Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Cognitive neuroscience could pave way for emotionally intelligent robots

Human beings have the ability to recognize emotions in others, but the same cannot be said for robots. Although perfectly capable of communicating with humans through speech, robots and virtual agents are only good at processing logical instructions, which greatly restricts human-robot interaction (HRI). Consequently, a great deal of research in HRI is about emotion recognition from speech. But first, how do we describe emotions?
Categorical emotions such as happiness, sadness, and anger are well-understood by us but can be hard for robots to register. Researchers have focused on “dimensional emotions,” which constitute a gradual emotional transition in natural speech. “Continuous dimensional emotion can help a robot capture the time dynamics of a speaker’s emotional state and accordingly adjust its manner of interaction and content in real time,” explains Prof. Masashi Unoki from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), who works on speech recognition and processing.
Studies have shown that an auditory perception model simulating the working of a human ear can generate what are called “temporal modulation cues,” which faithfully capture the time dynamics of dimensional emotions. Neural networks can then be employed to extract features from these cues that reflect this time dynamics. However, due to the complexity and variety of auditory perception models, the feature extraction part turns out to be pretty challenging.
In a new study published in Neural Networks , Prof. Unoki and his colleagues, including Zhichao Peng, from Tianjin University, China (who led the study), Jianwu Dang from Pengcheng Laboratory, China, and Prof. Masato Akagi from JAIST, have now taken inspiration from a recent finding in cognitive neuroscience suggesting that our brain forms multiple representations of natural sounds with different degrees of spectral (i.e., frequency) and temporal resolutions through a combined analysis of spectral-temporal modulations. Accordingly, they have proposed a novel feature called multi-resolution modulation-filtered cochleagram (MMCG), which combines four modulation-filtered cochleagrams (time-frequency representations of the input sound) at different resolutions to obtain the temporal and contextual modulation cues. To account for the diversity of the cochleagrams, researchers designed a parallel neural network architecture called “long short-term memory” (LSTM), which modeled the time variations of multi-resolution signals from the cochleagrams and carried out extensive experiments on two datasets of spontaneous speech.
The results were encouraging. The researchers found that MMCG showed a significantly better emotion recognition performance than traditional acoustic-based features and other auditory-based features for both the datasets. Furthermore, the parallel LSTM network demonstrated a superior prediction of dimensional emotions than that with a plain LSTM-based approach.
Prof. Unoki is thrilled and contemplates improving upon the MMCG feature in future research. “Our next goal is to analyze the robustness of environmental noise sources and investigate our feature for other tasks, such as categorical emotion recognition, speech separation, and voice activity detection,” he concludes.
Looks like it may not be too long before emotionally intelligent robots become a reality!
/Public Release. This material comes from the originating organization and may be of a point-in-time nature, edited for clarity, style and length. View in full here .
What’s next on the ABSURD Covid-19 “medical” technology chopping block?
( Natural News ) Today, if you’re pro-science, then you’re labeled anti-science, because the Covid-19 vaccines don’t really work. That’s why it doesn’t matter what they invent next for the 150 million American sheeple who worship Western Medicine and are too dumb to know any better. The brainwashed 150 million Americans are all staring at their televisions and smartphones now, waiting for instructions from the corrupt CDC on when to get their next phase of the deadly mRNA vaccine series.
Meanwhile, they’re all going crazy from breathing in their own spent, stinky, bacteria-laden breath in their carbon-dioxide-trapping masks. Since less oxygen is available with each breath, symptoms begin to develop, including rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, emotional upsets, and chronic fatigue. As less and less oxygen becomes available, victims incur nausea, vomiting and begin collapsing, as we’ve witnessed health officials themselves experiencing while talking about how great mask wearing is for you.
Their immune systems are all compromised and shocked to the core, and they’re begging for more punishment to quell their propaganda-crafted fears. So here they come. Probable Covid-19 ‘medical’ interventions, inventions and guidelines (laws) coming your way soon
Pre-soaked, slow-release antibiotic-laden masks: All masks include chemical disinfectants that combine bleach with ammonia for added safety, and to kill any bacteria in and around the mouth.
Phase III and IV of Covid-19 vaccine series , a.k.a. “kill switch”: These two vaccines will enable the next, more virulent strains of Covid-19 to eliminate the vaccinated without a hitch, and it can all be blamed on a ‘stronger’ mutation, never the vaccines themselves, even though it will mainly be the vaccinated who die from the new strains.
Social distance tasers for all Americans : Infrared laser-tasers that zap anyone within 6 feet of you with a tiny shock so they will remain at a safe distance . The closer they get, the worse the shock hurts. Works with any Bill Gates government-approved software and smart device (that’s all of them soon). Comes with mandatory automated voice over that warns your space intruder about increasing and possible fatal shock current.
Combination Super Vaccine : Flu-Zika-Swine-Measles-Covid-19 vaccine. Manufactured in China, this vaccine features lots of mercury to ensure ‘stability’ and as a preservative. Also includes human abortion cells, aluminum, MSG, and two deadly pig-virus strains called circovirus .
Mandatory full-head bubble mask globe: Nothing keeps you safer from Covid-19 than a large plastic bag or ‘bubble mask’ that covers your whole head like a globe and wraps tightly around your neck. It’s great because once you’re dead from that, no more hypochondriac worries and fears about catching the China Flu. Problem solved.
Antibiotic gummy bears for kids: These are great because antibiotics don’t fight viruses, but make them worse, as they kill all bacteria in the gut, including flora that helps you fight off disease. Perfect for population reduction scheming.
Mask/bracelet shocker app : Smart device tracking app with matching permanent bracelet (for wrist or ankle) that shocks you if you take off your mask or enter a ‘quarantined’ area, restaurant, school, workplace, etc.
Covid-19 mRNA-embedded government-issued wrist tattoos – with serial numbers and nano-technology for ‘boosting’ your immune system with amazing ‘protein prions’ should you enter a ‘high capacity’ Covid-infected region of the country (any Blue state). In case you don’t know, prions are misfolded proteins with the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein, characterizing several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and other animals.
BONUS: Gun buyback program where “all proceeds go to fighting Covid-19” – this would serve as the beginning of the massive gun confiscation campaign so the globalists and Marxists can attack specific “enemies of the state” and fulfill the socialist/communist nightmare takeover/destruction of America.
More dirty and deadly mRNA vaccines are on the way for the sheeple of the world
Expect the coronavirus vaccines to keep getting worse, more dangerous and more frequently required, as new strains of Covid-19 mutate into more virulent versions that are immune to the previously administered dirty and useless vaccines. Every season is China Flu season in America, so run out and get your booster shot today. It’s free everywhere because it kills you slowly at your own expense.
Remember, psycho governments don’t give away medicine for free to protect their people. Think about that one for a minute, then tune your internet frequency to MedicalExtremism.com for updates on vaccines that do more harm than good.
Sources for this article include:
Can Medical Cannabis Help the Elderly?

With clear evidence that cannabis can improve quality of life, more and more people are engaged in its medicinal purposes. Furthermore, states are taking into consideration the laws for the consumption of cannabis. This also explains why there is a high demand for medical marijuana autoflower seeds that leads to the supply of medical cannabis across America.
According to a CBS report, Americans over 55 frequently consume cannabis, many of them living in areas where weed is legal. Benefits of Medical Cannabis
In other words, the use of cannabis among the elderly is on the rise. Medical researchers have found it to be safe compared to opioid drugs. Common Diseases Of Elderly People Who Can Be Treated With Medical Cannabis
The cannabis plant contains over 100 cannabinoids, interacts with the ECS, thereby regulating pain, memory, etc. Recent surveys indicate that the number of medical prescriptions has decreased considerably following the legalization of cannabis for medical purposes in many US states. Alzheimer’s Disease
About 5.8 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease. By 2050, that number is expected to reach 14 million. Patients usually forget important dates, events, etc., and ask the same repeatedly.
Other symptoms are difficulty concentrating, hopping from stray objects, social anxiety, inability to problem solve, and confusion with time and place. Researchers have found that cannabis can help Alzheimer’s patients improve their relaxation, thereby promoting a way of life. The cannabinoids present in the plant are effective for symptoms such as depression and wasting. THC slows the advancement of beta-amyloids, thereby treating Alzheimer’s disease. Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is common in older people. A recent NIH study report indicates that approximately one per cent of the elderly suffer from bothersome pain. At the same time, ¾ of them have pain in more than one place.
Cannabinoids in cannabis work by interacting with the ECS, a complex biological system responsible for various bodily functions. Cannabinoids themselves bind to the receptors present in them, thus reducing pain and impairing other functions. Medical studies have shown that CBD stimulates a neurotransmitter that reduces pain, swelling and hyperactivity. Anxiety & Depression
Anxiety and depression are common mental disorders and can interfere with a patient’s ability to carry on daily tasks. As people get older, the chances of developing these disorders increase. The main reasons are that the elderly take medical prescriptions and have had more troubles, attachments, fear of death, etc. However, obsessive thoughts can cause attacks of anxiety, dizziness, etc.
Medical researchers have discovered that CBD is used to treat mental health problems such as panic attacks, PTSD, OSD and general anxiety. CBD works by inciting receptors in the brain, providing mood-boosting relaxation effects. Unlike prescription drugs, cannabis is less addictive and has no side effects. Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are common in older people. About 80% of deaths in older people are from anorexia, which involves loss of desire to eat due to false beliefs about body image for other psychological reasons. A poor diet can lead to risks of heart, bone and other chronic conditions. Researchers have confirmed that diet patients have an impaired ECS, which can help them correct it.
Cannabinoids bind to receptors in the ECS, inciting appetite and making the brain appear like food as a reward. Antidepressants and antipsychotics can also help, but they can cause several side effects, making symptoms worse. However, cannabis can be used as a safe and effective option for prescription drugs. Cancer
Cannabis can help manage the side effects of chemotherapy, drug therapy to treat cancer. Here is how cannabis can help.
Pain: Cannabis reduces cancer-related pain by binding to receptors in the brain and other regions. In addition, they can help relieve inflammation which leads to pain. Nausea & Vomiting: Cannabis Drugs like Nabilone and dronabinol effectively treat nausea and vomiting, the symptoms of which are difficult to control with a pill. Appetite: Cannabis stimulates appetite by interacting with the system. Legalization Of Cannabis In The United States
Cannabis legalized states have dispensaries to help patients purchase weed products. To legally access medical cannabis, you must consult a doctor and obtain proper documents. In most cases, people tend to buy grandaddy purple feminized marijuana seeds and grow them at home for a convenient supply of cannabis. Conclusion
In conclusion, cannabis is an effective natural medicine to treat various conditions. It can help the elderly to fight anxiety, depression, eating disorders, etc. To completely relieve your symptoms, make sure you buy the right ones with optimal levels of CBD and THC.
Select ratingGive Can Medical Cannabis Help the Elderly? 1/5Give Can Medical Cannabis Help the Elderly? 2/5Give Can Medical Cannabis Help the Elderly? 3/5Give Can Medical Cannabis Help the Elderly? 4/5Give Can Medical Cannabis Help the Elderly? 5/5
Novel drug rejuvenates cellular cleaning to reverse Alzheimer’s in mice
An artist’s impression of tau tangles taking hold in the brain, which are considered one of the drivers of Alzheimer’s disease A key focus for medical scientists working to prevent or potentially treat Alzheimer’s is coming up with ways to avoid the buildup of toxic proteins in the brain, which could include the use of ultrasound or maybe even regular deep sleep . A team at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine has uncovered another promising pathway, discovering that an experimental drug can supercharge a natural cellular cleaning mechanism to rid mice of these unwanted waste products, and reverse key symptoms of the disease.
At the heart of the research is a cellular cleaning process called chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), which sniffs out unwanted proteins in the body and digests and recycles them. Professor of developmental and molecular biology Ana Maria Cuervo discovered this CMA system in the 1990s and, having learned that it becomes less efficient as people age, drew up a study to investigate its potential links to Alzheimer’s.
Cuervo and her team started by genetically engineering mice to feature excitatory brain neurons that lacked CMA, which led to a range of Alzheimer’s-like symptoms, including short-term memory loss and impaired walking. This also disrupted the cells’ ability to regulate the proteins inside them, causing what would normally be soluble proteins to become insoluble and prone to clumping.
Next, the team looked at the other side of this equation, investigating how Alzheimer’s disease might impair the function of CMA. This part of the study involved what is considered to be a hallmark of the disease, the protein tau, which tends to clump together and form neurofibrillary tangles. These tangles are thought to help drive the neurodegeneration associated with the condition.
The scientists used mice engineered to produce defective copies of tau proteins, and examined their impact on CMA activity in neurons of the hippocampus, the part of the brain associated with memory and learning. CMA activity was found to be significantly reduced in these neurons, compared to a group of control animals.
To investigate whether Alzheimer’s has similar effects in humans, the scientists looked at single-cell RNA-sequencing data on neurons collected from the brains of deceased Alzheimer’s patients. Compared to a control group of healthy subjects, these subjects indeed exhibited suppressed CMA activity, with the more advanced the disease, the greater the damage.
“By the time people reach the age of 70 or 80, CMA activity has usually decreased by about 30 percent compared to when they were younger,” says Dr. Cuervo. “Most peoples’ brains can compensate for this decline. But if you add neurodegenerative disease to the mix, the effect on the normal protein makeup of brain neurons can be devastating. Our study shows that CMA deficiency interacts synergistically with Alzheimer’s pathology to greatly accelerate disease progression.”
Armed with this new knowledge, the scientists developed a drug to breathe new life into the CMA process. Normally, CMA involves chaperone proteins that bind to damaged and defective proteins in cells, but to digest and recycle these proteins, the chaperones need to latch onto protein receptors called LAMP2A. This process deteriorates as we age, but the novel drug developed by the team boosts the amount of these LAMP2A receptors and restores them to youthful levels, and therefore allows for greater CMA activity.
Called CA, the drug was tested in two mouse models of Alzheimer’s via oral doses over four to six months. Both groups of mice showed improvements in memory, depression and anxiety and closely resembled healthy mice at the end of the experiment. The treatment also improved walking ability in mice suffering from mobility issues, and in both groups, tau levels and protein clumps were significantly reduced. Albert Einstein College of Medicine Fewer protein clumps can be see in mice treated with a novel drug to boost cellular cleaning “Importantly, animals in both models were already showing symptoms of disease, and their neurons were clogged with toxic proteins before the drugs were administered,” says Dr. Cuervo. “This means that the drug may help preserve neuron function even in the later stages of disease. We were also very excited that the drug significantly reduced gliosis – the inflammation and scarring of cells surrounding brain neurons. Gliosis is associated with toxic proteins and is known to play a major role in perpetuating and worsening neurodegenerative diseases.”
The researchers have created a spin-off company to work on the development of CA into a clinical treatment for Alzheimer’s and similar conditions. While aware of the limitations of their research in mice, the fact that they uncovered evidence of similar processes at play in humans offers plenty of room for optimism.
“Discoveries in mice don’t always translate to humans, especially in Alzheimer’s disease,” says Cuervo. “But we were encouraged to find in our study that the drop-off in cellular cleaning that contributes to Alzheimer’s in mice also occurs in people with the disease, suggesting that our drug may also work in humans.”
The research was published in the journal Cell .
Here are 5 Potential Benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushrooms

The growth of plant-based products
Whether you’re an omnivore, vegan, or something in between, you’ve probably noticed a profusion of meatless products on supermarket shelves.
The market for plant-based meat substitutes is booming, growing 17 percent between 2014 and 2018, according to market research company Statista. And demand is still on the rise.
Though more and more people are open to meatless proteins like seitan and sea moss , there’s an ongoing hunt for plants that offer a more meat-like texture. There’s also a growing interest in medicinal plants, according to market research company Technavio.
All of that makes the market ripe for hearty fungi like lion’s mane mushrooms. They’re sold as everything from mushroom “steaks” and mushroom jerky to powders and supplements.
“People are always looking for a quick fix, and mushroom supplements are some of the newest and most innovative,” says Amy Gorin, a plant-based registered dietitian nutritionist and owner of Plant-Based Eats in Stamford, Connecticut.
Low in calories and packed with potential health benefits, this fungus could be a fun, nutritious addition to your diet.
Here’s everything you need to know about lion’s mane mushrooms, including the benefits, risks, nutrition, and how to eat them. What is lion’s mane mushroom?
Lion’s mane, also known as Hericium erinaceus , is a mushroom with a long history of medicinal and culinary use in Asia. It’s blond and shaggy—hence the name “lion’s mane.”
Though the ragged, fleshy white fungus grows naturally on dying wood, you can now find lion’s mane mushrooms in processed supplements, extracts, and powders. Whole lion’s mane mushrooms also have a chewy texture and umami flavor that makes them an effective meat substitute in many dishes.
Lion’s mane is often marketed as a healing ingredient, but its benefits in that area aren’t well understood.
“Medicinal mushrooms have been used and revered for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine, [but] more human studies are needed for safety, efficacy, and proper dosage,” says nutrition expert Vicki Shanta Retelny, RDN, host of the “Nourishing Notes” podcast. Mushroom nutrition facts
Lion’s mane mushrooms have a similar nutritional profile to many other mushroom varieties . In general, fungi are low in calories and fat, with a sizable helping of antioxidants and minerals, such as iron and potassium.
One cup (70 grams) of the average raw mushroom contains the following nutrients:
Calories: 15.4
Protein: 2.16 g (4 percent recommended daily value, or DV)
Fat: .24 g (0 percent DV)
Carbohydrates: 2.28 g (0.8 percent DV)
Fiber: 0.7 g (2.5 percent DV)
Calcium: 2.1 mg (0 percent DV)
Iron: 0.35 mg (2 percent DV)
Potassium: 223 mg (4.7 percent DV)
Magnesium: 6.3 mg (1.5 percent DV)
Phosphorus: 60.2 mg (4.8 percent DV) Varieties
There are several varieties of lion’s mane mushrooms. The fungus is native to Asia, Europe, and North America. In North America, it is common to find at least three distinct species: Hericium erinaceus , Hericium americanum , and Hericium coralloides .
All three types have a similar look and nutritional profile. They are also all edible. Here’s what the experts have to say about these shaggy mushrooms’ health benefits. Lion’s mane mushroom benefits In general, mushrooms are healthy because they deliver disease-fighting phytochemicals in a tasty, low-calorie package. Lion’s mane mushrooms offer all the nutritional benefits of other mushrooms, including plant-based iron and other essential minerals.Some research suggests that lion’s mane might offer more health perks than other common mushrooms, such as portobello or shiitake.”Research on the health benefits of lion’s mane mushrooms is preliminary, and more studies need to be done,” says Gorin. “From the research that we do have, there may be benefits for cognitive function and gastritis (inflammation of the lining of the stomach).”Though lion’s mane mushrooms are nutritious, there is little evidence to support claims that they boost energy, prevent disease, or speed up weight loss.”Although lion’s mane may have benefits, by no means is adding them to your diet a magic elixir,” says Shanta Retelny. “More human studies are needed.” Provides a plant-based source of iron A one-cup serving of lion’s mane provides about 2 percent of your recommended daily value of iron.Plant-based sources of iron are vital for vegetarians and vegans, according to Gorin. That’s because most high-iron foods are also animal products—think beef, chicken, and oysters.Since an iron deficiency can lead to anemia, consuming plant sources of iron , like lion’s mane, sea moss, and chia seeds , can help you keep your levels in the safe zone. Might boost mental health “Lion’s mane is believed to be beneficial for … fending off depression and anxiety,” Shanta Retelny says.As with the majority of research on lion’s mane, however, studies linking the mushroom to mental health benefits have mostly been done in animals. That’s a good start, but in no way do animal studies prove they’re useful in humans. For that, we need human studies. May protect against dementia According to Shanta Retelny, lion’s mane mushrooms may have a beneficial effect when it comes to dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.That could be because lion’s mane mushrooms contain plant compounds known to stimulate new brain cell growth , according to research published in the International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms. Gorin adds that in one small study of older Japanese adults with mild dementia, taking 1,000 milligrams of lion’s mane three times per day for four months seemed to improve mental clarity . “Compared to the placebo, these adults saw cognitive increases—but the benefits began to diminish within a month of termination of the treatment,” she says.So while lion’s mane mushrooms might improve your mental health, research is still too limited to confirm precisely if and how this works. More studies are necessary to recommend supplementation for specific mental health conditions. Could soothe abdominal pain “Research shows that lion’s mane may help with upper abdominal pain for people with gastritis ,” Gorin says.In a mouse study published in the International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms , scientists pinpointed a compound in lion’s mane mushroom extract that can fight against gastric ulcer activity.Just keep in mind that this study was done […]
Lion’s Fuel Fitness-Enhancement Products are Now Available on Amazon

Lion’s Fuel Fitness-Enhancement Products are Now Available on Amazon
Athletic-Performance Enhancements Focus on Post-Pandemic Health
Ageless Global, LLC. (The “Company” or “Ageless”), a leading developer and supplier of physician-backed, clinically tested wellness products, announced today its suite of fitness enhancement products, Lion’s Fuel, is now available for purchase through Amazon.
Lion’s Fuel aims to deliver performance-enhancing ingredients to help users get into and stay in shape, recover faster, fight fatigue, and perform better. As many fitness enthusiasts are looking to get back in shape after quarantine, these products are designed for athletic and life-performance enhancement to keep users feeling their best before, during, and after getting active.
Lion’s Fuel Diet Fuel can be purchased directly on Amazon here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B092RKTWTS?ref=myi_title_dp
Lion’s Fuel Mental Edge Capsule here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B092RHPP3C?ref=myi_title_dp
Lion’s Fuel Muscle Refresh Cream here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08VM76GN6?ref=myi_title_dp
Lion’s Fuel Diet Fuel is a zero-calorie weight loss supplement powder added to water or other drinks, supercharged with key minerals, metabolism enhancers, electrolytes, and fat burners to accelerate and support weight loss efforts. The formula is packed with essential minerals like chromium, vanadium, magnesium, guarana, and potassium, used as fat burners to lose weight and stay lean. The drink is currently offered in a 30-serving size for $29.95.
Lion’s Fuel Mental Edge Capsules are a brain-booster supplement for focus, memory, clarity, energy, and attention span. The product contains targeted nootropics and adaptogens to naturally support your body’s dopamine levels delivering a mental edge. Mental Edge contains L-theanine and caffeine, which can boost brain health and performance on cognitive tasks. The blend also contains Panax ginseng, which may help improve mental performance, enhance mood, reduce memory loss and anxiety, and boost overall brain health. Each dose of Mental Edge contains 1000 mg of nootropics and adaptogens to support dopamine levels and enhance mental clarity. The product is currently offered in a 60-capsule bottle for $29.95.
Lion’s Fuel Muscle Refresh Cream is a pain-relieving muscle cream that helps an achy body bounce back and feel better. Loaded with natural pain-relieving essential oils that work faster and are more effective, this cream provides deep relief for aches and pains in your muscles or joints. The product is currently offered in a 4-oz bottle for $29.95.
“We are excited to list our suite of fitness enhancement products on Amazon’s platform to extend our customer base and overall audience reach,” commented Darren Lopez, Co-Founder and Managing Member of Ageless Global. “As many people return to gyms after quarantining during the pandemic, we created Lion’s Fuel products to give those looking to reset focus on their health and fitness a helping hand. These products complement standard exercise programs, weight loss programs, and specialized diets, such as Keto or intermittent fasting plans.”
You can find more information on Lion’s Fuel here: https://www.lionsfuel.com/diet-fuel
About Ageless Global, LLC.:
Ageless Global, LLC. was founded by medical professionals specializing in anti-aging, alternative/integrative medicine, health & wellness, and pain management. The Company’s portfolio of technology and products currently include two patent-pending products. In addition, the Company has developed a suite of natural wellness products in the pain management, focus and brain health, ECS health and weight loss markets.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210422005413/en/
Seven surprising ways exercise can boost human health

We all know exercise is good for us, but science continues to reveal new benefits to getting moving If you are partaking in regular bouts of exercise, you can expect to experience a range of benefits, like the burning of excess fat, lower risk of heart trouble and a healthier state of mind. Recently, however, scientific studies have started to shine a light on how regular physical activity can benefit human health in more subtle ways, some of which you might not expect. Let’s take a look at some interesting examples. Enhanced learning from a single workout
bernardbodo/Depositphotos A study involving mice found a short bout of exercise enhanced the expression of a particular gene that increases synaptic connections between neurons The idea of going jogging to clear one’s mind or de-stress after a tough day at work isn’t new, but a big part of our growing knowledge around the benefits of exercise is a better understanding of its effects on cognition. In 2019, scientists at Oregon Health & Science University looked at a very specific example of this by zeroing in on the potential neuronal changes that can take place after a single exercise session.
The experiments were conducted on mice, which were subjected to an exercise session equivalent to a game of basketball. Just one hour later, the mice exhibited enhanced synaptic activity in the hippocampus, the part of the brain associated with memory and learning. The team also discovered heightened expression of a gene involved in synapse formation, which was found to promote new synaptic connections between neurons. The upshot? A single exercise session before a college class or important work meeting might just help you learn and retain important information. Just don’t forget to squeeze in a shower. Boosting brain plasticity through high-intensity training
undrey/Depositphotos Research has pointed to two types of workout in particular that can improve brain elasticity Last year, we learned of another way exercise can improve cognitive function, with a group of researchers at the University of South Australia turning their attention to neuroplasticity. Similarly, this refers to the brain’s ability to rewire neural connections as we move through life and experience new environments, form new memories and learn new skills.
The scientists set out to learn what types of exercise can most benefit the development and maintenance of these vital pathways, by subjecting health participants to a range of workouts. They used transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to monitor the subjects’ neuroplasticity throughout and found the most profound changes were after either 20 minutes of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or 25 minutes of continuous aerobic exercise. So, if brain plasticity is the name of your game, then it might be time to turn up the tempo. Fighting brain degeneration associated with dementia
AndrewLozovyi/Depositphotos Studies have shown a healthy lifestyle can significantly offset any genetic predisposition a person may have in developing dementia or Alzheimer’s disease A string of studies over the past couple of years have begun to shine a light on the relationship between physical activity and a slowing of the cognitive decline associated with dementia and Alzheimer’s. This has included findings around how exercise can lessen the effects of mild cognitive impairment , induce a hormone that can protect against the disorders, and limit the risk of them developing in vulnerable adults .
One interesting example came in July of 2019, in which a team led by University of Exeter scientists examined the impacts of a healthy lifestyle on the genetic risk for Alzheimer’s and dementia. This involved looking at nearly 200,000 adults that were given risk scores for developing dementia based on previous genetic studies, with the scientists then seeing how the probability of developing the disorder was impacted by four factors: smoking, physical activity, diet and alcohol consumption.
The scientists found that the likelihood could be reduced across the board by a healthy lifestyle, irresepective of genetics. Interestingly, however, a healthy lifestyle was found to reduce dementia cases by 32 percent in the high-risk genetic group. In this way, forming good habits around exercise, together with diet and smoking, may just offset the genetic risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s. Fending off anxiety and building a bigger brain
VitalikRadko/Depositphotos Research has shone light on the importance of healthy eating and physical activity during childhood Research has shown how aerobic exercise can help alleviate chronic anxiety, but a recent study from scientists at the University of California, Riverside revealed how forming healthy habits early in life can help prevent it later in life, and even lead to larger brains as adults.
The scientists subjected young mice to unhealthy diets and gave them no access to exercise, and another group was given healthy diets and regular exercise, with the groups compared once the rodents reached sexual maturity. Despite both groups eating healthy diets from that point onwards, the mice that exercised and ate well during early life exhibited less anxious behavior as adults, and also featured increased muscle and brain mass. Fighting blindness
stokkete/Depositphotos Research has offered experimental evidence that exercise can slow macular degeneration Last July, we saw the first experimental evidence that exercise can directly slow or even prevent macular degeneration, one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide. The research from the University of Virginia involved one group of mice given an exercise wheel in a cage, and another group that was not.
Four weeks later, the scientists used lasers to induce vision loss in both sets of rodents, but found that in the group that had been exercising, eye damage was between 32 and 45 percent lower. Exercising the mice afterwards did nothing to reverse the damage, it was only in the mice with a history of exercise that the benefits around the preservation of vision were observed. While the study suggests small amounts of exercise can help prevent vision loss, further research is needed to understand the exact biological mechanisms behind it. Boosting the immune system to kill cancer
nd3000/Depositphotos Research suggests certain metabolites released by muscles into the bloodstream […]
A New Study Finds CBD May Help Combat the Onset of Alzheimer’s

CBD already has a well-earned reputation as a natural wellness therapeutic that can help ease anxiety and combat pain. But recently published research has shown CBD has real potential as a therapy for one of the biggest health issues impacting the country: Alzheimer’s disease.
A study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease associated CBD with changes in brain chemistry that restore function of two proteins. Both proteins help the brain battle buildup of plaque that is associated with the onset of cognitive decline and dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
The research offers hope for millions impacted by Alzheimer’s disease and points to yet another way that CBD has the potential to improve health as well as help people use less potentially dangerous prescription painkillers . The impact of dementia is increasing.
Alzheimer’s is the best known of the diseases that lead to dementia. It’s an issue of increasing importance as the United States’ population continues to age. By 2034, the number of people over 65 is expected to be larger than the number of children in the U.S. for the first time in history. Seniors will make up about 20% of the population.
Experts estimate that Alzheimer’s may currently impact 5.5 million Americans. The disease ranks as the sixth leading cause of death in the U.S. but may rank as high as third, behind only heart disease and cancer, for seniors, according to the National Institute on Aging.
Most people first experience symptoms in their mid-60s.The damage caused by Alzheimer’s disease is irreversible. The disease slowly robs people of their memory and thinking skills. Eventually, they have difficulty performing even the most basic tasks. CBD strengthens proteins that combat Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers from Augusta University in Georgia and the European Medical Association conducted the study. They used mice in the experiment, putting them on a two-week regimen of CBD. They found that CBD led to increased amounts of the proteins TREM2 and IL-33 in the brains of mice.
That’s important because the two proteins are critical to fighting the buildup of beta-amyloid plaque in the brain. Experts consider buildup of this plaque as a biomarker for the onset of Alzheimer’s disease. The study found that CBD treatment increased levels of IL-33 sevenfold and levels of TREM2 tenfold.
They also found that CBD improves cognition by reducing levels of the immune protein IL-6, which is associated with the high inflammation found in brains affected by Alzheimer’s.
In a press release about the study, researchers said that the findings are important because there is a dire need for novel therapies to improve outcomes for patients with Alzheimer’s, which they called “one of the fastest-growing health threats in the United States.”
Select ratingGive A New Study Finds CBD May Help Combat the Onset of Alzheimer’s 1/5Give A New Study Finds CBD May Help Combat the Onset of Alzheimer’s 2/5Give A New Study Finds CBD May Help Combat the Onset of Alzheimer’s 3/5Give A New Study Finds CBD May Help Combat the Onset of Alzheimer’s 4/5Give A New Study Finds CBD May Help Combat the Onset of Alzheimer’s 5/5
Brain Gains: 7 foods to boost kids’ academic performance

Combine three of these healthy brain foods into a yogurt, berry and granola parfait Photo courtesy of Metro Creative Services To keep your kids’ performance at optimum levels, we’ve rounded up seven of the best brain foods to help boost their mental power, and also talked to Brainly’s parenting expert, Patrick Quinn, for pro parenting tips on how to incorporate them into your kids’ daily diet.
Nuts and seeds are packed with nutrients that are essential for brain health including essential fatty acids, protein, zinc, and B-vitamins. They’re also natural mood boosters that are portable and versatile, making them an excellent choice for study snacks.
Parent tip: Kids aren’t always going to love these. But mixing them in a trail mix with a few chocolate pieces or yogurt chips is a great way to get them munching on the healthy nuts and seeds. Just be careful not to send this in as a school snack in districts where nut allergies can affect other kids.
Full-fat Greek yogurt packs a lot more protein than other yogurts (and much less sugar), and can help keep brain cells in good form for sending and receiving information. It’s also full of protein and B-vitamins—essential for the growth of brain tissue, neurotransmitters, and enzymes. Greek yogurt is also a great source of Calcium and Vitamin D.
Parent tip: Mix in a teaspoon of honey and some cinnamon to turn this healthy option into a delicious one as well. The problem for me at that point is avoiding eating it myself before the kids get it.
Berries are rich in a variety of compounds that may help promote academic performance and protect brain health. Berries (including blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries) are especially high in flavonoid compounds called anthocyanins, believed to improve mental performance by increasing blood flow to the brain. They also protect against inflammation and improve certain signaling pathways that promote nerve cell production and cellular processes involved in learning and memory.
Parent tip: Berries make an easy study snack, but they can cause sticky fingers that can lead to messy keyboards and homework papers. Try putting several different types of berries on kid-friendly skewers for a fun, healthy, and mess-free desk snack.
Fish is an excellent source of Vitamin D and the Omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA— both essential for brain growth and function. Consuming more Omega-3s means kids will have sharper minds and better mental skills.
Parent tip: You can make fish tasty for kids by serving it simply grilled, like fish sticks, or including it in tacos or in tuna sandwiches. Another option is using canned salmon to make delicious salmon salad sandwiches that can be mixed with reduced-fat mayo or non-fat Greek yogurt, raisins, chopped celery, and carrots.
The versatile egg is a great source of protein, and egg yolks are packed with choline, which helps memory development. Eggs can be served in a variety of ways and can be enjoyed at breakfast, as a mid-afternoon snack, or even at dinner.
Parent tip: Eggs are great for making grab-and-go breakfasts kids can eat on the road. Scramble eggs into a whole grain tortilla to make a grab-and-go breakfast burrito, or make your own version of an Egg McMuffin at home by putting a fried egg on top of a toasted English muffin and topping it with a slice of low-fat cheese.
Oats are extremely nutritious and they can provide the energy and fuel for the brain that kids need first thing in the morning. Oatmeal is also a fiber-rich food that keeps heart and brain arteries clear. In one study, kids who ate sweetened oatmeal did better on memory-related school tasks than those who ate sugary cereal.
Parent tip: You can dress oatmeal up with applesauce, dried fruit, almonds, and banana to make it tastier and more appealing to kids. Due to its natural compounds, adding cinnamon also gives oatmeal an extra ingredient that will help to protect brain cells.
Kids usually have a craving for sweets. Apples and plums are lunchbox-friendly items that contain quercetin, an antioxidant that helps fight the decline in mental skills. Keep them organic to get the best benefits.
Parent tip: For a heartier snack, you can also cut apples into chunky slices and spread them with almond or peanut butter, or you can freeze pitted plums and add them to a favorite nutrient-rich fruit smoothie.
Brainl y is the world’s largest online learning and homework help community.
The Afternoon Slump: 12 (Mostly) Caffeine-Free Ways to Perk Up
I’m writing this in the midst of an afternoon slump, and dear reader I confess: I’m not practicing what I’m about to preach. Or at least, not in its entirety. I’m fending off the urge to lay down my head with green tea (sanctioned) coupled with a gluten-free ginger cookie (rookie mistake).
I don’t believe I’m the only one battling the wave of afternoon exhaustion. According to the National Sleep Foundation, adults’ strongest biological urges to sleep occur between 2 and 4 a.m. and between 1 and 3 p.m. First comes the initial slump, then the yawn, and then the coup de grace—eyes so heavy that it takes everything you have to pry them open. Why does the afternoon slump happen?
Scientifically speaking, the afternoon slump is a period of decreased alertness, focus and productivity in the afternoon. Afternoon fatigue sets in because of a natural dip in your biological sleep-wake cycle. The slump can get amplified, however, by skimping on sleep, eating a heavy lunch, or having a particularly draining morning. Before you reach for the cookie, here are 12 sound ways to get the better of afternoon sleepiness. Afternoon Slump Solutions
Move
A 2017 study published in the journal Physiology & Behavior found that short periods of physical activities, such as 15 minutes of stair walking was more energizing than a cup of coffee. The study focused on chronically sleep deprived adults, who found themselves more invigorated by a brief spurt of activity versus the equivalent to a cup of coffee—a 50-milligram caffeine capsule. If you are feeling the approach of a wave of tiredness, stroll around the office, run up and down the stairs, or do a few stretches or pushups. Catch a whiff
Certain scents can make us more alert or more relaxed. Peppermint is a known energy-enhancing scent. The scent stimulates the hippocampus area of the brain, the area that controls mental clarity and memory, particularly long-term memory. Peppermint’s menthol component triggers you to wake up and pay attention. Put a few drops of peppermint essential oil on your hands, rub them together, then rub them over your face (avoid your eyes). Get outside
Take a break and get outside, as the outdoors has an inherently revitalizing effect. A 2010 study found that spending just 20 minutes outdoors could elevate energy levels. Chew gum
Chewing increases the amount of blood and oxygen flowing through your head, brain included. As a result, gum chewing makes people more alert and can speed up your thinking. A 2013 study reported in the journal Brain and Cognition found that reaction times are up to 10 per cent faster while chewing gum. Nap
Embrace the nap —in moderation. Done right, a nap won’t decrease your productivity and can actually boost your energy. The sweet spot for a power nap is somewhere between 20-30 minutes. According to the sleep foundation, researchers found that five-minute naps are too short to produce a notable benefit. On the other hand, sleeping for 30 minutes or longer gives the body enough time to enter deep sleep. But napping for too long can leave you feeling drowsy for up to an hour.
For extra credit, supercharge your naps with caffeine. Although it sounds counterintuitive, if you drink coffee or tea about 20 minutes before a nap, you can time it so your energy will peak just as you wake up. If you’re caffeine-sensitive, avoid caffeine after whatever you have deemed your cut-off point. Green tea
A cup of green tea , packed with active compounds called phytochemicals, can give you sustained focus in the afternoon without the jitters or making it tough to fall asleep that night. Hydrate
Medical research shows that dehydration can make you feel tired even when you’re rested. Men in a study on dehydration reported they felt fatigue, lethargy and tiredness. Being properly hydrated helps raise energy levels and help you feel your best. Music
If you feel lethargic during your workout music can help, so why not at the office? Several studies suggest that the benefits of music include enhanced attention, mental efficiency, speed, accuracy, memory and creativity. If you enjoy listening to music while you work, consider choosing a song without lyrics to cut down on getting carried away. Snack
Treat snacks as mini-meals that contribute to your overall nutrition for the day. Healthy snacks can provide your body with time-released fuel. Opt for fruits and vegetables to boost your intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Mix that with some protein-dense choices such as a handful of nuts , homemade trail mix, a hard-boiled egg or Greek yogurt with seeds to keep your mojo at its max. Stand up
Studies have shown that even short bursts of activity can keep you alert. Instead of emailing or calling colleagues, stop by their desks to ask a question face to face. If you have a standing desk, push yourself to stand up when you feel the most tired. Humor
When you laugh , your body increases its oxygen intake and releases endorphins. Among laughter’s many other benefits, it provides you with a quick, refreshing reboot. In one University of Nebraska study, participants who watched a funny video afterwards enjoyed an immediate energy boost. Sex/masturbation
If you are working remotely and the afternoon slump hits, you can snap out of if by literally snapping of (masturbating). Orgasms can flush your body with endorphins, reduce stress, increase blood flow, boost concentration and invigorate you. And sex can serve as a quick pick-me-up as well, releasing a host of endorphins that can bump up your energy considerably.
Effects of Depression on the Body’s Immune System
Introduction
The World Health Organization projects that depression will cause more years in life lost to disability than any other illness by 2030 (WHO 2008, cited in Blume et al. 2011). Perhaps many of these lives lost will be affected by a weakened immune system stemming from a mental illness? This newly researched topic is opening the door for the health community and those afflicted by clinical depression to better understand the link between depression and its subsequent dysfunctional immune system.
Nearly 20 million adults in the United States alone suffer from Major Depressive Disorder, and that number is only representational of the patients who actively report their occurrence of symptoms.
Hire verified writer
Many more are unable to afford or even find the aid they need to treat their mental health disorders. According to Kiecolt-Glaser and Glaser (2002), “Depression is the most common psychiatric illness.” Clinical depression has long been understood and treated solely as a psychiatric illness, however more research has emerged about its somatic ramifications.
Depression includes a variety of both psychological and somatic symptoms that differs with every case.
Psychiatrists and doctors often utilize the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (“DSM”) to diagnose mental health disorders and suggest a treatment journey. Because the mind is so complex, there are a wide array of treatment plans and medications for nearly every psychological disorder. Antidepressants medication and talk-therapy are among the most commonly prescribed treatments for mental health afflictions.
According to WebMD (2018), Major Depressive Disorder affects twice as many women than men, traced back to female changes in hormones and pregnancy.
Historically, however, women exhibiting these symptoms were treated as hysterical by psychiatrists until fairly recently. Today, a general stigma around mental illness remains and permeates through society, namely the United States. Depression and other mental illnesses are often treated without the same urgency as physical ailments. This country also lacks many public mental healthcare facilities, such as rehab centers and psychiatric wards for those unable to afford treatment. It is important to highlight new research on depression and raise awareness around mental illness in order to evolve the healthcare system to include more of those suffering from mental disorders and trauma.
Depression is widely treated solely in a psychiatric manner, yet treating depression with a holistic approach will improve the body’s overall somatic health. In this paper, research about the interconnection of immunology and depression will be presented in order to better understand the effects and possible treatments. Clinical depression has a similar effect on the immune system to chronic stress, causing a hyperactive inflammatory response and degrading the success of the immune system, even to the point of vaccination potency.
To understand the effects of depression on the body’s immune system, one must first be introduced to the diverse symptoms of depression, the basic operations of the human immune system, and the body’s reaction to stress. Depression Overview
Symptoms and severity of such symptoms vary among people, however most with depression report feeling in a generally low mood and loss of interest throughout their daily activities. Although most people experience instances of sadness or periods of difficulty, clinical depression is more serious and chronic. According to the DSM-5, symptoms of depression must present themselves for at least a two-week period in order to be clinically diagnosable. Other symptoms of depression include hypersomnia or insomnia, restlessness or sluggishness, fatigue, inability to concentrate, anhedonia, weight loss or weight gain, and thoughts of suicide or self-harm (Mayo Clinic Staff 2018). Symptoms may escalate others, such as an untreated depression case spiraling into a drug or alcohol addiction. Likewise, lack of motivation and constant fatigue may lead to social isolation. This interconnectedness of symptoms perpetuates the depressive cycle and feelings of hopelessness. These symptoms may amount to a single depressive episode or appear chronically throughout a patients’ life, which is more detrimental to the immune system functioning, much like chronic stress.
Because of the wide range of symptoms and complexity of the human psyche, depression may be caused by many variables. The most common perceived causation of depression is a biochemical imbalance of the neurotransmitters in the brain needed to function properly (Leonard 2001), including serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Antidepressant medication is a leading treatment for clinical depression; typically, neurotransmitter reuptake inhibitors maintain a higher level of mood-boosting chemicals in the brain, seemingly easing the symptoms of depression (Leonard 2001). This chemical imbalance can be triggered through traumatic experiences or genetically inherited. Other sources of depression arise from hormonal imbalances, notably in females, and environmental circumstances such as seasonally affective depression. Immune System Overview
The body’s immune system is an intricate network of barriers and defense mechanisms protecting against unwanted foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. In this system there are three key processes in protecting the body: the innate immune system, the antibody-mediated response, and the cell-mediated response.
The innate immune system is the first line of defense, including the body’s physical and chemical barriers. A key response in this system is inflammatory response, which is likewise a notable aspect in the stress response that will be covered next. As the body is invaded by an unwanted substance, it ignites the inflammatory response to attack the intruder and speed up healing. Four aspects of inflammation are pain, swelling, redness, and heat; each of these responses force further blood flow into the area and encourage the presence of cytokines. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are small proteins released by cells to signal other helpers, like phagocytes ad Natural Killer Cells, to mobilize.
After the antigen has been destroyed, anti-inflammatory cytokines, with the assistance of suppressor T-cells, are activated and this signals the body’s immune defense to retreat from the healed area. (Pearson Learning Solutions 2017) Thus, cytokines and their role in inflammation, if in balance, protect the body from pathogens and boost overall immunity. Both the antibody-mediated immune response and the cell-mediated immune response rely on a multitude of similar-functioning cells to discern non-self cells or abnormally-functioning self cells and destroy them. Each of these intricate processes rely heavily […]
Combination of an active plant compound and a form of vitamin E shows promise as an anti-cancer treatment

( Natural News ) Naturally occurring compounds derived from plants make the best anti-cancer agents. These bioactive chemicals are not only effective at stopping the growth and proliferation of cancer cells, but they also cause very few, if any, side effects. In contrast, synthetic drugs used in chemotherapy cause a variety of unpleasant side effects , such as tiredness, mouth soreness, loss of appetite, pain, stomach problems and hair loss.
In a recent study, Malaysian researchers investigated the anti-cancer activities of y -tocotrienol, a form of vitamin E found in plants, and 6-gingerol , the active component of ginger. According to previous studies, tocotrienols can inhibit the growth of various malignancies , including those of the breast, lung, ovary, prostate, liver, brain, colon and pancreas. 6-Gingerol, on the other hand, has anti-tumor activities against renal, colon and melanoma tumors .
The researchers looked at the effectiveness of these anti-cancer agents when used together as treatment. They also explored the mechanisms underlying their beneficial effects. The researchers reported their findings in an article published in the Journal of Natural Medicines . Combination therapy with 6-gingerol and y -tocotrienol shows promising results against colorectal cancer
In their previous study, the researchers reported that y -tocotrienol ( y T3) and 6-gingerol (6G) synergistically inhibited the proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells . To shed light on the mechanisms involved in this suppression, they used RNA sequencing techniques and conducted transcriptome analysis of the total RNA from both untreated and y T3 + 6G-treated human colorectal carcinoma cells (SW837).
The researchers found that changes in cancer-specific gene expression occurred in the y T3 + 6G-treated cells. Functional enrichment pathway analysis suggested that the combination of y T3 and 6G modulated more than one signaling pathway. Together, y T3 and 6G interfered with the cell cycle, downregulated the Wnt signaling pathway and induced caspase-independent apoptosis. They did so by triggering mitochondrial dysfunction, activating the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) unfolded protein response (UPR), disrupting DNA repair mechanisms and inactivating the cell cycle.
According to the researchers, the latter was made possible by the downregulation of proliferation-related genes like FOXM1. Meanwhile, y T3 + 6G exerted a cytotoxic effect by upregulating genes involved in stress response activation. The combination treatment also exerted cytostatic effects (inhibiting cell growth and division) by downregulating the main regulator genes involved in the cell cycle.
RNA sequencing and RT-qPCR results revealed that genes like ATF6, DDIT3, GADD34, FOXM1, CDK1 and p21, which are involved in stress response-, apoptosis- and proliferation-related pathways, displayed concordant patterns of gene expression.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that bioactive plant compounds like y -tocotrienol and 6-gingerol can be used to effectively suppress cancer cell growth . Sources and other facts about y -tocotrienol and 6-gingerol
Tocotrienols and tocopherols are two groups of chemicals that make up the vitamin E family. Both exist in four different forms, namely, alpha-, beta-, delta- and gamma-tocotrienol and -tocopherol. Tocotrienols are less commonly found in the human diet than tocopherols, and only tocopherols are capable of correcting vitamin E deficiency. Nevertheless, research suggests taking both tocotrienols and tocopherols because they offer substantial health benefits.
Tocotrienols, for instance, have antioxidant properties, and d -tocotrienol and y -tocotrienol have shown potent anti-cancer activities in pre-clinical trials . Tocotrienols can be sourced from the following foods: Barley
Crude palm oil
Rice bran
Rye
6-Gingerol, on the other hand, is present in the rhizome of ginger ( Zingiber officinale ), a flowering plant widely used today as both a spice and a medicinal herb. 6-Gingerol is the pungent component of ginger and is best known for its anti-inflammatory properties . Together with curcumin from turmeric, capsaicin from chili peppers and piperine from black pepper , it is one of the most extensively studied plant compounds at present. Other beneficial properties of 6-gingerol include antioxidant, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic and anti-cancer properties . It is safe to consume and is easily absorbed into the bloodstream.
There are plenty of edible plants out there that are rich in compounds with remarkable medicinal properties. You can learn more about these plants at PlantMedicine.news .
Sources include:
UIHC.org
MDPI.com
ScienceDirect.com 1
ScienceDirect.com 2
Nature.com
Lion’s Fuel Fitness-Enhancement Products are Now Available on Amazon
Apr 22, 2021 15:02 UTC
SALT LAKE CITY–(Business Wire)– Ageless Global, LLC. (The “Company” or “Ageless”), a leading developer and supplier of physician-backed, clinically tested wellness products, announced today its suite of fitness enhancement products, Lion’s Fuel, is now available for purchase through Amazon.
Lion’s Fuel aims to deliver performance-enhancing ingredients to help users get into and stay in shape, recover faster, fight fatigue, and perform better. As many fitness enthusiasts are looking to get back in shape after quarantine, these products are designed for athletic and life-performance enhancement to keep users feeling their best before, during, and after getting active.
Lion’s Fuel Diet Fuel can be purchased directly on Amazon here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B092RKTWTS?ref=myi_title_dp
Lion’s Fuel Mental Edge Capsule here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B092RHPP3C?ref=myi_title_dp
Lion’s Fuel Muscle Refresh Cream here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08VM76GN6?ref=myi_title_dp
Lion’s Fuel Diet Fuel is a zero-calorie weight loss supplement powder added to water or other drinks, supercharged with key minerals, metabolism enhancers, electrolytes, and fat burners to accelerate and support weight loss efforts. The formula is packed with essential minerals like chromium, vanadium, magnesium, guarana, and potassium, used as fat burners to lose weight and stay lean. The drink is currently offered in a 30-serving size for $29.95.
Lion’s Fuel Mental Edge Capsules are a brain-booster supplement for focus, memory, clarity, energy, and attention span. The product contains targeted nootropics and adaptogens to naturally support your body’s dopamine levels delivering a mental edge. Mental Edge contains L-theanine and caffeine, which can boost brain health and performance on cognitive tasks. The blend also contains Panax ginseng, which may help improve mental performance, enhance mood, reduce memory loss and anxiety, and boost overall brain health. Each dose of Mental Edge contains 1000 mg of nootropics and adaptogens to support dopamine levels and enhance mental clarity. The product is currently offered in a 60-capsule bottle for $29.95.
Lion’s Fuel Muscle Refresh Cream is a pain-relieving muscle cream that helps an achy body bounce back and feel better. Loaded with natural pain-relieving essential oils that work faster and are more effective, this cream provides deep relief for aches and pains in your muscles or joints. The product is currently offered in a 4-oz bottle for $29.95.
“We are excited to list our suite of fitness enhancement products on Amazon’s platform to extend our customer base and overall audience reach,” commented Darren Lopez, Co-Founder and Managing Member of Ageless Global. “As many people return to gyms after quarantining during the pandemic, we created Lion’s Fuel products to give those looking to reset focus on their health and fitness a helping hand. These products complement standard exercise programs, weight loss programs, and specialized diets, such as Keto or intermittent fasting plans.”
You can find more information on Lion’s Fuel here: https://www.lionsfuel.com/diet-fuel
About Ageless Global, LLC.:
Ageless Global, LLC. was founded by medical professionals specializing in anti-aging, alternative/integrative medicine, health & wellness, and pain management. The Company’s portfolio of technology and products currently include two patent-pending products. In addition, the Company has developed a suite of natural wellness products in the pain management, focus and brain health, ECS health and weight loss markets. View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210422005413/en/
Wilma Lu
Manager
(801) 245-0559
wilma@agelesslabs.com
COVID-19 restrictions take a toll on brain function, but there are techniques to help you cope

(MENAFN – The Conversation) Confinement — which has been frequent during the pandemic — has undeniable effects on the brain. There’s the inability to concentrate enough to read or write, the lack of perseverance in tasks, agitation. All this is normal! The brain is not working the way it usually does and it’s being used differently.
An electric current enables the brain to co-ordinate our movements, control our breathing, feel hunger, pain and emotions. This current must circulate properly. The more intense the electrical activity of the brain, the more we will need sleep or feel the effects of lack of sleep. This can affect physical health in many ways, such as weight gain and developing conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Mental health effects can include behavioural changes, difficulties in concentration and mood swings.
Electrical activity in the brain has long been thought to be related to serious psychological problems . Each brain rhythm has a particular frequency and the brain communicates in five frequency bands (delta, theta, alpha, beta and gamma). Each corresponds to different levels of wakefulness and sleep located in different areas of the brain.
As associate professor at the École nationale d’administration publique since 2009, I recently obtained certificates in neuroscience as well as a graduate diploma in specialized studies in mental health. I study the different variables that influence the competence and expertise of individuals and organizations, as well as mental health issues.
The brain, your powerhouse
The electrical activity of the brain can be measured by placing electrodes on the scalp in different areas. The unit of measurement obtained is a rhythm potential expressed in hertz indicating, by its frequency, the nature of the activity in the measured area. This makes it possible to evaluate the electrical voltage, the speed of propagation, the rhythm and the synchronization of an activity in the brain. Electrical activities in the brain. (Shutterstock)
By combining these measures with heart rate and respiration, we can estimate heart rate variability , a non-invasive measure that explores the influence of the autonomic nervous system on the cardiovascular system. Heart rate variability provides an indicator to assess an individual’s ability to cope with stress or to manage stressful situations. This helps explain why two individuals, faced with the same situation, react differently.
When dealing with a difficult event, such as a pandemic, people don’t sleep as well. They become overwhelmed with information by listening to the news more and by constantly talking about the same event and its consequences. They activate more of the neurons responsible for the emotions that are at the heart of the brain. More stress is placed on the frontal and temporal lobes and electrical activity increases in these areas.
The observed effects of this include trouble concentrating or persevering in tasks that require reflection, and problems mustering the motivation to undertake demanding actions
In addition, the hormones responsible for mood and joy are likely less stressed in times of crisis. The things that give us pleasure and generate, among other things, serotonin and dopamine are also less frequent. For some, situations that decrease or disorder these hormones or neurotransmitters may be multiplied or intensified, altering the transmission of information between neurons.
Neurotransmission
Serotonin is involved in several behaviours and abilities, including body heat control, eating and sexual behaviours, sleep management and anxiety. Dopamine is especially linked to cognition, motor functions, motivation, sleep and memory.
When these neurotransmitters are ‘disturbed’ by increased electrical activity in the brain, these behaviours and abilities are altered as well. Neuroactivity of human neuronal cells: brain binding nodes, neurotransmitters, axons, active nerve synapses with chemical electrical signals. (Shutterstock)
It is normal to feel more agitated during this disruption, or to not act as effectively as usual. Consequently, compensation or defence mechanisms may develop. Some will make lists or take on tasks that require less thought or concentration (cleaning, cooking). Others will consume more substances that promote the production of dopamine or serotonin (tobacco, alcohol, coffee, sugar). They will seek comfort (baking bread) and pleasure (running) to feel better or less restless.
This management of emotions also has an impact on the functioning of the immune system, which is responsible for the body’s defence against external aggressions. Some studies show that when an individual experiences negative emotions, their immune system weakens, diminishing its ability to protect the body against these attacks. Therefore, the more positively we manage our emotions, the more our immune system is favoured, which is very useful in times of pandemic.
The question is whether we can improve this variability and influence the efficiency of the brain’s electrical activity. There is a way to recover your faculties and capacities.
Self-regulation or ‘big belly, little belly, 5-5’
What does ‘big belly, little belly, 5-5’ mean? It is a playful version of the practice of cardio-respiratory coherence (CRC), often wrongly called cardiac coherence.
CRC is a research-backed technique to help people control emotions or manage mental health problems such as anxiety and depression, or to quit smoking, lose weight or just relax .
CRC is performed by taking a deep breath for five seconds, until the belly swells (hence the expression ‘big belly, little belly, 5-5’). This activates the sympathetic branch of the nervous system, the one that provides energy to flee from a threat.
Exhale after five seconds to stimulate the parasympathetic branch, which takes care of rest and the restoration of our system.
For relaxation, perform the same action but breathe in deeply for four seconds and breathe out for six seconds, which will further promote rest and restoration.
CRC can help us better manage our emotions. It allows the heart and lungs to generate a frequency of electrical activity corresponding to relaxation (10-12 hertz), and to initiate the rest and restoration process necessary to restore balance to the autonomic nervous system and, ultimately, to send a message to the brain that ‘everything is fine!’
Some studies show that after applying this technique for three to five minutes, the level of https://www.hormone.org/your-health-and-hormones/glands-and-hormones to-z/hormones/dehydroepiandrosterone-dhea,dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA, a natural hormone produced from cholesterol by the adrenal glands) increases, and is a precursor to […]
Easy ways to improve your brain health
The brain is arguably the most important organ in our body. Not only does it control and coordinate our actions, it’s at the very centre of our human experience – it allows us to think, feel and form memories, and shapes our personalities too.
Yet many of us know nothing about how our brains actually work, let alone how to care for them.
“There has been a dramatic switch in the science over the last couple of decades and we’ve completely lifted the lid on what we know about how to look after our brains,” says Professor James Goodwin, neurologist and author of new book Supercharge Your Brain: How To Maintain A Healthy Brain Throughout Your Life .
Goodwin is special advisor to the Global Council on Brain Health, holds a chair at Exeter University Medical School and is a visiting professor of physiology at Loughborough University.
“If you were to ask people at a dinner party how to look after your heart, most people would be able talk about watching their cholesterol or doing exercise. But if you ask them about the brain? You’ll often be met with a blank stare,” Goodwin adds.
However, as cognitive decline continues to be a major long-term health concern, and the number of people with dementia in the UK is forecast to increase to 1,000,000 by 2025, perhaps we do need to know more about how to look after our brain health. Goodwin shares four easy ways to help keep your brain fighting fit at any age…
Make movement a part of your day
If your good intentions to complete a fitness plan in lockdown are flagging, here’s a good reason to set your alarm earlier and make sure you show up on the mat.
“In the past few years, researchers have found that exercise rejuvenates the brain,” says Goodwin. “It produces a chemical that stimulates new cells, and 30 minutes per day is all you need to reap the benefits – for five days a week at a moderate intensity.”
It could be something as gentle as brisk walking or moderate jogging, but the key is to make sure your chosen activity elevates your heart rate enough to get your blood pumping. Goodwin calls it a dose effect. “The more you do, the better the effect – but you can ruin the effects of that exercise completely by sitting down for more than eight hours per day. The longer we sit, the faster we age, so make sure you’re getting up every 20 minutes.”
Be a social butterfly
Social distancing rules have made it more difficult to catch up with friends, but being socially connected to others makes us feel safe and cared for, and this has big benefits for our brains.
“Humans would have never survived if we’d have been solitary animals,” stresses Goodwin. “We survived because we were in groups, and over 1.5 million years of social structure has cemented that into the brain. We’re highly dependent for brain health on this social interaction for others.”
Goodwin claims loneliness is as bad for our health as 15 cigarettes per day or a bottle of vodka, and that those who are persistently lonely have a 50% greater chance of dying than those who are not. “Another 12-year study found that those who said they were lonely showed a 20% faster rate of decline in their brain.
“The sensation of loneliness is quite natural. It’s like a hunger or thirst – it’s the brain telling us you need to seek out some company, in the same way hunger tells that you need to eat food,” says Goodwin.
Have a healthy sex life
“Frequent sexual intercourse with a close partner is beneficial to the brain too,” says Goodwin. According to the neurologist, it can foster better memory, better verbal fluency, and even better numeracy skills.
“A study on male rats, who had between 14-28 days of daily access to a receptive female, found that the number of new cells in that brain increased massively – and it worked better on the older rats, where it had a reverse ageing effect.”
Essentially, the older rats were reaching younger levels of brain rejuvenation, which Goodwin says is astonishing. But here’s the catch – he reckons it’s sex with familiar intimate partner that really has benefits. “Rats who got dumped in with a strange female were stressed out, and while they still eventually had sex, the brain benefits were much more profound in those regular partner rats.”
Eat well
“These days, we’ve got the choice of eating what we want, but that doesn’t mean we always eat what’s best for our brain,” says Goodwin. “Vitamin B12, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc and omega three are what I call the ‘big five’. These are the nutrients we know people are short of in Western diet.
“For a start, most of people in the Northern Hemisphere, above 35 latitude, don’t get enough sunshine to get enough vitamin D for six months of the year. B12, meanwhile, is only found in a very few foods which are mostly animal products.”
Aside from eating a varied diet with lots of plants and wholefoods, Goodwin has a couple of standout kitchen staples to keep in mind. “Spinach and flaxseed are two brain-benefiting foods packed full of Omega 3s that we need for our diet. If you’re sprinkling flaxseed on your porridge in the morning, then crack on, as you’re doing good.”
It’s not just what you’re eating that matters, but the amount you’re eating too. “The Okinawa is a Blue Zone – one of the five lucky areas of the world where people regularly live to over 100 years,” says Goodwin. “They have this Japanese expression called ‘hara hachi bu’, which means ‘leave the table 80% full’.
“The result of that eating habit is they will live longer, and rates of Alzheimer’s in Okinawa are 75% less than everywhere else in the world.” Essentially, those all-you-can-eat buffets and bottomless brunches might not be as good a deal as they seem.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, brain […]
Taking Antioxidant during Pregnancy Prevents Memory Problems in Adult Offspring, Rat Study Finds

A study in rodents has uncovered a direct link between low oxygen in the uterus during pregnancy—causing fetal hypoxia—and impaired memory function in adult offspring. The research, carried out by a team at the University of Cambridge, found that chronic fetal hypoxia led to a reduced density of blood vessels, and a reduced number of nerve cells and their connections, in the hippocampus. Giving the mother antioxidant supplements—in this study high levels of vitamin C—during pregnancy protected the growing fetus from the harmful effects of low oxygen, and from hypoxia-related memory problems later in life.
“It’s hugely exciting to think we might be able to protect the brain health of an unborn child by a simple treatment that can be given to the mother during pregnancy,” said research lead Dino Giussani, PhD, from the University of Cambridge’s Department of Physiology, Development and Neuroscience, who led the study. “In medicine today there has to be a shift in focus from treatment of the disease, when we can do comparatively little, to prevention, when we can do much more. This study shows that we can use preventative medicine even before birth to protect long term brain health.” The team acknowledged that while vitamin C is a well established antioxidant, the high doses required to be effective in their reported study could cause adverse side effects in humans, so follow-up work will be needed to identify alternative anti-oxidants that might treat chronic fetal hypoxia in humans.
Giussani and colleagues describe their studies in The FASEB Journal , in a paper titled, “ Maternal antioxidant treatment protects adult offspring against memory loss and hippocampal atrophy in a rodent model of developmental hypoxia .”
The interaction between our genes and lifestyle plays a role in determining our risk of disease as adults. There is also increasing evidence that the environment experienced during sensitive periods of fetal development directly influences our long-term health—a process known as ‘developmental programming.’ Brain health problems that may start in the womb due to complicated pregnancy range from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, to brain changes in later life that have been linked with Alzheimer’s disease.
“During the last 40 years, significant evidence derived from human epidemiological studies as well as from preclinical animal models has accumulated to show that suboptimal intrauterine conditions can increase the risk of adverse health outcomes in the offspring; a process known as developmental programming,” the authors wrote.
Chronic fetal hypoxia—low oxygen in the uterus—is one of the most common complications in human pregnancy. It can be diagnosed when a routine ultrasound scan shows that the baby is not growing properly and is caused by a number of conditions including pre-eclampsia, infection of the placenta, gestational diabetes or maternal obesity. However, just how gestational hypoxia might affect the long-term health of the brain in offspring isn’t well understood, the team continued.
For their newly reported studies, the researchers used a rat model to investigate more closely how chronic fetal hypoxia might affect brain development. “We investigated in rats whether hypoxic pregnancy affects brain structure and function in the adult offspring and explored underlying mechanisms with maternal antioxidant intervention,” they wrote.
To conduct the research, the researchers housed different groups of pregnant rats under conditions in which the ambient air contained either a normal level of oxygen (21%), or a low, 13% oxygen level, which caused hypoxic pregnancies. Half of the rats in each group were given the antioxidant vitamin C in their drinking water throughout the pregnancy. Following birth, the baby rats were raised to four months old, equivalent to early adulthood in humans, and were then assessed using various tests to assess locomotion, anxiety, spatial learning and memory.
The results showed that rats born from hypoxic pregnancies took longer to perform the memory task, and didn’t remember things as well. However, rats born from hypoxic pregnancies in which mothers had been given Vitamin C throughout their pregnancy performed the memory task just as well as offspring from normal pregnancies.
Analyzing the brains of the rat offspring, the researchers found that the hippocampus—the area associated with forming memories— was less developed in rats from hypoxic pregnancies. “The data show that prenatal hypoxia reduced neuronal number, vascularity and synaptic density in the hippocampus and impaired memory function in the adult male offspring,” the investigators stated.
Further analyses then showed that hypoxic pregnancy caused excess production of reactive oxygen species, called ‘free radicals’, in the placenta. “Levels of oxidative stress in the placenta, but not in the fetal or adult offspring brain, were increased in hypoxic pregnancy,” they further noted. In healthy pregnancy the body keeps the level of free radicals in check by internal anti-oxidant enzymes, but excess free radicals overwhelm these natural defenses and damage the placenta in a process called ‘oxidative stress’. This reduces blood flow and oxygen delivery to the developing baby.
In the reported study, the researchers found that placentas from the hypoxic pregnancies showed oxidative stress, while those from the hypoxic pregnancies supplemented with Vitamin C looked healthy. The results showed that chronic fetal hypoxia led to a reduced density of blood vessels, and a reduced number of nerve cells and their connections in parts of the offspring’s brain. When the offspring then reached adulthood, its ability to form lasting memories becomes reduced and there is evidence of accelerated brain aging. Antioxidant treatment of the pregnant mothers effectively prevented these effects. “… maternal antioxidant treatment in hypoxic pregnancy restored placental oxidative stress to normal levels and prevented the programmed adverse effects on cerebral structure and function in the adult offspring, implicating placental oxidative stress as a mediating factor,” the team stated. “
Taken together, the study findings indicated that low oxygen in the womb during pregnancy causes oxidative stress in the placenta, affecting the brain development of the offspring and resulting in memory problems in later life. ” Maternal supplementation with vitamin C during hypoxic pregnancy protected against oxidative stress in the placenta and prevented the adverse effects of prenatal hypoxia on hippocampal atrophy and memory loss in the adult offspring,” the authors commented. […]
The 9 Most Essential Vitamins You Need in Your Diet, According to Yale Experts

Vitamins are an essential part of how our body functions, but there is a lot of misunderstanding and misinformation about how to best get them into your cells and throughout your body.
Our parents and caretakers routinely reminded us that eating our vegetables was essential to getting all of the healthy vitamins and minerals we need to grow. Oftentimes, we might think taking a supplement is the best way to get essential vitamins the body needs, but sourcing these nutrients through food is even more effective. Shutterstock Many times vitamins are advertised as “natural” but the most natural approach is how people have done it for thousands of years— a healthy and nutritious diet filled with diverse and colorful fruits and vegetables. The more colors and varieties of produce you are eating, the more likely you are to consume a scope of key vitamins. Purchasing from small local farms that practice organic techniques can also help to ensure that your produce is as nutrient-dense as possible. Who may require supplementation?
There are certainly times when people may require vitamin supplementation because of a circumstance or condition that prevents them from adequately obtaining them. For example, people who follow a vegan diet may need to supplement with vitamin B12 (which is largely found in animal-based protein and sources) or people with cystic fibrosis may require supplements because they do not properly absorb many vitamins.
It is important to keep in mind that most supplements did not originate in pill form but, instead, are derived from traditional diets, such as the Mediterranean diet , that kept people healthy for thousands of years. While some people may need to take their vitamins in a pill form, for the average person, food can often be your medicine.
Below, you will see nine vitamins your body needs as well as several foods that are rich in each. Then, don’t miss The 7 Healthiest Foods to Eat Right Now . Shutterstock Vitamin A isn’t actually a single vitamin but a whole family of different ones sometimes referred to as ‘retinoids’ such as retinol and carotenoids, including alpha-carotene and beta-carotene.
Function in the body: Vitamin A is important in keeping our reproductive and immune systems functioning and helps to keep our kidneys, heart, and lungs working well. It’s also essential for normal bone and tooth development. Another important job that vitamin A carries out is that it helps our eyes allow us to see in dark or dim light.
Risks of deficiency: The risk of vitamin A deficiency is pretty rare in well-nourished populations (such as the U.S.) because vitamin A is stored in the body, particularly in the liver. However, certain conditions such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, cancer, and prostate disease may cause your body to excrete too much vitamin A.
People with fat malabsorption may not be able to absorb enough vitamin A and certain medications may also interfere with vitamin A absorption, such as cholestyramine and orlistat. A lack of vitamin A can cause your immune system to function poorly. It can also cause a number of eye diseases (such as blindness), poor bone growth, and skin problems at your hair follicles.
Risks of overuse: Vitamin A is stored in fat in the body, therefore, too much of the vitamin can lead to accumulation and toxicity. Symptoms include headache, double vision, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, or vertigo. Too much vitamin A can also lead to osteoporosis, bone fractures, and liver toxicity. Larger than recommended doses of vitamin A may cause birth defects, and so pregnant women or women of childbearing age should not intake more than the RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance). Beta-carotene toxicity is much less likely, but eating large amounts of carrots daily can lead to yellow-orange skin color changes.
Top foods with vitamin A: Beef liver (3 oz cooked)
Baked sweet potato
Frozen spinach (½ cup cooked)
Raw carrots
Skim milk fortified with vitamin A
Shutterstock Vitamin C is also known as ascorbic acid and is key for immune function .
Function in the body: Vitamin C is important in the growth and repair of tissue and helps to maintain healthy skin, teeth and bones. Vitamin C is also an antioxidant that helps protect our cells from being damaged by free radicals, toxins, and radiation. Vitamin C can also help absorb iron from food in the intestines. Despite being highly advertised for preventing and treating the common cold , good data to support this claim is still unavailable.
Risks of deficiency: Deficiency of vitamin C can lead to a condition known as scurvy. Scurvy can present with fatigue, gum swelling, corkscrew hairs, and poor wound healing. It was common many years ago among sailors who did not have access to fresh fruits on long journeys. Scurvy is very rare in the U.S. because only a very small amount of Vitamin C is needed from a normal diet to prevent a deficiency.
Risks of overuse: Vitamin C is a water soluble vitamin and is not stored in the body, which just means that excess vitamin C is eliminated through urine. Large doses can still cause side effects, including nausea, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and more severely, can lead to the development of kidney stones. Patients with diabetes, recurrent kidney stones and poor kidney function should avoid high doses of vitamin C due to increased risk and complications of kidney stones.
Top foods with vitamin C: Raw red peppers (½ cup)
Orange juice (¾ cup)
Kiwi (one medium)
Frozen broccoli (½ cup cooked)
Baked white potato
Shutterstock Vitamin D is also known as calciferol. Research has shown that vitamin D can play a vital role in supporting the immune system and may help to mitigate the severity of symptoms associated with COVID-19 .
Function in the body : Vitamin D seems to have an endless number of functions in our body. These include bone mineralization and helping to maintain normal calcium levels in our blood. It also helps to reduce inflammation throughout the body and to maintain […]
Physical activity as medicine
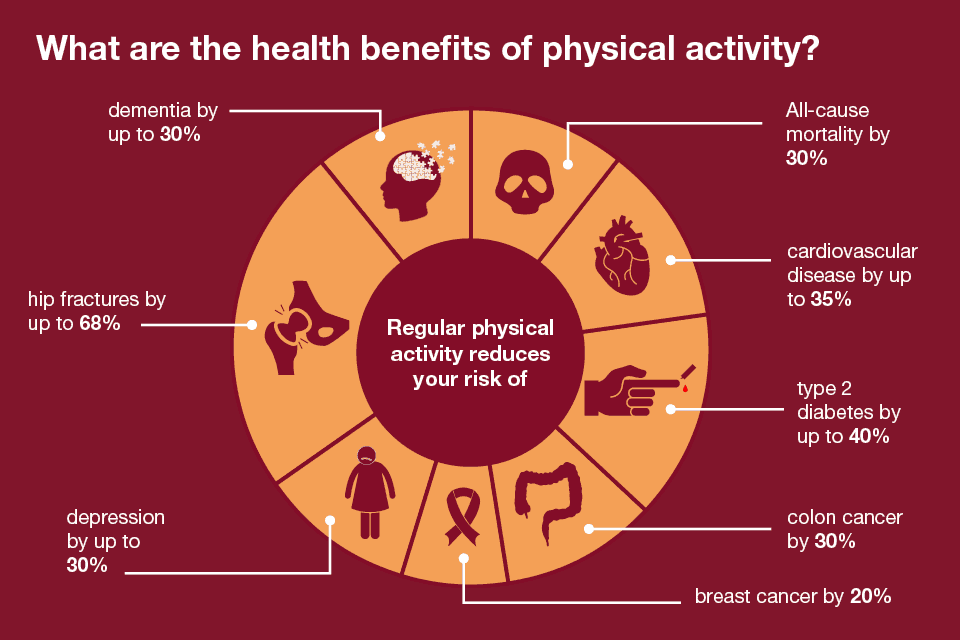
Physical Activity – The Single best Medicine CREDIT: https://www.greasbroughmedicalcentre.co.uk * EIM, NHF recommended adequate physical activity as a potent force in the fight against COVID-19
*Regular exercise helps make heart stronger, lowers blood pressure, increases blood flow
*Vigorous session improves sleep, helps curb low-grade inflammation in children
*Drinking coffee before activity may help burn more fat, researchers find
*Eating just one cup of leafy green vegetables daily could boost muscle function
More reasons have emerged why most medical practitioners now recommend increased exercise or rather physical activity as medicine.
Doctors are unanimous that regular exercise such as walking tops 15 natural ways to combat high blood pressure. They say regular exercise helps make one’s heart stronger and more efficient at pumping blood, which lowers the pressure in the arteries.
In fact, they say 150 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, such as running, per week, can help lower blood pressure and improve heart health.
Scientists have demonstrated in recent studies how exercise increases blood flow to the brain; can modulate various parameters associated with improved sleep, and helps curb low-grade inflammation in children. Even as other studies found drinking coffee before exercise may help burn more fat, and eating just one cup of leafy green vegetables every day could boost muscle function.
A new movement formed by Exercise is Medicine (EIM) and the Nigerian Heart Foundation (NHF) has recommended adequate physical activity as a potent force in the fight against COVID-19. They said the role of physical activity in regulating immunity and providing optimum health for people with non-communicable diseases are germane in the fight against the pandemic.
Indeed, globalisation and urbanisation have brought rapid changes in lifestyle and the consequences of decreased physical activity, increased sedentary living, unhealthy diets, and increased tobacco use, with rising in Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs). NCDs, especially cardiovascular diseases are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality as reflected in the past 18 months even with the COVID-19 pandemic all over the world.
Chairman of physical activity committee, Nigerian Heart Foundation (NHF) and Director, Exercise is Medicine (EIM) Nigeria National Centre, Prof. Fatai Adeniyi, told journalists at a press conference organised ahead of the 2021 World Physical Activity Day (WOPAD) that considering the global surge in non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and heart diseases among others, and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it becomes expedient to reiterate the benefits of being physical activities for all generations of people.
The theme for the first WOPAD adopted by NHF is “Exercise for a Healthy Heart.” The press conference was organised by the NHF in collaboration with EIM, Nigeria National Centre, the Advisory Board, and the Ambassadors.
Adeniyi said physical activity when adopted by everyone has the benefit of preventing, maintaining, and controlling the complexities surrounding non-communicable disease onset, progression, and complications. “While these aforementioned benefits are probably well known about non-communicable diseases, it is necessary to emphasis that adequate physical activity can serve as a potent force in the fight against COVID-19 as the role of physical activity in regulating immunity and providing optimum health for people with noncommunicable diseases are germane in the fight against the pandemic,” he said.
Adeniyi said the EIM Global Centre and the Nigeria National Centre are profoundly committed to the adoption of health-enhancing physical activity among the general population. They, however, believe there is a wide gap between what people know about physical activity and what they practise. “Therefore, as we celebrate the 2021 World Physical Activity Day, the EIM Nigeria calls on individuals, groups, corporate entities, traditional institutions, government and non-governmental agencies including all policy influencers and makers to pay more attention to the issues around physical activity at every level of our daily routines to narrow the gap between knowledge and actual uptake of physical activity,” he said.
Executive Director, NHF, Dr. Kingsley Akinroye, said that the discussion about physical activity has been on for many decades; hence it is not a new innovation.
Akinroye, however, the WOPAD is a day set aside to propagate in stronger terms, the benefits inherent in the adoption of physical activity. The cardiologist said the WOPAD celebrated globally on April 6 every year features various programmes to enhance the uptake of physical activity by the general public. “For the year 2021, the Exercise is Medicine (EIM) Nigeria is organising series of events in Osogbo, the Osun State capital on April 6 and 10, 2021. The programmes include radio and other sensitization talks, health screening and counselling on physical activity, group physical exercise sessions, and working Gyms and Wellness Centres in Lagos, Ibadan, Kano, Port-Harcourt, Abakaliki, and Osogbo,” he said.
Akinroye said the EIM Nigeria, domiciled and nurtured by the Nigerian Heart Foundation is an agency of the American College of Sports Medicine, with its headquarters in Indianapolis, United States of America (USA), but with a global presence in over 40 countries. He said Nigeria is one of the three countries in Africa with this global presence and NHF is proud to be part of this global family.
The cardiologist said WOPAD provides a unique opportunity for the EIM to reach out to the different strata of the community, as it is an opportunity to further reinforce the core visions of the EIM. Akinroye said the EIM visions include: making health care providers assess every patient’s level of physical activity at every clinic visit; determining if the patient is meeting physical activity guidelines; providing patients with brief counselling to help him/her meet the guidelines; and/or refering the patient to either health care or community-based resources/experts for further physical activity counselling and guidance.
Akinroye said: “We use the medium to call on individuals, groups, corporate entities, traditional institutions, government and non-governmental agencies including all policy influencers and makers to pay more attention to the issues around physical activity at every level of our daily routines to narrow the gap between knowledge and actual uptake of physical activity.”
Meanwhile, physical exercise has long been prescribed as a way to improve the quality of sleep. But now, researchers from Japan have found that […]
Chaperone protein imbalance promotes toxic tau buildup in the aging brain
Tau pathology resembling that seen in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Credit: Laura Blair’s laboratory, USF Health/University of South Florida Chaperone protein imbalance can play a significant role in initiating toxic accumulation of tau in the aging brain—an early step in the development of Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders known as tauopathies, a new preclinical study by University of South Florida Health (USF Health) neuroscientists suggests.
In humans, misfolding of the protein tau leads to its toxic accumulation inside brain cells , the formation of these tau aggregates into hallmark neurofibrillary tangles, neuron death, and eventually symptoms of cognitive decline such as memory loss and diminished thinking skills.
In this study the USF Health Morsani College of Medicine researchers used mice that were not genetically modified (wild-type mice) to examine the effects of Aha1 and FKBP52, two co- chaperone proteins of heat shock protein Hsp90, in the aging brain. They modeled molecular chaperone imbalance by overexpressing production of Aha1 and FKBP52 in these old, wide-type mice. The findings, highlighted below, were reported April 8 in Acta Neuropathologica Communications.
Hsp90 is a chaperone protein abundant in neurons and other cells in the brain. Normally, co-chaperone proteins assist chaperone proteins in monitoring and sustaining the balance (homeostasis) of proteins critical to cell health.
“The chaperone protein network is your cell’s natural defense to maintain homeostasis throughout life, and this study emphasizes the importance of protecting that balance in the aging brain,” said principal investigator Laura Blair, Ph.D., an assistant professor of molecular medicine at the USF Health Byrd Alzheimer’s Center, Morsani College of Medicine. “We’re excited about using this new model of tauopathy in finding ways to restore chaperone protein balance to delay or stop the progression of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.”
Among their many quality-control functions, chaperone protein networks ensure proteins are folded to conform to the proper 3D shapes, transported precisely where needed to do their jobs, and pushed toward degradation if they are abnormally modified or no longer useful. Heat shock proteins like Hsp90, triggered when a cell is under stress, play a particularly important “triage” role in correcting protein misfolding to prevent aggregation. Laura Blair, PhD, assistant professor of molecular medicine at the USF Health Byrd Alzheimer’s Center, University of South Florida, was principal investigator for the study. Credit: USF Health “But in the aging brain , the balance of the chaperone proteins shifts and creates a system not working as efficiently as it normally would. Large numbers of the chaperone molecules decrease in expression, and a smaller but significant number increase in their expression,” Dr. Blair said.
Increasing age is the greatest known risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. So, the USF Health team investigated whether increased levels of FKBP52 and Aha1 alone could initiate pathological features mimicking human Alzheimer’s disease in aged wild-type mice—those with no genetic manipulations predisposing their brains to abnormally increase tau aggregation.
Key findings from their new mouse model of tauopathy include: High levels of FKBP52, and to a lesser extent elevated levels of Aha1, increased tau accumulation over time in the aged, wild-type mice.
The tau accumulation promoted by overexpression of FKBP52, but not Aha1, correlated with increased neuroinflammation through exaggerated activation of neuronal support cells, namely microglia and astrocytes. This was complemented by loss of neurons and cognitive impairments.
Existing mouse models, including those that add or subtract genes, introduce tau mutations, and seed mice brains with human tau, help scientists learn more about the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. However, they tend to be limited in capturing the physiological aspects of neurodegeneration in the context of both normal and abnormal aging.
“We hope this (chaperone imbalance) model will help us better understand the dynamics of tau aggregation and neuroinflammation, including the timing and connections among pathological events, without directly regulating one pathway or the other,” Dr. Blair said.
Dr. Blair’s team has designed follow-up studies to help unravel if, and when, tau accumulation or neuroinflammation is more influential in causing brain cell toxicity during aging. That could help determine which chaperones—FKBP52, Aha1, or others—may be the best therapeutic target options for restoring protein balance, she said.
More information: Marangelie Criado-Marrero et al, Hsp90 co-chaperones, FKBP52 and Aha1, promote tau pathogenesis in aged wild-type mice, Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1186/s40478-021-01159-w
Provided by University of South Florida

