain health, research has also found that vitamin D can affect gut function and health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and supporting the integrity of the gut lining. This hints at vitamin D’s role in your mental health since there is a “complex and deep relationship between gut health and mental well-being.”
Many studies also point to the connection between vitamin D status – or how low or high your vitamin D levels are in the blood – and your mental health. One 2020 review reported that, based on the findings of numerous studies, people with mood concerns often have lower vitamin D levels.
A paper released in 2010 called for more research on the use of vitamin D supplementation to support emotional health because it was a “simple and cost-effective solution for many” with mood concerns. (Related: A worldwide health problem: Numerous studies warn that low levels of vitamin D can increase premature death and disease risks .)
Scientists still have a lot to learn about the exact mechanisms that connect vitamin D and mental well-being, but recent studies suggest that the vitamin’s role in the regulation of melatonin and serotonin , two hormones that affect mood, has something to do with it. According to preclinical research, vitamin D can help buffer the brain from oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways. Circulating vitamin D levels and mental health of young people
For their systematic review, scientists analyzed 15 studies published in the peer-reviewed journal Clinics.
Their findings highlight the importance of vitamin D for maintaining mental health. According to the review, a lot of studies have identified “consistent links” between vitamin D and “overall mood and feelings of anxiousness.”
The scientists reported that based on current evidence, boosting circulating vitamin D levels can significantly improve mental health, especially in young people. They also warned that having circulating vitamin D levels lower than 20 ng/mL, which is considered a clinical deficiency, is linked to “suboptimal mental well-being.”
Unfortunately, an estimated one-third of American adults suffer from vitamin D deficiency. Foods rich in vitamin D
Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels is crucial for many aspects of your health, especially if you want to improve your mood and mental well-being.
Many health experts say that 50 ng/mL is the ideal concentration of vitamin D in the blood. You need a daily intake of at least 5,000 international units (IUs) of vitamin D3 to maintain optimal blood levels.
There are two types of vitamin D in the human diet . Vitamin D2, which comes from plants, and D3, which comes from animals.
Cholecalciferol, or vitamin D3, is the vitamin that your body naturally produces. Vitamin D3 is the most sought-after form of vitamin D, as it’s more easily absorbed and utilized by the body than vitamin D2.
Listed below are superfoods rich in vitamin D3: Canned sockeye salmon
Cisco
Cod liver oil
Fish oil
Halibut
Herring
Mackerel
Organic soy milk
Rainbow trout
Rockfish
Sturgeon Swordfish Whitefish Whole milk Yogurt Aside from eating foods rich in vitamin D, you can also take supplements to ensure that you get enough of the sunshine vitamin regularly. Follow a healthy diet and maintain your circulating vitamin D levels to ensure your overall well-being. Sources include: MindBodyGreen.com
Chinese skullcap can kill brain cancer cells, thanks to its active component baicalein
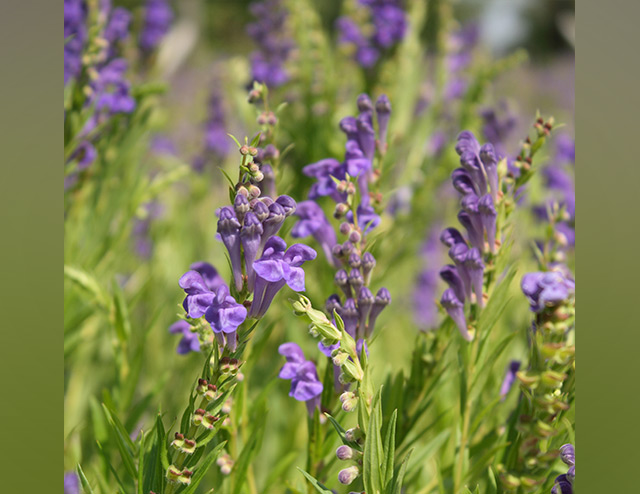

( Natural News ) Researchers from Qingdao University in China have found that a flavonoid present in Chinese skullcap ( Scutellaria baicalensis ) has potential anti-cancer properties.
In their report, published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine , the researchers noted that baicalein, a flavonoid derived from the roots of Chinese skullcap, can induce cell autophagy and apoptosis — two processes that help clear out damaged cells from the body. In particular, the team investigated the mechanism behind the anti-cancer activity of baicalein using human glioma cells. Exploring the anti-cancer activity of baicalein
A glioma is a tumor that develops in the brain or the spinal cord . This type of tumor originates from the glial cells, which provide support for the neurons. Among the types of glial cells found in the brain and the peripheral nervous system, three types of glial cells can produce tumors. Astrocytomas are tumors that develop in astrocytes , star-shaped glial cells found in the brain. Astrocytes are the most abundant type of glial cell in the brain, and they are responsible for many important functions , including forming and maintaining the blood-brain barrier, regulating blood flow and maintaining brain energy metabolism, among others. Astrocytomas may develop in both children and adults at differing severity: Tumors that develop in children are often localized and grow slowly, while those that develop in adults grow rapidly and require immediate treatment.
Ependymomas are tumors that form from the ependymal cells that line up the ventricles in the brain and spinal cord. These ventricles contain cerebrospinal fluid, which helps protect the brain and spinal cord from injury and infection. Ependymomas can develop at any age; however, these are seen more often in young children. This type of glioma is rare, with only 200 new cases reported each year.
Oligodendrogliomas are tumors that develop in oligodendrocytes , a type of glial cell that supports and insulates axons in the central nervous system. The most common symptom of oligodendroglioma is seizures: Six out of 10 people with the condition report having a seizure before diagnosis. Men between the ages of 35 and 44 are more likely to develop this type of tumor, but it can occur at any age.
For the study, the team treated glioma cells with baicalein in vitro . In particular, they were interested to see whether baicalein triggers autophagy and induces AMPK activation in glioma cells. The researchers found that baicalein can induce autophagy – that is, the body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells to regenerate healthier cells – in the glioma cells. In addition, treating glioma cells with baicalein also activated the AMPK pathway, one of the most important signaling networks for cell growth. This caused baicalein-induced autophagy and cell death. Researchers say this activation plays a vital role in the anti-cancer effect of baicalein.
“Surprisingly, our research provides new insight with the function of anticancer of [baicalein], and the potential of the promotion in glioma cell apoptosis might be related to autophagy activation,” they wrote in their report. “These results demonstrate the anticancer activity of [baicalein], which can be used as potential therapeutic agents for cancer therapy.” (Related: Cannabis oil saves infant from inoperable brain tumor .) Other benefits of Chinese skullcap
Despite the foreboding name, the Chinese skullcap is a member of the mint family and has long been used in traditional Chinese medicine . In traditional medicine, the roots of the plant, called huang qin , are used to treat conditions ranging from insomnia, anxiety and tension to inflammation, hepatitis and cardiovascular disease.
In addition to baicalein, research has shown that Chinese skullcap contains other active ingredients that provide health benefits. In a study published in Neuroscience Letters , researchers from China found that oroxylin A – an antioxidant present in the roots of Chinese skullcap – may prevent the development of brain plaques linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
Follow AntiCancer.news for more novel natural treatments for glioma and other cancers.
Sources include:
ABTA.org
VeryWellHealth.com 1
Cancer.gov
VeryWellHealth.com 2
This Brain-Boosting Herbal Shot Is Loaded With Ingredients That Help You Live Longer
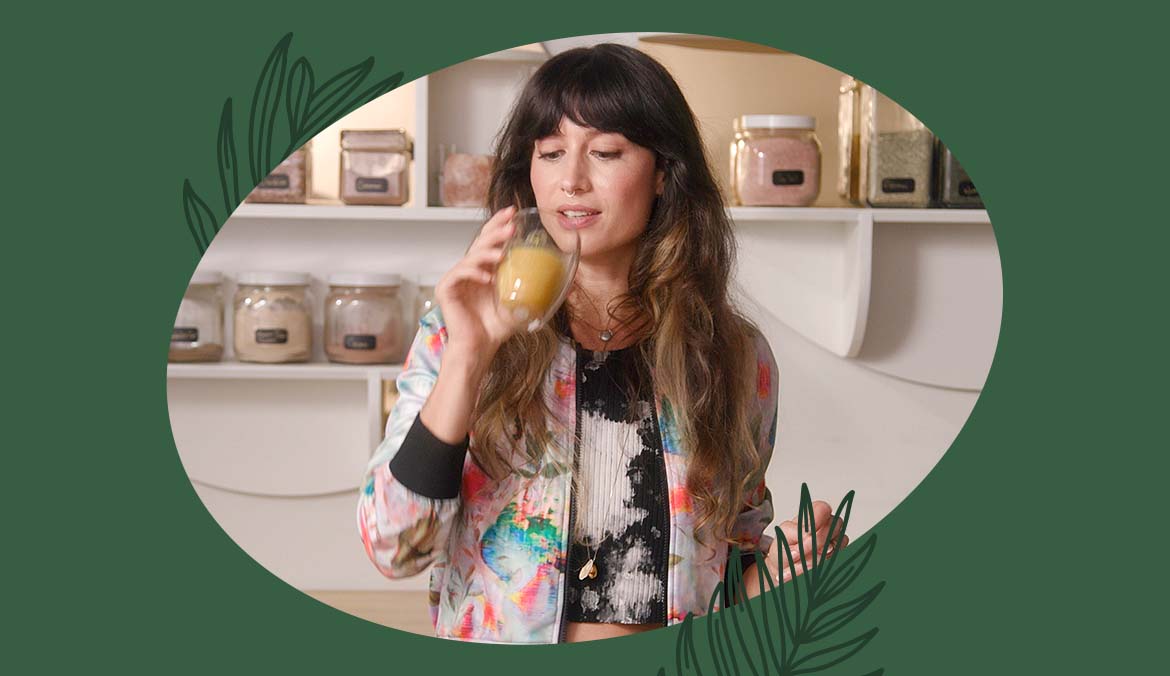

Longevity has been a hot button topic for a long time (shocker!). Subjects such as what to eat , drink , practice , or value to live a long, happy, and healthy life are top-of-mind for many us. After all, isn’t that sort of The Goal?
Well, according to both functional medicine doctor Mark Hyman, MD and Dan Buettner , author and researcher of the world’s Blue Zones (AKA regions around the world where the longest-living people reside), what you consume on a daily basis is a key part of boosting your body’s potential to stay fit and functional for the long haul. On this episode of the Well+Good YouTube series, Plant-Based , Rachelle Robinett teaches us how to make a brain-boosting herbal shot that is packed with longevity-boosting ingredients.
Follow along as Robinett concocts an herb-filled shot that is catered specifically towards brain health and neuro-longevity. It includes adaptogens like rhodiola and ginseng, cerebral tonics like bacopa, and so much more. Just remember: To really commit to improving your lifespan in a healthy way, you have to take a holistic approach. 4 of Robinett’s favorite herbs and spices for longevity
1. Rhodiola
Rhodiola is one of the best herbs when it comes to brain health and longevity benefits. This is because it plays a strong role in boosting mental recovery. “We need to be able to flip into a system that is performing well, but we also need to be able to flip out of it and be in that rest and digest and neutral state,” says Robinett. She adds that rhodiola also helps inhibit the release of cortisol, which is supremely helpful because—no shock here— stress can be very detrimental to your brain health in chronic doses. 2. Ginseng
The beverage also includes ginseng , which helps to reduce inflammation in the brain. According to Robinett, neuroinflammation can cause anxiety, depression, and longer term neurological disorders, so ginseng is essential to keeping your brain happy, calm, and not overworked. It’s also filled with antioxidants, which fight against free-radical damage and help your immune system function in top form. 3. Nootropics
Robinett’s recipe features nootropics like bacopa—a common component of many ADHD and ADD treatments—and functional mushrooms. Nootropics , she explains, help support memory, cognition, and learning in the brain. The bacopa also helps increase circulation in the brain and supports brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. The functional mushroom blend in the shot helps optimize brain functioning and focus, plus it works to balance out your mood (thanks to the reishi ) and promote nerve health (thanks to the Lion’s Mane). 4. Turmeric
Finally, and most importantly, the recipe also includes turmeric . Turmeric is a delicious spice that’s great for your whole body, from your skin to your joints and your gut. It’s also a known anti-inflammatory agent.”Turmeric is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals, is linked to lower risk of brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia, and has also been shown to lower the risk of heart disease,” Buettner previously told Well+Good . This is because turmeric contains plant compounds called curcuminoids, which are also highly anti-inflammatory. In a double-blind study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychology, curcumin was shown to have a significant effect on memory and attention in adults aged 50 to 90 who had mild memory complaints. Over 18 months, curcumin improved memory in this population by 28 percent. They also experienced mild improvements in mood. Though the exact mechanism by which this effect happens is not known, Gary W. Small, M.D. , director of the UCLA Longevity Center, told Well+Good that it likely has something to do with curcumin’s anti-inflammatory benefits.
Ready to knock back a bounty of longevity-promoting vitamins, minerals, and adaptogenic herbs? Stir up Robinett’s recipe to boost your memory, focus, creativity, and overall brain functioning in one quick sip. Robinett’s herbal shot for longevity recipe
Ingredients
2 ounces of plant-based milk
1/2 tsp rhodiola
1/2 tsp ginseng
1/2 tsp bacopa
1 serving mushroom blend
1/2 tsp astragalus
1 tsp turmeric
Pinch of black pepper
Use a milk frother or whisk to mix all of the ingredients together.
For more healthy recipes and cooking ideas from our community, join Well+Good’s Cook With Us Facebook group.
Japanese plum offers protection against fatty liver, reveals study
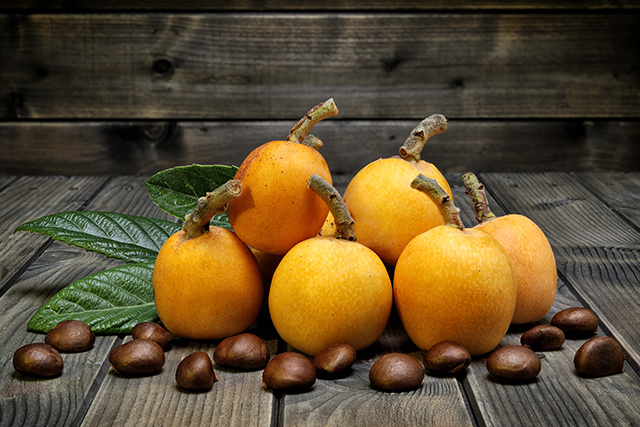

( Natural News ) Researchers from Chonnam National University in South Korea have found that Eriobotrya japonica , commonly referred to as Japanese plum or loquat, can help protect the liver from damage caused by diet or alcohol intake . In their report, they looked at how Japanese plum can help liver cells at risk of damage from alcohol or free fatty acids. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Medicinal Food . Poor diet, heavy alcohol use damage the liver
The liver is an essential organ of the body. The largest organ inside the body, the liver helps digest food and store energy — even remove poisons. However, its many functions put it at higher risk of disease and injury, in particular, hepatic steatosis.
Hepatic steatosis , better known as fatty liver disease, happens when extra fat is stored in the liver . While the liver stores a small amount of fat, it becomes a problem when fat reaches around 10 percent of the liver’s weight.
It’s worth noting that fatty liver disease has no symptoms at its onset. However, the condition can get worse over time and progress in three stages: Steatohepatitis , marked by liver inflammation and tissue damage
Fibrosis , which occurs when scar tissue forms in damaged areas of the liver
Cirrhosis , a serious condition where scar tissue replaces healthy tissue
Cirrhosis can often lead to liver cancer and even outright liver failure. Advanced cirrhosis is life-threatening.
Hepatic steatosis has two main forms: Alcoholic liver disease , wherein a person develops a fatty liver due to heavy alcohol use. In the U.S., around five percent of adults have this form of disease.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) , wherein a person develops a fatty liver even if they aren’t drinkers. NAFLD is worrisome, as it is prevalent: A third of American adults — and 10 percent of children — have this condition. According to studies, several factors like obesity and diabetes can increase a person’s risk of getting NAFLD.
Japanese plum can protect liver from damage
In their report, the researchers looked at whether Japanese plum can help prevent fatty liver .
Earlier studies had shown that the plant could help in treating hepatic steatosis. A 2017 study published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy concluded that leaf extracts from Japanese plum could potentially treat NAFLD . In addition, a study published in The Korean Journal of Community Living Science concluded that leaf extracts from the Japanese plum could protect the liver from alcohol-induced damage .
The team also used Japanese plum leaves to create a hot water extract. They used this hot water extract to pretreat liver cells before exposing them to ethanol and free fatty acids to induce alcoholic liver disease and NAFLD, respectively. The findings revealed that the hot water extract from Japanese plum exhibited antioxidant properties and inhibited lipid accumulation in pretreated liver cells. Lipid accumulation, according to research, not only increases a person’s risk of hepatic steatosis but also his risk of developing insulin resistance — a precursor to diabetes and other chronic conditions.
In addition, liver cells pretreated with hot water extract from Japanese plum exhibited increased 5’adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity. When activated in the proper tissues — like the brain, liver and skeletal muscles — this brings about multiple benefits , including improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced muscle performance and reduced inflammation, among others.
The results suggest that Japanese plum extract can prevent both alcohol- and free fatty acid-induced oxidative damage and lipid accumulation in liver cells.
Learn more natural treatments for liver damage at NaturalMedicine.news .
Sources include:
My.ClevelandClinic.org
LipidWorld.BioMedCentral.com
5 Kid-friendly herbs for treating different ailments
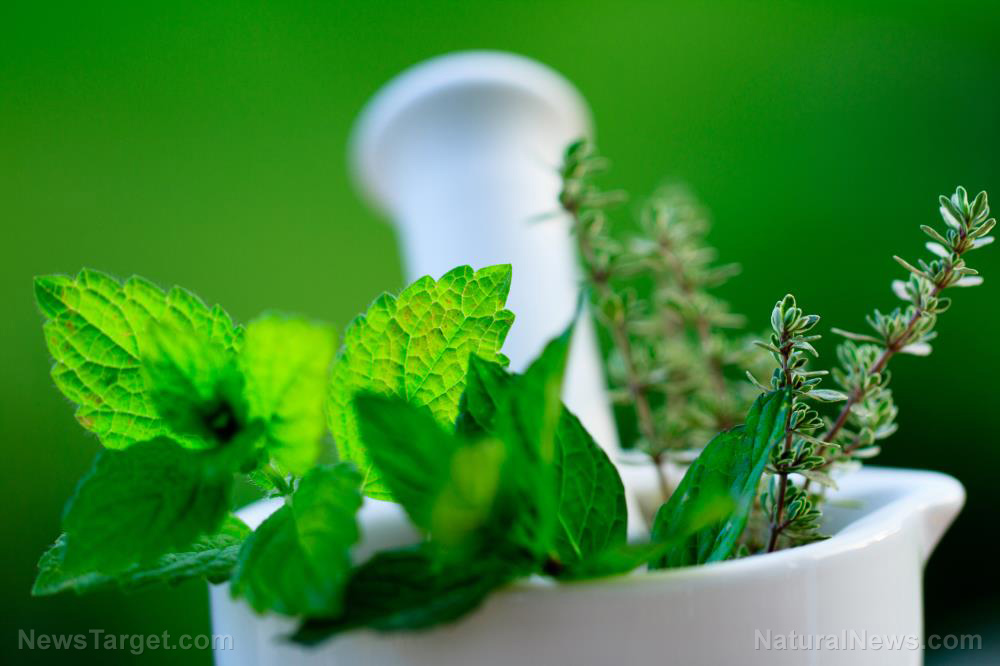

( Natural News ) Natural remedies have long been known for effectively addressing different ailments without the dangerous side effects that come with conventional medicine. Many parents nowadays are choosing natural cures whenever their children get sick. They head over to their gardens instead of the nearby pharmacy whenever their children experience a fever.
But with the many different herbs around, some might not be safe for young ones and could cause more harm than good. Here are five effective herbs that treat different ailments, and are proven safe for children. Elderberry
Elderberries are known to boost the immune system and decrease the risk of getting sick. They also possess antimicrobial properties that prevent bacteria inside the body from multiplying and causing an infection.
Back in 2004, medical experts found that elderberry syrup is effective in helping people with influenza recover faster than those who did not take it or who only relied on a placebo. This is because of a compound in elderberries that prevents the flu virus from sticking to cell walls and replicating inside human cells. Oregano
Oregano is more known as an herb that can be added into different dishes. But oregano oil has also gained popularity due to its antibacterial, anti-parasitic and antiviral properties. (Related: Carvacrol, a compound found in oregano, exhibits powerful antimicrobial properties .)
Aside from this, oregano oil has been found to have natural pain-killing properties, thanks to a study by Turkish researchers. The study authors noted in their June 1996 study that essential oil from the Greek oregano exhibits similar activity to conventional pain relief medicine, with the content of the compound carvacrol determining how effective its pain-killing properties are. Cinnamon
Cinnamon is commonly used to flavor baked goods for children. This fragrant herb – whether in the form of bark, powder or essential oil – also helps boost children’s health. When given to babies , cinnamon contributes positively to their brain development due to its phytochemicals that boost the brain’s ability to utilize glucose.
Cinnamon strengthens the immune system against mild to severe infection caused by pathogens. It also possesses antioxidant properties, making it a suitable herb for removing harmful substances in the body. Chamomile
Adults often drink chamomile tea to relax, but children can likewise benefit from drinking it. Chamomile naturally addresses anxiety, tension and nervousness, making it a good choice for helping children settle down before bedtime.
Hot chamomile tea relieves digestive problems in children such as stomach ache and colic, while cold tea relieves teething discomfort, nausea and diarrhea. Chamomile can also be used on wounds, insect bites and different skin conditions. Lemon balm
Similar to chamomile, children who experience anxiety or difficulty sleeping may find lemon balm to be helpful in calming them down. This herb is known for relieving mild anxiety, making it suitable for children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). (Related: Lemon balm is excellent survival medicine: Review of its medicinal properties and how to use it .)
A 2004 study showed that people who took a 600 milligram (mg) dose of lemon balm reported calmer moods following assessment. The same study has found that people taking 300 mg of lemon balm have reported improvements in cognitive function after a battery of tests. Thus, lemon balm not only helps relieve children’s anxiety – it also helps them concentrate. Safety precautions on these herbs
While these herbs are known for their healing properties, it is important to note that giving children too much of these may cause more harm than good. Most herb-based remedies come in the form of essential oils, so diluting them in base oils is advised before giving to children.
While some essential oils can be used directly, several kinds are not advised entirely for children under a certain age. Oregano and cinnamon essential oils are not advisable for use among children below two years. This is because their skin is extremely sensitive and their bodies metabolize oils differently compared to older children or adults.
Possible allergies to these herbs should also be monitored. While chamomile and cinnamon are generally safe for children, some may show allergic reactions to them. Symptoms include red spots where the herbs touch the skin, runny nose and watery eyes.
PlantMedicine.news has more articles about natural and child-friendly remedies.
Sources include:
OnlineLibrary.Wiley.com
Journals.LWW.com
Essential oil from this Turkish medicinal plant found to reduce dementia-related anxiety and depression

( Natural News ) A species of St. John’s wort ( Hypericum ) that’s native to Central Asia may alleviate depression and anxiety, especially for those with dementia. In a report published in the Journal of Essential Oil Research , researchers from Firat University in Turkey examined the anti-anxiety and anti-depression properties of Hypericum scabrum . Behavioral changes among those with dementia
Dementia isn’t a specific disease; rather, it’s the umbrella term for conditions which are marked by a decline in cognitive function and loss of functional independence . According to estimates from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 5 million people around the age of 65 have been diagnosed with a type of dementia, the most common of which is Alzheimer’s disease. Experts predict these figures could go as high as 14 million by 2060.
It’s easy to dismiss dementia as a part of normal aging. However, many older adults live their lives without developing dementia. While these individuals experience age-related memory changes, such as occasionally forgetting names and recent events, their knowledge, skills and experiences stay intact.
People with dementia also experience memory changes, but these cause them to get lost even in familiar places or ask questions repeatedly. Compared to those experienced by healthy older adults, these changes can disrupt daily life. People with dementia also have problems with attention, communication, visual perception and reasoning.
In addition, people with dementia suffer from behavioral and psychological symptoms . It’s very common for them to exhibit apathy, depression and anxiety. Four out of 10 patients with dementia suffer from depression, while nine out of 10 patients show apathy in the latter stages of the disease.
Anxiety , on the other hand, is often seen in patients who still have good insight and awareness of their condition , such as those suffering from vascular or frontotemporal dementia (FTD). It’s worth noting that the causes of anxiety for those with dementia are similar to those without the condition. They include having a history of traumatic events, extreme worry and damage to parts of the brain that regulate emotion. Hypericum scabrum has anxiolytic and anti-depressive properties
In their report, Turkish researchers looked at H. scabrum , a plant native to Central Asia and western China, and its potential as a treatment for dementia-related depression and anxiety. The plant has long been used in traditional medicine: In Uzbekistan, it is used to treat diseases ranging from cystitis to heart disease , while in southwest China, the plant is used as a local remedy . Meanwhile, folk healers in Iran use H. scabrum to relieve pain and treat headaches, among others.
For their study, the researchers examined the effects of H. scabrum essential oil on anxiety and depressive-like behavior using an animal model of dementia. They made rats inhale the essential oil regularly for three weeks. They then treated the rats with scopolamine, a drug that can induce memory deficits similar to those seen in older adults. After scopolamine treatment, they subjected the rats to behavioral tests.
The researchers found that rats treated with H. scabrum essential oil performed markedly better on tests than untreated ones, suggesting that the oil has anti-anxiety and antidepressant effects. (Related: St. John’s wort: A scientific review of its remarkable antibacterial and antioxidant properties .)
In a follow-up study, the team also explored the potential memory-enhancing properties of H. scabrum essential oil using a rat model of dementia. For this, the researchers evaluated how well the essential oil can improve the spatial memory of rats with dementia compared to conventional drug therapies (diazepam and tramadol). They found that H. scabrum essential oil can be used as a complementary therapy for reducing memory impairment in patients with dementia and similar diseases.
Learn more about natural treatments for dementia at Alzheimers.news .
Sources include:
CDC.gov
IJPRS.ir
3 Foods That Could Be Causing Your Bout of Brain Fog, and What RDs Recommend Eating Instead

e all know the feeling. It’s 3pm (or 3am), the edges have blurred, nothing is really registering, and it would be a challenge to tell someone your name—much less answer the question your boss just levied at you. It is not a hangover, you’re not under the weather or dealing with low blood sugar, and you actually got eight hours of sleep last night. So what gives? Chances are, you’re dealing with a minor bout of brain fog , a relatively common feeling that folks experience, sometimes without a clear catalyst.
“Brain fog is a term used to describe a feeling of not being able to think as sharply and clearly as you’re used to,” says Samantha Cassetty, RD . “Sometimes people say they feel fuzzy or cloudy, and it can be associated with peri-menopause and menopause.” That said, Cassetty adds that brain fog often exists in the absence of any known cause.
“Brain fog is not a medical condition, but rather a symptom,” says Keri Gans, RDN , in agreement. “There may be many factors, such as lack of sleep, too much sleep, depression, certain medications or illness, dehydration, or diet.” While it can be difficult to control many of these factors, there are certain foods that may amplify some of the symptoms associated with brain fog . We chatted with both Cassetty and Gans to learn more about the foods that may be making us a little more drowsy and a little less sharp—i.e. somewhere generally south of our usual mental clarity and focus A-game. 3 foods that contribute to brain fog, according to RDs
1. Heavily processed foods, including processed meat and sugary beverages
“In general, heavily-processed foods that are high in refined grains, added sugars, and sodium are likely culprits of brain fog,” says Cassetty. “Processed meats and artificial sweeteners may also be linked to brain fog.” These categories can indeed be applied to that sweet late-afternoon latte you were hoping would give you a mental boost.
Cassetty notes that when folks swap out heavily-processed foods for whole or minimally-processed plant foods, some will experience better mental clarity and energy. “Sometimes people don’t even realize how foggy they feel until they start feeling sharper by making some lifestyle adjustments,” she notes.
When it comes to choosing a snack that will help you focus, Maya Feller, MS, RD , recommends balancing fresh produce with lean protein or fat, and drinking plenty of water. “I encourage afternoon snacks that provide sustained energy, rather than heavily processed, sugary ones that give a boost followed by a crash,” she previously told Well+Good . Her number-one tip: “Combine nutrient-rich fruits or veggies that give quick energy and hydration with a lean protein or fat for staying power.” 2. Alcohol
Yes, sometimes, the culprit of your foggy feeling is indeed none other than alcohol. As such, experts recommend being careful about over-imbibing on a daily basis. “It is a good idea to stay within the alcohol limits of no more than one drink a day for women and no more than two drinks a day for men,” Cassetty recommends. While occasional celebrating is only natural, excessive consumption of alcohol is dangerous and linked to increased risk of chronic illness, liver disease, and insomnia, among many other serious health concerns.
If you’re in search of a beverage that will give your brain health a boost, try this delicious (and energizing) herbal tea made with cacao, rosemary, and other nootropics. According to herbalist Rachelle Robinett , nootropics are a great way to get a boost of energy and clarity. Since these herbs don’t have caffeine, you can sip the tea in the evening in place of your nightcap—plus they may help you feel “more balanced, which ultimately results in better energy,” she says.
Find the recipe and all of its brain-boosting benefits here: 3. A lack of fruits and vegetables
If you’re looking to cut processed foods, an easy way to do so is to opt toward fruits and vegetables in their purest form. “Fill half your plate with vegetables or fruits or a mix of the two,” Cassetty recommends. “If you’re not anywhere close to eating this way, don’t worry. Work your way up, starting with one meal or one snack. Numerous studies suggest that this eating pattern can sharpen thinking and improve memory and cognitive skills.”
Feller agrees, saying that two great brain-boosting snacks are veggies and a protein-packed dip (like hummus) or fruit. “Fruit’s a great choice in the afternoon as long as you balance it out with protein and fat, like a serving of nuts and one ounce of cheese.” You can also up your fruit intake by pairing dried fruit like raisins with nuts for a heart-healthy trail mix. RD tips and foods for preventing brain fog
In addition to keeping an eye on processed foods, alcohol, and a lack of fresh produce in your diet, there are other ways to reduce brain fog, experts say. “Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory-rich plant foods can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation that may induce the feeling of brain fog,” Cassetty notes. That means that instead of a piece of white toast, opt for whole-grain toast. Try to eat brown rice or quinoa in place of white rice, and switch from sugary cereals to whole-grain, low-sugar versions. The addition of fiber in these lesser-refined foods will help your blood sugar levels stay stable, which also helps with focus and mental clarity.
Moreover, it’s worth paying attention to the source of fat in your diet. Replace saturated fats with better-for-you unsaturated options like extra virgin olive oil and avocado oil when possible, and snack on avocados, walnuts, and chia seeds.
Gans and Cassetty both also strongly emphasizes the importance of brain-boosting behaviors, including resting, being active, and managing stress. “Aim to get 7-9 hours of sleep per night,” Gans says. Cassetty agrees, saying that “exercise, sleep, and finding healthy ways to cope with stress are all beneficial to your brain health and can help you prevent brain fog.”
All of this aside, it’s […]
Bone Marrow Butter

🖨️ Print post
Traditional peoples who consumed large animals did not ignore the marrow hidden away in the bones; in fact, they valued the marrow as an extremely nutritious food.
Weston A. Price provides us with a good example in his book Nutrition and Physical Degeneration : “For the Indians living inside the Rocky Mountain Range in the far North of Canada, the successful nutrition for nine months of the year was largely limited to wild game, chiefly moose and caribou. During the summer months the Indians were able to use growing plants. During the winter some use was made of bark and buds of trees. I found the Indians putting great emphasis upon the eating of the organs of the animals, including the wall of parts of the digestive tract. Much of the muscle meat of the animals was fed to the dogs. It is important that skeletons are rarely found where large game animals have been slaughtered by the Indians of the North. The skeletal remains are found as piles of finely broken bone chips or splinters that have been cracked up to obtain as much as possible of the marrow and nutritive qualities of the bones. These Indians obtain their fat-soluble vitamins and also most of their minerals from the organs of the animals. An important part of the nutrition of the children consisted in various preparations of bone marrow, both as a substitute for milk and as a special dietary ration.” Read more about bone marrow in our article on the topic. We previously published another variation of this recipe provided to us by Monica Corrado as well.
Despite bone marrow being a staple in the human diet for most of our existence, it’s not nearly as popular today as it once was. It’s starting to regain popularity in culinary circles and in fine-dining restaurants because of its unique, pleasant, and creamy taste. Ingredients
4 oz boiled or roasted organic, pasture raised bone marrow
(use bones to make a broth)
4 oz soft organic, pasture raised butter
1 tsp salt flakes
1 tsp dried ramps (optional) Instructions
Blend everything with immersion blender. Use as you would butter. It tastes so much better than a butter; it has a sweet, nutty flavor and a lighter, more delicate texture.
🖨️ Print post
🖨️ Print post
Learn about the meaning behind our logo above.
This is a Web version of 28-page printed informational 28-page printed informational booklet . You may order printed copies via our Store.
The Weston A. Price Foundation only accepts contributions from members and/or private donations, and does not accept funds from the meat or dairy industries. Life in all its splendor is Mother Nature obeyed. – Weston A. Price, DDS
Contents
About Dr. Weston A. Price
Characteristics of Traditional Diets – 11 Principles
Dietary Guidelines
Dietary Dangers
Confused about Fats?
The Many Roles of Saturated Fats
The Fat-Soluble Activators
What’s Wrong With “Politically Correct” Nutrition?
Traditional vs. Modern Diets
Myths and Truths About Nutrition
Myths and Truths About Soy
Soy Infant Formula: Birth Control Pills for Babies
Coronary Heart Disease: What the Expert Say
Principles of Holistic Dentistry
The Weston A. Price Foundation
Become a Member of the Weston A. Price Foundation About Dr. Weston A. Price
In the early 1930s, a Cleveland dentist named Weston A. Price (1870-1948) began a series of unique investigations. His portrait on the left is provided courtesy of the Price-Pottenger Nutrition Foundation who owns the copyright.
For over ten years, he traveled to isolated parts of the globe to study the health of populations untouched by western civilization. His goal was to discover the factors responsible for good dental health. His studies revealed that dental caries and deformed dental arches resulting in crowded, crooked teeth are the result of nutritional deficiencies, not inherited genetic defects.
The groups Price studied included remote villages in Switzerland, Gaelic communities in the Outer Hebrides, indigenous peoples of North and South America, Melanesian and Polynesian South Sea Islanders, African tribes, Australian Aborigines and New Zealand Maori. Wherever he went, Dr. Price found that beautiful straight teeth, freedom from decay, good physiques, resistance to disease and fine characters were typical of native groups on their traditional diets, rich in essential nutrients.
When Dr. Price analyzed the foods used by isolated peoples he found that, in comparison to the American diet of his day, they provided at least four times the water-soluble vitamins, calcium and other minerals, and at least TEN times the fat-soluble vitamins, from animal foods such as butter, fish eggs, shellfish, organ meats, eggs and animal fats—the very cholesterol-rich foods now shunned by the American public as unhealthful. These healthy traditional peoples knew instinctively what scientists of Dr. Price’s day had recently discovered—that these fat-soluble vitamins, vitamins A and D, were vital to health because they acted as catalysts to mineral absorption and protein utilization. Without them, we cannot absorb minerals, no matter how abundant they may be in our food. Dr. Price discovered an additional fat-soluble nutrient, which he labeled Activator X, that is present in fish livers and shellfish, and organ meats and butter from cows eating rapidly growing green grass in the spring and fall. All indigenous groups had a source of Activator X, now thought to be vitamin K2, in their diets.
The isolated groups Dr. Price investigated understood the importance of preconceptual nutrition for both parents. Many tribes required a period of special feeding before conception, in which nutrient-dense animal foods were given to young men and women. These same foods were considered important for pregnant and lactating women and growing children. Price discovered them to be particularly rich in minerals and in the fat-soluble activators found only in animal fats.The isolated people Price photographed—with their fine bodies, ease of reproduction, emotional stability and freedom from degenerative ills—stand in sharp contrast to civilized moderns subsisting on the “displacing foods of modern commerce,” including sugar, white flour, […]
Why is eating large amounts of processed meat bad for your health? It comes down to the toxic additives and preservatives

( Natural News ) The lean component of red meat is an excellent source of essential nutrients . According to a study published in the journal Nutrition & Dietetics , you can get vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6 and B12 from red meat, as well as minerals like iron, phosphorus, selenium and zinc. The lean component of red meat is also a great source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which offer significant benefits for your heart and brain. In addition, phytochemical analysis reveals that it is rich in endogenous antioxidants and bioactive components like taurine, carnitine, glutathione and creatine that support overall health.
But despite all of these nutritional benefits, eating large amounts of red meat is still considered unhealthy. This prompted a team of Spanish researchers to investigate why frequent consumption of red meat increases health risks . In their report, which appeared in the journal Food Science and Human Wellness , the researchers attributed its negative effects to the presence of “substances of safety concern” in various meat products. These harmful chemicals are linked to certain food additives and are generated when red meats are subjected to various types of processing. The dangerous chemicals in red and processed meats
According to numerous studies, there is a clear link between high intake of red and processed meats and an increased risk for heart disease, diabetes , cancer and premature death. Among these negative consequences, cancer is the most commonly associated with diets that include large portions of meat. (Related: RED MEAT and CANCER – more than just a “correlation” .)
In a 2015 report released by the World Health Organization , the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified all kinds of red meat (i.e., beef, veal, pork, lamb, mutton, horse and goat) as Group 2A, or probably carcinogenic to humans , and processed meats (e.g., fried, salted, cured, fermented or smoked) as Group 1, or carcinogenic to humans. The IARC based their classification on limited evidence from epidemiological studies for red meat and sufficient evidence for processed meats.
To further explore existing evidence, the Spanish researchers reviewed studies that focused on the carcinogenic compounds found in meat products and the mechanisms by which they are generated. They listed the following toxic chemicals as substances of safety concern in meats : N-nitrosamines — Also called N-nitroso compounds, these carcinogens are formed via the reaction between nitrite, a common food additive, and secondary amines, which are produced when the proteins in meat are degraded during cooking. Studies show that N-nitroso compounds can induce cancer in at least 40 animal species , including humans.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) — PAHs are naturally occurring chemicals produced when coal, gas, wood or tobacco are burned . They also form in meats when meats are grilled or charred. According to studies, activated PAHs can induce multiple mutations in cancer genes that could result in tumor formation.
Heterocyclic aromatic amines (HCAs) — Like PAHs, HCAs are formed when meats are cooked using high temperature methods like pan frying or grilling. When amino acids, sugars, creatine or creatinine are exposed to high heat (above 300 F), they produce HCAs. These carcinogens also cause DNA damage that can lead to the development of breast, colon, liver, skin, lung and prostate tumors.
Maillard reactions products (MRPs) — The Maillard reaction, also known as non-enzymatic browning , refers to the chemical reaction that occurs when foods are cooked at high temperatures. Studies show that frying meats promotes the formation of an MRP called acrylamide . This compound is broken down inside the body and forms glacidamide , which causes DNA mutations that can damage the nervous system and trigger cancer development.
Biogenic amines (BAs) — BAs are nitrogen-containing compounds found in fermented meats like sausages. They are produced through the decarboxylation of amino acids by fermentative bacteria . BAs are the precursors to carcinogenic N-nitrosamines ; when present at high levels in food, they can cause headaches, nausea, rashes and unwanted changes in blood pressure.
According to the Spanish researchers, knowledge of these substances and their generation routes is important as it facilitates the assessment of the safety of meat products. It could also help food scientists come up with ways to reduce or eliminate the presence of these substances of concern in meats , making them much safer sources of nutrition.
Sources include:
OnlineLibrary.Wiley.com 1
OnlineLibrary.Wiley.com 2
WHO.int
ScienceDirect.com 1
ScienceDirect.com 2
ScienceDirect.com 3
CDC.gov
Cancer.gov
Hindawi.com
NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
Bone Marrow Custard

Print post
My version is based off this recipe from Kasey Culinary Adventures . Learn about the benefits of bone marrow in one of our articles! Ingredients
5 lbs beef marrow bones, unsliced
1 cup of cream
3 egg yolks
3 whole eggs
1 Tbs vanilla extract
2 teaspoons honey or maple syrup — optional
½ teaspoon of sea salt
1 tablespoon of cinnamon, or to taste
Instructions
In bowl, combine marrow (try not to include the oil), 1 cup cream, 3 egg yolks, 3 whole eggs, 2 tsp honey or maple syrup (optional), cinnamon to taste, dash of sea salt. Blend all together.
Pour into custard cups or cake pans (I used 2, 5” cake pans) and place those in a water bath.
In oven preheated to 350°F, bake until center is set. My pans took 40 minutes. Turn off oven and open door, allowing water bath to cool.
Print post
Print post
Learn about the meaning behind our logo above.
This is a Web version of 28-page printed informational 28-page printed informational booklet . You may order printed copies via our Store.
The Weston A. Price Foundation only accepts contributions from members and/or private donations, and does not accept funds from the meat or dairy industries. Life in all its splendor is Mother Nature obeyed. – Weston A. Price, DDS
Contents
About Dr. Weston A. Price
Characteristics of Traditional Diets – 11 Principles
Dietary Guidelines
Dietary Dangers
Confused about Fats?
The Many Roles of Saturated Fats
The Fat-Soluble Activators
What’s Wrong With “Politically Correct” Nutrition?
Traditional vs. Modern Diets
Myths and Truths About Nutrition
Myths and Truths About Soy
Soy Infant Formula: Birth Control Pills for Babies Coronary Heart Disease: What the Expert Say Principles of Holistic Dentistry The Weston A. Price Foundation Become a Member of the Weston A. Price Foundation About Dr. Weston A. Price In the early 1930s, a Cleveland dentist named Weston A. Price (1870-1948) began a series of unique investigations. His portrait on the left is provided courtesy of the Price-Pottenger Nutrition Foundation who owns the copyright.For over ten years, he traveled to isolated parts of the globe to study the health of populations untouched by western civilization. His goal was to discover the factors responsible for good dental health. His studies revealed that dental caries and deformed dental arches resulting in crowded, crooked teeth are the result of nutritional deficiencies, not inherited genetic defects. The groups Price studied included remote villages in Switzerland, Gaelic communities in the Outer Hebrides, indigenous peoples of North and South America, Melanesian and Polynesian South Sea Islanders, African tribes, Australian Aborigines and New Zealand Maori. Wherever he went, Dr. Price found that beautiful straight teeth, freedom from decay, good physiques, resistance to disease and fine characters were typical of native groups on their traditional diets, rich in essential nutrients.When Dr. Price analyzed the foods used by isolated peoples he found that, in comparison to the American diet of his day, they provided at least four times the water-soluble vitamins, calcium and other minerals, and at least TEN times the fat-soluble vitamins, from animal foods such as butter, fish eggs, shellfish, organ meats, eggs and animal fats—the very cholesterol-rich foods now shunned by the American public as unhealthful. These healthy traditional peoples knew instinctively what scientists of Dr. Price’s day had recently discovered—that these fat-soluble vitamins, vitamins A and D, were vital to health because they acted as catalysts to mineral absorption and protein utilization. Without them, we cannot absorb minerals, no matter how abundant they may be in our food. Dr. Price discovered an additional fat-soluble nutrient, which he labeled Activator X, that is present in fish livers and shellfish, and organ meats and butter from cows eating rapidly growing green grass in the spring and fall. All indigenous groups had a source of Activator X, now thought to be vitamin K2, in their diets.The isolated groups Dr. Price investigated understood the importance of preconceptual nutrition for both parents. Many tribes required a period of special feeding before conception, in which nutrient-dense animal foods were given to young men and women. These same foods were considered important for pregnant and lactating women and growing children. Price discovered them to be particularly rich in minerals and in the fat-soluble activators found only in animal fats.The isolated people Price photographed—with their fine bodies, ease of reproduction, emotional stability and freedom from degenerative ills—stand in sharp contrast to civilized moderns subsisting on the “displacing foods of modern commerce,” including sugar, white flour, pasteurized milk, lowfat foods, vegetable oils and convenience items filled with extenders and additives.The discoveries and conclusions of Dr. Price are presented in his classic volume, Nutrition and Physical Degeneration. The book contains striking photographs of handsome, healthy, indigenous people that illustrate in an unforgettable way the physical degeneration that occurs when human groups abandon nourishing traditional diets in favor of modern convenience foods.The photographs Dr. Weston Price took illustrate the difference in facial structure between those on native diets and those whose parents had adopted the “civilized” diets of devitalized processed foods. The “primitive” Seminoles pictured on the left have wide, attractive faces with plenty of room for the dental arches. The “modernized” Seminole girl on the right, born to parents who had abandoned their traditional diets, has a narrowed face, crowded teeth and a reduced immunity to disease. Photos courtesy of the Price-Pottenger Nutrition Foundation , who owns the copyrights. All rights reserved. Characteristics of Traditional Diets – 11 Principles> The diets of healthy, nonindustrialized peoples contain no refined or denatured foods or ingredients, such as refined sugar or high fructose corn syrup; white flour; canned foods; pasteurized, homogenized, skim or lowfat milk; refined or hydrogenated vegetable oils; protein powders; synthetic vitamins; or toxic additives and artificial colorings. All traditional cultures consume some sort of animal food, such as fish and shellfish; land and water fowl; land and sea mammals; […]
Mexico City sinking at “unstoppable rate” of up to 20 inches a year, study finds
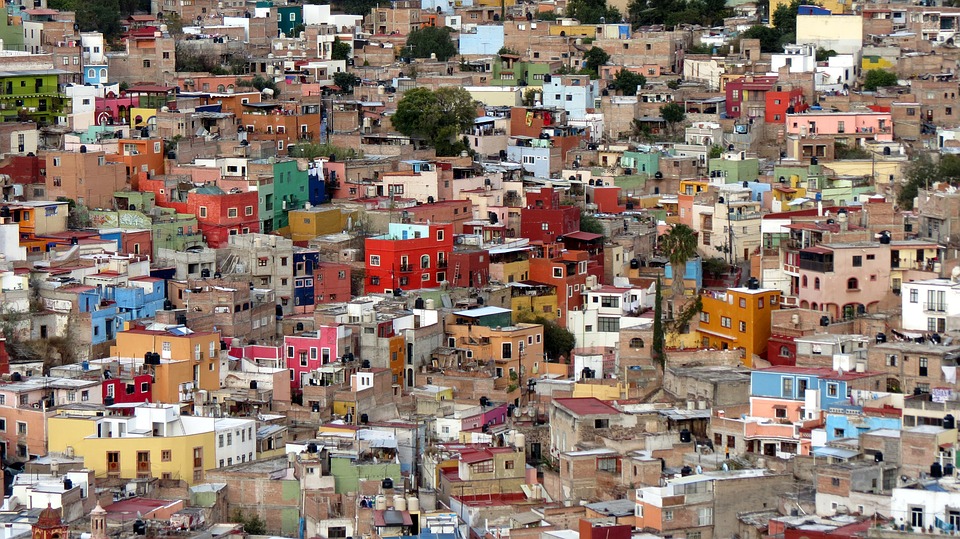

( Natural News ) A recent study found that Mexico City is sinking at a rate of up to 20 inches per year . Researchers explained that this unstoppable plunge occurs because the ground on which the city rests is rapidly compacting after being drained of water by decades of groundwater extraction.
The Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico is built on what was once Lake Texcoco, home of the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan. Also called the Greater Mexico City, the crowded metropolis encompasses Mexico City and other surrounding areas. It obtains more than three-quarters of its drinking water from beneath the ground. But water extraction in the region dates back several centuries, beginning during colonial Mexico .
This long-term pumping pushed the groundwater further underground, drying the lake bed so much that clay sheets began to crack and compress. With the earth repacking itself more tightly, the ground started to shrink and subside.
Authorities first noticed that Greater Mexico City was sinking in 1900 when the metro was sliding at a rate of around 3.5 inches a year. When the government placed a cap on water extraction in the late 1950s, it was sinking 11 inches a year.
The cap slowed the rate of sinking back to 3.5 inches a year but failed to eradicate the problem. In the years since, land subsidence worsened as the metro’s population ballooned to 21 million and urbanization increased exponentially.
The study, which was published March in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth , showed that parts of the city, including the historic downtown in Mexico City, are now sinking up to 16 inches a year. In the underdeveloped northeast, the ground is dipping 20 inches a year. If the northeast were to become more industrialized, land subsidence would get even worse. (Related: The San Joaquin Valley is rapidly sinking due to groundwater extraction… some areas have fallen 28 feet… and it’s accelerating .)
The aquifer system beneath the metro was 17 percent compacted as of 2020. After analyzing more than a century of data, including recent satellite information, researchers predicted that the aquifer system would compact further to 30 percent, causing the metro to sink almost 100 feet in the next century.
The lost elevation is irreversible, leaving the region vulnerable to plenty of disasters. For one, subsidence makes the metro more prone to heavy flooding, which, in turn, can cause water shortages since floods can pollute the groundwater. Subsidence in the metro also fractures the ground , which previously damaged buildings, historical sites, sewers, and gas and water lines. This fracturing can also open up the earth to contaminated surface water, which can further restrict access to potable water.
“The stage is set for a dual water and subsidence crisis if no drastic water management actions are implemented,” the researchers concluded in their paper. What is land subsidence?
According to the U.S. Geological Survey , land subsidence occurs when large amounts of groundwater are withdrawn from certain types of rocks, such as fine-grained sediments. Rocks compact because groundwater is partly responsible for holding the ground up. When sufficient amounts of groundwater is withdrawn, rocks fall in on itself, causing the ground to sink.
Land subsidence affects more than 17,000 square miles in the U.S., or roughly the size of New Hampshire and Vermont combined. More than 80 percent of these sank due to the exploitation of groundwater, as well as the increased development of land and water resources.
California experiences the greatest losses in elevation among 45 states affected by land subsidence. In the San Joaquin Valley, some areas sank by as much as 28 feet since record-keeping began. Water pumping is intensive in the region, which is one of the most productive agricultural lands in the country. Over time, over-pumping dramatically reduced groundwater levels, drying out the aquifer system and causing it to compact.
Visit Environ.news to learn more about how human activities like intensive agriculture damage the environment.
Sources include:
EOS.org
USGS.gov 1
( Natural News ) Researchers at the University of Washington found that cadmium exposure, combined with a genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease, might accelerate cognitive decline. The researchers arrived at this finding after exposing mice with an Alzheimer’s risk gene to cadmium. They detailed their findings in a paper published in the journal Toxicological Sciences . The effects of cadmium plus an Alzheimer’s risk gene
The so-called human apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene codes for a protein called apolipoprotein. This combines with fats to form lipoproteins, which carry cholesterol through the bloodstream. The APOE4 gene is a variant of the APOE gene. It significantly raises a person’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s , which is why it is considered an Alzheimer’s risk gene.
For their study, the researchers wanted to know how being carrier of this gene, combined with exposure to cadmium, affects cognition. Cadmium is a heavy metal that is extremely toxic to the brain. It occurs naturally and is extracted during the production of copper, lead and zinc. Cigarette smoke and polluted air also contain this toxin.
Over a period of 14 weeks, the researchers gave a group of mice with the APOE4 or the APOE3 gene water that contained low doses of cadmium. APOE3 is another variant of the APOE gene. It is widespread, with around half of the population carrying it.
The maximum amount of cadmium that the mice ingested was equivalent to the amount that Americans have in their blood, including people who never smoked .
As part of their experiment, the researchers put the rats through standard novel object location tests and T-maze tests, both of which engage the hippocampus, a region of the brain that is crucial for learning and memory. The hippocampus is one of the brain areas that is damaged the most during the early stages of Alzheimer’s.
The mice that ingested cadmium performed worse in the novel object location tests than untreated mice, indicating poorer short-term spatial working memory. This deficit in memory appeared earlier in mice with the APOE4 gene than those with APOE3, and earlier […]
Animal study reveals cadmium exposure and Alzheimer’s risk gene may be linked to cognitive impairment

( Natural News ) Researchers at the University of Washington found that cadmium exposure, combined with a genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease, might accelerate cognitive decline. The researchers arrived at this finding after exposing mice with an Alzheimer’s risk gene to cadmium. They detailed their findings in a paper published in the journal Toxicological Sciences . The effects of cadmium plus an Alzheimer’s risk gene
The so-called human apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene codes for a protein called apolipoprotein. This combines with fats to form lipoproteins, which carry cholesterol through the bloodstream. The APOE4 gene is a variant of the APOE gene. It significantly raises a person’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s , which is why it is considered an Alzheimer’s risk gene.
For their study, the researchers wanted to know how being carrier of this gene, combined with exposure to cadmium, affects cognition. Cadmium is a heavy metal that is extremely toxic to the brain. It occurs naturally and is extracted during the production of copper, lead and zinc. Cigarette smoke and polluted air also contain this toxin.
Over a period of 14 weeks, the researchers gave a group of mice with the APOE4 or the APOE3 gene water that contained low doses of cadmium. APOE3 is another variant of the APOE gene. It is widespread, with around half of the population carrying it.
The maximum amount of cadmium that the mice ingested was equivalent to the amount that Americans have in their blood, including people who never smoked .
As part of their experiment, the researchers put the rats through standard novel object location tests and T-maze tests, both of which engage the hippocampus, a region of the brain that is crucial for learning and memory. The hippocampus is one of the brain areas that is damaged the most during the early stages of Alzheimer’s.
The mice that ingested cadmium performed worse in the novel object location tests than untreated mice, indicating poorer short-term spatial working memory. This deficit in memory appeared earlier in mice with the APOE4 gene than those with APOE3, and earlier in males than females with the same genetic makeup.
Later in life, mice with the APOE4 gene performed worse in the T-maze test than those with APOE3. This indicated a reduced tendency to explore new environments and therefore poorer short-term spatial working memory. In addition, the researchers found that cadmium exposure negatively impacts nerve cell development in the hippocampus of male mice with the APOE4 gene. Cadmium pools in the brain due to Alzheimer’s risk gene
These findings led the researchers to conclude that interactions between the APOE4 gene and cadmium accelerates cognitive decline, with young male mice being more susceptible to this effect than young females. The researchers pointed to impaired nerve cell development in the hippocampus as one of the underlying mechanisms, which possibly occurs because the APOE4 gene lets cadmium into the brain.
“It is possible that APOE4 may cause leakage on the blood-brain barrier and lead to a higher degree of cadmium accumulation in the APOE4 brain,” the researchers wrote. (Related: Cadmium could have adverse effects on brain development, reducing neurogenesis .)
Zhengui Xia, a professor of toxicology at Washington University and one of the study’s researchers, commented: “Exposure to cadmium through our daily lives could have a detrimental effect on our cognition. If you have the APOE4 gene, the risk is significantly higher.”
“This heavy metal is bad for you,” she added.
Follow HeavyMetals.news to learn more about the health risks of cadmium and other heavy metals.
Sources include:
Academic.OUP.com
Matcha Vs Green Tea: What Is The Difference?
One of the most powerful drinks and a healthy beverage green tea is something which has been popularised for years now and is known for the various health benefits it comes with from keeping your heart healthy to aiding weight loss and from improving the brain function to helping prevent cancer this drink can do it all. While we all were busy enjoying the benefits of green tea and sipping a hot cup in the morning a new similar kind of beverage, Matcha emerged and has taken over the internet and especially the social media websites. Here let us understand about the health benefits of both these drinks, the difference between them and some quick and amazing recipes that you can enjoy, as explained below by Nutritionist And Public Health Expert Swati Bathwal . Green Tea
here could be nothing better and healthier than starting your day with a nice cup of green tea along with some honey and a few drops of lemon. Green tea is known to be one of the most healthy beverages which helps to detoxify your body, is good for your skin and hair and is also proven to lower the risk of various types of cancers. Let us take a closer look at the health benefits of drinking green tea.
Also Read: 5 Health Benefits Of Drinking Green Tea Everyday 1# Prevents Type 2 Diabetes
As type 2 diabetes has been increasing rapidly at a very high rate all over the world, an easy solution which helps to improve the insulin sensitivity green tea helps to reduce the blood sugar levels in the body which is usually increased by the body’s inability to produce insulin naturally which is the reason behind the body’s elevating blood sugar levels. 2# Aids weight loss
Rich in antioxidants and low in calories , green tea is a magical beverage that aids fat burning and weight loss due to the presence of catechins compounds in it by boosting the metabolic rate and improving the overall digestive system. Green tea helps to reduce the dangerous fat in the abdominal region by boosting the metabolism rate in a short span of time and helps in reducing the weight size, body fat, belly fat, body weight and the overall body fat percentage as well. 3# Lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases
With heart attacks being one of the leading causes of deaths world wide, green tea is a beverage that can lower the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases is consumed on a regular basis. This light and aromatic drink helps in lowering the lower LDL cholesterol levels and triglycerides which as a result lowers the risk of getting a heart attack or stroke hence is considered to be healthy for heart . 4# Helps prevent cancer
Not just by preventing but also by lowering the risk of a chronic disease like cancer green tea helps in reducing inflammation and prevent various types of cancer like breast cancer, prostate cancer, mouth cancer, stomach cancer, kidney cancer, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer , cancer in mammary glands and pancreas, Cancer is a deadly disease caused by the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells in the body is becoming one of the leading cause of death worldwide. Consuming green tea on a regular basis can actually reduce the risk of getting this chronic deadly disease as it consists of antioxidants and is rich in polyphenols, it helps in reducing inflammation and fight the inflammation causing oxidative stress. Green Tea Recipe
As we now know about the different health benefits a cup of green tea comes with, let us take a quick run through the quick and green tea recipe that you can enjoy early in the morning.
Ingredients Green tea bag
1 tablespoon of honey
3-4 drops of lemon juice
1 cup water
How to Make? Take a cup of water and boil it on medium flame.
Once boiled, transfer the water to a cup and add honey and lemon juice to it.
Stir it well and add the tea bag to the cup and let it steep in for 3-5 minutes.
Matcha
A Japanese beverage that has skyrocketed popularly lately, Matcha comes in many forms and is an ingredient which has various uses and health benefits. This beverage can be found on most of the coffee shops around and hasn’t failed to show its presence all over the social media websites. With high antioxidant content matcha can help to protect your lover and might also be helpful in preventing cancer. Let us dig a little deeper into the health benefits this trending drink has. 1# Helps to protect the Liver
Matcha decreases the risk of liver diseases by preventing liver damage. Researches have shown that matcha supports the liver’s natural detoxification process and is proven to control the liver enzymes as high amounts of liver enzymes can be dangerous for the liver and can cause damage. 2# Boosts Brain Functioning
Rich in polyphenols matcha is also known as the brain booster which when consumed on a regular basis helps to enhance memory, improve attention span and faster the reaction time. Its nutritional properties act as a nootropic that helps in boosting the cognitive functions of the body like attention, memory, concentration and motivation along with making the brain work as a vasodilator and makes it healthier by increasing the flow of oxygen to the brain. 3# Promotes Heart Health
Known for promoting a healthy heart by reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes matcha helps in reducing both cholesterol LDL levels and triglycerides. The nutrients present in matcha can help in achieving peace of mind, elevating ood, weight loss in people suffering from obesity and the presence of antioxidants, caffeine, amino acids, vitamins, minerals and fibre can help to fight morbid illness. Matcha Latte Recipe
An easy recipe to prepare a rejuvenating and nutritious cup of matcha latte to enjoy […]
Study: Extreme adiposity associated with obesity starts with inflammation in the brain

( Natural News ) Obesity is a metabolic disease that is now considered to be an epidemic. In the United States, obesity is a major contributor to some of the leading causes of death among Americans, which include heart disease, diabetes and some types of cancer.
The main defining feature of obesity is the excessive accumulation and storage of body fat . Researchers have identified several contributing factors to this abnormal event, such as genetics and behavioral, metabolic and hormonal influences on body weight. But the culprit most commonly associated with obesity is the intake of too many calories coupled with a lack of exercise or physical activity. As pointed out by many studies, calories that are not burned through physical activities are stored by the body as fat.
Not surprisingly, the adult obesity rate in the U.S. is considerably high , exceeding 40 percent, because the standard American diet is made up of mostly sugar-laden beverages and fatty, highly processed foods. Aside from providing very little nutrients, research has found that these high-calorie foods make a person eat more than he actually needs because they are not satiating. This, combined with a sedentary lifestyle, is behind the alarming rise in both childhood and adult obesity rates seen in the country. The link between inflammation and obesity
In an effort to understand what drives obesity at the molecular level, researchers at Ewha Womans University in South Korea decided to explore the mechanisms that lead to obesity . Their study, which appeared in the journal Nutrition Research, focused mainly on inflammation. Chronic inflammation has been linked to obesity and other serious conditions like heart disease and cancer.
According to an article published in Science , alterations in the gene sequence and increased expression of RIPK1 , a key regulator of inflammation, are some of the main contributors to metabolic disease. When researchers inhibited the expression of RIPK1 in mice on a high-fat diet, they found that it not only reduced inflammatory responses, but also body weight and fat accumulation. This suggests that this inflammatory gene plays a crucial role in the development of obesity .
For their study, however, the Korean researchers focused on a mechanism that has only been proposed recently. This mechanism also involves inflammation, albeit in the brain instead of adipose tissue. Recent studies suggest that inflammation in the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that governs systemic metabolism, may also be a driving force behind obesity. (Related: Researchers conclude that drinking soda during pregnancy causes obesity in offspring .)
The researchers hypothesized that a high-fat diet could trigger metabolic inflammation via transcriptional changes (i.e., changes in gene expression) in the hypothalamus. To test their hypothesis, they characterized obesity-related in vivo transcriptional alterations in the hypothalamus and their effects on functional networks.
The researchers fed two groups of mice either a control diet or a high-fat diet for 20 weeks before conducting microarray and gene ontology analyses of the animals’ hypothalami. They reported that in the brains of mice on a high-fat diet, immune-related pathways such as inflammatory signaling were overly activated. This was not the case with mice on the control diet.
Meanwhile, in mice deficient in leptin — the hormone released by fat cells to tell the brain, particularly the hypothalamus, to suppress appetite — the researchers found that genes involved in inflammatory pathways and cancer pathways were highly expressed. They noted a similar overexpression in the hypothalami of mice on a high-fat diet, which confirms their hypothesis that brain inflammation is heavily involved in obesity.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that, rather than dietary fat and genetic mutation, inflammation in the hypothalamus is likely to be the cause of excessive fat accumulation associated with obesity.
Sources include:
Science.news
CDC.gov
TFAH.org
HSPH.Harvard.edu
The science of why the sun makes us feel so happy

With the hottest day of the year so far coinciding with the last step in the Government’s lockdown roadmap, it is clear that the sun has put many of us in a cheerful mood, especially after the dark winter spent indoors.
Although we are not able to go to many of the popular sun spots across the globe, this summer has shown that we are able to soak up the rays in the UK and that provides us with the feel good factor that we may have missed in the past 18 months.
But what is it about the sunshine that makes us feel so happy? Here is the science behind why those rays are so good for us. It boosts our mood
Most of us will agree that it’s hard to feel unhappy in the sun. This is down to the link between sunlight and our serotonin levels – the hormone that makes us feel happy. It’s also why people are more likely to develop Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) when the shorter autumn days arrive and we creep into winter with fewer daylight hours.
There is plenty of research to back up this idea. One study undertaken in Australia found that people had higher levels of serotonin on bright sunny days than cloudy ones. Increased levels of this hormone generally lead to greater feelings of satisfaction and calmness and lower levels of depression and anxiety.
There is even research to show that people who use tanning beds may experience more frequent feelings of euphoria, which could explain why people develop a dependence on regular sessions. Although the connection isn’t entirely established yet, researchers speculate this could be down to the way UV light forces melanocytes, the cells that produce dark pigment in skin, to release endorphins. However, most experts also agree that the increased sun cancer risk negates the feel good factor. Sun improves our sleep
Regular exposure to sunlight encourages the production of melatonin – the hormone which helps to regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle. This encourages feelings of drowsiness, allowing us to drift off easier at night, which leads to us feeling happier in the day. Melatonin also helps to regulate our circadian rhythm – the body’s internal clock that signals when to be alert and when to rest – which can be thrown out of sync by exposure to blue light from technology, disrupted work patterns and light pollution.
In turn, this allows us to feel happier. Research shows that our amygdala – the emotional part of the brain – is significantly more reactive after a bad night’s sleep, meaning we are more likely to feel cranky throughout the day if we have spent the night tossing and turning. Time spent in the sun can help us sleep soundly. Our sex drive is given a lift
Believe it or not, even our sex drive is affected by time spent in the sun, so a spring heatwave is good news for those who have found their libido dampened somewhat in lockdown. Researchers at Medical University of Graz in Austria found that spending just one hour in the sun can boost a man’s testosterone levels by 69 per cent. In turn, this helps to balance mood, sex drive and cognitive function. The experts put this down to the role of vitamin D, which is produced after exposure to sunlight .
It’s the same situation for women. Researchers in China, who conducted a study on post-menopausal women, identified a link between low levels of vitamin D and low levels of oestrogen, the female sex hormone. Your bones will be given a boost
Vitamin D is also crucial for helping our body to absorb calcium, which is responsible for strengthening your bones. A lack of vitamin D has been associated with both osteoporosis, rickets and autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
A review by the Cochrane Library found that the rates of falls in elderly people – which are partly down to the effects of brittle bones – could be cut by more than a quarter if the elderly were given supplements of vitamin D. However, in recent years many studies have questioned how effective supplements are in reducing rates of osteoporosis.
That’s not to say that sunlight can’t help though: more than 90 per cent of a person’s vitamin D requirement tends to come from casual exposure to sunlight, making it the best source of the nutrient. So how much exposure do we need to boost our health? On average, experts believe we should be aiming for 10–30 minutes of midday sunlight, several times per week. So make sure you head outside for a walk today to get a boost of bone-strengthening vitamin D. It improves midlife brain health
While most of the research around sunlight and the brain has focused on serotonin levels, a dose of vitamin D could also be good for our intellect. In 2009, scientists from the University of Manchester found that higher levels of vitamin D are linked with improved mental ability in middle-aged and older men. Men in the study were tested for memory and speed recollection, as well as for mood and physical activity levels, before their blood samples were taken. The researchers found that men with higher levels of vitamin D performed consistently better than those with lower levels. Your eyes need sunlight
Dr Rangan Chatterjee, GP and author of Feel Great, Lose Weight , explains that light is measured in a unit called lux: if we spend 20 minutes outside – even on a cloudy overcast day – we are exposed to around 10,000 lux, compared with 500 lux if we spend time indoors. This is particularly important for children. Researchers at King’s College London, the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, found that regular exposure to sunlight lowered the risk of nearsightedness – or myopia – in children and young adults by helping the eye produce dopamine, which aids in healthy eye development.
Exposure to natural light can also help […]
Breakthrough brain implant allows paralysed man to ‘speak’ by transcribing his thoughts
Paralyzed Speech Device (Photographs©2017 Barbara Ries. All rights reserved. 415-460-1440) An experimental brain implant that translates brain signals into words has been a success, say researchers in California.
It’s a major step towards the development of a technology that could help people communicate by thinking, potentially changing the lives of those who lose the ability to speak through injury or illness.
Scientists at the University of California, San Francisco, worked with a man in his 30s who suffered a paralysing stroke more than 15 years ago and lost the ability to speak, reports the Wall Street Journal . He agreed to have electrodes surgically attached to the outer surface of his brain to test the neuroprosthesis.
The experiment was detailed in a paper published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Over the course of 50 separate sessions, the researchers recorded the man’s brain activity as he observed words displayed on a screen and imagined saying them aloud.
The researchers said they could identify the word the man was saying almost half the time, which rose to 76% when the scientists incorporated word-prediction algorithms.
“To our knowledge, this is the first successful demonstration of direct decoding of full words from the brain activity of someone who is paralyzed and cannot speak,” said neurosurgeon Dr. Eddie Chang, the paper’s senior author. “It shows strong promise to restore communication by tapping into the brain’s natural speech machinery.”
Experts say the high error rate, limited vocabulary – this study used just 50 words – and the time it takes to train the system to recognise imagined words mean there’s still a long way to go before the technology could be used practically in the real world.
However, the experiment has shown that the brain region responsible for speech continues to function even years after the ability to speak has been lost and that computers can be taught to decode full words from brain activity.
Read More


