Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
29+ Foods High in Vitamin C & Deficiency Symptoms
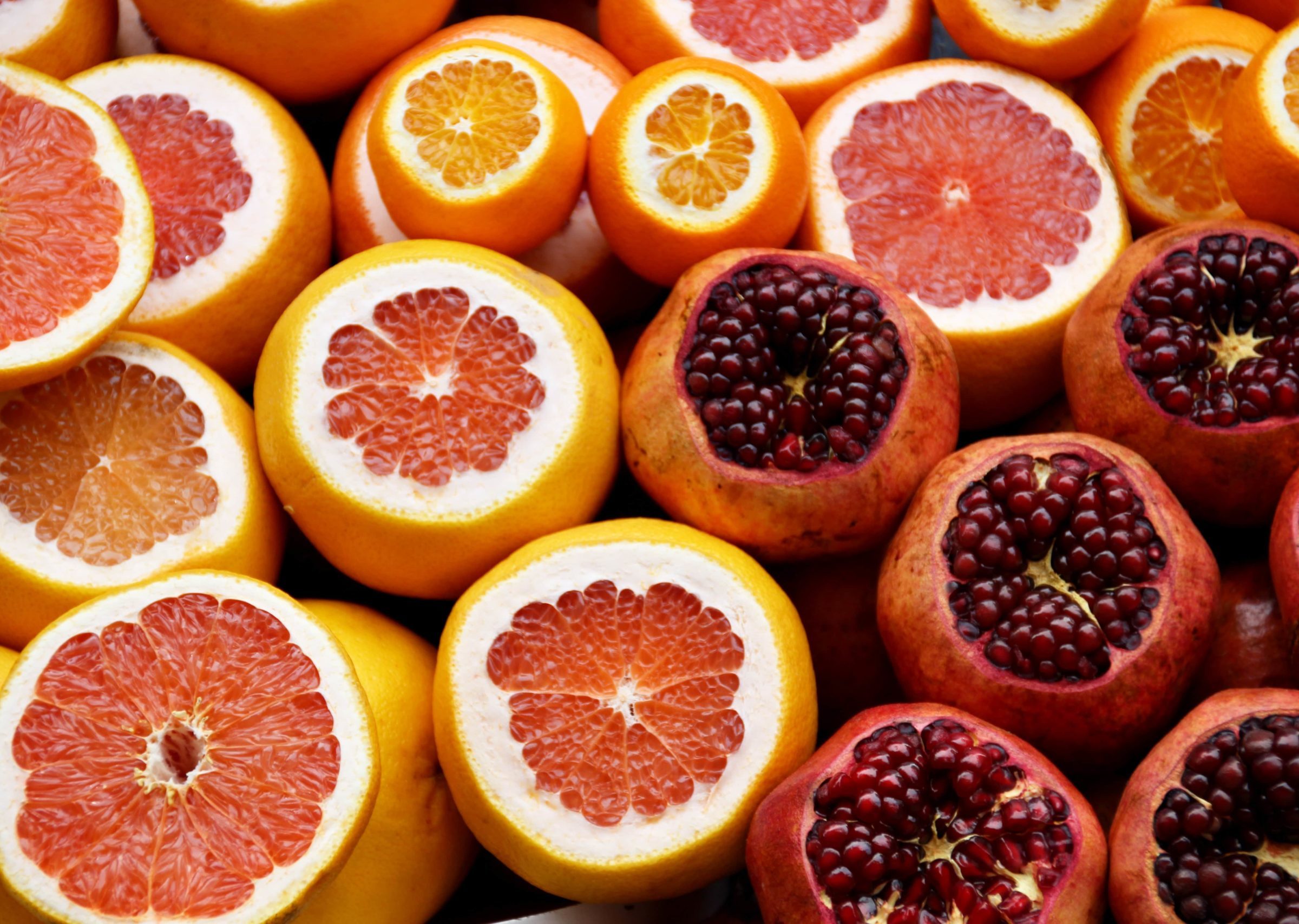

Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that’s found in many foods, but some exotic fruits contain it in exceptionally high amounts. Vitamin C deficiency is rare, but it can have serious health consequences. Read about the top dietary sources of vitamin C and which symptoms might signal deficiency in this post. Vitamin C Deficiency
Early indications of Vitamin C deficiency are fatigue, malaise, depression, and they may manifest as a reduced desire to be physically active [ 1 ].
Scurvy (pathological Vitamin C deficiency) leads to blood vessel fragility resulting in hemorrhage, as well as connective tissue damage due to failure in collagen production, often leading to loss of teeth and tendon rupture. At worse, scurvy can lead to death [ 2 , 3 ].
Other signs and symptoms of severe vitamin C deficiency include [ 4 ]: Poor wound healing
Fatigue
Weight loss
Gum inflammation and bleeding
Petechiae (tiny purple, red, or brown spots on the skin), ecchymosis (type of bruise), and purpura (purple colored spots on skin)
Joint pain
Dry eyes and dry mouth
Corkscrew hair
Clinical scurvy can be avoided by intaking as little as 10 mg of Vitamin C per day. Scurvy is extremely rare in developed countries [ 5 ].
However, mild Vitamin C depletion has been observed in 10-30 % of the presumed healthy population [ 5 , 6 ].
Causes shown here are commonly associated with vitamin C deficiency. Work with your doctor or other health care professional for an accurate diagnosis.
One of the major causes of low vitamin C levels is eating a poor diet lacking in fresh fruits and vegetables. This is commonly seen in:
People with malabsorption issues caused by certain gut conditions (i.e., Crohn’s disease, celiac disease) are also at risk for vitamin C deficiency [ 13 ].
Low vitamin C levels can also be caused by:
Certain drugs can lower vitamin C levels: Assessing Deficiency ( Vitamin C Levels )
Vitamin C levels can be measured with a blood test.
Generally, blood Vitamin C concentration of: <11 μM is considered to be deficient
11–28 μM is depleted or marginally deficient
28–40 μM is adequate
Some researchers believe that up to 22% of the U.S. may have below adequate Vitamin C status (blood concentrations < 28 µmol/L), and about 6% of the adult population is classified as Vitamin C deficient (<11 µmol/L) [ 1 ].
The following factors can significantly increase the body’s requirements for vitamin C and the risk of vitamin C deficiency [ 13 , 17 ]:
In addition, one study suggested that non-supplementing men aged 20-49 are particularly at risk of poor Vitamin C status [ 1 ].
Patients receiving kidney dialysis are prone to deficiency of Vitamin C [ 23 ].Schizophrenic patients tend to have significantly lower levels of blood Vitamin C, according to limited research [ 24 ].Genetics can also play a role. Blood Vitamin C levels differ according to polymorphisms of SVCT2 and SVCT1 [ 5 ]. Organs With the Highest Vitamin C Requirements Vitamin C is found in high concentrations in the pituitary, adrenals, and the ovaries, but muscle, brain, and liver contain the largest stores of this vitamin. However, being water-soluble, vitamin C is not stored in large amounts in the body [ 25 ]. Absorption Vitamin C is absorbed from the intestinal lumen and kidney tubules and then distributed throughout the organism by the bloodstream [ 26 ].The uptake and distribution of Vitamin C in the body is under close control and primarily regulated by tissue-specific, sodium-dependent Vitamin C co-transporters (SVCT) 1 and 2, which transport Vitamin C in exchange of sodium [ 6 ]. 29+ Foods High in Vitamin C Many fruits and vegetables contain plenty of vitamin C, including citrus fruits, peppers, berries, and broccoli [ 27 ].You need 5–9 servings of fresh, minimally processed, or frozen fruit and vegetables per day to get about 200 mg of vitamin C [ 28 ].Here is a list of foods high in vitamin C, including some little-known superfoods [ 12 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ]: > Kakadu plum or Terminalia ferdinandiana (vitamin C content estimated at 2,300 to over 5,000 mg per 100 grams )–this fruit is native to Australia and is also a good source of protein, zinc, calcium, iron, linoleic acid, and other nutrients [ 34 , 35 , 36 ]. Camu camu or Myrciaria dubia , a relative of guava, is a berry that grows in the Amazonian rainforest (contains from 1570 up to 3,000 mg of vitamin C per 100g ). The pulp is usually dried, pulverized, and formulated into supplements [ 37 ] Acerola cherries ( 1000 to 4500 mg per 100 grams ), which are also rich in diverse antioxidants like carotenoids, phenolics, anthocyanins, and flavonoids [ 38 ] Rosehip, especially the pulp ( 300-1200 mg per 100 mg –large variation between different species, highest in Rosa nitidula ) [ 40 ] Baobab pulp ( over 100 mg per 100 grams )–this African superfood is also rich in calcium, protein, and various antioxidants [ 41 , 42 ] Peppers, sweet, raw (97 mg) Kiwi (about 93 mg) Broccoli (91 mg) Brussel sprouts (85 mg) Papaya (61 mg) Strawberries (58) Citrus fruits, including oranges and lemons (20-53 mg) Guava (50 mg) Pineapple (48 mg) Cauliflower (48 mg) Mango (38 mg) Cabbage, raw (37 mg) Guanabana (28 mg) Blackberries (21 mg) Arugula (15 mg) Cranberries (14 mg) Tomatoes (13-27 mg) Apricots (10 mg) Apples (4 mg) Vitamin C is destroyed by heat and long storage times, so eating raw (or minimally processed), fresh fruits and vegetables is the only effective way to get adequate amounts of dietary vitamin C [ 27 ].Fruits and vegetables are available to most people nowadays, even in cold regions where vegetation is sparse for long periods of time, such as in Northern Europe and Canada.Vitamin C is also added to many foods as a natural preservative–it works to protect against oxidation [ 12 ].Traditionally, people living in cold environments relied on […]
Drink Up: Consulting the Experts On the Latest Health Craze in a Cup

Trendy new beverages often create buzz because of the supposed health benefits, especially when they’re mentioned on social media. “They’re given hype by influencers, so people want to try them,” says Théa Demmers, a registered dietitian at Concordia University in Montreal. But drinking your calories may often mean taking in extra sugar or falling short on dietary fibre. Besides, not all these concoctions have evidence to support their health claims – some even carry risks. We’ve got the juice on five of the latest liquid fads. Celery Juice
Kim Kardashian tried celery juice for her psoriasis. Miranda Kerr says it gives her more energy and eases indigestion. But celery is 95 per cent water, so any purported benefits such as reduced inflammation and fatigue are likely due to the extra hydration. On the downside, any time you juice a fruit or vegetable, you remove essential fibre. “This can impact our gut bacteria long term,” says Demmers. Those friendly microbes rely on fibre for food, so you won’t do your digestive system any favours if you starve them. You’re better off eating celery sticks or try water with a squeeze of lemon – Kardashian admitted on Instagram that the beverage tasted “pretty gross.” Photo: Edalin Photography/Shutterstock Mushroom Coffee
Mushroom coffee and other mushroom-supplemented foodstuffs are listed on Pinterest’s 100 trends for 2019. According to product manufacturers such as Four Sigmatic and Terrasoul Superfoods, cutting coffee with powdered mushroom can boost your energy, brain power and immune system. Unfortunately, these health claims aren’t based on solid research. Sure, mushrooms contain antioxidants, but so does the coffee they’re replacing. “It is not clear whether the antioxidant content of mushroom powder found in mushroom coffee is higher than what you would find in fresh, raw mushrooms,” adds Demmers. Mushroom coffee might be an option, though, if you want to reduce caffeine – and if you also happen to be someone who sees the charm in instant coffee. Photo: Natalia Klenova/Shutterstock Kombucha
This fermented form of tea made with sugar, yeast and bacteria has been spotted in the hands of celebrities like Jake Gyllenhaal and Lady Gaga. Kombucha contains probiotics, bacteria that help the digestive tract do its business. It’s not the only way to get more of these gut-friendly microbes – you can eat yogurt or sauerkraut – but fans of kombucha claim the drink also fights conditions like cancer and hypertension. There isn’t strong evidence to back up those claims, however. But if you do want to test kombucha’s probiotic benefits and plan to ferment your own at home (you can buy starter kits or find instructions online), be mindful of possible contamination. The temperature, humidity and other brewing conditions are an ideal environment for mould or harmful bacteria growth. It’s recommended to use glass, stainless steel or new plastic containers and “run your equipment in the dishwasher at a high temperature,” says Demmers. Photo: MasterQ/Shutterstock Golden Milk
We’ll give you this one, Gwyneth Paltrow. Turmeric contains curcuminoids, compounds with well-established anti-inflammatory properties. Curcuminoids also give turmeric-based curry dishes and stews their yellow hue and, as such, will transform your latte or milk into a burst of morning sunshine. “The antioxidants in turmeric are best absorbed with the vehicle of fat,” says Demmers, so having it with a milk product can actually help you reap its benefits. Furthermore, turmeric is being investigated for a potential role in cancer treatment, diabetes control and memory preservation, among other uses. It’s early days, but results so far are promising. And benefits have been seen in as little as a gram a day, so no need to overdo it – too much turmeric can cause diarrhea, constipation or upset stomach. Photo: Fascinadora/Shutterstock Activated Charcoal
It may feel wrong to gulp down something that looks like it was siphoned from a brackish swamp. But those who’ve tried charcoal mixed with water or lemonade say it doesn’t change the taste much. And if you believe Dr. Josh Axe, naturopath and author of Eat Dirt, it’s a natural way to absorb the chemicals and toxins that he believes can build up in your body (conventional medical wisdom believes the body detoxifies itself). Activated charcoal is, after all, a standard treatment for accidental poisonings. The problem, though, is a lack of proof that drinking it is good for you. It’s not advisable to try activated charcoal without talking with a health-care professional, says Demmers, as it interacts with a long list of medications, including lithium, lorazepam and codeine, or can block a medication’s efficacy altogether. And it can reduce absorption of the vitamins and minerals you want to hold on to.
A version of this article appeared in the Jan/Feb 2019/20 issue with the headline, “Drink Up,” p. 74.
Is this the real reason you’re so anxious?

Work, money, kids – there could be many reasons you feel more anxious than usual. But it turns out, reducing your anxiety could be as simple as increasing your magnesium intake. Olivia Hartland-Robbins reports
Whether it’s a mild nervous feeling, a sense of increasing worry or all out panic attacks, feeling anxious is not a pleasant feeling. And, if it happens to you, one thing is certain, you’re not alone.
Whether you are facing money troubles, a job loss or just general worries and woes, a growing number of us feel anxious on a daily basis.
In fact, anxiety is among one of the most common mental health problems in the UK – with more than one in ten people experiencing disabling anxiety at some point in their lives, according to Anxiety UK.
There are many known reasons people suffer from anxiety, including stress, medication and illness. But while most of us are aware that there are effective treatments such as anti-anxiety medication and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) – both available on the NHS – what most people don’t know is about the clear link between anxiety and magnesium deficiency.
Indeed, a recent study concluded that daily supplementation with magnesium can lead to a significant decrease in symptoms of anxiety, which suggests a definite link between the two.
The randomised cross-over trial was carried out on adults with mild to moderate depression symptoms. Six-wekk supplementation with magnesium chloride saw improvements in symptoms of depression regardless of age, gender or the use of antidepressants.
Most patients experienced improvements in just two weeks of starting supplementation.
Plus, researchers in 2017 published a study in the journal PLoS One, and found that adults who received 248 mg magnesium a day for six weeks saw a significant improvement in their levels of depression and anxiety. Could you be magnesium deficient?
Despite the fact that magnesium is found in every day foods such as brown rice, leafy green vegetables, beans, avocados, almonds and even dark chocolate, it turns out, a staggering 70 per cent of us have low levels.
That’s according to one study that tested 8000 participants’ hair samples between August 2014 and January 2016 carried out by the testing company Mineral Check.
A natural relaxant, for both muscles and mind, magnesium is one of the body’s most important essential minerals. It plays a crucial role in more than 300 different enzymatic reactions in the body each day including helping the muscles to relax for a restful night’s sleep, regulating the nervous system and reducing tiredness and mood swings.
Indeed, one in five women aged 19 to 34 have magnesium intakes below the Lower Reference Nutrient Intake (LRNI), according to the British Nutrition Foundation.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of magnesium for adults is 375 milligrams (mg), daily although requirements are increased during pregnancy because of how your body absorbs vitamins and minerals whilst pregnant. You would have to eat 130 grams of cashew nuts to reach the RDA of magnesium – 375 milligrams So how much do you have to eat to get your daily magnesium allowance? According to nutritional expert Keeley Berry, here’s how: 160 grams of dark chocolate – roughly four small bars (Green & Blacks) or one and a half large bars of Lindt 70% but think of the sugar and fat…
130 grams of cashew nuts – and 100 grams of cashew alone have 550 grams!
470 grams of cooked spinach – a giant bowl wouldn’t be enough
870 grams of brown rice – it’s impossible to eat that!
Why are so many of us magnesium deficient?
‘Magnesium deficiency could be down to our western diets which contain processed foods and refined grains, often with minimal consumption of leafy green vegetables,’ says Berry.
But we don’t only have the western diet to blame, it seems that the amount of magnesium found in common foods has also declined over the years.
‘Decreasing nutrient levels in western diets have long been reported. This may be due to over-farming and increased pollution,’ adds Berry. ‘The amount of magnesium in most common foods has declined by 20 per cent since the 1950s. Signs of magnesium deficiency include:
Poor quality sleep
Stress
Anxiety
Restless legs
Joint discomfort Muscle tension and pain Muscle or eye twitching Weak bones Low mood Headaches Migraines Poor concentration One symptom of magnesium deficiency is muscle and eye twitching. So how does magnesium deficiency affect anxiety? Among many others, poor sleep, exhaustion, feeling low and a weak immune system are all well-known symptoms of magnesium deficiency.Often when experiencing such symptoms though, it’s unlikely that our first thought would be magnesium deficiency. Instead, we tend to blame lifestyle factors such as, family, hectic social lives and work pressures.But actually, these common symptoms of magnesium deficiency could be the reason you feel so anxious.Let’s have a look at which of these symptoms could be making your anxiety worse. Symptom #1 You can’t sleep (or sleep badly) Poor sleep is probably one of the main reasons you’re feeling so anxious.When it comes to getting a restful night’s sleep, magnesium is instrumental in helping the body to relax, unwind, and in helping our brains switch off before bed.The reason magnesium is beneficial for sleep is through its interaction with a neurotransmitter called GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA is an amino acid responsible for reducing anxiety, promoting relaxation and preparing our body for sleep.Magnesium helps the body relax by ensuring these GABA receptors in our brain and nervous system are working as efficiently as possible.Plus, the GABA receptors are necessary to help our brains switch off, so that our minds don’t continue to race when trying to fall asleep. Think of them as hushing out those noisy late night thoughts that so many of us seem to experience.It seems that sleep deprivation and anxiety create a vicious cycle, says Berry. ‘ Research suggests that sleep deprivation can cause anxiety, yet experiencing anxiety can also cause sleeping problems – either one can come first,’ says Berry.‘Some form of sleep disruption is present in nearly all psychiatric disorders and studies […]
Development of an Immune Infiltration-Related Prognostic Scoring System Based on the Genomic Landscape Analysis of Glioblastoma Multiforme
1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital (The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University, The College of Clinical Medicine of Human Normal University), Changsha, China
2 Department of Neurosurgery, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China
Introduction: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common deadly brain malignancy and lacks effective therapies. Immunotherapy acts as a promising novel strategy, but not for all GBM patients. Therefore, classifying these patients into different prognostic groups is urgent for better personalized management.
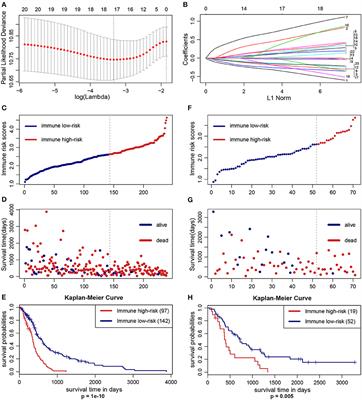
Materials and Methods: The Cell type Identification by Estimating Relative Subsets of RNA Transcripts (CIBERSORT) algorithm was used to estimate the fraction of 22 types of immune-infiltrating cells, and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression analysis was performed to construct an immune infiltration-related prognostic scoring system (IIRPSS). Additionally, a quantitative predicting survival nomogram was also established based on the immune risk score (IRS) derived from the IIRPSS. Moreover, we also preliminarily explored the differences in the immune microenvironment between different prognostic groups.
Results: There was a total of 310 appropriate GBM samples (239 from TCGA and 71 from CGGA) included in further analyses after CIBERSORT filtering and data processing. The IIRPSS consisting of 17 types of immune cell fractions was constructed in TCGA cohort, the patients were successfully classified into different prognostic groups based on their immune risk score ( p = 1e-10). What’s more, the prognostic performance of the IIRPSS was validated in CGGA cohort ( p = 0.005). The nomogram also showed a superior predicting value. (The predicting AUC for 1-, 2-, and 3-year were 0.754, 0.813, and 0.871, respectively). The immune microenvironment analyses reflected a significant immune response and a higher immune checkpoint expression in high-risk immune group.
Conclusion: Our study constructed an IIRPSS, which maybe valuable to help clinicians select candidates most likely to benefit from immunological checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and laid the foundation for further improving personalized immunotherapy in patients with GBM.
Why are people putting mushroom in their coffee?

Mushrooms have long been a popular pizza topping or salad bar option, but these days, people are adding them to their coffee or drinking them in tea. In fact, superfood mushroom powder is currently one of the more popular products on Amazon.
Certain mushroom strains have been deemed a superfood, meaning mushrooms have taken their place alongside kale, spirulina, wheatgrass, and all those other veggies that claim to be packed with micronutrients and promise miraculous health benefits.
Wondering what the claimed benefits of mushrooms are and debating whether it’s worth it to add fungi to your morning cup of coffee… or if you’re better off skipping this trend? Here’s what you need to know.
The four primary micronutrients in mushrooms are vitamin D, selenium, glutathione, and ergothioneine. These are all known antioxidants, and ergothioneine contains an amino acid that humans need and can only acquire through dietary sources. Traditionally, mushrooms have been used for their medicinal benefits for centuries.
Here’s what is known: The micronutrients above, as well as fiber, protein, and B vitamins (all of which are found in mushrooms), are good for you. Like, really good for you.
Antioxidants prevent oxidative stress, which is a key cause of diseases like cancer, dementia, and heart disease. Fiber helps maintain digestive health, lowers cholesterol, and helps control blood sugar. B vitamins promote red blood cell growth, higher energy levels, and improved brain function.
While we doubt mushrooms will reverse major diseases or drastically improve your quality of life overnight, a balanced and nutrient-rich diet can only help you. Mushroom powder is a convenient way for busy people to add key micronutrients to their diets without too much effort; meaning if you prioritize your well-being but don’t always have time to prepare thoughtful, healthy, home-cooked meals, it might be a good idea to add a mushroom superfood supplement to your diet.
There are a lot of ways to get the benefits of mushrooms without centering your whole diet around these fungi. You can get coffee, protein powder, tea, creamer, and supplements that have superfood mushrooms mixed in for easy use. Here are our faves:
Coffee seems to be the most popular way to sneak in superfood ‘shrooms. This particular blend has everything you need, both the ground coffee and the mushroom powder. Good news: It tastes like coffee, not mushrooms, and it has half the caffeine of a typical cup.
Here’s an idea: a mushroom and adaptogen protein powder. This creamy, plant-based powder contains 18 grams of protein per serving and is compliant with most diets (vegan, keto, etc.). Add it to a smoothie or just mix it with your favorite milk and drink for breakfast, after a workout, or as a meal replacement.
Prefer to stick to your usual coffee and just add mushroom powder when you feel like it? This powder is made of red rishi mushrooms, which claim to boost the immune system. You can also brew this as a tea or add it to hot cocoa or chocolate milk.
If you take creamer in your coffee or tea, or if you enjoy a morning smoothie, consider this plant-based creamer with a blend of superfood mushrooms for a nutritional boost. You won’t have to refrigerate this all-natural creamer, so it’s easy to take anywhere and throw in any drink.
If you have the time and patience, you can grow your own mushrooms at home (though this won’t be as convenient as the other options listed). However, it is surprisingly fast — it only takes 10 days for the fungi to grow, so you’ll be able to enjoy the fruits of your labor in no time.
The 7-day brain workout
It’s never too early to start maintaining your brain health – but should you do crosswords or CrossFit to protect your grey matter? The experts weigh in on the proven ways to stay mentally sharp.
How often do you break a mental sweat? It’s not an insignificant question. More than 400,000 Aussies are currently living with dementia , a number that’s expected to rise to more than 600,000 by 2030, and there’s evidence that challenging your brain in the same way you work out your body can offer protection against its ravages.
But are ‘brain training’ apps helpful? Or are you better off doing a crossword or learning a new language? Should you set aside brain training time like you schedule in gym sessions?
Firstly, it’s important to make a distinction between cognitive decline and dementia. The first is a natural part of ageing, while the second is a disease.
“People’s cognitive abilities slow down naturally with age,” explained dementia researcher Dr Clare Walton.
“But when they have a disease, that decline can be about four times faster. And just like other diseases, dementia has causes and we’re starting to learn there are things we can do to prevent the likelihood of it developing.” Where’s the evidence?
The ones with the most evidence to support them are eating healthily and exercising, so tackle them first. And brain training?
“A key problem is that most studies are observational, so they ask people how often they do things like crosswords and then see how that correlates with their chances of developing dementia,” said Dr Walton.
“Nobody’s taken a large group and said ‘OK, you guys watch TV and you guys do puzzles and then we’ll see how that affects things in 20 years.’ It’s possible that people who do crosswords also do something else that has a protective effect. Maybe they enjoy things that cognitively challenge them, or take a lifelong approach to learning in general.”
This last part is key, because lifelong cognitive stimulation may protect against Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
“It’s about challenging yourself in your daily life,” sayid expert puzzle-setter Dr Gareth Moore.
“If you have a job that hugely challenges you all the time, then brain-training may be fun, but it’s probably not necessary.”
Similarly, it’s not necessary for children or anyone in higher education since they’re getting plenty of mental stimulation already.
In fact, there’s a theory that people who challenge themselves in early life – by growing up bilingual or pursuing higher education – make themselves more resilient to dementia.
“It’s called cognitive reserve,” said Dr Walton.
“And it’s basically about how resilient your brain is. Everyone can accumulate some amount of damage to their brain, but the theory is if you’ve built up cognitive reserve, the connections in your brain are stronger, so you can tolerate more damage.”
One key takeaway is that it’s never too early to take steps to preserve your brain health.
“You can do things like travel, because when everything’s new your brain works on overdrive to process what’s happening,” said Dr Moore.
“If that isn’t possible, just being observant on your normal route to work can give your brain some variety. Even learning a new word a day can help.”
And brain training specifically? This is where things get tricky – at least one company has been hit with a hefty fine for making claims about its effectiveness that aren’t supported by evidence.
“There isn’t very good evidence that brain-training games can slow cognitive decline or prevent dementia,” said Dr Walton.
There’s a positive side, however, where one of the largest studies on brain training on 67,000 people found that those who did brain training for a couple of months reported getting on better with things like managing their finances and using public transport.
Like what you see? Sign up to our bodyandsoul.com.au newsletter for more stories like this. It’s all about the challenge
All in all, the evidence suggests that mental fitness has parallels to physical fitness – find something that offers short-term benefits that you enjoy and any beneficial effects further down the line are an added bonus.
“It’s better if they challenge you,” said Dr Moore.
“If you can do them in your sleep, try something new. Mix it up. Do a crossword one day, read something complicated the next.”An even better bang-for-your-buck option is to combine physical and mental workouts with socialising.”There’s evidence that people who are more lonely and socially isolated are at higher risk of dementia,” said Dr Moore.Activities like table tennis and dancing, for example, that are physical, have a social aspect and are mentally taxing, are great for your brain.The bottom line?Eating well and moving are your best options for your brain and body. And while the benefits of everything else are less well-defined, you should still find something that stimulates your grey matter. The goal is to find something that gives you the best chance of a high quality of life in your older years, without causing you too much pain in the short term. Your weekly brain workout Monday Play puzzle rush for 5 minutes This free chess mini game – played by beginners and grandmasters alike – offers up set-piece board positions and challenges players to find the correct move, aiming to complete as many increasingly tough problems as possible against the clock, under three-strikes-and-you’re-out conditions. Chess masters can do 50 in five minutes, but you should aim for two or three. Tuesday Learn a new word for two minutes You don’t have to comb through the dictionary.Merriam-Webster offers a Word of the Day podcast that includes definitions, derivations and examples of words like ‘desuetude’, ‘adscititious’ and ‘calliope’ (it’s pronounced kahLYE-oh-pee), as well as examples of these words in use and interesting trivia to accompany them. Available at Apple Podcasts. Wednesday Listen to the news in French for 4 minutes Don’t worry if you can’t parlez at full speed – languagel earning resource Linguistica 360 provides short breakdowns of current events in slowed-down French, German, Italian or Spanish, picking out keywords to build your vocabulary as you follow […]
Leftovers from chocolate manufacturing can help manage obesity and lipid disorders: Study

( Natural News ) Cocoa ( Theobroma cacao ) is the main ingredient of chocolate, one of the most popular foods on the planet. The seeds of cocoa, also known as cocoa beans, are the only parts used for the production of chocolate. It is estimated that about nine tons of fresh byproducts — which end up as waste — are generated for each ton of cocoa beans used. Cacao byproducts that are discarded during manufacturing include the outer pod husk (cacao shell hulls and pericarp), the kernel husk and mucilage. According to research, byproducts such as these contribute to environmental pollution because they are often not properly processed or disposed of. Hence, there is a growing interest in finding a good use for these byproducts in the scientific community.
Among the many proposed applications for cacao byproducts, the possibility of using them to make nutraceuticals is the most appealing.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food , researchers from the National Polytechnic Institute in Mexico explored the potential of a nutraceutical generated from cacao byproducts to fight obesity and regulate blood lipids . They found that rats with diet-induced obesity responded well to the nutraceutical, exhibiting reductions not only in blood cholesterol and triglycerides, but also in body weight, after five weeks of treatment. Chocolate production waste can be turned into something that benefits human health
The shell of the cocoa pod or pericarp is a rich source of protein, fats, carbohydrates, soluble and insoluble fiber, and phenols. Phenols are a class of plant compounds that possess properties beneficial to human health. In the case of cocoa phenols, a previous study by the researchers showed that these bioactive compounds possess antioxidant properties that may be useful for disease prevention.
Other studies also suggest that the flavonoids in cocoa-derived products could prevent cardiometabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, hypertension and central adiposity. These flavonoids have the ability to decrease body weight by reducing abdominal fat, making their source a potential therapeutic alternative to conventional treatments for obesity.
For their study, the Mexican researchers prepared pellets and extracts from the outer pod husk and kernel husk of cacao. They fed these products to rats with high-fat diet- and fructose-induced obesity for five weeks.
The researchers reported that the treatment reduced the animals’ body weight by 39 percent; systolic blood pressure by 27 percent; blood triglyceride levels by 55 percent; total cholesterol by 24 percent; low-density lipoprotein by 37 percent; and the triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein ratio by 54 percent. Reductions in triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL, also known as the bad cholesterol) spell good news for the heart, as high levels of these are linked to heart disease and other serious conditions.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that cacao byproducts can be used to make nutraceuticals that improve metabolic function in obese subjects without causing adverse effects. The health benefits of cacao
Cacao , particularly the raw, organic kind, is a bona fide superfood that offers plenty of health benefits. Besides having large amounts of antioxidants, cacao also contains theobromine, a plant compound that supports heart health, respiratory health and oral health. Cacao is also rich in minerals like copper, iron and magnesium, all of which are necessary for various bodily functions.
Here are some of the amazing benefits associated with raw, organic cacao: (h/t to SelfHacked.com ) It helps prevent heart disease
It lowers blood pressure
It helps reduce blood cholesterol
It enhances brain function
It helps improve skin elasticity
It improves mood
It speeds up bowel movement
It helps stabilize blood sugar levels
It helps reduce mental fatigue
It promotes dental health
It helps treat cough
Cacao can be consumed in the form of cacao nibs or dark chocolate . To get the full benefits of this superfood, opt for raw, organic cacao products or chocolates with a high cocoa content (at least 70 percent).
Sources include:
Illuminate Festival premiere of HeartMath Experience Feb. 23 at Hilton Sedona Resort

HeartMath has helped to create 26 years of research with over 300 independent peer-reviewed studies on heart intelligence and has created useful tools and techniques to help improve stress reduction, well-being and heart coherence. The Illuminate Film Festival presents the festival world premiere of The HeartMath Experience, a unique and educational conscious interactive film about the science behind the heart’s intelligence.
The event, which will include a live healing experience connecting to the heart’s natural wisdom, will take place on Sunday, Feb. 23 at the Hilton Sedona Resort from 6:30 to 9 pm.
Live speakers will include Dr. Deborah Rozman, co-CEO, bestselling author and President of HeartMath; Howard Martin, international speaker, Executive Vice President of HeartMath and bestselling author of The HeartMath Solution; and Gregg Braden, five-time New York Times bestselling author and internationally renowned scientist and visionary.
The heart is an intelligent system that actually sends more signals to the brain than the brain sends to the heart, and produces an electromagnetic field that helps to synchronize the entire body.
HeartMath has helped to create 26 years of research with over 300 independent peer-reviewed studies on heart intelligence and has created useful tools and techniques to help improve stress reduction, well-being and heart coherence.
Extensive six-week scientific studies have shown that after using these methodologies, there was a 24% improvement in the ability to focus, 30% improvement in sleep, 38% improvement in calmness, 46% drop in anxiety, 48% drop in fatigue and 56% drop in depression. All of these results came from the HeartMath techniques presented in the film.
Additionally, other electrophysiological studies and scientific data show that the heart has a direct correlation with intuition. In fact, the heart has 40,000 neurons that lend itself to what’s called the “little brain”.
This little “heart brain” gives the heart the ability to make decisions, process information, sense and even have the ability to learn and store memory.
The HeartMath Experience will further explain the healing abilities in the heart and help viewers move from depletion to renewal, separation to connection, and mind to heart.
This 90-minute documentary-course hybrid will help everyone rediscover their highest potential and best self. Attendees will learn how to reconnect to their heart and its innate wisdom, shift heart coherence in the world and help create a planet that honors heart intelligence.
The speakers will facilitate HeartMath techniques throughout the evening, participate in a live Q&A, and lead a ground-breaking post-screening exercise to get real-time audience heart/brain coherence results.
Gaia, the world’s largest resource for consciousness expanding videos, will be the official presenting sponsor of the ILLUMINATE premiere event. Producing sponsors include Stellar Productions, Sedona Chamber of Commerce, Amanda Romania LLC and Dr. Shaida Sina of Breakthrough Medicine.
The premiere of The HeartMath Experience will be held on Sunday, Feb. 23, 6:30-9 p.m., at the Hilton Sedona Resort, 90 Ridge Trail Drive, in connection with the Self-Empowered Wisdom conference, Feb. 20-24.
The premiere is not included in the conference pass.
Through Feb. 21, 50% off screening tickets for Sedona locals. Details and $15 tickets available at illuminatefilmfestival.com/sedona-tickets.
6 Natural Ways to Gain More Energy Throughout the Day
Getty Images Do you start feeling lethargic around the same time every day? Uncover the reason for your daily slump — and the body-clock secrets that guarantee nonstop energy. Groggy midmorning? Try knitting.
Wish midmorning naps were a “thing”? That’s because your brain’s prefrontal cortex, which helps you stay clearheaded and focused, is experiencing an early day dip in electrical activity. Fortunately, researchers say you can energize your prefrontal cortex—sharpening concentration, memory and energy by 32 percent — by taking a 10-minute break to focus on a creative task like sketching or knitting. Daniel H. Pink, author of When: The Scientific Secrets of Perfect Timing, notes that brief, restorative breaks are key to better AM brain function. Sluggish after lunch? Munch on macadamias.
Your pancreas, which produces sugar-controlling insulin, is most likely to misfire in the early afternoon, letting blood sugar dip to snooze-inducing levels, says neurologist Daniel Amen, MD.
To increase your energy and stamina by 65 percent, add one ounce of macadamias to your lunch, or enjoy these crunchy treats as an early afternoon snack. UCLA researchers say the nuts’ healthy plant oils energize a tired pancreas, plus prod tissues to use up insulin, allowing fatigue-fighting blood glucose to reach brain and muscle cells that need it. Dozy in the afternoon? Cool your brow.
Your nervous system craves an afternoon break and tries coaxing you to catnap by tamping down the production of energizing beta brain waves. But Australian scientists say a brief drop in skin temperature — try splashing cool water on your cheeks, holding a cold pack to your eyes or stepping outside if it’s chilly — can kick-start beta wave release in 30 seconds, boosting your energy and focus by 50 percent for 90 minutes. Weary all the time? Sniff vetiver before bed.
The number-one cause of all-day fatigue is poor sleep. Thankfully, there’s an easy Rx: Take 15 minutes before lights-out to enjoy the aroma of 100 percent vetiver essential oil (place four drops on a tissue and set it beside you as you read or relax).
A study in the journal Natural Product Research reveals vetiver’s earthy aromatic compounds prompt the release of sleep-enhancing theta brain waves, helping you drift off 45 percent faster and sleep 25 percent more deeply, increasing daytime energy by 65 percent. Beat by dinner? Beautify with plants.
We’re exposed to twice as much tiredness-triggering carbon dioxide when we’re cooped up in tightly sealed homes and offices, say researchers at Washington State University. And that exposure can dampen the central nervous system, leaving us dragging by dinnertime.
But Portuguese research suggests that decorating rooms you frequent with air-purifying plants like ferns and spider plants cuts indoor carbon dioxide levels by 30 percent to prevent evening energy dips.
Best Tips To Prevent Dementia From A Neuroscientist

The brain is the body’s most important organ, a control center that directs its steps everyday. Sadly, that is one fact that we basically take for granted, not only resulting in a variety of diseases that affect our mood and mental health, but also leading to an early death, and one of these are dementia and its common and more notorious form Alzheimer’s disease. In fact, according to Alzheimer’s Association, dementia is the 6th leading cause of death in the United States. And the worst part is that there is currently no cure to the disease to date.
Fortunately, dementia is preventable. The following tips from award-winning neuroscientist Dr. Sabina Brennan will prove it:
Have A Consistent Daily Sleeping Schedule
Sleep is important for brain health, a simple fact that is now ignored in today’s hyperactive world since we fail to get the recommended hours of sleep, which is 7 to 8 hours at most for adults. Only one of three people get enough sleep, making the World Health Organization count sleep loss as an official pandemic.
Sleep detoxes both the brain and the body, clearing out neural waste products that build up inside the central nervous system every day. Without it, the brain does not have ample time to flush them away, leaving the buildup untouched. One example of the waste building up inside the brain is beta-amyloid, the nasty and sticky protein that serves as the primary cause of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
To prevent the rise of dementia, Brennan said that it is important to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day. That is because research has shown that a regular sleeping schedule results in getting both rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep.
Sleep has five stages, whether or not REM sleep occurs. Non-REM sleep “is characterized by slow brainwaves interspersed with a burst of activity called spindles,” per Brennan. During the first half of the night, most of your sleep is non-REM, with the deepest being in non-REM stages 3 and 4. REM sleep, on the other hand, occurs during the second half, when you dream. It is during this stage where the electrical activity recorded is very similar to that of an “awake” brain. All of this means is that to completely repair your brain for the next day, you must both do the recommended hours of sleep and experience REM and non-REM sleep.
Also on MSN:
Making Your Home Workouts Harder Isn’t Just About Adding More Weight – a Trainer Explains
So, about our struggling healthcare system, Mr President
What Happens to Your Body When You Get the New Coronavirus?
Be Excited Every Day
If you either feel forgetful, lost your sense of humor or have unhealthy eating habits, then it could be a sign of stress that can build up and increase dementia risk.
Of course, you may be wondering how to reduce stress while revitalizing your brain. It is good to know that stress does have its own benefits. Brennan focused on the positive aspects of stress and how you need an optimal amount, asserting that “the total absence of stress is associated with boredom and disengagement, neither of which is good for your brain health or indeed your mental health.”
Brennan advised one way to manage stress is to be excited every day especially at the small pleasures of life, some of which may actually be challenging as opposed to being stressful. In fact, what would life be without your first date, job interview or prom?
Do 10 Minutes Of Social Activity Daily
Loneliness kills. More accurately, loneliness can cause dementia and other brain diseases through disturbed sleep patterns, abnormal stress responses, unhealthy blood pressure levels and greater cognitive decline.
To prevent dementia-causing loneliness, Brennan said that it is best to devote just 10 minutes of social activity every day. These activities can be any activity that brings you joy, be it reading, drawing or even writing.
Watch Your Drinking
Red wine may be healthy in small doses, but how healthy is it? Heavy drinking results in increased blood flow, causing disrupted blood flow and damage to the heart, indirectly resulting in brain damage.
In the U.K., there are government guidelines that measure safe alcohol consumption, called alcohol units, with the safest, “low risk” amount being less than 14 units of alcohol (equivalent to about 10 small glasses of low-alcohol wine) weekly. Moderate drinking, on the other hand, amounts to 14 to 21 units per week, and is shown in a recent study to have lethal effects on the brain.
With these in mind, it is best to drink alcohol in very limited doses because even small amounts can increase dementia risk.
Exercise Everyday
Although exercise benefits you physically, it can also help your brain. Brennan suggested that to keep your brain healthy, it is a must to exercise daily even at an old age. Even low to moderate intensity exercise can aid in reducing dementia risk, and has been proven by research to boost memory learning skills.
For an improved memory and cognitive function, it is best that you start getting physically active now so that you will experience more fruitful years later in life.
Smile Smiling as a solution to dementia may seem odd, but science proves just that. Aside from scientifically triggering happiness, smiling itself releases happiness-causing chemicals. These chemicals are serotonin, dopamine and endorphins, which all activate your brain’s reward circuits, and, in turn, increase the feeling of happiness, giving your overall brain health a positive boost.Brennan added that the serotonin that your smile releases doubles as a natural anti-depressant, while the endorphins act as natural pain relievers. 100 Ways to Live to 100 (Best Life)
The Dangers Of Using Smart Drugs

Image from https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20131212-smart-drugs-at-work-good-idea The competitive nature of life today has resulted in a lot of pressure for many individuals. There is pressure to study harder, work harder, and work for longer hours. As a result of this people often suffer from fatigue, poor concentration and look for ways to enhance cognitive abilities. There have also been movies and TV shows which create a narrative that we only use a small percentage of the brain. In order to tap into more brain potential one only has to use a cognitive enhancing drug. Hence some people look for these drugs out of curiosity. The combination of these circumstances has seen increased and continuous use of smart drugs, also known as nootropics.
Nootropics are drugs that boost brain performance. The name nootropics is literally translated from Greek and means ‘towards the mind’. Smart drugs affect cognitive abilities in at least one of these domains: memory, attention, arousal and creativity. They do this by altering neurochemicals, enzymes or hormones in the human brain. The neurochemical alteration leads to increased catecholamine signalling.
Most of the popular smart drugs that healthy individuals abuse are prescription drugs. These drugs are used on ADHD , Alzheimer’s , narcolepsy and other sleeping disorders. Modafinil or Provigil is a popular smart drug which is used to treat narcolepsy through the stimulation of the central nervous system. It increases alertness and keeps an individual awake. Adderall , Ritalin or methylphenidate and racetams are other popular smart drugs. Adderall treats ADHD and contains amphetamines. It increases focus and reduces impulsive behaviour. Ritalin treats ADHD and narcolepsy.
In the short term, these drugs produce the desired effect since they increase the user’s alertness and focus. However, in the long term, the drugs could have a negative impact. Addiction
The abuse of nootropics raises concerns because the Drug Enforcement Administration categorizes Adderall, Ritalin as other smart drugs as Schedule II controlled substances. This puts them in the same category as cocaine in terms of potential for abuse. The pleasure effect that the users feel from altering the dopamine system can lead to addiction. Diminished abilities
To accomplish the short term results of increased alertness, the drugs overstimulate the central nervous system. As a result, they end up damaging cells. Users of these drugs end up having diminished abilities in several areas like multitasking and organization. Such consequences are ironic since the initial reason for abusing the drugs is to enhance cognitive abilities. Impulsive behaviour
Some studies show that prescription nootropics affect brain function. As a result of the improved brain function, users tend to have a higher risk of impulsive behaviour. Users tend to engage in risky sexual habits. Health problems
Studies show that a common side effect of prescription nootropics includes health problems such as high blood pressure, eyesight problems, as well as insomnia and other sleep disorders.
Smart drugs could lead to fast heart rates. Additionally, the use of smart drugs by healthy individuals could result in psychosis and anxiety. For drugs like Adderall and methamphetamine a user could have psychotic symptoms that last for months or years after the use of the drugs. Users of the drugs could also experience memory loss, damage to nerve cells leading to strokes, convulsions and tremors.
Research on the long term effect of smart drugs use on healthy individuals is however limited as previously most of the studies conducted on the effectiveness of prescription nootropics were mainly done in elderly individuals. The prescription nootropics, as the name suggests, require a prescription to control the amount an individual needs to treat their condition. However, healthy individuals taking the drugs to enhance brain performance take excessive doses which increase their risk of experiencing the negative effects of the drugs. Check out this story on the danger of smart drugs Little white pill(s)
The BBC has an interesting article on smart drugs .
Read about Scopolamine: The Mind Control Pill Used To Facilitate Crime In The Streets Of Nairobi
If You’re Going to Use Nootropics, Shouldn’t You Know Exactly What You’re Taking?
More and more people are using nootropics to give themselves a mental boost, and it’s not hard to understand why. Studies have shown that nootropic supplements may enhance cognitive functions such as reasoning, memory, alertness, focus, willpower, creativity, flexibility, and verbal fluency.
But with so many different nootropics currently on the market, how do you know which type is right for you? The best solution is to find a company that is fully committed to science and transparency, so you always know exactly what you’re putting in your body and why. And when it comes to science and transparency, nobody beats Neurohacker Collective , the group behind Qualia Focus and Qualia Mind , two of the most advanced and comprehensive nootropics supplements in the world. Neurohacker Though some health and wellness companies market nootropics as “smart drugs,” they won’t actually make you smarter. A nootropic is really just any chemical compound that helps create the biological conditions necessary for optimal brain function. These include amino acids, vitamins, minerals, nutrients, and stimulants. Some of these compounds serve as fuel for cognition. Others modulate various processes involved in neurotransmission.
We mostly get nootropics through our diet. But some, like caffeine or L-theanine, we get from things like coffee and tea. However, there are a lot of other nootropics that we never get because the modern Western diet doesn’t include obscure plants, roots, and seeds like rhodiola, bacopa, or celastrus seed extract. To get these brain-boosting substances into our bodies, we have to rely on supplements. However, creating these supplements is not as simple as many companies would have you believe.
Creating an effective nootropic supplement requires a deep understanding of the complex interplay and synergy between specific ingredients at specific dosages. And Neurohacker Collective’s ability to analyze and unravel this complex interplay is what sets it apart from other companies.
Neurohacker Collective’s team of scientists and medical professionals takes a “whole systems” approach to the science of nootropics. What this means is that instead of simply trying to produce a certain effect in one system of the human body, they study the interrelation between all systems. For their Qualia nootropics supplements, Neurohacker Collective used this pioneering whole system approach and complex systems modeling, along with thousands of hours of research in neuro-biology and organic chemistry, to create products specifically designed to fuel neurotransmission and improve overall brain health.
Qualia’s supplements come in two different formulas, both of which are designed to help you feel focused, clear-headed, and ready to take on any task. Neurohacker Qualia Focus is Neurohacker Collective’s introductory nootropic supplement. It’s a fast-acting blend of five nootropic compounds, seven neuro-vitamins, six adaptogen extracts, five amino acids, and one choline donor. These ingredients promote neuron and synapse development, neuroplasticity and neurogenesis, increased energy, healthy cell structure, and cerebral blood flow. Nuerohacker Qualia Mind is designed to produce effects similar to Qualia Focus . It just turns the efforts up a notch by adding a few extra ingredients and increased dosages to produce additional nutrient synergies. Qualia Mind features six nootropic compounds, seven neuro-vitamins, two antioxidants, six adaptogen extracts, five amino acids, and two choline donors. The key additions not found in Qualia Focus are PQQ, Phosphatidylserine, DHA, and CDP-Choline. These improve responsiveness to neurotransmitters and aid the formation of synaptic connections in the neurons used for memory. Thus, Qualia Mind provides more robust support for attention and focus in stressful or demanding situations.
How do you know which of these nootropics are right for you? It really depends on your specific needs. Qualia Focus is less powerful, but more affordable. Qualia Mind has a bigger impact, but is also more expensive. Transparency and Quality Control
Regardless of which option you choose, Qualia Focus or Qualia Mind, you can always rest assured that you are getting a product of the highest quality.
Unlike some companies which keep the “proprietary” formula of their nootropics a secret, Neurohacker Collective believes the only way you can truly build trust is by telling customers exactly what they are putting in their bodies, and why . That’s why they provide lists of every single ingredient in every one of their supplements, as well as painstakingly detailed accounts of what these ingredients actually do. Want to see for yourself? Just click here .
Neurohacker Collective also wants to make sure you are completely satisfied. That’s why your first purchase comes with free before-and-after cognitive assessments from Cambridge Brain Sciences. If you are not completely satisfied with your results, Neurohacker Collective offers a 100-day money back guarantee.
So if you’re thinking about trying nootropics and you want to deal with a company you can actually trust, Neurohacker is the answer. Click here to read more about their industry-leading Qualia Focus and Qualia Mind nootropics, today.
Futurism fans: To create this content, a non-editorial team worked with an affiliate partner. We may collect a small commission on items purchased through this page. This post does not necessarily reflect the views or the endorsement of the Futurism.com editorial staff.
Start your day with lemongrass tea and enjoy its brain-boosting benefits

Advertisement Lemongrass ( Cymbopogon citratus ) has a lemony aroma and a refreshing citrus flavor. This superfood offers many health benefits, thanks to its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
A study published in the Journal of Herbs, Spices and Medicinal Plants also found that lemongrass boosts brain health ! Battling amnesia with lemongrass
For the study, the researchers set out to determine the brain health-boosting properties of lemongrass . They used a mouse model with scopolamine-induced amnesia to test if lemongrass can protect memory function.
The researchers gave three groups of mice either 25, 50 or 100 milligrams of lemongrass extract per kilogram (mg/kg) body weight and the control group 10 milliliters (mL) of a saline solution per kg for seven days.
For the interaction studies, they administered treatment 30 minutes before the animals were given amnesia-inducing scopolamine. After each treatment, they evaluated memory function using Y-maze and object recognition tests. They also measured biomarkers of oxidative stress (i.e., malondialdehyde and glutathione) and acetyl-cholinesterase activity in the brains of the treated mice.
The researchers reported that lemongrass increased memory performance and reduced scopolamine-induced amnesia.
Scopolamine increased oxidative stress and induced acetyl-cholinesterase activity in the mice, but treatment with lemongrass extracts reversed these effects.
Based on their findings, the researchers concluded that lemongrass can be used in as an alternative medicine for memory decline . The health benefits of lemongrass
Lemongrass smells like lemon but has a milder, sweeter taste. This superfood is often used in different Asian cuisines to give meat, poultry and seafood a tangy, lemony flavor.
Lemongrass is also used as a natural preservative and bug repellent. Because lemongrass has a zesty, refreshing aroma, it is often used to make cosmetics, perfumes and soaps.
Lemongrass is used in aromatherapy to relieve stress and improve mood. Every part of the plant offers health benefits that can be incorporated in natural treatments. It improves digestive health
Lemongrass is good for your digestive health because it is rich in dietary fiber .
The superfood is a prebiotic that helps repopulate the “good” bacteria in your colon. Lemongrass also contains citral, an antimicrobial compound that can help eliminate “bad” bacteria. Studies show that citral can help get rid of Salmonella and E. coli , two common causes of gastroenteritis .
Lemongrass can be used to address digestive problems, such as: Bloating
Constipation
Cramps
Diarrhea
Flatulence
Heartburn
Indigestion
It has cardioprotective properties
Lemongrass not only benefits heart health, it also contains antioxidants that help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Lemongrass is rich in potassium, which helps lower and regulate blood pressure. To manage your blood pressure, use lemongrass as a seasoning instead of salt. How to make lemongrass tea
For dosing recommendations, consult a qualified natural health practitioner. If you’re not used to drinking lemongrass tea, limit your intake to one cup daily. If you can tolerate one cup of lemongrass tea well, feel free to drink more.
If you experience any adverse side effects, stop drinking the tea or reduce the amount you consume. It is best to avoid drinking lemongrass tea if you are pregnant or taking any medications. Do not give lemongrass tea to small children.
Ingredients for 1 serving: 1 cup boiling water 1-3 teaspoons of fresh or dried lemongrass Preparation: > Pour boiling water over the fresh or dried lemongrass. Let the mixture steep for about five minutes. Strain the tea before drinking. If you prefer a cold drink, add ice cubes to make iced lemongrass tea. Purchase loose lemongrass tea or lemongrass tea bags at natural food stores or online. Another option is to purchase organic lemongrass at nurseries where herbs are sold. This will allow you to grow fresh lemongrass at home.If you don’t want to drink lemongrass tea, you can also cook with it ! When eating lemongrass raw, mince it well because it’s stringy. Add it to poultry or fish before baking. Add a stalk or two of lemongrass to a cup of chicken noodle or other savory broths. Improve brain function and boost your digestive and heart health by drinking lemongrass tea . Sources: TAndFOnline.com Top10HomeRemedies.com Healthline.com Advertisement
6 Morning Energy Drinks That Wake You Up Better Than Coffee

Most people wake up to a warm cup of joe in the morning to give them a much-needed energy boost. For others, coffee serves as a source of comfort and routine practice. However, some studies have found that large amounts of caffeine can harm our bodies and minds. After all, caffeine is still a drug, and with the current popularity of energy drinks, one of the most widely consumed of them all. What the FDA says about coffee and caffeinated energy drinks
According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), “In the U.S., 80 percent of adults consume caffeine every day – the average adult has an intake of 200 mg per day, the amount in two 5-ounce cups of coffee or four sodas. A study of 7th, 8th, and 9th grade students in Ohio found that students took in an average of 53 mg of caffeine per day, but almost one in five students took in more than 100mg of caffeine each day.” The FDA states that a 5 oz (small) cup of coffee contains 60-150 mg of caffeine, depending on the darkness of the roast.
Small amounts of coffee have negligible side effects, but it still raises cortisol and adrenaline, which activates the fight-or-flight response. Many people report feeling calmer and less restless without caffeine in any form. In our on-the-go society, most of us resort to caffeine to help us get through the day, but perhaps we should ask ourselves why we feel the need to keep such a busy schedule in the first place. Instead of needing more caffeine to power through the day, we could carve out more time for ourselves to rest. However, I digress, back to talking about coffee. FDA calls caffeine a widely-used drug
Caffeine is classified as a drug as well as an additive, according to the FDA . Plus, it is still one of the most widely consumed sources of caffeine in the world. Even though it’s a drug, it does not seem to cause harm in most cases, so the government does not regulate it.
However, just like other drugs, caffeine can cause withdrawal symptoms and fall under a substance abuse disorder, according to the American Psychological Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual version 5 . Using large amounts of caffeine to the point where the user feels physical and mental symptoms classifies it as a substance abuse disorder. Benefits of trading coffee in for natural energy drinks
If you’ve been looking to give up coffee, here are some reported findings of benefits you might notice after just seven days:
– Reduced headaches after an initial withdrawal period
– Reduced muscle tension and tightness
– Better concentration
– Feeling more alert in the morning without restlessness
– More regular and healthy bowel movements
– Return to regular sleep cycles
– Better awareness of hunger and fewer junk food cravings
– More balanced, healthy response to stress Enjoy improved cognition when you try these natural energy drinks and give up the java
According to the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics , caffeine from coffee can affect sleep, alter mood and blood flow in the brain, your metabolism and genes, and the neurotransmitters in the brain that affect memory processing and cognitive performance. Their research found that ‘Peak plasma caffeine concentration is reached between 15 and 120 min after oral ingestion in humans.’ Also, keep in mind that caffeine takes about six hours to leave the body altogether, so if you have an afternoon cup, it may still be in your system when you go to sleep. This might be contributing to the insomnia epidemic sweeping the globe, in combination with other factors such as stress and using technology at night.
While many people believe that caffeine helps them function better, studies have shown that it doesn’t help in all cases. The above-cited research found that ‘An increase in arousal improves the performance of tasks where relatively few sources of information have to be monitored, particularly under conditions when the need for selective attention is stressed by time pressure. When, on the other hand, multiple sources of information or working memory have to be used, an increase in arousal and attention selectivity has no apparent beneficial effect on performance, which may consequently even decrease.’
One of the metabolites of caffeine in the body is paraxanthine. Paraxanthine blocks the body’s adenosine receptors, which then raises epinephrine levels in the blood and diastolic blood pressure. So, in other words, when you drink coffee, your body responds as if there is a threat and activates the fight-or-flight response. This explains how so many people get through their days on caffeine because they’re running on pure adrenaline.
So, now that we’ve gone over the potential dangers of coffee and how it can affect the mind and body, what are some alternatives? We will go over six natural energy drinks you can make in the morning that will give you just the boost you’re looking for! THESE SIX HEALTHY, NATURAL ENERGY DRINKS CAN IMPROVE YOUR MOOD AND BOOST YOUR ENERGY LEVELS
1 – APPLE-BANANA SMOOTHIE
Both bananas and apples provide a ton of vitamins and minerals, and the natural sugars will give you a huge boost of energy in the morning! Bananas have a ton of potassium and B vitamins to help boost brain health and increase stamina. Apples contain a lot of potassium as well, and also Vitamin C.
Ingredients: 1-2 peeled apples
Two bananas
¼ cup cold, non-fat milk or dairy-free alternative
½ cup crushed ice
Directions: Mix all ingredients in a blender until smooth and serve the energy drink chilled. 2 – KOMBUCHA TEA
Kombucha – a type of fermented green tea – contains probiotics, vitamin K-2, vitamin B-12, and fatty acids. The last two ingredients are very beneficial for a healthy brain. Keep in mind that making it yourself can be dangerous if you don’t follow the recipe exactly, or use ceramic wares to make it. Lead from these containers can seep into your kombucha, so avoid ceramic at all costs. […]
Want to improve your memory while staying fit? Try exercising for at least half an hour regularly

( Natural News ) Regular exercise is a key component of a healthy lifestyle, but its benefits go beyond just strengthening muscles and reducing fat. Researchers from the University of Maryland (UMD) found that exercising for at least 30 minutes each day can help improve memory. Their study, which appeared in the Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , is one of many that seek to explore the connection between exercise and cognitive function . How does exercise affect the brain?
Aerobic exercise improves memory and brain function by promoting neurogenesis. Neurogenesis refers to the growth of new cells in the brain, which is faciliated by an increase in the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
BDNF is a brain protein involved in the growth, maturation, maintenance and survival of nerve cells. Besides being active at the synapses, where communication between nerve cells occur, BDNF is also found in brain regions that control important physical activities, such as eating and drinking. Additionally, BDNF influences learning and memory as it regulates the ability of synapses to adapt in response to experience.
According to studies, exercise prompts the release of large amounts of BDNF. High levels of BDNF, in turn, boosts memory and improves brain function. (Related: Regular exercise can keep dementia at bay – adding more hours reduces the brain’s aging process .)
Despite establishing this link, scientists are still unsure about the right amount of exercise needed to acquire this benefit. Research is still ongoing to determine the right combination of exercise intensity and duration that can produce desirable cognitive outcomes. The present study contributed to the search by exploring how acute exercise – a single bout of exercise – can affect semantic memory .
Semantic memory is the recollection of information not related to individual experiences. This refers to memories associated with language, names and words. Recent studies suggest that the hippocampus, the brain region that regulates emotion, learning and memory, contributes to semantic memory .
“While it has been shown that regular exercise can increase the volume of the hippocampus, our study provides new information that acute exercise has the ability to impact this important brain region,” said Carson Smith, one of the study authors.
To shed light on the effects of long-term exercise on cognitive function, Carson and his colleagues looked at brain activation during a semantic memory task after a single session of exercise. They recruited 26 participants (aged 55 to 85) for their experiment and used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI).
The participants underwent two experimental visits. During each visit, they engaged in either 30 minutes of rest or stationary cycling exercise before doing a Famous and Non-Famous name discrimination task during fMRI scanning.
The researchers reported that engaging in acute exercise resulted in greater semantic memory activation. They also detected significantly greater activation in the hippocampus of the participants after exercise than after rest.
The researchers theorized that acute exercise produces a short-term effect on neurotransmitters and neural growth factors – both of which play key roles in the brain’s overall function. This effect leads to increased neural activation.
The researchers believe that engaging in acute exercise daily will be beneficial in the long run, as the acute increase in neural activation could spur the brain to adapt to it over time. This adaptation could lead to improvements in brain function and delay symptoms of cognitive decline.
“Just like a muscle adapts to repeated use, single sessions of exercise may flex cognitive neural networks in ways that promote adaptations over time and lend to increased network integrity and function and allow more efficient access to memories,” Smith explained.
To learn more about how to improve cognitive function, visit BrainFunction.news .
Sources include:
What Is Dopamine & Is It Bad In Excess?

Without dopamine, we wouldn’t feel driven and motivated. But what happens when dopamine stops being a means to an end and turns into an end in itself? Dopamine has been blamed for many destructive behaviors of our modern lifestyle, making “dopamine fasting” the newest Silicon Valley craze. Is an excess of this neurotransmitter turning us into insensitive pleasure junkies or is the science a bit more complicated? Read on! What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells [ 1 ].
Many areas of the brain produce dopamine. It is produced in the ventral tegmental area (VTA in the image above) of the midbrain, the substantia nigra pars compacta, and the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus [ 2 ].
The most important dopamine pathway in the brain controls reward-motivated behavior [ 1 ].
Most types of rewards, such as new experiences or accomplishments, can increase dopamine levels in the brain. In addition, most addictive drugs and behavioral addictions can increase dopamine [ 3 ].
In addition, dopamine has many other important roles in humans, including movement, memory, attention, learning, sleep , and mood [ 2 ].
Dysfunctions of the dopamine system contribute to Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, restless legs syndrome, and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [ 1 ].
Schizophrenia is characterized by high striatum dopamine, but abnormally low prefrontal dopamine activity [ 4 ].
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter that many brain areas produce. It is thought to control reward-motivated behavior. Genetics Behind Dopamine
See this post for a more comprehensive guide on the genetics of dopamine . Cons of Excessive Dopamine
Dopamine levels are a marker of mental health. Low or high dopamine levels don’t necessarily indicate a problem if there are no symptoms or if your doctor tells you not to worry about it. 1) Plays a Role in Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is characterized by negative symptoms such as apathy and poor social functioning, and positive symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions [ 4 ].
The dopamine hypothesis proposes that schizophrenia is caused by excessive production of dopamine in the brain [ 7 ].
Studies support the idea that an overactive dopamine system may result in schizophrenia. Medications that block dopamine receptors, specifically D2 receptors, reduce schizophrenia symptoms [ 8 ].
Additionally, some evidence suggests that the negative symptoms and some of the cognitive deficits in schizophrenia may be related to lower prefrontal cortex function. This, in turn, may be associated with decreased dopamine activity. However, there is only indirect evidence to support this [ 9 ].
Thus, some features of negative schizophrenia (social withdrawal, apathy, and the inability to feel pleasure) are thought to be related to low dopamine levels in certain areas of the brain [ 2 ].
One theory says that antipsychotic medications work by blocking dopamine and that dopamine excess may worsen or trigger schizophrenic symptoms. 2) Can Drive Drug Addiction
Drugs such as cocaine, nicotine , and amphetamines act to increase dopamine in the striatum. This can lead to drug addiction [ 10 ].
The reinforcing effects of these drugs don’t only come about because of increased dopamine, but also because of the fast rate that dopamine increases. The faster the increase, the more intense the reinforcing effects [ 11 ]. This can reduce (“down-regulate”) the dopamine receptors over a period of time, causing increased need (“cravings”) for the drugs, as well as many other chronic problems.
Long-term drug use seems to be associated with decreased dopamine function. The reductions in D2 dopamine receptors and dopamine release in the striatum in addicted subjects supports this hypothesis [ 11 ].
Some evidence suggests that too much dopamine can start off drug addiction, which later results in a blunted dopamine response. 3) Involved in Porn Addiction (and Other Behavioral Addictions)
Dopamine may contribute to compulsive sexual behaviors [ 12 ].
Both sexual experience and drugs act through dopamine D1 receptors (nucleus accumbens) [ 13 ].
Sexual novelty is compelling because it triggers bursts of dopamine in regions of the brain strongly associated with reward and goal-directed behavior. However, compulsive internet pornography users show a stronger preference for novel sexual images. Also, they get used to them more rapidly, which fuels the search for more novel sexual images [ 13 ].
In Parkinson’s disease, dopamine replacement therapies (levodopa, dopamine agonists) have been associated with compulsive sexual behavior and other impulse-control disorders [ 12 ]. Some patients reported uncharacteristic compulsive pornography use and had greater brain activity in response to sexual pictures, correlating with enhanced sexual desire [ 13 ].
Is porn addiction a problem? Some link porn to the increase in sexual performance problems and low sexual desire in men under 40. When a porn user has linked his sexual arousal to internet pornography, sex with desired real partners may register as “not meeting expectations”, resulting in a corresponding decline in dopamine, and erectile problems [ 13 ].It is important to consider this question: are we, as a society, becoming “dopamine junkies”?A lot of people today may succumb to “pleasure-maximizing choice behavior”. Some argue that we may be turning ourselves into mindless pleasure junkies, looking for the next dopamine shoot [ 14 ].Basically, our choice behavior becomes biased towards short-term pleasure-maximizing goals, just as in the addicted brain and away from long-term prosperity and general well-being maximizing objectives [ 14 ].Various types of addictive behavior–from porn addiction to other “shortcuts” to pleasure–have been associated with dopamine excess. A clear link has yet to be established. 4) Affects Weight Dopamine, along with serotonin, opioids, cannabinoids , orexin , leptin , and ghrelin , mediates the rewarding effects of food [ 15 ].It is associated with the desire to eat the food and with the conditioning of food cues. It is also involved with the motivation to perform the behaviors necessary to buy, prepare, and consume the food [ 15 ].So, dopamine will cause you to desire food when you simply smell it. It causes you to ‘want’ food as opposed to just ‘liking’ the food [ 15 ].Because […]
Is Too Much Acetylcholine Bad & What Reduces Its Levels?

The brain needs acetylcholine to form memories. The nerve bundles of our “rest-and-digest” system require it to balance “fight-or-flight” activity. But can too much acetylcholine be bad? Check out this post to learn when an excess of this neurotransmitter might be unwanted and whether lowering its levels or activity can be beneficial. Can You Have Too Much Acetylcholine ?
Due to its wide range of roles throughout the body and brain, high acetylcholine levels or activity in certain brain areas have been implicated in the development, progression, or symptoms of a some health conditions listed in this article.
However, most of the studies we bring up dealt with associations only, which means that a cause-and-effect relationship hasn’t been established.
For example, just because depression has been linked with higher acetylcholine activity in certain brain areas doesn’t mean that depression is caused by too much acetylcholine. Data are lacking to make such claims.
Also, even if a study did find that too much acetylcholine contributes to depression, acetylcholine levels are highly unlikely to be the only cause. Complex disorders like depression always involve multiple possible factors – including brain chemistry, environment, health status, and genetics – that may vary from one person to another.
Assessing acetylcholine levels in the brain is extremely difficult. This is mostly because acetylcholine levels can’t be directly measured. A direct measurement would require brain tissue, blood from the brain’s circulation, or cerebrospinal fluid.
Even with indirect measurements (using state-of-the-art brain imaging techniques), acetylcholine levels may vary across brain areas and quickly change depending on many factors.
Therefore, whether or not a person can have “too much acetylcholine” is highly uncertain. However, science has suggested a link between certain health conditions and higher acetylcholine levels or activity in specific brain areas. Is Too Much Acetylcholine Bad?
There are no symptoms associated with high acetylcholine levels per se. Instead, people may only show symptoms of mental health, neurocognitive, or immune disorders. Your doctor will discuss your symptoms with you and run tests to pinpoint the underlying cause.
Low or high acetylcholine levels don’t necessarily indicate a problem if there are no symptoms or if your doctor tells you not to worry about it. Associated Conditions:
1) Depression
Although serotonin is the neurotransmitter most commonly associated with depression and other mood disorders , other major neurotransmitters — including acetylcholine — may also play important roles in these psychiatric conditions.
Although the exact role of acetylcholine in depression is not yet fully-understood, a handful of preliminary animal studies have reported that drugs which block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) — such as mecamylamine — appear to have “antidepressant-like” effects in rodents [ 1 , 2 ].
Building on this, according to two early phase-II clinical trials in humans with treatment-resistant depression (TRD), mecamylamine was reported to alleviate some depression symptoms when used in combination with more traditional antidepressants (such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors , or SSRIs) [ 3 ].
Nonetheless, while acetylcholine may play some role in depression, it is likely to be only one piece of a much larger and more complex puzzle. In the meantime, most scientific research on the development and treatment of depression will likely continue to focus primarily on the role of other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which have relatively much more research behind their role in depression and mood disorders. Smoking And Depression
Interestingly, some of the preliminary findings described above may account for some of the widespread associations that many studies have reported between smoking and depression [ 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Specifically, some researchers have proposed that short-term ( acute ) nicotine exposure can result in a reduction (“ down-regulation ”) of acetylcholine receptors [ 7 ]. This may initially produce an “antidepressant” or “anti-anxiety” effect in relatively new smokers, which could in turn contribute to the development of an addiction to (or dependence on) nicotine.
However, chronic exposure to nicotine may eventually cause nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to actually increase in number, which would reverse these initial effects. Therefore, smoking may actually lead to increased negative moods and anxiety in the long term [ 8 , 9 ].
These adverse long-term effects, then, could potentially explain why rates of depression and other mood disorders tend to be higher in people who smoke [ 4 ]. 2) Hives
Scientists think that high acetylcholine may contribute to hives, as immune cells produce histamine in response to it [ 10 , 11 ].
According to one unverified hypothesis, people with hives seem to have higher acetylcholine in the skin, but their cells are less sensitive to it. This causes issues with sweating and histamine release. Drugs that block acetylcholine are being investigated for preventing outbreaks, but their effectiveness is still uncertain [ 10 , 11 ]. 3) Sleep Cycle Alterations
Acetylcholine increases during the dreaming, REM phase of sleep . Limited data suggest that choline supplements may even induce lucid dreaming by boosting acetylcholine in the brain. Acetylcholine levels are low during restorative, slow-wave sleep, during which memory is consolidated [ 12 , 13 ]. Factors That May Decrease Acetylcholine Levels
Because low acetylcholine is believed to be involved in the development of some diseases, there are many potential uses that have been proposed for substances that can block the acetylcholine system.
Many compounds and drugs may decrease acetylcholine levels or reduce its activity.
In general, drugs or other compounds that reduce acetylcholine levels — or otherwise inhibit its activity — are commonly known as “ anticholinergics .” ( To learn more about these substances and how they work, we recommend checking out our detailed SelfDecode posts on anticholinergics, which you can find here and here . )
Once again, these drugs may exert this effect by targeting one or more of the multiple different potential mechanisms and pathways related to the creation or release of acetylcholine.Some of the supplements, dietary compounds, and drugs that have been proposed to have some potential anticholinergic effects and mechanisms include: If you believe you have a health condition or other reason to try to influence […]
Understanding healing power of nature

MOST of us spend our days inside in environments devoid of natural influence.
Combined with the rapid rise of technology in our everyday lives, from computers and TV’s to ipads and smart phones, more and more people have limited time, access, and desire to experience the natural world.
If you’re like many people, you spend a large part of your life on your computer, watching TV, and skimming or checking your smart phone, driving in your car, and sitting at your desk looking at a screen. You rarely get out into nature.
And while you may realize that this isn’t healthy, you simply don’t have the time or energy to make a change, and besides, it’s important to be “connected.” Note that our natural surroundings are full of beauty, medicines, shelter, sustenance, resources and spiritual renewal.
Being in balance with nature inspires us to walk gently on this earth, and live in harmony with the seasons and rhythms of our planet. Our body also has the natural ability to establish, maintain, and restore health. This internal healing is supported by our connection with nature so being in nature restores us, calms us, and gives us a new perspective in life.
Science and popular culture may soon be starting to appreciate something that you have likely known for a long time, which is; being in nature benefits the human body, mind, and spirit.
It comes as no surprise to hear that being outside in the woods, surrounded by living, breathing plants, birds, and animals, can decrease your stress levels, improve your mood and fight depression, improve your memory, as well as improving your general sense of well-being.
Many of us lead a balanced and healthy lifestyle but don’t realize just how nature-deprived we really are. Studies have shown that screen time is associated with increased fatigue, depression, anxiety and Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD) in children.
People who live closer to green space have fewer health complaints and live longer since the green space itself is a stress buffer which helps people cope better with life’s adversity. Studies have found that invisible chemicals (called phytoncides) in some trees can reduce stress hormones, lower anxiety, and improve blood pressure and immunity.
As you know, being outdoors provides you with the benefits of getting natural sunlight, giving you much needed vitamin D and natural stabilization of melatonin levels, which are offset when you spend a lot of time with the screen.
Useful tips on how we can bring more nature into our lives include; Taking 20 minutes a day to spend time in nature by hiking, walking, gardening, sitting, or meditating.
Without you knowing it, you will get exposure to unseen elements that will positively affect your brain and body, like negative ions that improve your immune system and relax your body as opposed to positive ions that are emitted from electronics that can wreak havoc on your system.
Spending time in nature, by engaging all your senses, observing your surroundings without judgment, and appreciating everything around you will bring your body and mind into a state of calm. Another useful tip is putting a plant in your office or wherever you spend a lot of time.
Studies show that a plant in a room can improve cognition, energy, and can even decrease pain. If possible, try to spend the majority of your time when in your home or office in the room that provides you with views of greenery.
If this is not possible, you can hang photos of nature and add a photo of nature that you love as a screen saver on your computer or smartphone. Note that getting away, relaxing, and spending time in nature meditating, eating healthy and sleeping deeply is sure to make you feel rested, renewed, and back on track.
Meditation retreats are moderately to largely effective in reducing anxiety, depression, and stress and improving quality of life. Think about bringing nature into your body, especially if you can’t get out into nature on a regular basis.
Eat foods that are naturally available on this earth and shop in the outside perimeters of the grocery store, buying vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds, lean and hormone-free protein, and wholesome grains. Even better, plant your own vegetables if you can since you will get the combined benefits of eating healthy, spending time in nature, and getting some exercise.
Bring green to your fitness routine since when you exercise outdoors, you get the benefits of being in nature like any other time and you also get the benefits of being able to enjoy the process a little more.
For instance, jogging through the woods results in faster 1,800-meter completion times and, in the psychological realm, more satisfaction, more enjoyment, and less frustration when compared to the open laps. Jogging in the open is associated with less fatigue, diminished anxious thoughts, less hostility, more positive mental thoughts, and an overall feeling of invigoration.
Lastly, Plan your life around nature. As I mentioned earlier, the closer you live to some greenery, the better your health and the lower your stress. Green space can include neighbourhood parks, gardens, or even just grassy areas, so you don’t have to drive to a nearby forest or mountaintop.
Research your own neighbourhood and find where the parks are and spend some time there or start your own garden. Perhaps as we realize the human health benefits of nature, support for the permanent conservation of places to provide access to nature will grow as well.
Revisit your special places in nature or find new ones but whatever it may be, take a step out of your daily routine and say hello to nature again!
● The Author, Racheal Masibo, is an Assistant Lecturer at St John’s University of Tanzania (SJUT)-School of Nursing, P.O BOX 47 Dodoma Tanzania. Email: rackelmasibo@yahoo.com Mobile: 0717513598 The first decade of my engagement in the Public Service (1960–1970)
I WAS appointed, on promotion from Clerk-Assistant, to …
tags : Columnist
6 Natural Remedies for Brain Fog and Fatigue

Getty Images Women who feel worn-out are often told to prioritize “me time.” But according to David Perlmutter, M.D., and his son, Austin Perlmutter, M.D., co-authors of Brain Wash ( $16.80, Amazon ) , for millions of us, the brain is in a biochemical state that makes it impossible to feel calm and energized. To blame, they say: technology. “Smartphones and social media remodel the brain so the anxiety- producing amygdala becomes dominant, while the prefrontal cortex (PFC), the region that restores energy, becomes less active.”
Fortunately, research reveals the brain can quickly rewire itself, making your PFC more active and helping you feel better in just 10 days — without giving up your gadgets! Here’s how. Snack on pistachios.
Eating foods rich in the amino acid tryptophan will help you feel calmer and happier for four hours, report scientists at Canada’s University of Ottawa. “Tryptophan is a building block of a mood-boosting hormone that soothes the anxiety-producing amygdala, reducing stress,” says Dr. David Perlmutter, author of the bestselling book Grain Brain. The study-proven dose: 50 pistachios or 1⁄4 cup of sunflower seeds daily. Load up on ‘vitamin N.’
“Decorating with potted plants will give you a daily dose of vitamin N (nature), which is proven to sharpen problem-solving skills,” Dr. Austin Perlmutter asserts. In fact, research shows that indoor plants can increase energy by 30 percent and promote healthy activity in the PFC. Tip: Pick gardenia, begonia, or mint, which stimulate your brain with their beauty and their scent. Tune into silence.
Relaxing in silence for 15 minutes prompts the release of hormones that improve brain function for 24 hours, says Dr. David Perlmutter. In fact, more than 600 studies prove the brain-healing power of daily doses of silence, which also foster a 55 percent improvement in happiness by encouraging the growth of new brain cells in the region associated with memory and emotion. Breathe in a calming scent.
“Cedarwood essential oil calms an overactive amygdala, easing anxiety and sharpening focus within seconds,” says Dr. Austin Perlmutter, who adds that this plant extract is rich in compounds that promote healthy activity in the PFC. Indeed, a recent research review suggests that this soothing scent heightens electrical activity in the PFC by 50 percent, reducing anxiety in as little as two minutes. Use a ‘first-aid kit.’
“Moving acts as a first-aid kit for aging brain cells,” says Dr. Austin Perlmutter. That’s because using large muscle groups stimulates the growth of new connections throughout the brain. What’s more, Harvard studies show that women are 75 percent less likely to be fatigued and can focus three times better when they move regularly. Dr. Perlmutter notes: “Just getting out of your chair for two minutes each hour can help.” Take a brain booster.
DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid, makes up 97 percent of the fat in the brain, UCLA researchers say. And studies suggest keeping DHA levels high doubles your ability to think clearly. To get the benefits, Dr. David Perlmutter suggests taking 1,000 mg. daily, adding: “Supplements often contain multiple omega-3 fats. Check the label to make sure you’re getting enough DHA.” One to try: Nordic Naturals DHA ( $23.14, Amazon ).
This article originally appeared in our print magazine.
We write about products we think our readers will like. If you buy them, we get a small share of the revenue from the supplier.
Why Aging Adults Are Turning To Nootropic BPG For Memory Loss

SAN FRANCISCO, Jan. 30, 2020 /PRNewswire/ — Chris Hatton, CEO of Genesis Nutrients, created BPG (Brain Power Genesis) because he and his wife, Mary, had their own heartbreaking experience due to memory loss. Mary’s mother, Vivian, died from Alzheimer’s Disease and Chris decided to have his company’s research team develop a memory support supplement that would revolutionize the industry. After two years of testing, his company created BPG.
BPG does, in fact, differ greatly from other memory pills, in that it’s key components are highly purified while many other supplements contain a mixture of components that are under-dosed, ineffective and aren’t tested and certified for purity. BPG is different enough from other memory support formulations because it is the only trademarked multi-nootropic™ formulation in the world for memory support. (Nootropics are substances that enhance cognition and support healthy brain function). This trademarked formulation produced in an FDA approved lab protects BPG from competitors. The company is working overtime to keep up with demand by aging adults who want to think clearly and improve their memory.
What Are Nootropics?
You may have heard of them referred to as “the limitless pill” or “the smart pill”. They were originally developed for younger consumers, often ivy leaguers, who demand a mental edge. And for those in the prime of their careers, who need to stay sharp, alert and laser focused in order to advance. But now, emerging evidence suggests that they may work even better for our aging demographic due to their outstanding ability to clear away amyloid fibrils (brain plaque) ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5448442/ ). And of all the nootropics out there, one stands out among the rest… and it’s poised to change everything.
Sales are skyrocketing since the release of BPG and there are several important reasons. To start, the clinical studies have been very impressive. People taking the active ingredients in BPG saw a dramatic improvement in mental performance. Remarkably, they experienced a significantly stronger memory, better recall, mental clarity, focus and some were less depressed and anxious. Its active ingredients are made of safe, legal and natural compounds which are allergen free. There are also no known side effects and it can be taken safely with another medications. Plus, it’s made in an FDA registered facility. For these reasons, BPG is receiving rave reviews from nootropics researchers and brain health experts.
In a double-blind placebo controlled clinical study by Brain Sciences Institute, 107 people significantly improved their memory, both long and short term after using just one ingredient in BPG. ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18683852 ) In another double-blind placebo controlled major clinical study published in The Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 35 adults 55-60 years of age, several of the participants showed significant improvement within 8 – 12 weeks on mental control and logical memory while using another ingredient in BPG. ( http://www.indianjpsychiatry.org/article.asp?issn=0019-5545;year=2006;volume=48;issue=4;spage=238;epage=242;aulast=Raghav ) In laymen terms, they were sharper and were able to solve problems faster. With these results it’s easy to see why sales are booming.
World’s First And Only Multi-Nootropic™
BPG does not require a prescription. It’s a brain health pill that is taken one time daily. Scientists believe BPG works so well because the key ingredients help the hippocampus-part of the brain responsible for both short-and-long term memories. The ingredients help brain cell synapses to fire easier and faster, resulting in significantly improved memory recall, more focus and clarity. Plus, the ingredients promote acetylcholine, GABA and serotonin which are brain chemicals that are tied to better moods, motivation, self-confidence and empower clarity of thought. This means that for the first time there is a Multi-Nootropic™ brain health formula that unlocks all of your brainpower, removing all limitations, optimizing as many brain functions as possible while improving memory, mood, attention, mental energy, creativity, motivation, clarity and focus. The nutrients also breaks up brain fog and fatigue and promotes quick thinking while regenerating brain neurons and oxygenizing the brain ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19726646 / https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12675022 ).
To order BPG call 800-661-1027 or go to www.brainpowergenesis.com
View original content to download multimedia: http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/why-aging-adults-are-turning-to-nootropic-bpg-for-memory-loss-300996395.html
SOURCE Brain Power Genesis
