Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
SOS for Menopause
Sharone is a busy 51-year-old working mother of two teenage boys who lives in the Boston area. When she turned 48 years old, she began experiencing night sweats, which woke her and prevented her from getting a sound slumber nightly. Lying in bed, she ruminated about her life stresses and tossed and turned until the sun came up. She was constantly tired during the day and often missed routine appointments due to forgetfulness. She gained 30 pounds in three years. A trip to her doctor provided her with a diagnosis. Sharone, along with millions of other women, was experiencing the menopausal transition.
Menopause is the time period when a woman begins the journey of ceasing her monthly menstrual period. Menopause typically starts somewhere in the middle to late 40s to mid-50s for a woman. Leading up to this time, a woman begins to produce less estrogen and other hormones in her ovaries, which can cause some of the symptoms that Sharone is experiencing, including sleep disruption and night sweats.
Her memory problems and anxiety levels are also classic during this transition. When a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without experiencing her period, she’s considered to have gone through menopause and is considered postmenopausal.
Is there anything that a woman can do to reduce these unpleasantries of menopause ?
I dug deep into the science and reached out to Elizabeth Ward and Hillary Wright, both registered dietitian nutritionists and the authors of the new book, The Menopause Diet Plan: A Natural Guide to Managing Hormones, Health, and Happiness (Rodale Books, 2020), for their advice.
Here’s some good news for combating the issues of sleep, weight gain and memory loss during this transition:
According to Ward, “Women may experience more trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, and sleeping deeply during the transition to menopause.” To improve a woman’s sleep, Ward recommends avoiding caffeine-containing beverages, such as coffee , tea, energy drinks and some soft drinks, later in the day, as well as downsizing the size of the dinner meal.
Also, people wrongly think that an alcoholic drink before bed will improve their sleep , when in fact it has the opposite effect. Although an alcoholic drink within an hour before bed may help you to fall asleep sooner, it will disrupt your sleep and you will find yourself potentially awakening in the middle of night.
On the flip side, adding a bout of moderate or vigorous exercise during the day can reduce the time it takes to get to sleep at night and help you to sleep both more deeply and for longer, says Ward.
Unfortunately, being chronically sleep deprived can also be a problem for your waist. “Research has linked inadequate sleep with higher body weight, possibly due to effects on the hormones that control hunger. The less you sleep, the hungrier you will be and the more you may eat,” says Ward. If sweats and hot flashes awaken you at night, try reducing the temperature in the bedroom, turning on a fan and layering your clothing so that you can remove some when you feel hot and put some back on should you get cold.
Mother Nature is not very nice to aging adults, and Sharone experienced this firsthand. As you age, your metabolism slows down, reducing the number of calories you need to maintain your weight. If you don’t make an adjustment in your intake or activity level, weight gain is inevitable.
“The declining estrogen levels in a woman’s body also makes it easier to lose lean mass and can contribute to the shift of fat storage in the body,” claims Wright. “Lower estrogen levels redirect body fat to our middle, producing the dreaded belly bulge accumulation that even lean women report experiencing as they near menopause.”
When you eat during the day may also give you additional ammunition to fight the battle of the bulge. Emerging research is shedding light on how eating most of your daily calories later in the day and evening may not be good for your waist . At play are the body’s circadian rhythms, which are the 24-hour rhythms in your body that are in lockstep with the everyday light and dark cycle. Eating too many calories later in the day fouls up the circadian rhythms in your body and can influence the activity of enzymes and hormones that regulate your metabolism and weight.
“One of the ways that our circadian rhythms can affect body weight is by influencing the way we use the hormone insulin,” says Wright. “Research supports that most people use insulin more effectively during the sun-up time of the day versus the night.” So, eating a large carbohydrate-rich dinner and tons of evening snacks will trigger the release of insulin, prompting the body to store fat. According to Wright, “a better bet would be to start off eating a good breakfast and eating regularly over the day, with a goal of winding down our eating as we enter the evening.”
While there aren’t any hard and fast rules about when to stop eating in the evening, Wright believes that a benefit appears to kick in with 12 to 13 hours of fasting. Given the importance of eating breakfast , trying to keep eating to a 12 hour window from breakfast time is reasonable. So if breakfast is at 8 a.m., try to wrap up eating before 8 p.m.
“ Brain fog is real,” says Ward, referring to the fact that women can become moody, more tired, and experience memory lapses, starting in their 40s. “Declining estrogen levels, and aging in general, increase the incidence of conditions that affect the brain, including anxiety and depression. It’s important to note that stress can mess with memory and other cognitive skills,” she says. “The years leading up to menopause often coincide with a stage of life that’s full of other stressful transitions too.”
While stress management is key, she also recommends eating a brain-nourishing, plant-based diet that’s low in saturated fat, sodium and added sugars, and rich in high fiber foods such fruits and veggies. Choline, which […]
Research Shocker: Baby Boomers Less Mentally Sharp Than Their Parents

Many of us take for granted that we will be better off than previous generations.
That is a sensible assumption.
History shows that over time, living standards increase, people become better educated, technology advances, lifespans get longer, and health improves.
That’s why a new study comes as a shock.
It shows that when it comes to mental ability, baby boomers are actually lagging behind their parents. They have poorer cognitive skills than their mothers and fathers did at the same age.
The research was published in the Journals of Gerontology: Social Sciences . Dr. Hui Zheng analyzed tests of memory and thinking ability taken by different generations of Americans. [1]
Dr. Zheng found that cognition scores of adults increased from the greatest generation (born 1890 to 1923) through war babies (1942-1947).
But then scores declined with the early baby boomers (born 1948-1953). They dropped even lower with mid-baby boomers (1954-1959).
“It is shocking to see this decline in cognitive functioning among baby boomers after generations of increases in test scores,” said Dr. Zheng. [2]
But what he found most surprising was that the decline occurred “in all groups: men and women, across all races and ethnicities and across all education, income and wealth levels.”
Why are baby boomers losing their mental sharpness at a younger age?
Dr. Zheng said it’s largely due to four factors: Lack of exercise
Obesity
Depression
Loneliness
Baby boomers suffer from these issues more than previous generations did. And it has taken a toll on their brain health.
“Part of the story here is the problems of modern life,” said Dr. Zheng.
Baby boomers were helped by some trends. They had better childhood health, more education, and higher income than previous generations.
If it weren’t for those factors “baby boomers would have even worse cognitive functioning,” said Dr. Zheng.
The situation is alarming because impaired cognitive function is linked to a higher risk of dementia. That means baby boomers may suffer from Alzheimer’s at higher rates than their parents.
“This study suggests (dementia rates) may be worse than we expected for decades to come,” said Dr. Zheng. 4 Ways to Stop the Baby Boom Brain Drain
There are steps you can take to alleviate the factors that lead to cognitive decline:
> Exercise. Physical activity is strongly linked to mental sharpness. But many people complain they don’t have time to exercise. [3]
That’s why we recommend high-intensity interval training (HIIT). It gives you a great workout in less than 20 minutes a day.
A 2019 study published in the journal Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise found that HIIT improves blood flow to the brain better than steady state cardio like jogging. Brain blood flow reduces the risk of dementia. [4] [5]
HIIT is adaptable to many activities. You can run, cycle, swim, do calisthenics, or use a rowing, stair climber, or elliptical machine.Warm up for three to five minutes doing your chosen form of exercise slowly. Then do the exercise at almost the highest intensity you can for the next minute.Slow down for a minute or two to catch your breath. Then go hard again for another minute.Repeat this process five to seven times. Afterward, do the activity slowly for at least two minutes to cool down.The idea is to push your body for a brief burst, and then allow it to recover.Lose weight. Research shows that a low-carb diet is the best way to drop extra pounds. A study published in the journal PNAS found that a low-carb diet can slow brain aging. [6] And it’s easy to follow:Avoid sugar and starchy foods like bread, pasta, rice, beans, and potatoes.Eat meat, fish, eggs, non-starchy vegetables, and natural fats like olive oil and butter.Fruits that are high in fiber and low in sugar are OK. They include berries, avocados, grapefruit, kiwis, pears, and watermelon. But avoid fruit juices. They are typically high in sugar.The most important rule of low-carb eating? Avoid sugary foods and drinks that push insulin higher, especially soda.You don’t have to count calories or weigh your food. Eat when you’re hungry and until you’re satisfied.Keep depression at bay. Research shows non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen are 79% more effective than a placebo at treating major depression. [7] Omega-3 fatty acids, the active ingredient in fish oil, work against depression as well. [8] If you suffer from mild to moderate depression, talk to your doctor about trying aspirin and/or an omega-3 fish oil supplement. They may work better for you than prescription antidepressants without the potential dangers.Combat loneliness. Dr. Paul Nussbaum is one of the world’s leading experts on brain aging. He says loneliness profoundly damages the structure of the brain.Here are his five recommendations to reduce social isolation: Reach out. Call a friend or family member. Don’t wait for them to contact you. Tell yourself you’re not imposing and they’ll be glad to hear from you. Get a pet. A dog or cat provides companionship. Join a club. Find one that focuses on one of your special interests and ignites your passion. It could be cooking, knitting, movies, whatever. The important thing is to meet others who share your enthusiasm. Join an online chat group. It’s important you get to know the others in the group personally. Engage them on an emotional level. Make plans for the future. Giving yourself something to look forward to fights depression and a lack of purpose in life. Editor’s Note: Discover the most effective natural methods to improve your health. Read our monthly journal Independent Healing . It’s your best source for unbiased, evidence-based medical information you won’t find anywhere else. To find out more, go HERE. Related Articles [1] https://academic.oup.com/psychsocgerontology/advance-article/doi/10.1093/geronb/gbaa107/5877935 [2] https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2020-08/osu-bbs073120.php [3] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/01/190130161638.htm [4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30768552/ [5] https://www.bicycling.com/news/a28483856/hiit-may-prevent-dementia/ [6] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/does-a-low-carb-diet-keep-your-brain-young [7] https://jnnp.bmj.com/content/early/2019/08/29/jnnp-2019-320912 [8] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-020-0786-5
The Amazing Health Benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushrooms – II
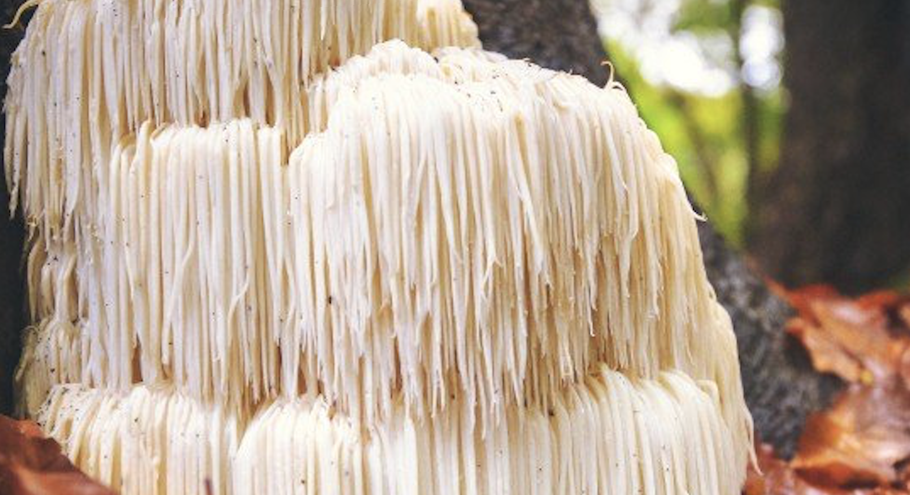

Lion’s Mane Mushroom is known for stimulating Nerve Growth Factor, improving cognition and memory, and relieving depression.
Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus) is unique in the mushroom family both in appearance and function. Lion’s Mane Mushroom is extremely effective at stimulating Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) in the brain.
Known for its powerful effects as a “brain tonic”, Lion’s Mane is said to have been used as a tea for thousands of years by Buddhist monks. To enhance brain power, and heighten their ability to focus during meditation.
Lion’s Mane is a powerful catalyst for brain cell regeneration helping improve memory and cognition.
The primary active compounds in Lion’s Mane are hericenones and erinacines. Hericenones help your brain produce more Nerve Growth Factor. And erinacines easily cross the blood-brain barrier to boost the production of neurons.
Lion’s Mane helps:
•Nerve Growth Factor. Lion’s Mane Mushroom prevents and treats nerve damage in the brain. Once past the blood-brain barrier, Lion’s Mane stimulates enzyme production that release Nerve Growth Factor (NGF). Nerve regeneration helps relieve neurodegenerative disease symptoms such as Alzheimer’s, dementia, and Parkinson’s Disease.
•Neurogenesis. Lion’s Mane stimulates the repair and creation of neurons. Boosting neurotransmitters and signaling that effects memory, learning, recall, and mood.
•Brain Optimization. Lion’s Mane helps eliminate brain fog. Restoring memory and mental alertness. And improves anxiety and depression symptoms.
Overview
Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus) is a medicinal mushroom proven to benefit the brain, nerves and immune system.
Unlike other mushrooms sporting a cap and stem, Lion’s Mane has long, flowing, white tendrils. Resembling a lion’s mane. Other names include Monkey’s Head, Bearded Tooth, Pom Pom Blanc, Hedgehog Mushroom and Satyr’s Beard.
This parasitic fungus grows hanging off logs and trees. And is native to North American, Europe and Southeast Asia. In Japan, it’s called yamabushitake or “those who sleep in mountains”. Referring to the Shugendo sect of hermit monks and their long, flowing robes.
As a nootropic, Lion’s Mane has been shown to be particularly effective in stimulating Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) in the brain.
NGF is produced in the hippocampus throughout life. Modulating cholinergic receptors and neuroplasticity.[i] And is essential for learning.
Nerve Growth Factor are special proteins that function to regenerate neurons. Lion’s Mane contains two unique classes of NGF’s – hericenones and erinacines which easily cross the blood-brain barrier.
Lion’s Mane, like other medicinal mushrooms, contain high amounts of the antioxidant beta-glucoxylan and four other polysaccharides and polypeptides. Having a significant impact on enhancing your immune system. And decreasing tumor growth.
Lion’s Mane has also been studied in reducing amyloid plaques. These clumps of beta-amyloid proteins block signals between neurons. And are implicated in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Lions’ Mane is also used to treat Lyme’s Disease, and digestive tract issues.
Here we’re talking about Lion’s Mane Mushroom and its effects on brain health and chemistry.
Why green tea is good for you

Looking for a natural source of caffeine? Nutritionists say green tea, a popular beverage consumed worldwide, is the way to go. Green tea is derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant and comes in several varieties.
It can be enjoyed hot, cold or even in powdered form, and it’s recognized for its high antioxidant content and health benefits. But how much green tea should you drink to achieve these benefits?
Marie Ann Munezero, a Kigali-based nutrition consultant, says green tea contains less caffeine than coffee.
This, she says, means that one can take the beverage without significantly disturbing their sleep pattern.
Munezero explains that our cells naturally accumulate oxidative damage during regular cell metabolism.
“A class of molecules called antioxidants can prevent or even reverse that damage. One of the most powerful antioxidants is called epigallocatechin gallate,” she says.
Munezero says that epigallocatechin gallate has been shown to reduce the growth of breast and prostate tumours.
The minimal amount of processing of green tea means that it retains many of the phytonutrients that are available in the actual tea plant.
According to Munezero, green tea may also be good for the heart.
She says the phytonutrients in green tea may also help one lose weight and maintain it.
Studies have shown that the caffeine present in green tea acts as a stimulant that has been shown to aid fat burning and improve exercise performance in various studies.
And that the massive range of antioxidants known as catechins helps burn fat and boost the metabolism that is key to lose weight.
Besides, studies on black or green tea leaf have demonstrated that they may have positive effects in the areas of cardiovascular health, osteoporosis, obesity, and bowel conditions.
Munezero goes on to note that the green tea contains antioxidants, which have been shown to inhibit cardiovascular disease development and inflammation.
She says that tea may also have psychological and neurological effects, such as increases in alertness and information processing, that is not due to caffeine but a chemical (theanine) in the tea leaves.
Not all cholesterol is bad for you. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol is associated with cardiovascular risk, while high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol could actually protect one against heart disease.
Research also shows that the phytonutrients in green tea appear to be connected to balanced LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, helping to keep them in a healthy range.
Erick Musengimana, a nutritionist at Rwanda Diabetes Association, Kigali, says green tea contains the amino acid L-theanine, which is found almost exclusively in tea plants.
He says that L-theanine acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain, meaning that it sends signals to neurons.
Several studies have shown that L-theanine appears to increase alpha-wave generation in the human brain, signalling a state of relaxation.
Alzheimer’s disease is characterised by profound changes in memory and thinking abilities. This neurodegenerative disease currently has no cure.
However, Musengimana says the antioxidants in green tea appears to reduce the likelihood that one will develop Alzheimer’s disease.
On the other hand, the flavonoids in green tea, including epigallocatechin gallate, have been shown to decrease the liver’s glucose production.
Musengimana says that this means that the body regulates blood sugar more effectively, keeping the glucose levels within a healthy range.
He points out that type 2 diabetes is becoming a big health condition all over the world, due to the lifestyle people are exposed to.
He says that it has been proven that drinking green tea could lower the risk of one developing this condition, therefore, its ideal to take it on a regular basis.
9 Ways Moving Your Body Helps Your Brain

Outdoor exercising is, without a doubt, healthy and highly beneficial to your body and mind.
However, a large number of people perceive exercising negatively, seeing it as more of an obligatory and stressful routine than a healthy practice. But if you think of it, exercise is the simple act of moving your body. It isn’t as burdensome as you probably imagine. Instead of seeing exercise as a drag, start seeing it as your body’s most basic function– movement. Now start moving your body more within a day and with higher intensity. Simple! Moving your body will not only help you lose weight but will also foster your feelings of joy and optimism. It improves your mood by tackling mental disorders such as anxiety and depression. Research shows that people who exercise at least once a week handle stressful tasks better than those who don’t exercise at all. And because you will always encounter stressful tasks and situations for as long as you live, you simply cannot overlook the necessity of routine exercise. How Moving Your Body Can Improve Mood Disorders
If you haven’t been moving your body as regularly as you should, here are 9 ways through which you can start boosting your mental ability through exercise. 1. Increased tolerance for your “fight or flight” instincts
Your mood is dependent on a system within your brain that is known as the “fight or flight” system. This system reacts to physiological changes within your environment, either by becoming extremely frightened or by wanting to fight back. A good example is when you hear a sudden loud noise and your heart rate fluctuates rapidly. If this system isn’t tolerant enough for different symptoms of fear, then you are a prime candidate for anxiety and stress.
You can boost the system’s tolerance levels by engaging in regular aerobic exercises. Train your heart to beat normally even when exposed to sudden physiological changes. Another proven way of boosting this tolerance is engaging in social games such as soccer and paintball. Get yourself soccer or paintball equipment and, together with your close relatives or friends, create a support system around the game. This sport not only boosts your physical activity but also is a great way of engaging and connecting with your friends and family. 2. Increasing BDNF
BDNF is a healthy brain protein that aids the growth of nerve fibers. When your brain has this protein in abundance, you experience lesser severe depressive symptoms. Psychotherapists agree that some of the best medications for anyone suffering from an acute shortage of the BDNF protein are regular cycling, flexibility exercises, and balance exercises. In order to make these activities even more appealing, you can try something new and invest in an electric bike , definitely the trend amongst outdoor enthusiasts. 3. Perfect medication for ADHD
Moving your body regularly helps you cope better with attention-deficit disorder (ADHD). Experts suggest that moderate-intensity exercises and attention-grabbing tasks are the best in this regard. Moderate-intensity exercises include cycling and dancing. Games that grab your attention and improve your focus include paintballing, scavenger hunts, and more. A single 20-minute exercise session will significantly lower your feelings of fatigue, confusion, and depression. 4. Meditation helps you cope better with traumatic experiences
Meditative movement is a known therapy for most depressive symptoms. It helps you to focus on your body, mind, and soul. When you meditate, you live in the moment, paying close attention to your gut feelings and bodily sensations. It helps you note your body’s breathing and heartbeat rhythms, even as you move around a position in space. That allows you to appreciate you for who you are and forget the many stressful occurrences that threaten to dim your mood.
Some of the meditative movements that you should try include qigong, yoga, and Tai Chi. Those will alleviate your symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, especially after you go through a life-threatening experience. However, it is important to note that post-traumatic disorder is best diagnosed by psychiatric experts. You can also seek the help of a qualified life coach who will assist you in finding your inner peace even as you continue shaking off the traumatic symptoms. The idea here is to move your body and at the same time seek professional help. 5. Exercise is a powerful depression reliever
Running for 15-20 minutes per day, for example, can be a better alternative to antidepressant medication.
From a scientific perspective, moving your body promotes feelings of calm and well-being by expediting the generation and release of endorphins. Endorphins are powerful chemicals that, when released into the human brain, uplift spirits and make people feel energized. They are the natural painkillers and mood elevators in your body. Science aside, exercise can be a good distraction from negative thought patterns. When you go hiking in the woods, for example, the cycle of negative thoughts that feed depression is discontinued, and that affords you some quiet time to feed positivity into your brain. That is why according to a recent study by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, moderate exercise can be an effective remedy to mild and moderate depression. The study also found out that walking for at least an hour per day can lower your chances of suffering from major depression by up to 26%. For people recovering from depression, maintaining a regular exercise routine can lower your chances of relapsing. 6. Lowering levels of stress hormones
Besides stimulating the production of endorphins, moderate workouts such as aerobic exercises can significantly lower the levels of your body’s stress hormones, particularly adrenaline and cortisol. This neurochemical effect boosts the feelings of relaxation and optimism, which are vital for enhanced mood and spirits. 7. The confidence boosting factor
The emotional benefits of exercise can be attributed to the physical changes that your body experiences as a result of regular exercise. Physical fitness gives you a sense of mastery and control, renew your vigor and energy, and helps […]
From boosting memory to fighting hair loss, here’s how ‘Brahmi’ herb can benefit your health
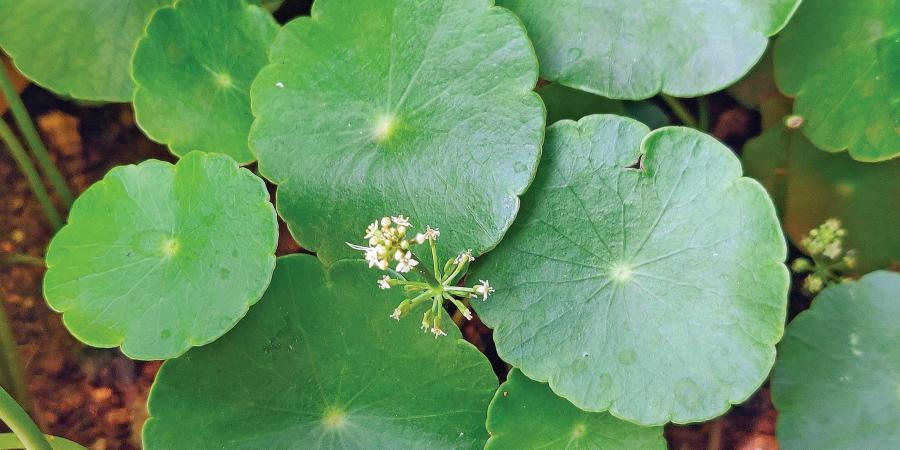

Often called the herb of grace, Brahmi has been known for its medicinal properties since time immemorial and is amenable to use in a multitude of ways. This therapeutic herb, known as a memory booster, an aphrodisiac and a health tonic that lowers blood pressure, reduces inflammation and improves concentration, among other things. If a child faced trouble with maths or had difficulty memorising at school, the remedy given was simple—a spoonful of Brahmi in powder or paste form.
This therapeutic herb, known as a memory booster, an aphrodisiac and a health tonic that lowers blood pressure, reduces inflammation and improves concentration, among other things, is hardly mentioned today. However, in not knowing about it enough, we’ve kept ourselves away from its rewards.
Multiple benefits
The herb’s name is derived from Brahma aka the creator of the universe. It’s been used for a variety of reasons, including reducing anxiety, improving sleep, boosting brain health, hair loss, and skin disorders like abscess, eczema and even psoriasis.
“When consumed regularly, it strengthens the immune system too. The antioxidant compounds present in Brahmi supplement the nutrients extracted through food and help the body fight foreign bacteria or viruses.
“Chewing a few Brahmi leaves reduces the secretion of cortisol, the stress hormone,” says Ludhiana-based Garima Goyal, dietician and certified nutritionist. The herb reduces oxidation of fats in the body’s bloodstream and is good for cardiovascular health. Unique quotient
Brahmi is often used in cases of Alzheimer’s, dementia, Parkinson’s, Epilepsy, and attention deficit disorder to boost cognitive health, memory, focus, and to reduce inflammation in the brain.
“The research behind this herb has shown that it has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Free radicals and oxidation are often seen as a side effect of inflammation in the brain of an Alzheimer’s patient and Brahmi is a power herb to halt or scavenge these free radicals to prevent further damage to the brain,” says Luke Coutinho, holistic lifestyle coach-integrative medicine.
The active ingredients present in it that lead to all these benefits are bacosides and betulinic acid, types of triterpenoid saponins or chemical compounds.
Bacosides are known to enhance nerve impulse transmission and repair damaged neurons, while betulinic acid is replete with anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
The nerve impulse transmission plays a vital role in promoting healthy cognitive functions like attention span, focus, concentration, learning and memory.
On your plate
You can add small quantities of the herb to your soup, salads, chutney powder or even roti dough or dosa batter.
Add a couple of leaves to your coriander chutney and you’ve given yourself a natural health supplement. Timare chutney, and Tambuli (a curd-based gravy) are popular dishes made from its leaves in the South.
“We often encourage our clients to use it in the form of tea by brewing a few Brahmi leaves in water with pepper and honey,” adds Coutinho. It can also be added to lassi or neer mor. “Pesto is again a great way to consume this herb.
Sauté a tablespoon of onions with some garlic and a couple of chillies.
Add a tablespoon of walnuts and 1/2 cup of coconut milk and cook for a minute.
Cool this mixture and blend it along with a cup of Brahmi leaves and a pinch of hing. Toss this with cooked chilled rice noodles and you have a wholesome dish ready,” says Chef Vicky Ratnani.
Boost its power
“Brahmi combined with ghee works as a miracle. When used with neem, manjishtha and turmeric, it helps in skin conditions with pitta imbalance,” says Goyal.
Benefits of Brahmi Good source of Vitamin C
Used to treat cough, bronchitis and asthma
Effective in regulating blood sugar levels
Known to provide relief from arthritis, joint pain and other inflammatory conditions
Provides relief from gastrointestinal disorders and problems such as indigestion and ulcers.
Antioxidant-rich and known to possess anti-cancer properties
Trauma may increase cognitive decline with age

People who experience trauma in child- and adulthood may experience a greater amount of cognitive decline as they age than individuals who haven’t experienced trauma, a new study found.
The research also showed that recent trauma in adulthood has a larger impact on some aspects of cognitive functioning than trauma in childhood.
“We found that the more adverse events experienced, such as your parents’ divorce or a parent dying, the greater the cognitive decline,” says coauthor Margie Lachman, professor of psychology at Brandeis University.
The researchers studied roughly 2,500 adults, ages 28 to 84, between 2004 and 2013. The participants were part of the Midlife Development in the US (MIDUS) study, a national longitudinal study of health and well-being in adulthood.
Participants were given a list of 12 potentially traumatic events and asked if they’d experienced any, and how negatively they were affected.
The events on the list included divorce or death of a parent during childhood, emotional or physical abuse , parental alcohol or drug addiction, combat experience , and losing a home to fire, flood, or natural disaster. For any of these to be considered traumatic, respondents needed to indicate they caused severe emotional distress.
Researchers also asked subjects a series of questions that tested their cognitive abilities in two areas: executive functioning (EF) and episodic memory (EM). EF pertains to such skills as focusing attention, planning, problem-solving, and multitasking. The test of EM involved remembering recently learned information.
The scientists compared the results of individuals who says they had lived through trauma with those who indicated they hadn’t and tested their EM and EF over the course of nine years.
Those respondents who says they had experienced more traumatic events showed greater declines in both EF and EM.
Lachman says this may be because trauma has been linked to stress and depression , both of which are known to impair cognitive functioning.
Trauma is also linked to metabolic disease, inflammation, and disruption of the body’s immune system, which are likewise also known to harm the brain’s performance.
Lynch stresses that trauma does not automatically mean an individual will experience greater cognitive impairment in later life. The impact of trauma varies and some people are more resilient or receive treatment that can mitigate the effects.
Lynch, who is now a PhD student at the John Jay College of Criminal Justice in New York, also says the effects of cognitive decline can be subtle and may go unnoticed.
“It might not feel like there’s an effect on your day-to-day functioning,” she says.
The researchers also looked at whether childhood or more recent traumatic experiences had a greater effect on cognition. They found that individuals exposed to trauma later in life had a greater decline in EF than individuals whose first traumatic event occurred earlier in life. The amount of decline in EM did not vary based on when the event occurred in life, a finding that the researchers says required further study.
Lachman speculates there may be more of an opportunity to recover from trauma that occurs years before, in childhood. She says children may be more likely to receive supportive interventions or the increased plasticity of their brains may make them more likely to adapt in the long term.
The research appears in the Journal of Traumatic Stress .
Mushrooms May Do Magic for Your Immune System – and Your Portfolio

The MarketWatch News Department was not involved in the creation of this content.
Aug 20, 2020 (Baystreet.ca via COMTEX) — Mushrooms could do magic for your health. In fact, according to researchers form Griffith University, mushrooms have the “ability to activate cell immunity in humans, according to The New Daily. “They do this through their possession of beta-glucans, which humans don’t have.
So, when human cells come into contact with this foreign body, the immune system starts to fire up and respond.”
Mushrooms such as Reishi can help with sleep, anxiety, and depression, according to Teelixir. Lion’s mane can help with memory, according to Healthline. Chaga can help with inflammation for example, according to Best Products. Turkey tail can help support the immune system, and assist with some cancer prevention, says Healthline. Such discoveries could do the trick for investors, too. All as the global market for functional mushrooms was $5.8 billion in 2018, according to market research firm, Mordor Intelligence. Between 2019 and 2024, it’s expected to grow 6.4% a year, according to a CNBC report. That’s creating opportunity for companies such as Better Plant Sciences Inc. (CSE:PLNT)(OTC:BOSQF), United Natural Foods Inc. (NASDAQ:UNFI), Starbucks Corporation (NASDAQ:SBUX), New Wave Holdings Corp. (OTC:TRMND)(CSE:SPOR), and Amazon.com Inc. (NASDAQ:AMZN).
Better Plant Sciences Inc. (CSE:PLNT)(OTC:BOSQF) BREAKING NEWS: Better Plant Sciences Inc. announces that subsidiary Neonmind Biosciences has completed final product development for four unique Ayurveda-inspired and botanical-enhanced mushroom coffee blends which are now moving into the mixing stage with a co-packer.
The coffees are fair trade and organic, with Ayurvedic organic botanicals and organic mushroom extracts. Each is formulated with adaptogenic, immune-boosting medicinal mushrooms that are antioxidant and nutrient-rich. The formulas contain special blends of reishi, cordyceps, lion’s mane and turkey tail mushrooms, all of which are widely regarded for their health benefits.
“Four unique blends will be available: two instant mushroom coffee blends and two roasted coffee blends. Functional mushrooms are booming in popularity as a supplement to boost immunity and brain function,” said Penny White, CEO of Better Plant Sciences.
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global medicinal mushroom market is expected to reach US$78.7 billion by 2025, from US$38.1 billion in 2017 growing at a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period of 2018 to 2025.
“We worked directly with Ayurveda botanical companies in India that are fair trade to source the highest quality ingredients,” said Bhavna Solecki, Director of Research and Product Development at Better Plant Sciences. “Fair trade is important to us because we want to support producers in developing countries and contribute to building sustainable communities.”
The coffees will contain Ayurvedic botanical ingredients such as holy basil, which naturally decreases anxiety; moringa, which acts as an antiviral and antidepressant; gotu kola, which reduces anxiety and stress while improving circulation, and amla; a potent fighter against bacteria and viruses.
All four blends have been sent to a third-party lab for nutritional facts testing as per Health Canada regulations for functional foods. This will test for things such as: moisture, nutrition labeling, fat and fat composition, protein, carbohydrate, cholesterol, sugar, dietary fiber, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, ash content, and energy.
NeonMind has completed the box and packaging design for the coffees, and has sourced environmentally friendly packaging for the products. NeonMind has commenced development of a website with full e-commerce capabilities, which it intends to launch in tandem with its expected initial product launch in October 2020. The website will be powered by Shopify, which will allow for an optimized user experience across all devices and encourage sales conversions.
Other related developments from around the markets include:
United Natural Foods Inc. (NASDAQ:UNFI), North America’s premier and largest food wholesaler delivering the widest variety of products to a diverse and expansive customer base, today issued the following statement regarding the long-term labor agreement that it has reached with Teamsters Local 414 in Fort Wayne, Indiana. Jill Sutton, UNFI’s Chief Legal Officer, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary, commented: “We’re very pleased that Teamsters Local 414 has ratified a new long-term labor agreement for our distribution center in Fort Wayne, Indiana. UNFI’s four-year contract with Local 414 maintains competitive benefit and wage terms in line with other facilities in the Midwest. The contract also includes language updates that afford UNFI the flexibility it needs to operate and succeed as a competitive distribution business in today’s landscape. We believe this resolution is a positive development for UNFI, our valued associates in Fort Wayne and our customers.
Starbucks Corporation (NASDAQ:SBUX) reported financial results for its 13-week fiscal third quarter ended June 28, 2020. GAAP results in fiscal 2020 and fiscal 2019 include items that are excluded from non-GAAP results. Please refer to the reconciliation of GAAP measures to non-GAAP measures at the end of this release for more information. “Since the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak in January, we have taken a principled approach to navigate the crisis, true to our mission and values. Every step of the way, we have thoughtfully addressed the needs of Starbucks stakeholders and are particularly proud of the industry-leading investments we have made to support our partners while creating a safe, familiar and convenient experience for our customers. Starbucks partners have risen to the occasion, and our near-term focus is to recover sales safely and responsibly by offering our customers the comfort and care that differentiate the Starbucks Experience,” said Kevin Johnson, president and CEO.
New Wave Holdings Corp. (OTC:TRMND)(CSE:SPOR) announce that it will support the Delos Psyche Research Group in its study designed to determine the impact of ingesting small amounts of hallucinogenic or psychedelic substances such as lysergic acid diethylamide for medicinal or therapeutic purposes. “We are pleased to support Delos Psyche and look forward to working with their team as they begin this new study,” said Trumbull Fisher, President of New Wave. “This is an important step toward bringing psychedelic therapies to the people that may greatly benefit from these potential treatments.” The purpose of this observational study is to determine some of the effects of microdosing LSD on patients suffering from depression, anxiety, stress, and a variety […]
Natural Kaempferol Delays Parkinson’s Symptoms in Fruit Fly Model

The natural compound kaempferol — which acts as a potent antioxidant — can reduce the physical and behavioral symptoms of Parkinson’s in a fruit fly model of the disease.
According to the researchers, this molecule may exert its protective effects by blocking the aggregation, or clumping, of a protein called alpha-synuclein , which is one key culprit behind Parkinson’s development.
The study, “ Effect of kaempferol on the transgenic Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease ,” was published in the journal Nature Scientific Reports .
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the loss of nerve cells that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine (dopaminergic neurons) in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra , and by the buildup of alpha-synuclein, which forms clumps known as Lewy bodies .
Oxidative stress also can lead to an inflammatory response that may contribute to disease progression . Of note, oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between the production of free radicals — natural byproducts of chemical processes, such as metabolism — and the ability of cells to detoxify them. These free radicals, or reactive oxygen species, are harmful and result in cellular damage and death.
Kaempferol is a natural chemical commonly found in plants and plant-based foods. It has been shown to protect against induced oxidative brain damage and reduce neuronal damage.
To investigate kaempferol as a potential Parkinson’s treatment, researchers at the Aligarh Muslim University , in India, tested its impact in a disease model using the fruit fly ( Drosophila melanogaster ).
The fruit fly model mimics Parkinson’s by producing human alpha-synuclein, which is abundant in people’s brains. Clusters of alpha-synuclein lead to the formation of Lewy bodies, the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons, and a loss of motor abilities.
Flies with and without Parkinson’s symptoms were fed food (in separate compartments) mixed with increasing doses of kaempferol (10, 20, 30, and 40 micromolar). The control flies were fed a diet without kaempferol, and one group of Parkinson’s flies were given L-dopa, which is sold as levodopa for human treatment. Naturally found in the body, levodopa eases Parkinson’s symptoms such as stiffness and slowness of movement. The flies were tested after 24 days of feeding.
A measure for general physical activity found a dose-dependent delay in the onset of the loss of activity in Parkinson’s flies treated with kaempferol or L-dopa, compared with those that were not treated.
Distortion in the flies’ compound eyes, which reflects damage to the eye retina observed in human patients, was found in untreated Parkinson’s flies. In contrast, no disorganization in the eyes was seen in the treated flies.
An almost 4-fold decrease in the climbing ability of the Parkinson’s flies was significantly delayed in treated flies; normal flies exposed to kaempferol showed no significant difference compared with unexposed controls.
Measuring the levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances , or TBARS, can indicate tissue damage caused by oxidative stress. Compared with the tissue from the control flies, the Parkinson’s flies showed a 3.5-fold increase in TBARS. Meanwhile, the flies treated with kaempferol showed a significant, dose-dependent decrease. Flies treated with L-dopa had similar TBARS as those treated with 10 micromolar kaempferol. Additional markers for oxidative stress showed that kaempferol treatment resulted in the same protective pattern.
Two protein markers for cell death, Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 , also were measured. In the Parkinson’s flies, Caspase-3 activity levels were more than three times higher than control flies. A dose-dependent decrease in activity was found in the Parkinson’s flies exposed to kaempferol. The activity of Caspase-9 mirrored these results.
Three behavioral tests — the courtship index, the odor choice index, and a memory test — all showed a dose-dependent impact of kaempferol treatment in the Parkinson’s flies compared with the untreated flies.
The Parkinson’s flies also demonstrated a marked age-dependent reduction in the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase , an enzyme that generates L-dopa in human brains. Compared with untreated flies, higher levels of tyrosine hydroxylase were seen in brain tissue isolated from the treated flies.
The team found that kaempferol may be exerting its protective effects by binding directly to the alpha-synuclein protein, possibly blocking the formation of Lewy bodies. Because kaempferol is a potent antioxidant, the researchers also speculated that the “neuroprotection of the kaempferol is due to its antioxidant property.”
“Hence, it is concluded from our present study that kaempferol is also potent in reducing the [Parkinson’s disease] symptoms being mimicked in [Parkinson’s] flies and can be used as possible therapeutic agent against neurodegenerative disorders,” the researchers concluded.
Steve holds a PhD in Biochemistry from the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Toronto, Canada. He worked as a medical scientist for 18 years, within both industry and academia, where his research focused on the discovery of new medicines to treat inflammatory disorders and infectious diseases. Steve recently stepped away from the lab and into science communications, where he’s helping make medical science information more accessible for everyone.
14 proven health benefits of turmeric and curcumin

Turmeric originates from the root of the curcuma longa plant, which is part of the ginger family. Used in India as a medicinal herb for thousands of years, turmeric health benefits are largely due to the presence of a compound in called curcumin, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
We asked Aisling Moran, nutritional scientist at Thriva , and Shona Wilkinson, nutritionist at Superfood UK , to talk us through turmeric health benefits, explain what to look for in a supplement, and offer tips on dosage, absorption and safety: 14 scientific health benefits of turmeric
While turmeric has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, its only recently that scientists have started to test-run the spices’ medicinal chemistry.
In an American Chemical Society review of the existing scientific literature, scientists concluded that curcumin is unstable under physiological conditions and therefore not readily absorbed by the body – which means sprinkling some into a curry every now and again probably won’t bring about any of the health benefits below.
However, the preliminary science is promising, especially where small-scale human studies have been conducted, so it may not be long before science figures out how to make the compounds that contribute to turmeric health benefits more bioavailable to humans. Here are 14 scientific health benefits of turmeric: 1. Turmeric contains bioactive compounds
There are several powerful medicinal compounds in turmeric that are linked to a range of health benefits – the most notable being curcumin, which is responsible for its vivid yellow colour, says Moran. Curcumin is a part of a family of active compounds called curcuminoids. ‘Other curcuminoids in turmeric include demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin, but curcumin is the most abundant – tending to make up about 77 per cent of curcuminoid content – and as a result, it’s also the most researched,’ she says. 2. It’s an antioxidant
Research shows that curcumin can reduce oxidative stress, since it acts as an antioxidant and stimulates antioxidant enzymes in your body, says Moran. ‘Oxidative stress is when there are too many free radicals in your body and not enough antioxidants to ‘scavenge’ them,’ she explains. ‘These free radicals can then damage proteins, DNA, and so on, and over time, this can lead to long-term, low-grade (chronic) inflammation.’ 3. Anti-inflammatory
Inflammation is a natural process that is necessary for repair and healing, but when it becomes long-lasting or out of control it can cause health problems, says Wilkinson. ‘Many common health conditions involve inflammation, including heart disease, obesity, allergies, skin problems such as eczema , and even Alzheimer’s disease ,’ she explains. ‘In other words, many of the conditions that characterise 21st century living.’
In addition to scavenging free radicals through its antioxidant effects, curcumin can suppress molecules that play a big role in causing inflammation, says Moran. ‘So, in addition to lowering your risk of developing a chronic disease, it’s thought it might help ease exercise-induced inflammation and muscle soreness,’ she says. 4. May have anti-cancer properties
As well as showing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, curcumin has been shown to have anti-cancer properties in numerous test tube studies. One such study , conducted by the University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Centre, found that not only does curcumin inhibit the growth of melanoma cells, but it also causes tumour cells to destroy themselves. Further investigation into the effects of curcumin in animal models and clinical trials is planned, the authors wrote. 5. Protects your joints
Given that curcumin is a potent anti-inflammatory compound, it makes sense that it helps to protect your joints. Studies suggest that curcumin suppresses your body’s response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a chemical produced by the immune system that causes inflammation related to joints. ‘ Joint pain and arthritis are among the most obvious signs of inflammation,’ says Wilkinson. ‘Anything that helps to balance inflammation may relieve symptoms, or even help prevent the problem occurring in the first place.’ 6. May help treat arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term autoimmune condition that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joints. Some research shows that curcumin could be used to treat the condition, with similar effects to anti-inflammatory medication like ibuprofen – and without a lot of the side effects – but larger-scale studies are needed, says Moran. 7. Boosts brain health
Curcumin can increase levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in your brain — a growth hormone important for brain health, says Moran. It’s a key molecule involved in changes related to learning and memory, because it stimulates the growth of new neurons in your brain. Many common brain disorders have been linked to decreased levels of this hormone, and scientists believe it may help to delay or even reverse many brain diseases and age-related decreases in brain function.
Additionally, a bioactive compound found in turmeric called aromatic turmerone boosts the regeneration of brain stem cells, according to test tube research published in the journal Stem Cell Research & Therapy , which means it could be a future drug candidate for treating neurological disorders such as stroke. 8. May ward off dementia
Not only has curcumin been linked to improved brain health, but it might even help to reduce your risk of Alzheimer’s. Inflammation and oxidative damage play a role in Alzheimer’s disease, and curcumin has been shown to have beneficial effects on both. Daily curcumin consumption improved memory and mood in people with mild age-related memory loss, a study by the University of California found. Adding just one gram of turmeric to breakfast could help improve the memory of people who are in the very early stages of diabetes, which is linked to dementia, according to a Monash University study . 9. May help treat depression
Surprisingly, curcumin may be beneficial for people with depression. In a small study spanning 60 people diagnosed with depression, one group took an antidepressan t, a second group took one gram of curcumin, and a third group took both the antidepressant and curcumin. Six weeks later, the curcumin supplement had led […]
3 reasons you should be taking CoQ10 right now

If you’re not taking CoQ10, you’re missing out on one of the most powerful supplements available. In fact, the power of Coenzyme Q10 is found in its innate ability to generate energy in all of the cells of your body.
That’s why the supplement can pack a serious punch when it comes to your health.
Here are the three big benefits of CoQ10 that can help change your health for the better. #1 — Heart love
If there’s one supplement that’s a must-have for your heart, CoQ10 is it.
According to the Cleveland Heart Lab, not only could CoQ10 have “significant cardiovascular protective effects” that could help keep your heart healthy to ward off heart disease down the road, but studies show it also comes with big benefits if you’re already living with heart issues, like: Cardiovascular disease — CoQ10 may significantly boost HDL-C (good cholesterol) levels, even in patients already on statins. Supplementation has also shown to balance inflammatory biomarkers that are risk factors for heart disease.
Statin-related muscle symptoms — Statin therapy can lead to achy muscles and even weakness. Luckily, a 2014 study found that 75 percent of patients who took CoQ10 twice daily for 30 days reported reduced muscle aches.
Heart failure — Two separate studies found that CoQ10 is the supplement of choice for people with heart failure. The first found that over two years, CoQ10 supplementation reduced both symptoms and the risk of death. And the second showed that the supplement fewer serious complications and hospitalizations for worsening heart failure.
High blood pressure — A review of 12 clinical studies found that CoQ10 supplementation helped reduce systolic blood pressure (the top number in your blood pressure reading) by as much as 17 mm Hg and lower the bottom number (diastolic) by 10 mm Hg.
#2 — Headache hero
And CoQ10 does more than just make your heart happy, it can also help you cope with headaches better.
The supplement has been lauded for its ability to boost mitochondrial function (those are the powerhouses of your cells) and balance the inflammation that can happen during an attack.
One study comparing CoQ10 to a placebo found that CoQ10 supplementation was over three times more likely to decrease the number of migraines.
And a second study found that CoQ10 supplementation led to fewer and less severe headaches. #3 — Blood sugar regulator
If the heart-health and headache reducing benefits of CoQ10 weren’t enough, the supplement could even help you keep your blood sugar levels in the green zone to combat diabetes.
That’s because the supplement has been shown to help regulate blood sugar and even improve insulin sensitivity.
Is it any wonder then that one study found that just 12 weeks of CoQ10 supplementation significantly reduced fasting blood sugar levels as well as hemoglobin A1C (blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months). How to get more CoQ10 in your diet
Clearly, adding CoQ10 to your daily life can add up to some big health benefits for your heart and beyond.
Foods that contain CoQ10 include: Beef
Herring
Chicken
Rainbow trout
Peanuts
Broccoli
However, since it’s hard to get enough through your diet (since your body’s natural levels drop dramatically with age), experts recommend a quality crystal-free formula supplement for increased bioavailability, meaning your body can quickly and easily absorb it. And if you are on cholesterol-lowering medications that rob your body of CoQ10, supplementing is a must.
Editor’s note : Cholesterol-lowering medications don’t just rob your body of valuable CoQ10, they can also rob you of your most precious memories. This drug-induced memory loss is more common than Alzheimer’s and worse. To learn more, click here for a preview of The Cholesterol Super-Brain.
Sources: > Understanding A1C — American Diabetes Association Pros & Cons of Taking CoQ10 — MedShadow CoQ10: What are the Heart Health Benefits? — Cleveland Heart Lab Novel CoQ10 antidiabetic mechanisms underlie its positive effect: modulation of insulin and adiponectine receptors, Tyrosine kinase, PI3K, glucose transporters, sRAGE and visfatin in insulin resistant/diabetic rats — National Library of Medicine Effects of CoQ10 Supplementation on Lipid Profiles and Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial — National Library of Medicine Coenzyme Q10 for the treatment of heart failure: a review of the literature — National Library of Medicine The effect of coenzyme Q10 on morbidity and mortality in chronic heart failure: results from Q-SYMBIO: a randomized double-blind trial — National Library of Medicine Effect of coenzyme Q10 therapy in patients with congestive heart failure: a long-term multicenter randomized study — National Library of Medicine A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover, add-on study of CoEnzyme Q10 in the prevention of pediatric and adolescent migraine — National Library of Medicine Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 in migraine prophylaxis: a randomized controlled trial — National Library of Medicine Coenzyme Q10 deficiency and response to supplementation in pediatric and adolescent migraine — National Library of Medicine
Alzheon Awarded $47 Million Grant from U.S. National Institute on Aging for Phase 3 Clinical Study of ALZ-801, an Oral Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease
FRAMINGHAM, Mass.–( BUSINESS WIRE )– Alzheon, Inc. , a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on developing new medicines for patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders, announced today that the U.S. National Institute on Aging (NIA) of the National Institutes of Health has awarded the company a grant (NIA grant number R01AG065253) expected to total $47 million over 5 years to support a Phase 3 clinical study with ALZ-801 – an oral agent that blocks the formation of neurotoxic soluble amyloid oligomers. The study will enroll Early AD patients, who have two copies of the apolipoprotein ε4 allele (APOE4/4), as a cutting-edge precision medicine approach to Alzheimer’s disease. AD patients with this genetic profile have been shown to have a higher risk of rapid disease progression and to be responsive to agents targeting pathogenic amyloid oligomers. Alzheon Awarded $47 Million Grant from U.S. National Institute on Aging for Phase 3 Clinical Study of ALZ-801, an Oral Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease Tweet this “We are grateful to the NIA for their rigorous scientific review and funding support to advance ALZ-801 for Alzheimer’s patients in need of an effective treatment,” said Martin Tolar, MD, PhD, Founder, President and Chief Executive Officer of Alzheon. “Proposals to NIA are highly competitive and this award recognizes the contribution of Alzheon scientists to the targeting of toxic beta amyloid oligomers, which are now established as a key driver of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients. We are proud that Alzheon has stayed the course and, after seven years of pathbreaking efforts, emerged as a frontrunner in the development of the first oral treatment for Alzheimer’s that can slow or stop the progression of the disease.”
The award of this NIA grant is recognition of ALZ-801’s compelling clinical rationale and pioneering Phase 3 trial design in the field of Alzheimer’s treatment: a precision medicine focus on APOE4/4 patients to increase the probability of success, and a therapeutic mechanism selectively targeting neurotoxic soluble amyloid oligomers. 1,2 Independent research has shown that APOE4/4 patients have several-fold higher brain levels of toxic beta amyloid oligomers than APOE4 non-carriers, and are expected to benefit from an anti-oligomer agent like ALZ‑801. 1,2,6 In published research, Alzheon scientists demonstrated that ALZ-801 fully blocks the formation of soluble neurotoxic amyloid oligomers in the brain at the target clinical dose, and with a favorable long term safety profile. 4,5,7 Furthermore, Alzheon scientists uncovered the mechanism by which ALZ-801 augments the body’s natural defenses to inhibit formation of toxic amyloid oligomers. 3
“This innovative Phase 3 study is the first to initially focus on symptomatic APOE4/4 patients, and prospectively incorporate important new blood-based biomarkers, in particular phosphorylated tau and neurofilament light chain proteins, as well as volumetric brain imaging, to evaluate drug effects. If these biomarkers correlate with clinical efficacy, this would enable their use as potential surrogate outcomes in Alzheimer’s prevention trials, allowing more efficient trial designs,” said Dr. Anton Porsteinsson, Director of the University of Rochester Alzheimer’s Disease Care, Research and Education Program. “This trial has the potential to rapidly bring ALZ-801 to patients in need and help fulfill a key National Alzheimer’s Plan goal to develop effective treatments by 2025, while simultaneously advancing the science of treating Alzheimer’s disease at its early stages.”
The Phase 3 study is designed to evaluate ALZ-801 in 300 patients with Early AD and the APOE4/4 genotype. Subjects will be randomized to receive 265 mg tablets of ALZ-801 or a matching placebo twice daily for 18 months. The study will evaluate the cognitive endpoint, Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale–cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog), as the primary clinical outcome, and other functional, behavioral, and global clinical endpoints. Biomarker assessments will include plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) measures of core AD pathologies (amyloid and phosphorylated tau protein) and of neurodegeneration (neurofilament light chain protein, tau protein, and neurogranin), and neuroinflammatory markers. Imaging biomarkers will include measurements of hippocampal volume and cortical thickness. The independent co-chairs of the Steering Committee for the Phase 3 trial are Dr. Anton Porsteinsson and Dr. Marwan Sabbagh, Director of the Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health. Alzheon plans to initiate the Phase 3 trial in 1Q 2021.
“We have designed this study to have a higher probability of success than previous trials in Alzheimer’s patients. We are applying precision medicine by targeting patients who can be readily diagnosed, who develop the disease earlier when they are less likely to have comorbidities, and who are likely to benefit from the treatment,” said Susan Abushakra, MD, Alzheon’s Chief Medical Officer and principal investigator for the NIA grant. “We are integrating advanced fluid biomarkers into the Phase 3 program to increase our understanding of the effects of ALZ-801 treatment on the course of the disease. While initially we will focus on Early Alzheimer’s patients with the APOE4/4 genotype, future expansions will include investigations of ALZ-801 in prevention trials in healthy individuals with high risk for Alzheimer’s, and in APOE4 heterozygotes, who carry one copy of the APOE4 gene.”
The National Institute on Aging (NIA) leads the U.S. federal government effort conducting and supporting research on aging and the health and well-being of older people. The National Alzheimer’s Plan , originated in 2012, establishes five ambitious goals to both prevent future cases of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias and to better meet the needs of the millions of American families currently facing this disease.
ALZ-801 is a brain-penetrant oral small molecule prodrug of the active agent, tramiprosate, that has been previously studied in large, multi-national Phase 3 studies in 2,000 patients with Mild to Moderate AD. 4,5,7 Although the studies did not show significant outcomes in the overall AD patient population, a promising efficacy signal was observed in the subgroup of APOE4/4 patients, and the Mild APOE4/4 subgroup showed compelling evidence of long-term clinical efficacy, as demonstrated by stabilization of memory and thinking ability over 18 months. 5,7 The Phase 3 studies also showed a dose-dependent preservation of hippocampal volume on brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans compared with placebo. 1 In previous […]
End nicotine, sugar, or caffeine cravings using these five BRAIN FOOD supplements

( Natural News ) Most consumers who indulge themselves with mood-enhancing “treats” like sugar, nicotine, alcohol, or high doses of caffeine, are also paying a price on the back end when the dopamine “crutch” wears off, and they experience what has come to be known as the “chemical hangover.” With the chemical hangover, the only mainstream “relief” for it comes as more of the same, which compounds the pain and agony when it runs out or can’t be accessed due to location. Anyone who smokes, vapes or boozes up regularly knows this suffering all too well, like when they’re stuck at work, on a plane or train, at an event or training, or even at the movies. That’s when the chemical hangover kicks in, whether in the form of anxiety, headaches, energy crashes or just plain depression.
So why do people over-indulge in nicotine , sugar and caffeine to begin with? It’s not usually because of some dare to take as much as they can and see how “wild” they feel. It’s a long term curse that keeps getting worse, as your body builds tolerance, and you have to consume more and more to get that “fix.” Yes, it’s a fix, like a drug. And it’s got a hangover, like a drug.
Yet, Mother Nature has a cure for everything, you just have to find it and take it. There’s a counter for everything, and some of these supplements and superfoods have been around for thousands of years, working their magic for the health and longevity enthusiasts who know the secret power of the most powerful herbs, tinctures and powders. Some of these superfoods include: #1. Chaga Mushrooms
#2. Rhodiola
#3. Schisandra Berry
#4. Vitamin B-12 (as Methylcobalamin)
#5. Mucuna – Krave Kicker
Chaga spores levitate to fight aging and increase longevity
#1. Without a doubt, chaga mushrooms are the premiere way to boost immune function, cognitive function and longevity. If you take it by tincture, you’ll feel it kick in within minutes, heightening your awareness, your mood and your drive to improve your life and the world. For an elevated feeling that lasts for hours, try chaga mushrooms in powder (capsules) or tincture form, and look for organic to get the most bang for your buck. Ready to drop the “nic” crutch and boost your immunity with some cancer-fighting chaga spores ? Get with the program and “swallow it whole.” Get healthy.
#2. Ever heard of an herb called Rhodiola Rosea (pronounced like rodeo – la – ro – zay-ya), also known as rose root? Most smokers and people who eat processed food every day aren’t seeking out natural remedies like rose root, so they have no idea that the rewards for simply supplementing properly outweigh the hurt they’re inflicting on themselves from continued overuse of those immediately gratifying bad habits. It’s all about the reward with natural remedies, with no side effects, hangovers, crashes or ill-health effects. Looking to regulate those hormones and fix depression? Want to increase endurance and energy? Rhodiola is an adaptogen that helps your body adapt to stressful situations (mental and physical) that throw you off balance. Get it? That’s why smokers smoke and vapers vape – because stress throws them off balance and darkens their outlook. Stressed at work? Try rhodiola.
#3. Schisandra berry packs a stronger energy punch than most “energy” drinks out there, but few people know it. Native to Russia and northeast China, these sweet-n-pungent adaptogen berries are dried in the sun and put in supplements. For increased physical endurance due to fatigue reduction, schisandra berry also increases mental performance . How valuable is THAT when you’re trying to quit or cut back on nicotine, sugar or caffeine? Key supplement combination: Vitamin B-12 with mucuna pruriens makes a world of difference
Get numbers 4 and 5 together in new supplement beverage invention that kicks nicotine and sugar cravings for hours on end, and effectively. It’s time to balance your central nervous system and help boost dopamine production at the same time. That’s how you beat and defeat the chemical hangover from smoking, vaping or even over-consuming caffeine and sugar. That, my friends, brings us to the key supplement Vitamin B-12, and you should seek it in the form of methylcobalamin . This is how you find balance when the pesticides from cigarettes hit you, when that nicotine wears off and you can’t “resume” business as usual. Feeling anxious? Feeling nervous? Getting stressed and depressed as the nicotine, sugar and caffeine wear off?
Now, a revolutionary, evolutionary blend of key supplements that have never been introduced to the beverage industry before. The new supplement beverage Krave Kicker is the ultimate dopamine boost . Backed by solid science and peer-reviewed research , a superfood called mucuna pruriens helps boost dopamine levels in a safe and very effective way.
Tune your internet dial to StopSmoking.news for more info on the “nicotine challenge” and natural ways to end useless addictions.
Sources for this article include:
Boost your Cognitive Performance with Ayurvedic Nootropics.

*Editor’s Note: Elephant is not your doctor or hospital. Our lawyers would say “this website is not designed to, and should not be construed to provide medical advice, professional diagnosis, opinion, or treatment to you or any other individual, and is not intended as a substitute for medical or professional care and treatment. Always consult a health professional before trying out new home therapies or changing your diet.” But we can’t afford lawyers, and you knew all that. Have you heard of “nootropics?”
Sometimes called smart drugs or cognitive enhancers, they are a class of substances that may support brainpower, motivation, memory, and mood.
Is your brain aging? Brain fog, sluggish memory, and declining ability to learn new things are all natural processes of brain aging.
Researchers have discovered two Ayurvedic nootropic herbs that may help slow brain aging and improve processing speed, mental alertness, and ability to assimilate new information. Nootropics + Ayurveda
Ayurveda is quite interested in mental acuity because originally, it was an entirely oral tradition passed down in the form of songs, chants, or hymns. Much like Celtic bards (who came much later), volumes of Vedic information were memorized and therefore preserved . Their ability to memorize such a wealth of knowledge is staggering.
Many Ayurvedic techniques are designed to enhance memory, such as yoga, pranayama , and meditation, but two herbs stood out in ancient times for their ability to help promote memory and cognitive function: b acopa monnieri and brahmi ( c entella asiatica ). Elephant Academy’s best-selling course is back:
Studies find b acopa monnieri and brahmi ( c entella asiatica ) are synergistic, meaning that when combined, the effects on cognitive function and sharper intellect can be greatly enhanced .
Note: b oth b acopa and c entella are colloquially called “ b rahmi .” To avoid confusion, at LifeSpa , we call c entella “ brahmi ” or “ brahmi Brain ” and bacopa “ bacopa .” Bacopa monnieri
Ancient Ayurvedic scholars were given bacopa to sharpen their memories in order to maintain their oral tradition and memorize thousands of pages of Vedic hymns. Numerous studies find bacopa to be a powerful herb for supporting brain health.
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study on bacopa , dosages of 320 mg and 640 mg produced positive cognitive changes one and two hours after consumption. There were also positive mood changes and a reduction of the stress hormone cortisol, suggesting adaptogenic or stress-reduction properties.
In another double-blind, placebo-controlled study with 54 volunteers, bacopa was found to increase word recall and cognitive function, while supporting mood stability, focus, and attention.
An Australian study , also double-blind and placebo-controlled, measured the effects of just 300 mg of bacopa per day for 12 weeks. They concluded that bacopa significantly improved verbal learning, memory acquisition, information retention, and recall in healthy older Australians.
Finally, a study published in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found supplementing with bacopa at 300 and 600 mg for 12 weeks resulted in improved attention, cognitive processing, and working memory. Bacopa for mood
Studies find that in mood-related concerns, a protein called BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) decreases. BDNF is a member of the nerve growth factor family, which helps regrow brain and nerve cells.
In a handful of studies , bacopa was able to effectively support mood stability by boosting BDNF levels. The mechanism for bacopa ’s mood stability support is linked to promoting growth in the brain’s emotional cortex (hippocampus and amygdala). Brahmi brain (c entella asiatica )
Brahmi , or Centella asiatica , is also commonly called got u kola . In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study , the effect of Centella asiatica on the cognitive function of 28 healthy elderly volunteers was investigated. One hour after supplementation, researchers saw improvement in reaction time and attention in mental tasks. Working memory, word recognition, spatial memory, picture recognition, and alertness all improved at dosages ranging from 200 to 750 mg per day for two months.
Like bacopa , brahmi shows improved function and synaptic density of the hippocampus (or emotional cortex) of the brain. Centella also demonstrates antioxidant activity and increased mitochondrial proteins, suggesting it supports multiple facets of age-related cognitive decline. Brahmi brain for mood
In a study of 34 adults with issues related to worry and fear, brahmi supported healthy mood stability and improved cognitive function. Brahmi also effectively supported a healthy response to chronic stress. Brahmi was able to show a balancing effect on moods that were either overstimulated or understimulated (melancholy). Nootropic conclusion: take your fatty brain tissue tonics
According to Ayurveda, bacopa and brahmi are medha rasayanas (fatty brain tissue tonics), which boost memory, potentially restore cognitive deficits, and may help improve mental function.
A rasayana is a herb that supports longevity. Research on b acopa monnieri and c entella asiatica clearly indicates that both plants possess neuroprotective properties, causing nootropic activity with therapeutic implications for supporting memory, mood, emotional stability, focus, and cognitive longevity.
Have you tried brahmi brain and bacopa together to boost their nootropic benefits? What did you notice? Relephant Reads:
The Amazing Health Benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushroom
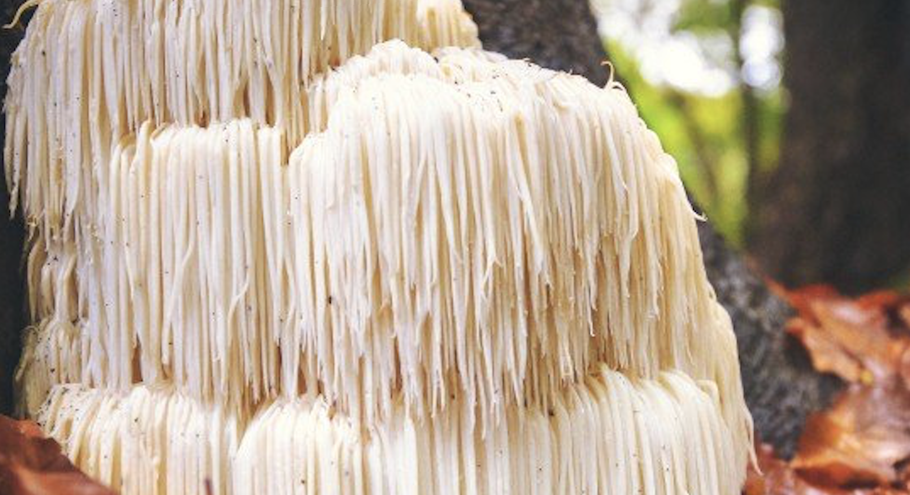

What would you think about eating a mushroom that looks a little like the scruff of a lion? Not totally convinced about lion’s mane mushroom? What if I told you that it’s associated with major brain repair, potential cancer-fighting power and is undergoing research on dozens of other health benefits?
Lion’s mane mushroom is a nootropic food very popular in traditional Chinese medicine. A large body of research has focused around this brain-boosting mushroom in the last few years, and the results are nothing short of astounding.
One study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry lists the benefits by stating lion’s mane mushroom is “antibiotic, anticarcinogenic, antidiabetic, anti-fatigue, antihypertensive, anti-hyperlipodemic, anti-senescence [anti-aging], cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, and neuroprotective, and improves anxiety, cognitive function, and depression.”
Wow. That’s quite a list!
Whether you’re interested in trying out lion’s mane mushroom in your mushroom coffee or are just curious what this odd-looking fungus might be good for, I’m sure you’re going to be impressed.
What Are Lion’s Mane Mushrooms?
Known in Latin as Hericium erinaceus, lion’s mane is native to North America, Europe and Asia, although it’s not cultivated widely in areas outside of Asia. It’s sometimes referred to as Hedgehog Mushroom, Yamabushitake or Houtou, and it belongs to the tooth fungus, or hydnoid fungi group.
Lion’s mane mushrooms have long, dangling spines that are usually greater than a centimeter in length. Unlike most mushroom species, whose spines project from a branch, the spines of Hericium erinaceus projects outward, giving it that unique look of a lion’s mane. These mushrooms grow on both living and dead broadleaf trees and are common in the late summer and fall months.
Research shows that lion’s mane possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunostimulating properties in cells, animals and humans. It has been used for thousands of years as a medicinal mushroom, especially among traditional Chinese medicine practitioners.
Lion’s Mane Mushroom Benefits
1. Enhances Brain Function
Maybe the most thoroughly researched feature of lion’s mane mushroom is its impact on brain cells and related functions. This incredible fungus may have revolutionary impact on neurodegenerative diseases.
One method by which lion’s mane affects brain function is by enhancing “neurite outgrowth” in the brain and related organs, according to research published in the International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms. Neurite outgrowth refers to the growth of axons and dendrites from neurons (anybody’s high school biology classes coming back?).
That’s a big deal in brain health research. By increasing this growth, it could potentially be possible to slow or reverse cell degeneration in the brain — the main characteristic of diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
A 2012 study conducted in Malaysia found that consuming lion’s mane mushroom could actually regenerate damaged cells from peripheral nerve injury, an injury affecting the delicate tissue between your brain and spinal cord.
When studying how brain diseases might be affected by particular medications or treatments, scientists often use what is known as the PC12 cell line for testing. Extracts and various forms of lion’s mane mushroom seem to have a major impact on PC12 cells, protecting them from damage and delaying their cell death significantly. This finding may prove to be extremely relevant for prevention or treatment of brain conditions.
In animal research published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, lion’s mane mushroom stimulates cognitive function and helps improve memory in rats, both with and without an Alzheimer’s model.
Multiple studies have found an inverse correlation between lion’s mane and Alzheimer’s-related symptoms, meaning that after consuming the mushroom extract, the rats’ symptoms improved.
An improvement of mild cognitive impairment in humans was also found in research published in Phytotherapy Research after eight to 16 weeks of lion’s mane supplementation, although this improvement did not last after subjects stopped taking this supplement.
The danger of ischemic injury (damage caused by a lack of blood flow) to neurons is also of significance when you’re talking about brain damage and disease. In laboratory tests conducted in Taiwan, lion’s mane mushroom has been shown to help prevent this type of injury.
Taking supplements of lion’s mane has also been found to have potentially protective effects on the spread of Parkinson’s disease, another neurodegenerative disorder, according to research published in the Journal of Translational Medicine.
While this research is still in its infancy and has not progressed to large-scale human trials in most cases, the consistent effect lion’s mane mushroom has been found to have on brain cells should not be ignored.
2. May Protect Against Cancer
Lion’s mane may also be significant in treating cancer, according to a host of research. In varying degrees, compounds from or supplementation with lion’s mane mushroom has been found to potentially slow the progression or reverse the spread of:
Is anyone safe from Covid-19? This is what we know so far about immunity

About nine months ago – as we now all know – a new coronavirus jumped to humans, causing a complex respiratory disease called Covid-19. The virus breezed through the planet with ease , hitching a ride on mostly unsuspecting carriers during the first months of infection. Scientists quickly realised that they were dealing with a new pathogen, and they warned the World Health Organi zation . The clues: severe flu-like symptoms that resulted in higher than usual mortality, particularly in vulnerable groups.
The new coronavirus spreads via secretions from our mouth and nose , but it took us far too long to implement face coverings to reduce transmission. What did we know from the start? Coronavirus gains entry through our eyes, nose or mouth, and we can protect ourselves by washing our hands with soap and keeping our distance from people who may be contagious but without symptoms, or who subsequently develop symptoms.
The first thing that baffled us was the series of organs affected in Covid-19, beyond the lungs. Symptoms range from mild to severe, and their impact is seen from brain to toes . T-cell immunity can build independently of antibodies, and vaccination can give rise to potent antibodies The Covid Symptom Study app holds data from more than 4 million users in the US, the UK and Sweden, and suggests that there are six different types of Covid. We still cannot predict who will develop severe disease symptoms that lead to fatality, so even children, who were considered safe earlier this year, have now presented at random with rare but severe disease .
The question remains, for researchers and everyone else, is anyone safe?
To answer this, we need to look at how our immune system eliminates the virus. In itself, that reveals a hugely important positive concept: unlike some viruses that turn us into lifelong carriers (remember herpes, or HIV?), we can actually eliminate this coronavirus. For most of us it takes about two weeks. You have heard that immunology is complicated ; here’s simply what we know so far.
Our bodies contain different types of defences , some evolved for speed, others for accuracy. Speedy defences deployed minutes after infection are part of the body’s innate immune system, and are powerful enough to control many pathogens. In researching Covid-19, scientists worried that if these were sufficient to control coronavirus, we would risk having no protection from reinfection. This is because rapid defences do not refine themselves to be more potent after the first infection, and they would be expected to mobilise in the same way when we become exposed to the same virus after recovery, suffering the same symptoms in the process.
Reinfection would fuel continuous transmission and extinguish hopes of herd immunity, which relies on the majority of the population becoming resistant to infection, to reduce the risk of transmission to vulnerable groups with poor defences. Thankfully, despite nearly 22 million recorded infections around the world, there is still no strong evidence of reinfection .
As months went by, some patients that cleared the virus started to report lingering symptoms. From brain fog to debilitating fatigue, heart damage to persistent muscle and joint pains, we recognise that some of us risk having “long Covid”, with a profound potential impact for our health and public health services. Protective immunity is critical to prevent disease.
The slower part of the immune system that has evolved for accuracy takes about seven days to kick off, and comprises B cells and T cells . These clever cells not only recognise that we’re suffering a virus infection, they are also able to pinpoint exactly which virus. How can they predict unknown threats? They can’t, so we have hordes of them patrolling our bodies with random recognition abilities for different parts of different germs.
If a lucky B cell recognises a virus, an activation cascade takes place that clones it into thousands of copies of itself and turns it into an antibody-producing workshop. This takes days, but antibodies and memory-type B cells persist after the virus is gone, so they can react rapidly if needed again.
Immunologists detected antibodies in the majority of people with confirmed Covid-19, but were unsure how long they would last for this virus. Studies showing that the early antibodies waned a few months after infection raised concerns for protective immunity. It is quite normal for early antibodies to dip a few months after infection. Remember, memory B cells are still left behind, ready to pounce if needed.
Other alarming research revealed a lack of antibodies in some patients who recovered. Some worried that this may mean lack of protection, or that vaccines were doomed to fail. Immunologists swiftly dispelled these myths , explaining that T-cell immunity can build independently of antibodies, and that vaccination can give rise to potent antibodies even if natural infection doesn’t.
Antibodies are Y-shaped molecules that use the two tips of the Y to stick to germs, but their other end is also important . The trunk of the antibody is recognised by immune cells that gobble up the antibody-germ complex, break it down into pieces and present it on their surface to activate T cells. They also release communication molecules to drive inflammation – and this can boost antiviral immunity, but may also cause collateral damage to tissues.
Patients with severe Covid-19 have higher antibody counts, and given the pro-inflammatory role of antibodies, there were concerns for antibody-dependent enhancement of the disease. We now appreciate that animals and humans given antibodies as therapy do not show disease enhancement. This is great news for antibody-based vaccination and therapeutic antibody treatments.
T cells drive antiviral response s and kill infected cells, and they also leave memory cells behind. They are more difficult to test than antibodies, but T cell tests are in development for broader use. T cells in coronavirus infections may persist longer than antibodies. Many of us also have pre-existing specific T cells, likely remnants from previous coronavirus infections that cause seasonal colds. This could explain why some get away with mild infection.
There […]
Keep your gut healthy and clean by avoiding these 4 types of food

( Natural News ) Good gut health has far-reaching benefits for human health, from better digestion to a stronger immune response to infection and disease. Therefore, a balanced diet ought to include foods that promote optimal gut health, such as those rich in fiber and probiotics.
But just as there are good foods for gut health, so too are there bad ones. Vincent Pedre, a certified practitioner of functional medicine and the founder of Pedre Integrative Health , explains that certain foods have a stronger, negative impact on gut health than others .
In fact, a lot of the foods considered bad for gut health are staples that people eat as part of their usual diets. Therefore, it’s important to take note of the foods that one eats on a regular basis as certain foods can take a toll on the gut and on other organs, he adds. Foods that can harm the gut
There are tons of foods that are considered bad for the gut, but nutritionists might group them into four general classifications : animal protein, high FODMAP foods, foods containing antibiotics and fried foods.
Read on for a closer look at their effects on the gut and other potential risks and consequences related to their consumption:
Animal protein
Meat and animal products like eggs and milk are often the go-to sources of protein, a macronutrient essential for important cellular and metabolic processes. These foods also offer other nutrients, including choline , an essential nutrient for brain health.
But recent studies find that people eating high amounts of animal protein are at a greater risk of suffering harmful changes in their gut microbiome.
In 2017, for instance, scientists found that a diet rich in animal protein and fat led to a significant decrease in the numbers of total beneficial bacteria in the gut. This has the effect of making the gut susceptible to chronic inflammation and oxidative stress.
In an earlier study, Italian researchers compared the gut bacteria of children raised in a rural area in Africa to those of Italian children. The African group consumed high-fiber diets and plant proteins. The researchers found that this group had more good gut bacteria and a reduced risk of inflammation in their guts.
The Italian group, on the other hand, ate more meat and, as such, had more bacteria in their guts linked to inflammation and disease.
High FODMAP foods
FODMAP stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols. These are the scientific terms used for identifying carbohydrates notorious for triggering the onset of gastrointestinal conditions, such as bloating, intestinal gas, indigestion and abdominal pain.
FODMAPs can be found in a number of foods, including those often consumed as part of a typical, unhealthy diet. High FODMAP foods include processed fruit juices, condiments, jams, relish, milk, baked beans, and foods rich in high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), an artificial sugar linked to numerous health risks.
That being said, take note that a lot of nutritious foods like figs , yogurt, lentils and chickpeas , among others, are also considered high FODMAP foods. Those suffering from chronic gut problems might need to consult a healthcare professional to determine the exact foods behind their ailments instead of just cutting back on all high FODMAP foods altogether.
Foods containing antibiotics
It’s common practice among commercial livestock farmers to add antibiotics to animal feeds. In most cases, this is done to reduce the risk of animals contracting serious infections from parasites, viruses, bacteria and other harmful biological agents.
That being said, the use of antibiotics is a controversial topic. In fact, there are strict regulations in place in a number of European countries to curb this practice. Studies found that exposure to antibiotics from contaminated meat and animal products can promote antibiotic resistance.
In the gut, antibiotics can kill beneficial bacteria, thus causing gut imbalance and raising the risk of gastrointestinal problems.
Fried foods
Fried foods are chock-full of saturated and trans fats that can irritate the gut. These fats harm good gut bacteria but stimulate the proliferation of bad bacteria, thus resulting in an imbalanced gut. (Related: Fried foods, especially overcooked potatoes, dramatically increase cancer risk .)
Maintaining good gut health is not just about eating fermented foods or adopting a high-fiber diet. It is also about avoiding harmful ones. Steer clear of the foods on this list to keep the gut clean and balanced.
Read more articles about bad and harmful foods for gut health at StopEatingPoison.com .
Sources include:
MindBodyGreen.com
Worried about homeschooling? Boost your child’s brain with the right nutrients

The adjustments to new learning arrangements can be both challenging for children and parents. But studies show there are key nutrients that help develop faster and stronger brain connections so kids can easily absorb and apply what they learn. Key nutrients such as DHA, vitamin E, and lutein help improve children’s cognitive performance. DHA Often referred to as the “good” fat, omega-3 fatty acid such as DHA plays a critical role in preserving cognitive functions of the brain, such as determining brain processing speed and memory. According to a 2014 study by Robert K. McNamara, et al., DHA promotes sustained attention, improved reading performance, improved verbal learning ability, and improved memory. Further, a 2016 study conducted in Sweden showed kids who took supplements with omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids had improved reading skills. Avocado, olive oil, and nuts are great sources of unsaturated fat, however, DHA is one of the hardest to obtain. DHA-rich food options include fatty fish such as tuna and salmon, so best introduce them early to children. Lutein Known for its benefits for eye health, skin health, and cardiovascular health, lutein is a carotenoid that is also becoming increasingly recognized for its benefits on brain health in people of all ages. In children, lutein protects important nutrients like DHA from oxidation so that they can be used for brain development. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Emily Bovier and others reveals that higher levels of lutein in the retina is significantly correlated with faster visual processing speed, it’s also found to result in overall academic achievement, higher mathematic test scores, and higher written language test scores, according to another study by Sasha M. Barnett, et al. Known sources of this nutrient are dark green leafy vegetables such as spinach and kale, as well as tomatoes. Natural vitamin E Naturally found in parts of the brain that are linked to memory, vision, and language development, natural vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that complements lutein in protecting DHA from free radicals in the environment. However, take note that natural vitamins is preferred over synthetic, as identified by Matthew Kuchan, et al.’s recent study that shows the brain preferentially accumulates naturally occurring vitamin E (labeled “d-alpha-tocopherol”) over synthetic (“rrr-a-tocopherol”). Best sources of natural vitamin E include eggs, broccoli, almonds, hazelnuts, and peanuts. 2’ – FL (fucosyllactose) HMO This immune-nourishing prebiotic serves as food for the good bacteria in the gut and prevents bad bacteria from attaching to gut cells, in order to boost a child’s immune system. Experts opine that when children have strong immunity, they have a strong foundation to keep learning, growing, and thriving. The following key nutrients that help in children’s cognitive performance are present in children’s milk brand Similac GainSchool by Abbott. “We believe in the power of nutrition for faster learning, which is especially relevant in today’s trying times. Similac GainSchool contains key brain nutrients such as DHA, lutein, natural vitamin E, ARA, choline, taurine, iron, selenium, zinc, and iodine that support faster brain processing, strengthen neuronal connections, and consequently, support better cognitive performance,” says Dr. Jose Rodolfo Dimaano Jr., medical director of nutrition at Abbott. Dr. Dimaano adds, “The HMO in Similac GainSchool helps strengthen the immune system by nourishing the good bacteria in the gut, where 70 percent of the immune system is located.” To further help parents assess how their kids are faring when it comes to learning, Similac GainSchool identifies the following: 1. Intellect demonstrated by the visual monitoring and integration ability of the kids. 2. Social skills are demonstrated when kids carry strong language skills and increased vocabulary. 3. Arts demonstrate children’s enhanced memory skills. 4. Sports demonstrate kids’ ability to listen, comprehend, and strategize. 5. Emotional outcomes are demonstrated by children’s ability to regulate their behavior and sustain attention.
Topics: Jose Rodolfo Dimaano , Similac GainSchool , nutrients , children , brain More from this Category:
COMMENT DISCLAIMER: Reader comments posted on this Web site are not in any way endorsed by Manila Standard. Comments are views by manilastandard.net readers who exercise their right to free expression and they do not necessarily represent or reflect the position or viewpoint of manilastandard.net. While reserving this publication’s right to delete comments that are deemed offensive, indecent or inconsistent with Manila Standard editorial standards, Manila Standard may not be held liable for any false information posted by readers in this comments section.
Colorectal cancer is a microbial disease: Changes in the gut microbiome can be used for early detection
( Natural News ) A study published in the journal Nature Medicine found an increase in specific microorganisms in the gut which are linked to colorectal cancer . The researchers said that these microorganisms can potentially be used to detect the disease long before it progresses to late-stage cancer.
“Our results show that changes in the gut microbiome are present at the very early stages of colorectal cancer development, which could potentially provide vital diagnostic and causative clues for this disease,” said Shinichi Yachida, one the study’s authors.
Yachida also adds that the findings of their study demonstrate how colorectal cancer is not only caused by genetic predilection. Interestingly, the gut microbiome may also play an important part in the development of this cancer. Detecting specific bacteria to diagnose early colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates that 104,610 new cases of colon cancer and 43,340 new cases of rectal cancer will be diagnosed in 2020 . Meanwhile, 53,200 deaths are projected in the same year.
Although these numbers are alarming, colorectal cancer is also a slow-moving disease. This means that the progression from early-stage to late-stage cancer will take some time. There’s a bigger window for the detection of the disease and preventing it from worsening. Thus, diagnosis is key to fighting the disease.
In the study, researchers are looking at one possible way to diagnose colorectal cancer early in its development. They conducted a DNA analysis of fecal samples, which were taken from more than 616 patients aged 20 to 90 years old. Then they assessed the characteristics of their gut microbiome in relation to colorectal cancer.
They found that those with early-stage cancer had twice to thrice the number of two bacterial types compared to healthy individuals. These bacteria are Atopobium parvulum and Actinomyces odontolyticus , and are also teeming in the mouth of colorectal cancer patients. Moreover, the team recorded differences in amino and bile acid levels in feces between individuals with early-stage cancer and healthy individuals. (Related: Epigenetics in action: Mouth bacteria activate cancer genes that cause colorectal cancer .)
Such differences can serve as markers of the disease and be used in early diagnosis, said the researchers.
Furthermore, they suggest that colorectal cancer may also be a microbial disease. Currently, the cause of colorectal cancer is unknown while risk factors are either demography-related or genetic . The findings of the study may help scientists in unraveling the disease.
The next step is to investigate the relationship between the gut microbiome and tumor characteristics in individual patients with colorectal cancer. This way, experts can expand their understanding of the role of the microbiome in the development of the disease. The gut microbiome in other health conditions
The gut microbiome refers to the large populations of microorganisms in your gut. They play a major role in digestion and overall health, having been connected to various physiological systems and health conditions.
For one, the gut microbiome is associated with obesity . Studies showed that having a smaller number of certain bacteria can predispose you to being overweight . The genes may be partly to blame, as they can determine the types of bacteria that populate your gut. (Related: Gut bacteria plays a role in youth obesity .)
On other other hand, gut bacteria can also contribute to the development of lymphoma , a cancer of the white blood cells. In particular, Lactobacillus johnsonii can elevate the risk of lymphoma in mice compared to those with a different composition of gut bacteria. This finding may not be too surprising as the gut microbiome plays an important part in the immune system by communicating with immune cells .
Furthermore, mental health is also linked to the gut microbiome, adding yet another facet to its incredible portfolio of roles. That’s because gut bacteria produce certain neurochemicals that are used by the brain in regulating physiological and mental processes — including memory, learning and mood. In fact, gut bacteria makes about 95% of the body’s supply of serotonin, which is said to stabilize mood, feelings of well-being and happiness .
Given the essential roles of the gut microbiome, having a balanced composition of gut bacteria is important for good health. Eating fiber-rich foods will help greatly in feeding the good, friendly bacteria that the body needs.
Learn more about the foods that are beneficial to gut health at Veggie.news .
Sources include:
Cancer.org
Asahi.com
Cancer.net
Healthline.com
Hormone.org

