Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
All About Galantamine: Uses, Mechanisms, Side-Effects and More

Galantamine is a medication that is FDA-approved for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. It has also been studied for its potential effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and other specific medical conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and autism – although the evidence for these uses is still only preliminary. Read on to learn more about this drug, how it works, and what the current science says about some of its other potential uses!
Disclaimer: This post is not a recommendation or endorsement for galantamine. This medication is only FDA-approved for the treatment of certain specific medical disorders, and can only be taken by prescription and with oversight from a licensed medical professional. We have written this post for informational purposes only, and our goal is solely to inform people about the science behind galantamine’s potential effects, mechanisms, and uses. What is Galantamine?
Galantamine is a nitrogen-containing compound that can be obtained synthetically, or from the bulbs and flowers of the Caucasian snowdrop ( Galanthus caucasicus ), Voronov’s snowdrop ( Galanthus caucasicus) , Galanthus woronowii , Daffodil ( Narcissus ) and red spider lily ( Lycoris radiata ) [ 1 , 2 , 3 ].
Galantamine has been used for decades in Eastern Europe and Russia as a folk remedy for muscular weakness ( myopathy ), as well as for sensory and motor dysfunction associated with disorders of the central nervous system [ 4 ].
Galantamine is commercially available as Nivalin , Razadyne / Razadyne ER , Reminyl , and Lycoremine , and has sometimes been used in the treatment of mild cognitive impairment alone or in association with Alzheimer’s disease [ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ].
Galantamine is an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease , and has been officially approved by the FDA for this medical use.
Many Alzheimer’s patients report benefitting from galantamine therapy that is initiated early, soon after diagnosis, and continued for at least 1 year [ 8 ].
Galantamine is believed to act by increasing the concentration and overall activity of acetylcholine in the brain, which has been preposed to account for its effects on the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease [ 9 , 10 ].
A key sign of Alzheimer’s disease is a decrease in hippocampal episodic memory function due to the build-up of β-amyloid plaques which cause a breakdown of cholinergic signaling. Galantamine is believed to be a useful treatment for Alzheimer’s due to its ability to increase hippocampal function via improving cholinergic neurotransmitter function [ 11 , 12 ].
Some evidence suggests that galantamine may help limit the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease. For example, one study reported that this effect may persist for up to 36 months after beginning galantamine treatment, suggesting that there may be some significant long-term potential for galantamine use in this medical condition [ 13 ].
In fact, long-term galantamine treatment has been reported to delay an individual’s placement in a nursing home, suggesting improved overall functioning and quality-of-life [ 13 ].
Although the precise mechanisms behind it aren’t fully known yet, some studies have concluded that long-term treatment with galantamine may effectively increase the connections between neurons in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. By extension, it has been proposed that these neuronal connections may help stabilize cognitive performance in these patients [ 14 ].
Galantamine may also have some effects on build-up of beta-amyloid plaques in brain cells, which is believed to be the main factor responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease. For example, one animal study reported that galantamine reduced the amount of beta-amyloid plaques in the brains of mice with Alzheimer’s disease, as well as decreased the activity of astrocytes (a type of cell in the nervous system that forms “scars” in areas where neurons have been damaged) [ 15 ].
According to some preliminary studies, galantamine has also been reported to have some “antidepressant”-like effects, and may have even improved sleep quality in dementia patients [ 16 , 17 ]. This may suggest some mood- and sleep-related effects, although more research will be needed to know for sure.
Galantamine has been reported to be just as effective as donepezil , a cognition-enhancing medication commonly used to treat Alzheimer’s disease [ 18 ].
However, galantamine has been proposed to be far more cost-effective than conventional Alzheimer’s treatment with typical cholinesterase inhibitors, which may give it a slight advantage when it comes to medical use [ 19 ]. Other Potential Effects & Uses of Galantamine
In addition to its FDA-approved medical use in Alzheimer’s disease, galantamine has also been studied for its potential effects on a number of other health-related functions and conditions.
However, much of this research is still in a relatively early stage, and in most cases it is difficult to come to any firm conclusions about its relative efficacy and safety in healthy human users.
Therefore, the potential effects listed below are still considered to have “insufficient evidence”, and should be taken with a grain of salt until further research work – including large-scale clinical trials in healthy human users – is performed.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a condition that involves a gradual loss of cognitive function over time. MCI sufferers often complain of memory failure. One study administered galantamine (4 mg twice per day) to sufferers of MCI for 7 days. These patients were reported to show a subsequent improvement in performance on memory tasks (episodic face-encoding and working memory tasks) [ 11 ].
Another similar study reported that patients with MCI showed evidence of improved episodic memory and reduced reaction times when treated with galantamine [ 20 ].
Cholinergic malfunction is believed to be responsible for some of the memory impairments commonly seen in MCI subjects. This shared mechanism may be why galantamine (an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor and modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors ) has been reported to be effective at improving brain function [ 11 ].
Some early evidence also suggests that galantamine may help promote brain growth – possibly via activation of the M1 muscarinic and α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors [ 21 ].
Additionally, according to one animal study In mice, galantamine (at 0.3-3mg/kg) was […]
Centrophenoxine: What We Know So Far (Potential Uses, Mechanisms, and Side-Effects)

Centrophenoxine is sometimes touted as a “ nootropic ”, or “cognitive-enhancing” compound. Some people claim that it can protect the brain, enhance cognitive function, and even extend lifespan. But what does the science say about its effects, and how much do we actually know about its safety in human users? Read on to learn more about what the current research says about this drug’s potential effects, mechanisms, possible side-effects, and more!
Centrophenoxine , also known as Lucidril and Meclofenoxate , is one of the earliest and most studied nootropics , or so-called “smart” drugs.
Originally developed in 1959, this drug has been studied for its potential to help age-related brain disorders, such as Alzheimer ’s and dementia. It is also used by healthy people to enhance memory and cognitive function and improve overall brain health [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Centrophenoxine is a combination of two chemicals: Dimethyl-aminoethanol (DMAE) , which is a natural substance found in some foods (fish, seafood) and in small amounts in the brain. It is a source of choline , and is believed to have stimulating effects on the brain [ 7 ].
Parachlorphenoxyacetic acid (pCPA) , a synthetic version of plant growth hormones called “ auxins ” [ 4 ].
DMAE is the main active component in this drug. Normally, DMAE doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier very well – however, in the form of centrophenoxine, some studies suggest that it can cross the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain effectively [ 8 , 4 , 9 ].
Once it is absorbed in the body, a portion of centrophenoxine breaks down into DMAE and pCPA in the liver. DMAE is then converted to choline, while the remaining centrophenoxine circulates throughout the body [ 2 , 9 ].
Although its precise mechanisms are still being actively studied, some early research has suggested a variety of potential mechanisms that may be responsible for some of centrophenoxine’s effects.
Some of these proposed mechanisms include: Increasing acetylcholine in the brain. This is a major neurotransmitter that is believed to be essential for cognitive functions such as memory and learning [ 8 , 10 ].
Reducing lipofuscin . Lipofuscin is a waste product that builds up in cells (including brain cells) as we age. This is the same waste product that causes brown liver spots on the skin [ 11 , 12 ].
Increasing glucose uptake (more energy) and promoting blood flow (more oxygen) throughout the brain and its cells [ 13 , 14 ].
Increasing RNA production . This may increase protein turnover in neurons where worn-out or free radical-damaged proteins can be more effectively replaced [ 13 , 15 ].
While a number of centrophenoxine’s potential effects have been studied, much of this research is still in a relatively early stage, and in most cases it is difficult to come to any firm conclusions about its relative efficacy and safety in healthy human users.
This is a common situation for many so-called “nootropic” supplements and compounds, as these tend not to receive as much scientific attention as other drugs, such as pharmaceutical medications that are used by doctors to treat specific medical conditions. As a result, even supplements and compounds that are relatively “well-studied” often still don’t have the amount of research needed to officially classify them as effective, or get FDA approval for specific uses.
Therefore, the potential effects listed below are still considered to have “insufficient evidence” , and should be taken with a grain of salt until further research work – including large-scale clinical trials in healthy human users – is performed.
As a so-called “nootropic”, or “cognitive-enhancing” compound, centrophenoxine has been claimed to be able to boost certain cognitive functions – such as learning and memory – in its users. But what does the actual science have to say about this?
Although some studies have reported centrophenoxine to be beneficial in certain populations of older individuals, there are no solid scientific studies to back up its use as a nootropic in young adults.
For example, centrophenoxine was reported to help promote the formation of long-term memories and increased alertness, according to one study in 60 healthy – but elderly – human subjects [ 17 ].
Similarly, centrophenoxine was also reported to improve memory in 50 elderly patients with dementia [ 1 ].
On the animal research side, one study mice reported that centrophenoxine improved learning and memory in aged mice [ 4 ].
However, both of the early human studies described above – while promising – were limited to older users, or those with specific age-related medical conditions. Therefore, these preliminary results can’t yet be taken as solid proof of nootropic effects in younger, healthy human users without much more additional research in appropriately representative human populations.
The following potential uses of centrophenoxine are based solely on animal- and cell-based studies, and lack any appropriate human trials so far. Therefore, these are only potential “launching-points” for future clinical studies in humans, and no solid conclusions can be made about these effects in human users until additional research is done.
One of the more widespread claims about centrophenoxine is that it may potentially help protect the brain and its cells from stress and damage – in other words, that it may be “neuro-protective.”
A few lines of research in animals have reported early findings that offer some preliminary support for this effect, although appropriate human trials are so far lacking.
For example, several animal studies have reported that centrophenoxine may protect nerve cells from oxidative damage due to toxin exposure or stroke. In rats with various types of brain injury, centrophenoxine was reported to reduce the damage caused by free-radicals, and may have prevented some cognitive deficits that sometimes result from elevated oxidative stress, such as impairments to memory, overall cognitive function, and movement/motor control [ 8 , 18 , 19 , 14 ].
Similarly, according to some other animal studies (in rats), centrophenoxine reportedly increases the activity of major antioxidant enzymes like glutathione and superoxide dismutase ( SOD ) in the brain, which […]
8 Tryptophan Benefits + Foods, Dosage & Side Effects

Tryptophan is an amino acid that produces serotonin, melatonin, and kynurenine. Supplementation may help with sleep quality, mental health, and PMS. However, there are important safety concerns and limitations. Read on to learn the benefits, food sources, and side effects of tryptophan. What is Tryptophan?
Tryptophan is one of the 8 essential amino acids, meaning it is vital but cannot be produced by the body. Hence, tryptophan must be supplied from dietary sources [ 1 ].
L-tryptophan is the natural version of the amino acid and a building block of protein in the body.
In humans, tryptophan is not stored for long periods and therefore has the lowest concentration in the body among all the amino acids. However, only small amounts of tryptophan are required [ 1 ]. Foods
Common foods that contain tryptophan include oats, bananas, dried prunes, milk, tuna fish, cheese, bread, chicken, turkey, peanuts, and chocolate [ 1 ]. Why Is It Important?
Tryptophan is converted to 5-hydroxytryptophan ( 5-HTP ) in the brain, which produces serotonin [ 2 , 3 ].
Tryptophan absorption into the brain is influenced by diet.
A high carbohydrate, low protein diet will release insulin , which ultimately increases the absorption of tryptophan into the brain and can, therefore, increase serotonin. This is the mechanism by which eating carbs may increase serotonin [ 4 ].
BCAAs compete with tryptophan absorption into the brain. Eating a high protein diet (high BCAAs) will cause less tryptophan to enter the brain, thus reducing serotonin levels [ 4 ].
However, higher protein diets usually have higher tryptophan, which can cancel out the effect from the BCAAs. Health Benefits
1) Sleep Quality and Insomnia
Tryptophan produces melatonin in the brain (pineal gland), the gut, the retina, and immune cells. Melatonin regulates the circadian rhythm and sleep patterns and is used as a supplement itself to help people sleep [ 5 , 6 ].
A study of 5 healthy volunteers showed that L-tryptophan supplementation increased average total sleep. All of them noticed some form of drowsiness a half hour before sleep [ 7 ].
In a study on 7 insomniac patients, L-tryptophan supplementation increased total sleep (by 28%). The supplementation also decreased early-morning wakefulness by an average of 37 minutes [ 7 ].
Tryptophan supplementation even helped induce sleep in manic patients. A study of 10 patients with mania showed improvements in total sleep after L-tryptophan supplementation [ 8 ].
In a dose-response study of 15 insomniac patients, L-tryptophan (250 mg) increased stage 4 sleep (deep sleep). Normal dietary intake is usually around ½-1 gram of L-tryptophan, so even minimal amounts may increase deep sleep [ 9 ].
Tryptophan supplementation may also improve obstructive sleep apnea (airflow blockage during sleep). A study of 12 patients showed that L-tryptophan supplementation increased sleep in those with obstructive sleep apnea during non-REM sleep. However, patients with central sleep apnea showed no improvements [ 10 ].
The above findings stem from small clinical trials and thus require further investigation. 2) PMS
The breakdown of tryptophan via the kynurenine pathway is affected by the phase of the menstrual cycle, which can also indirectly affect serotonin production. After ingesting tryptophan, kynurenine was 40% higher during the luteal phase than in the follicular phase [ 11 ].
In a study of 37 patients, L-tryptophan supplementation (6 g daily) improved the following symptoms in women suffering from premenstrual dysphoria (a severe type of PMS ) [ 12 ] :
Mood improved by 34.5% in those given L-tryptophan supplements. 3) Smoking Cessation
A study of 16 people trying to quit smoking showed that L-tryptophan and a high-carbohydrate diet along with regular smoke-ceasing therapies decreased anxiety and withdrawal symptoms. People given tryptophan supplements smoked fewer cigarettes compared to placebo. Further research is warranted [ 13 ].
No valid clinical evidence supports the use of grape seed extract for any of the conditions in this section. Below is a summary of up-to-date animal studies, cell-based research, or low-quality clinical trials which should spark further investigation. However, you shouldn’t interpret them as supportive of any health benefit. 4) Depression
Many depressed patients also suffer from insomnia and other sleep-depriving conditions. Therefore, tryptophan’s ability to help with insomnia could aid these depressed patients [ 14 , 9 ].
A randomized study of 25 young adults showed that high tryptophan diets increased mood and decreased depressive symptoms and anxiety [ 15 ].
In a study of 24 patients, clomipramine (a drug for depression) and L-tryptophan were more effective in improving depressed mood, suicidal intent, and anxiety compared to clomipramine alone [ 16 ].A meta-analysis of tryptophan’s effects on depression confirmed some positive effects, but the authors underlined the low evidence quality (only two trials included) and avoided making conclusions [ 17 ].A study of 6 depressed patients showed that L-tryptophan supplementation did not help and the patients needed further treatment before release [ 18 ].Depressed patients often have problems creating serotonin from tryptophan. Instead, they create other metabolites such as quinolinic acid, which can be toxic. For these patients, tryptophan supplementation may not help [ 19 ].When tryptophan is converted to kynurenine and not serotonin, depression may worsen. Some kynurenine metabolites are toxic and animal models have shown increased depressive symptoms with increased kynurenine [ 20 ]. Due to low-quality evidence and some conflicting results, further trials should clear up the potential benefits of tryptophan for depressive disorders. 5) Mania In a small study of five patients with mania, L-tryptophan supplementation improved the treatment with chlorpromazine hydrochloride (CPZ) and reduced side effects [ 21 ].In 24 patients with acute mania, L-tryptophan supplementation decreased manic symptoms by 43% outperforming a previous treatment with lithium (41%). Those who stopped receiving tryptophan showed worsening of the symptoms [ 22 ].However, in a clinical trial done on 10 female mania patients, the L-tryptophan supplementation did not perform better than placebo [ 23 ]. More studies are needed to clear out these conflicting results. 6) Appetite Reduction In a study of 15 healthy volunteers, those receiving L-tryptophan supplementation ate […]
9 Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Effects + What May Increase It

Scientists think that Nerve Growth Factor plays an important role in cognitive function, mood, inflammation & more. Learn about the proposed effects of NGF & factors that may increase it. What is Nerve Growth Factor?
Science now accepts that the brain continues to reorganize itself and create new brain cells throughout life. The birth of new neurons in the brain is referred to as neurogenesis .
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is one of a group of small protein-like molecules called neurotrophins ( BDNF is another) that are responsible for neurogenesis or the development of new neurons and for the health and maintenance of mature ones.
Based on animal findings, researchers consider that NGF may promote the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons and axons. It’s also thought to help repair the myelin sheath, which is the insulating coating around the axons [ 1 ].
Animal experiments found that as the production of NGF decreases in the brain, the animals’ ability to form new connections and to retain and access memories becomes impaired. They believe NGF might save degenerating nerves and help restore their function, but human data are lacking [ 2 ].
Dr. Rita Levi-Montalcini, an Italian American neurologist, won a Nobel Prize for discovering nerve growth factor in 1996. She shared the prize with biochemist Stanley Cohen.
Some of her later claims surrounded her personality with controversy. For example, she said that she used NGF eye drops to increase her life- and health-span.
Rita did live to be a centenarian. She died in 2012, aged 103 years old. Of course, the true secret to her longevity remains unknown. As far as science is concerned, evidence is lacking to claim that NGF has lifespan-increasing properties. Plus, the safety of NGF use in humans hasn’t been established.
Studies investigating NGF levels in people are in the early stages. Findings so far have been inconclusive. We simply don’t yet know how NGF levels relate to health and disease.
In a study of 157 normal people, NGF levels were on average 194 pg/ml. Age didn’t make a significant difference amongst the participants, but NGF was significantly lower in women (112 pg/ml) than in men (243 pg/ml) [ 3 ].
Another study found lower NGF levels in people with common, so-called Western diseases , including atherosclerosis, obesity, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome [ 4 ].
On the other hand, high NGF levels are found in a number of autoimmune diseases, accompanied by increased numbers of mast cells, which produce histamine and which are also able to produce NGF [ 5 ].
Some researchers have also suggested a link between higher NGF and BDNF levels in schizophrenia. They hypothesize that neurotrophins do not always support health – as is often popularly thought [ 6 ].
It’s important to realize that NGF levels can be different in different places. For example, NGF can be measured in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CDF), and in specific brain regions. No correlations between these measures have yet been established, as is the case with BDNF. We also don’t know if NGF from the blood can enter the brain [ 7 , 8 ].
Far more NGF human research is needed to understand this little brain-active protein and its roles. Proposed Health Effects of NGF
This section explores associations between NGF and aspects of health.
The majority of studies covered in this article deal with associations only, which means that a cause-and-effect relationship hasn’t been established.
For example, just because mood problems have been linked with low NGF in certain brain areas doesn’t mean that mood disorders are caused by low NGF. Nor does it mean that increasing NGF will improve mood, unless clinical data about a direct link are available. However, data are lacking to make such claims.
Additionally, even if a study did find that low brain NGF contributes to depression, NGF levels are highly unlikely to be the only causative factor. Complex mood disorders like depression always involve multiple possible factors – including brain chemistry, environment, health status, and genetics – that may vary from one person to another. 1) Mood
The link between NGF and mood disorders is still unclear.
In one small study, Blood levels of NGF were lower in those with Major Depressive Disorder compared to controls. Larger human studies are needed [ 9 ].
In rats, Exercise increased NGF (and BDNF & synapsin I), which was suggested to have improved the survival of neurons in the hippocampus and mood by increasing the serotonin -producing cells in the brain stem. This hasn’t been confirmed in humans [ 10 ].
Chrysin is a flavonoid found in honey and some plants. Some scientists think that the chrysin may improve mood in lab animals by raising NGF, but this hasn’t been proven [ 11 ]. 2) Myelin & Multiple Sclerosis
There’s no evidence about the effects of NGF on myelin and multiple sclerosis in humans.
In an animal model of human brain demyelinating diseases (e.g. Multiple Sclerosis), NGF delayed onset, lowered inflammation, and lessened tissue injury [ 12 ]. Scientists are investigating whether NGF can:
Promote the growth and repair of myelin damage [ 13 ].
Induce the production of BDNF , which is also thought to be important for the myelination of nerves [ 13 ]. Play a role in brain disorders, including Multiple Sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease [ 14 ]. None of these effects have been proven. We can’t apply the existing animal data to humans. 3) Alzheimer’s Disease According to one theory, substances that raise acetylcholine may be beneficial in Alzheimer‘s disease . Recent animal studies proposed that NGF might protect acetylcholine activated neurons, but its effectiveness and safety in Alzheimer’s patients has never been properly investigated [ 15 ].In a study of 10 Alzheimer’s patients receiving NGF gene transfer therapy, the authors observed degenerating neurons sprouting from their axons, tissue growth, and improvement of function. Larger clinical trials are needed [ 16 ].Some researchers hold that the ability of the brain to convert proNGF to mature NGF is faulty […]
15 Ginkgo Biloba Benefits and Side Effects

Ginkgo biloba is one of the oldest living tree species. Extracts of this plant can have positive effects on cognition, memory, blood flow, mood, and oxidative stress . Continue to read to know more about the other potential health benefits of ginkgo. What Is Ginkgo Biloba ?
Ginkgo biloba , known as gingko or maidenhair tree, is the only living species of the division Ginkgophyta , all the other members of which have gone extinct. For this reason, it has been referred to as a “living fossil”. Native to China, its seeds have been used in traditional medicine for thousands of years and occasionally eaten when cooked [ 1 ].
Ginkgo leaf extract has historically been used to treat a variety of ailments and conditions including asthma, bronchitis, and fatigue. Ginkgo extracts are also used in skin products [ 1 ].
EGb 761 is a standardized extract of Ginkgo biloba leaves with antioxidant properties as a free radical scavenger. It was developed by Dr. Willmar Schwabe Pharmaceuticals and has been available in Europe as a herbal extract since the early 1990s [ 2 ].
In Norway, ginkgo leaf extract products are approved by the Norwegian Medicines Agency to improve blood circulation [ 3 ]. Snapshot
Proponents
Antioxidant
May improve cognitive function and reduce cognitive decline
May improve blood flow and prevent blood clots
May help with anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia
May help with eye and hearing problems
May improve skin appearance
May help with diabetes and its complications
Skeptics
Insufficient evidence for several benefits
May cause bleeding and interact with anticoagulant and anti-platelet medication
Not safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women
Nuts and seeds are toxic
Health Benefits
Possibly Effective for:
1) Brain Function
Healthy People
In 4 trials on over 200 healthy young volunteers, ginkgo extract improved sustained attention (but not speed of attention), pattern recognition, and performance in subtraction tasks . However, only its acute administration was effective , suggesting that the participants developed tolerance [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ].
Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) improved memory and executive function in 5 clinical trials on over 500 healthy, middle-aged volunteers [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ].
In 3 trials on over 300 cognitively intact elderly people , ginkgo extract improved delayed free recall, recognition memory, speed of information processing, and overall cognitive functioning [ 13 , 14 , 15 ].
However, ginkgo extract had no effect on learning, memory, attention, concentration, and verbal fluency in 2 other trials on over 200 elderly people without cognitive impairment [ 16 , 17 ]. People with Cognitive Impairment In 3 clinical trials on over 100 people with mild cognitive impairment , ginkgo extract improved cognitive flexibility, response inhibition, dual-task gait performance, and general cognitive performance [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].In clinical trials on 820 people with Alzheimer’s or other types of dementia (e.g., vascular), Ginkgo biloba extract improved cognitive function, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and functional abilities [ 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ]However, it was ineffective in 2 trials on over 400 elderly people with dementia and age-associated memory impairment [ 25 , 26 ].A meta-analysis of 13 studies and over 2,300 people concluded that a 240-mg daily dose of ginkgo extract was safe and effective in the treatment of dementia [ 27 ].In any case, ginkgo extract seems ineffective at preventing Alzheimer’s or dementia based on the results of 3 studies on over 6,000 people [ 28 , 29 , 30 ].In rats and mice, Ginkgo biloba extract improved cognitive impairment due to aging, reduced oxygen supply to the brain, repeated stimulation of glutamate receptors, and fluoride and aluminum poisoning [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ].Additionally, EGb 761 extract reduced the damage to midbrain dopamine brain cells in animal models of Parkinson’s disease [ 35 ].Taken together, the evidence suggests that ginkgo extract may help enhance cognitive function in healthy people and reduce cognitive impairment symptoms in people with conditions such as Alzheimer’s or other types of dementia. You may discuss with your doctor if you may use this supplement as a cognitive enhancer or give it to your loved ones with cognitive impairment. 2) Blood Flow In a small trial on 16 healthy volunteers, Gingko biloba extract increased circulation in the forearm without changing overall blood pressure levels. In another trial on 70 healthy volunteers, EGb 761 extract prevented the rise of blood pressure caused by stress [ 36 , 37 ].Ginkgo extract also increased microcirculation in the skin and liver in a clinical trial on 32 elderly people [ 38 ].In a clinical trial on 80 people with coronary artery disease, ginkgo extract improved coronary blood flow . The extract was similarly effective in another trial on 60 healthy elderly people [ 39 , 40 ].Similarly, ginkgo extract improved blood flow to the brain, thus reducing the risk of stroke , in a clinical trial on 60 people with poor blood flow due to surgery [ 41 ].It also increased blood flow in the eyes in 3 clinical trials on 86 people, suggesting its potential to help with conditions such as glaucoma [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]. Ginkgo biloba improved blood flow and walking distance in 2 clinical trials on over 100 people with peripheral arterial insufficiency . However, ginkgo extract was i neffective in another trial on 22 people with this condition [ 45 , 46 , 47 ].In a clinical trial on 24 people with clogged arteries, Ginkgo biloba along with parenteral therapy decreased collagen -induced blood clotting [ 48 ].In another trial on 66 chronic peritoneal dialysis patients, Ginkgo biloba r eversed the blood clotting profile without increasing the risk of bleeding [ 49 ]. Ginkgo biloba extract prevented platelets from clumping together in both platelet-rich and whole blood [ 50 ].However, EGb 761 extract had no effect on blood clotting in 2 clinical trials on 82 healthy people [ 51 , 52 ].All […]
10 Negative Effects of Tryptophan Deficiency

Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that controls mental health, sleep, cognition, appetite, and more. The body can’t produce it, so the lack of dietary sources may result in a range of unpleasant health effects and associated conditions. Read on to learn the potential dangers of tryptophan deficiency and how to prevent it. Tryptophan Deficiency Symptoms & Associated Conditions
Tryptophan levels are a marker of nutritional status. Low or high levels don’t necessarily indicate a problem if there are no symptoms or if your doctor tells you not to worry about it.
Studies on the effects of tryptophan deficiency deplete this amino acid through a process called acute tryptophan depletion , where a patient is given a beverage of 15 different amino acids excluding tryptophan [ 1 ].
Drinking the beverage produces two effects:
> Other amino acids compete with tryptophan in crossing the blood-brain barrier thereby reducing the levels of tryptophan in the brain [ 1 ].
In a real-world setting, tryptophan deficiency is rare in developed countries and usually not severe enough to produce the effects described below [ 2 ].
A study of 76 people showed that tryptophan depletion intensifies dizziness, nausea, and the illusion of movement after induced motion sickness [ 3 ].
Depression worsened in healthy males after tryptophan depletion [ 4 ].
A study showed that patients with a family history of mental disorders were more likely to worsen their mood after tryptophan depletion [ 5 ].
Another study was able to show that women were more likely to feel the mood-worsening effect since gender affects serotonin production (males produce serotonin 52% faster than females) [ 6 , 7 ].
In a study of 30 patients, those with lowered tryptophan levels did worse in pattern recognition tests [ 8 ].
Another double-blind trial of 27 volunteers showed that tryptophan depletion impaired long-term memory in word recall and recognition tests [ 9 ].
Another study showed that women were more prone to these memory-damaging effects than men [ 10 ].
A study of 21 patients on antidepressants showed that lowering tryptophan levels caused the patients to return to their depressed states more often [ 11 ]. 5) Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
SAD is a disorder where the patient experiences depression based on seasons, mainly during the winter.
Two small studies found that tryptophan depletion contributes to SAD symptoms while supplementation may be beneficial [ 12 , 13 ].
A double-blind study of 7 bipolar patients on lithium treatment showed that after tryptophan depletion, manic symptoms reappeared [ 14 ].
Bulimia nervosa is a disorder of distorted body image with periods of excessive food intake followed by periods of self-induced vomiting, which is linked to changes in serotonin [ 15 ].
A study of 20 women showed that those with bulimia nervosa took in more calories (39% more) and showed increased agitation and mood irritability due to tryptophan depletion [ 15 ].
In a study done on 16 women with PMS, a depletion of tryptophan led to severe premenstrual symptoms, especially irritability [ 16 ].
A double-blind study on 22 patients with panic disorder showed that after tryptophan depletion, the patients had more anxiety and panic attacks. The controls, however, did not panic after tryptophan depletion [ 17 ].
A study of 12 patients with previous aggressive behavior and 12 without showed that after tryptophan depletion, those with aggressive tendencies became agitated and exhibited hostile behavior. Non-aggressive patients, however, decreased their aggression [ 18 ].
Tryptophan depletion increases impulsivity leading to aggression [ 19 ].
In a study of 22 highly and low impulsive patients with ADHD, the low impulsive patients became highly impulsive after tryptophan depletion [ 20 ]. Violent Behavior in Alcoholics
A study of 9 alcoholics with or without a history of violent impulsive behavior found that violent patients had lower tryptophan levels than the non-violent [ 21 ].
Another study showed that tryptophan levels decreased by 10% 30 minutes after alcohol consumption and up to 20 – 25% 1.5 to 2 hours after alcohol consumption [ 22 ].Decreased serotonin due to tryptophan depletion triggered violent behaviors in alcoholic people [ 23 ].Great food sources of tryptophan include [ 1 ]: Oats Bananas Dried prunes Milk and cheese Tuna fish Chicken and turkey Peanuts Chocolate L-tryptophan is available in different oral supplement forms, alone or in combination with other ingredients. While the usual dosage of L-tryptophan is 500 mg , many people take more and the supplement’s instructions often recommend 3 pills before bedtime.Due to potential drug interactions and other safety concerns, make sure to consult with your doctor before taking tryptophan supplements.Read more about tryptophan supplementation benefits and side effects .This section contains sponsored links, which means that we may receive a small percentage of profit from your purchase, while the price remains the same to you. The proceeds from your purchase support our research and work. Thank you for your support. RATE THIS ARTICLE
What Do We Know About Huperzine A? Potential Uses, Side-Effects, and More
Huperzine A is an alkaloid compound extracted from a club moss called Huperzia serrata . It has been touted to have a number of neuroprotective and “ nootropic ” (cognitive-enhancing) properties, and has even suggested as a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. But what does the science actually say about this plant-based supplement? Read on to learn more about Huperzine A, its potential effects, and how it might work!
Huperzine A (HupA) is an alkaloid compound extracted from club moss ( Huperzia serrata ).
Club moss (“ Qian Ceng Ta ”) has traditionally been used in Chinese medicine for fever, inflammation, and even schizophrenia [ 1 , 2 ].
Because of its long history of use in traditional medicine, huperzine A has been studied as a compound of interest for its potential effects on a number of important systems in the body and brain. While not all of its touted effects have been validated by science, there are a number of promising early findings that may suggest some potential applications of this supplement, which we’ll review in this post.
There are two forms of huperzine A: ‘(+)’ and ‘(-)’. The ‘(-)’ form is found naturally in the huperzia moss, and is believed to be more potent than the ‘(+)’ form.
Although the effects of huperzine A are still being actively studied by scientists, there are a few mechanisms that have been identified so far which may be responsible for some of its reported effects. Increases Acetylcholine
Huperzine A has been reported to be a potent, reversible, and specific inhibitor of the enzyme acetylcholine esterase (ACHE). This enzyme breaks down the major neurotransmitter acetylcholine , suggesting that some of huperzine A’s effects may come from generally increased levels of acetylcholine throughout the brain [ 3 ].
For example, according to one animal study, huperzine A was reported to increase acetylcholine levels in rat brains for up to 6 hours after administration [ 4 ].
Several animal studies have reported that huperzine A may result in a more prolonged increase in acetylcholine in the whole brain when compared to other compounds that raise acetylcholine levels, such as tacrine , physostigmine , and metrifonate [ 5 , 6 , 7 ].
According to one study, Huperzine A may work in similar ways to some Alzheimer’s disease medications which are also believed to affect the acetylcholine system of the brain, such as donepezil , rivastigmine , tacrine , and galantamine – although with fewer side effects and somewhat more favorable pharmacokinetics [ 8 ].
This potential increase in acetylcholine levels seems to differ between different parts of the rat brain. According to a few animal studies, following administration, maximum acetylcholine levels were observed in the hippocampus after 30 min, and in the frontal and prefrontal cortex after 60 min. These observations suggest that huperzine A may influence the function of different parts of the brain at different times [ 6 , 7 ].
However, some researchers have also stressed that huperzine A likely also has effects on other brain mechanisms that do not involve ACHE – so this effect alone is probably not the whole story [ 3 ]. Increases Norepinephrine and Dopamine – but not Serotonin
According to one animal study, huperzine A was reported to increase the levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the brains of rats, while not affecting the levels of serotonin [ 9 ].
However, a lot more studies will be needed to know if these effects apply to the human brain as well. Neuroprotective Mechanisms
Early evidence from a few studies suggests that huperzine A may have a few mechanisms that could help protect the brain from stress and harm. Some of these suggestive findings include: Muscarinic and GABA receptors may play a role in some of the reports that huperzine A protects against seizures (mouse study) [ 10 ].
One literature review on huperzine A hypothesizes that it may help promote neuronal growth by stimulating the production and secretion of nerve growth factor (NGF) [ 3 ].
One in vitro cell study proposed that huperzine A may help prevent or reduce cell damage from lack of oxygen ( hypoxia ). This protective effect may be partly mediated by the “cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway” through alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors [ 11 ].
However, all of these findings come primarily from animal and cell studies, which means that they are still quite far from having been proven. A lot more research will be needed to see what role, if any, huperzine A may have in protecting brain health in normal human users. Other Mechanisms
One animal study has reported that Huperzine A may help with inflammation in rats – in particular by reducing activities of NF-kB signaling, which may happen both through inhibition of acetylcholine esterase or in other ways [ 12 ].
Once again, though, a lot more follow-up studies will be needed to find out for sure how strong the effect is, as well as if it would apply to human users in any significant way.
In a systematic review of different interventions for Alzheimer’s, combined data from multiple studies was used to suggest that huperzine A may have a statistically significant effect in reducing cognitive decline during Alzheimer‘s disease [ 13 ].
However, while the early results are promising, there are some important limitations to note. For example, the quality of these studies is somewhat lower than the quality of studies of other medical interventions in Alzheimer’s disease and other dementia-related conditions. Many such studies are poorly-controlled or were not designed to rule out biases from the authors. In addition, most of the studies and clinical trials were from China, which raises some questions about their overall validity.
Nonetheless, according to some other researchers, huperzine A has been reported to prevent neuron loss during Alzheimer’s – specifically, by inhibiting the inflammatory responses caused by the build-up of amyloid beta , the main factor believed to be responsible for Alzheimer’s disease) [ 14 ].
In a related study, huperzine A was reported to inhibit the NF-kB pathway in immune cells in the brain. […]
Vegan/Vegetarian Possible Deficiencies & Ways To Prevent Them
A healthy diet is balanced and provides you with adequate amounts of all the essential nutrients. As a vegan or vegetarian, you may be at a higher risk of certain nutritional deficiencies, while having a lower risk of others. In this post, we summarize the most important risks together with lab tests you can take to make sure your diet is well balanced and your health is optimal. What to Monitor on a Vegetarian/Vegan Diet
We know your diet is often more than just what you eat – it’s a deliberate choice, a lifestyle, and a part of who you are. Food can be the key to achieving your health goals, improving your wellbeing, and making you feel like a part of a movement or community. Some people do better on animal-based diets, whereas others feel better on plant-based diets. This article will not debate the benefits of one vs. the other. Instead, it will focus on how to maximize your health on vegetarian and vegan diets.
Vegans and vegetarians are more at risk of certain nutritional deficiencies while being less at risk from others. In this post, we summarize the most important risks, and the tests you can take to make sure your diet is well balanced. Important Nutrients
1) Iron
Iron deficiency is the most prevalent nutritional deficiency worldwide, caused mainly by insufficient dietary intake. Vegetarians and vegans are especially prone to iron deficiency because their diets lack heme iron [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Heme iron is only found in animal foods (meat, seafood, and poultry) and is easily absorbed. Non-heme iron, on the other hand, is found in plants and is less-well absorbed in our gut [ 4 ].
In addition, plants are often rich in phytates and polyphenols, compounds that inhibit iron absorption. Other nutrients that inhibit iron absorption are calcium and certain animal (found in dairy and eggs) and plant proteins (soy proteins) [ 4 ]. Studies suggest that because of all these factors, people on vegetarian diets may have iron absorption reduced by as much as 85% compared to people on omnivorous diets [ 5 ].
If you are on a vegetarian or a vegan diet, it’s a good idea to check your iron once in a while. Better yet, check your ferritin levels. While blood iron can be influenced by recent meals, ferritin is not and is, therefore, a better indicator of your body’s overall iron stores. Unsurprisingly, it is often lower than optimal in people on plant-based diets [ 6 ].
If your iron is low, here’s a good hack to help you increase it – vitamin C. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) can bind iron and make sure it is well absorbed in your gut [ 4 ]. A simple way to get more vitamin C is to sprinkle some lemon juice to your salads. Also, cut back on tea, coffee, and dairy around your meals – all of these decrease the amount of iron your gut can absorb. 2) Zinc
Zinc is found in seafood, meat, eggs, and dairy. But it’s also found in whole grains, legumes, and seeds [ 7 , 8 ]. So if it’s present in plant sources, why are vegetarians and vegans more likely to experience zinc deficiency [ 9 , 10 ]?
Because plant sources also contain phytates (already mentioned in the iron section) that inhibit zinc absorption. Studies suggest that vegetarian diets have about 35% lower zinc absorption compared to omnivorous diets [ 5 ]. Some suggest that vegetarians may need to consume up to 50% more zinc than non-vegetarians [ 11 ].
Are your zinc levels optimal? If you notice your zinc levels decreasing over time, it may be time to make changes to your diet. You can increase your zinc levels by eating pumpkin seeds, nuts, and beans, or supplementing. Remember to always talk to your doctor before taking any supplements – they may interfere with your health condition or your treatment/medications! 3) Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for brain health and making DNA and red blood cells. It is mainly found in animal products such as meat, eggs, and dairy. When their diet is low in eggs and dairy, vegetarians can become B12 deficient, while vegans have to rely on vitamin B12 supplements [ 12 , 13 ].
Some amounts of vitamin B12 can be found in vegetables, algae, and mushrooms. Significant amounts have been reported in fermented vegetables, such as sauerkraut, natto, and tempeh. However, the amount of vitamin B12 in all of these foods is either negligible or highly variable. Neither of these foods can be considered a constant and sufficient vitamin B12 source. That is because the presence of vitamin B12 in these foods depends on bacteria that can but don’t have to be present in the soil or among the fermenting microbes [ 14 ].
The liver can store vitamin B12, so it can take years before low B12 consumption becomes full-on B12 deficiency [ 15 ]. During this time, your B12 levels may be in the normal range, but actually suboptimal for health.
You can monitor your vitamin B12 levels by doing a simple blood test. If you follow a plant-based diet or used to be plant-based for many years, you may want to tweak your diet to keep your B12 optimal. 4) Vitamin D
It’s best if you get your vitamin D from the sun. But many people don’t get enough sunlight, often due to climate or their jobs. That’s when diet becomes important.
Vitamin D is important for mood, immune function, and muscle strength [ 16 , 17 ]. Although a form of vitamin D is found in plants (vitamin D2), some studies suggest it is not as potent as cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), the type of vitamin D found in fish and dairy products [ 18 ].
Vegetarians, and especially vegans who don’t get enough sun, are at risk of having low vitamin D levels [ 19 ].
To increase vitamin D in your diet, opt for […]
10 Rehmannia Root Benefits + Side Effects

Rehmannia has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for thousands of years, but modern research on its potential benefits is relatively scarce. It has shown promise for anemia and kidney function; what other benefits might it have? Read on to find out. What is Rehmannia?
Rehmannia glutinosa is a flowering plant found in central China . It’s sometimes called Chinese foxglove because it looks somewhat like a foxglove flower, though the two aren’t actually related [ 1 ].
The roots of this plant have been used in Traditional Chinese and Korean Medicine for over 2,000 years [ 2 , 3 ].
According to the traditional outlook, the harmony of opposite, but complementary, forces – yin and yang – underlies good health. Rehmannia is thought to help with yin energy imbalances. It is traditionally used to fight bacterial infections, as a tonic, and for a variety of conditions associated with inflammation, like asthma and arthritis [ 4 , 5 , 1 ].
Rehmannia is also often combined with other herbs to remedy “yin deficiency”. For example, it’s one of the six ingredients in a popular Chinese herbal product called Rehmannia Six Formula and one of the seven ingredients in the traditional kidney-nourishing herbal formulation Yukmi-jihang-tang. It is also included in widely-used formulations, such as Liuwei Dihuang Pills [ 6 , 3 , 7 ]. Snapshot
Proponents:
May improve anemia by supporting blood cell production
May support kidney function
Early evidence of mood, blood sugar, and bone support
Skeptics:
Unclear which active components are responsible for the benefits
Researched and often used in multi-herb formulations
Weak or low-quality evidence for many benefits
Side effects largely unknown
Rehmannia Root
Although the above-ground parts are sometimes used, herbal remedies are much more often prepared from the orange roots of this plant [ 8 , 9 ].
Depending on how the roots are prepared, they are called [ 10 ]: Xian-Di-Huang (for the fresh root)
Sheng-Di-Huang (for baked roots)
Shu-Di-Huang (for steamed roots) in Chinese
Components
Over 70 active compounds have been found in Rehmannia , including amino acids , simple and complex sugars , vitamins , and plant-specific compounds. Their composition in extracts mostly varies according to the plant species and the root preparation method [ 5 , 9 ].
One of the most well-known plant-specific compounds in Rehmannia is called catalpol , which accounts for 0.3-0.5% of the dried root. Catalpol is an iridoid glycoside, a group of molecules plants create to defend against predators. They also have a range of health effects in humans [ 1 , 11, 12 ].
Catalpol is likely responsible for the plant’s sugar-lowering, inflammation-fighting, and immune-balancing effects in cells and animals. Rehmannia also contains rehmapicrogenin, a strong anti-inflammatory. This compound that helps deactivate one of the most important inflammation-triggering factors in cells ( NF-κB ) [ 13 , 14 ]. Mechanism of Effect
According to some researchers, Rehmannia may improve stress resilience and mood by enhancing the body’s antioxidant defense [ 15 ].
Certain complex sugars in Rehmannia may target the hippocampus, a part of the brain that plays an important role in memory and mood. Catalpol might also help brain cells resist damage. As a result, the plant’s compounds are currently being investigated for their effect on dementia and anxiety [ 16 , 17 , 11 ].
Rehmannia also affects energy use and is under investigation in people with diabetes and insulin resistance . Sugar extracts of this plant increased insulin production in mice and catalpol lowered glucose levels in diabetic rats. Catalpol also increases the secretion of endorphins from the adrenal gland, which helps transport glucose from the blood into the muscles [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ].Traditional practitioners claim that Rehmannia can reverse anemia, and some evidence suggests that it may protect the parts of the bone marrow that make red blood cells . Nourishing the blood is one of its main traditional indications, while anemia is considered to be a sign of yin deficiency. As such, early sickle-cell anemia clinical trials are in progress with a compound isolated from the steamed roots, but the results aren’t in yet [ 22 , 23 ].In cell studies, Rehmannia helped alleviate inflammation by sponging up free radicals – highly reactive compounds that can damage cells – as well as by causing immune cells to secrete fewer inflammatory signaling molecules. Importantly, it also blocked the expression of inflammatory genes in these cell studies. Reducing inflammation is beneficial in many conditions, but researchers are currently looking at its application in bone and kidney health [ 14 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ].What’s more, this herb caused kidney cells to express fewer receptors that drive high blood pressure. According to some researchers, if this effect translates to the human body, it could make it useful for protecting the kidneys that are already strained due to other diseases, like diabetes. Dried and steamed roots reduce renin in animals, thereby lowering blood pressure and reducing kidney damage [ 28 , 29 ]. Potential Benefits Rehmannia supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use and generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing. 1) Anemia Aplastic anemia is a rare disease in which the body stops making enough blood cells due to bone marrow damage. In a clinical study of 34 people with this disease, Rehmannia extract added to standard treatment sped up symptom remission better than standard treatment alone [ 30 ].A combination of traditional medicines, including Rehmannia , had promising effects in another trial of 64 people with the same type of anemia. An integrative medicine approach could protect the bone marrow and red blood cells and reduce inflammation. As a result, 12 participants had blood markers comparable to healthy people [ 23 ]. Rehmannia and its extracts, alone and in combination with other supplements, also improved anemia in […]
64 Complementary Approaches To Fighting Depression & Boosting Mood

Depression is one of the most common mood disorders out there. While a number of effective, safe, and medically-approved treatments for it currently exist, many of these involve the use of pharmaceutical drugs that can sometimes have unwanted side-effects. Because of this, some people are reluctant to use a medication-based approach, and instead choose to look for other, non-drug-based forms of treatment. In this post, we’ll review some of these “complementary” approaches, and what the science currently says about them. Do any of these actually work? Read on to learn more!
Disclaimer: This post is not a recommendation or endorsement for any particular type of mental health treatment. The only way to be sure you get effective treatment is to discuss your options with your personal doctor — and none of the complementary approaches described below should ever be used to replace what your doctor has prescribed or recommended. We have written this post for informational purposes only, and its goal is simply to inform our readers about the science behind some complementary treatment strategies, and what we know about how they might work. Introduction To Depression And How It Is Treat ed
Many of the most common treatments for a person diagnosed with clinical depression ( major depressive disorder , or MDD) involve the use of prescription medications (such as SSRIs) to alleviate or manage the symptoms.
While these medications can be highly effective in many cases, it is also unfortunately the case that many of these pharmaceutical drugs can potentially cause a number of unwanted side-effects in people who take them.
For this reason, some people are reluctant to rely on pharmaceutical treatments, and prefer to try non-chemical treatments instead.
In this post, we’ll review some of the many “non-pharmaceutical” approaches to mental health treatment — such as psychotherapy — as well as discuss what the science currently says about a number of lifestyle and dietary factors that may also have effects on a person’s mood.
We’ll also review a number of supplements and other compounds with at least some suggestive evidence of having effects on mood, although these findings are still early and are generally not yet strong enough to draw solid conclusions from.
However, before we begin we want to stress that this post is not an endorsement for- or against any particular mode of treatment! Nor are the strategies outlined in this post intended to be used as a replacement for conventional medical care in any way.
If you are ever diagnosed with a mental health condition of any kind, the only way to decide what the best treatment for your specific case might be is to discuss it with your doctor. Only a fully-qualified medical professional fully understands all the different advantages and drawbacks associated with the many different possible modes of treatment — and they will work with you to come up with the safest and most effective approach for your individual needs.
With that in mind, in the rest of this post we’ll discuss some of the many non-drug-based treatments for depression and other mood disorders, and what science currently says about them. Although most of these only have weak or insufficient evidence to support them, many of them have early studies that suggest that they could have some potential when used to complement other, more conventional forms of treatment. Nonetheless, all of these preliminary findings will still have to be extensively followed up on by future research to confirm their efficacy, safety, and underlying mechanisms.
Before we get into some of the “alternative” or “complementary” strategies for potentially improving mood, it’s important to be aware of what some of the more typical treatment approaches for clinical depression are, and how they work.
The approaches below are some of the ones that you might be likely to encounter if you were to book an appointment with a traditional qualified psychiatrist, psychologist, or other mental health professional.
Many of these treatment modalities have been used for a long time, and have been extremely well-studied. Therefore, these approaches are widely-used by doctors due to their having a lot of evidence to support them. 1) Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
One of the most common forms of therapy used by mental health professionals is cognitive-behavioral therapy — also known as “CBT”. This highly “evidence-based” approach to therapy is one of the most widely-used for preventing and reducing depression (as well as many other mental health conditions) [ 1 ].
The main idea behind the use of CBT in depression is to help patients change their patterns of thinking and make behavioral changes to improve coping and reduce distress [ 2 ].
CBT has been reported to be effective for both acute depressive episodes, as well as long-term prevention [ 1 ].
According to various studies (RCTs), CBT reportedly reduced depression symptoms in 177 seasonal affective disorder patients, as well as 87 patients with postpartum depression [ 3 , 4 ].
One specific type of CBT, called “acceptance and commitment therapy” (“ACT”), has been reported to decrease symptoms in cases of mild-to-moderate depression. It has also been claimed to help reduce overall severity of depression cases, as well as the occurrence of suicidal thoughts (“suicidal ideation”) [ 5 , 6 ].
According to some reports, CBT may help reduce the negative perceptions of emotions [ 7 ].
Some early neurobiological evidence suggests that CBT may work by reducing the activity in parts of the brain that are involved in emotional processing (such as the amygdala and hippocampus) as well as cognitive processing (such as the prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex) [ 8 ].
CBT is traditionally delivered face-to-face by therapists, but is also sometimes delivered “digitally” over the internet, such as through a mobile phone or personal computer [ 9 , 10 ]. 2) Psychodynamic Therapy
“Psychodynamic” therapy is probably the therapy you most associate with mental health treatment. It focuses on conscious and subconscious feelings from past experiences, and how they affect the patient.
The effectiveness of psychodynamic therapy for depression treatment is generally well-supported. In some cases, […]
8 Amazing Health Benefits of Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy uses certain wavelengths of light through the skin, with the goal of improving skin quality, inflammation, and even mental health with very few side effects. Does it work? Read on to learn more. What is Red Light Therapy?
Red light therapy shines red light wavelengths (620-750 nm) through human skin to elicit certain effects in the underlying tissue. It usually uses a whole panel of red light or an LED panel.
Treatment sessions tend to be short, lasting only seconds to minutes in duration, and are usually conducted every other day for weeks to months.
Surprisingly, unlike many other treatments used to address similar conditions, there are virtually no reported side effects. Mechanisms
Most of red light’s effects are through the cells’ mitochondria absorbing light. In cell studies, the cytochrome c oxidase in the mitochondria absorbs red light, which causes it to release nitric oxide, increase ATP, and decrease oxidative stress [ 1 ].
According to some researchers, this can then cause a chain reaction in the cells and affect responses such as cell formation, movement, death, and inflammation. However, its effects depend on the type of cell and its status [ 1 ].
This increased ATP (energy) production is a possible cause of light therapy’s positive effects on muscle recovery and physical performance [ 2 ]. Potential Health Benefits
While there are FDA-approved red light devices, these are broadly classified as class 2 devices; that is, while there is evidence to support their use in some health conditions (which we’ll discuss in this section), they are currently not sufficiently regulated to guarantee the effectiveness or safety of any particular device.
If you are interested in using red light therapy, we recommend talking to your doctor to choose the right device and determine whether this strategy is right for you. 1) Skin Quality
In a study of 31 subjects, a combination of red and infrared LED light therapy helped improve skin conditions. They had less sun -induced aging and wrinkles [ 3 ].
In a DB-RCT of 52 female patients, 12 weeks of daily treatment with red light therapy significantly improved eye wrinkles [ 4 ].
A similar study showed that LED therapy is effective against sunspots in middle-aged participants [ 5 ].
In a single-blinded RCT, red light was superior to infrared light in treating acne [ 6 ].
The addition of red light to blue light also improved acne symptoms significantly compared to blue light alone and benzoyl peroxide in an RCT of 107 acne patients [ 7 ].
Red light therapy also significantly improved skin complexion, roughness, and collagen density in an RCT of 136 participants [ 8 ].
However, in human cells, several characteristics associated with skin scarring increased with red light like reactive oxygen species and collagen formation inhibition [ 9 ]. 2) Oral Mucositis
A common side effect of chemotherapy is oral mucositis, which is when inflammation breaks down the lining of the mouth. In a systematic review of 11 RCTs, both red and infrared light therapy significantly reduced the incidence and severity of oral mucositis [ 10 ]. 3) Bipolar Disorder
A review of multiple types of light therapy found red light therapy improved depressive symptoms and prevented relapse after sleep deprivation in patients with bipolar disorder [ 11 ]. 4) Physical Performance
In a study of 39 heart disease patients, red light therapy improved performance and decreased chest pain during exercise tests [ 12 ].
In a DB-RCT, 40 healthy untrained men underwent an intensive exercise session. The participants that underwent red light therapy had significantly improved performance, decreased soreness, and reduced indicators of muscle damage compared to ones that did not have light therapy [ 13 ].
In female athletes, 2 weeks of red light therapy improved sleep quality and endurance [ 14 ].
Red light therapy also significantly improved recovery after high-intensity exercise in a DB-RCT of 40 volunteers [ 15 ].
Interestingly, these results have caused researchers to question whether it should be permitted in athletic competitions due to its effectiveness in enhancing athletic performance and improving recovery [ 16 ].
The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of red light therapy for any of the below-listed uses. Remember to speak with a doctor before using red light therapy, and it should never be used to replace something your doctor has recommended or prescribed. 5) Wound Healing
In a triple-blind RCT of 12 dental patients, red light therapy improved the healing rate after oral surgery . However, it did not reduce pain [ 17 ].
In an RCT of 16 diabetic patients, red light therapy significantly decreased diabetic foot ulcer size and reduced pain [ 18 ].Another RCT of 30 diabetic patients showed similar results; red light therapy combined with conventional therapy reduced ulcer size more than conventional therapy alone [ 19 ].In diabetic rat models of skin wound and burn injury, red light significantly improved healing and was superior to infrared therapy for burn wounds [ 20 , 21 ].Red light also enhanced the healing rate of incision wounds in diabetic rats and reduced the risk of infection [ 22 ].In rabbits with skin wounds, red light therapy decreased healing time significantly more than blue light or no light treatment. It promoted tissue and cell growth [ 23 ]. 6) Inflammation One of the main uses of red light therapy is to treat inflammation [ 24 ].Red light therapy limits the inflammatory response and reduces oxidative damage by reducing inflammatory cytokines ( TNF-a , IL-1A, and IL-6 ) [ 25 ].A review on muscle repair (in animal models) concluded that red light therapy has the capacity to reduce inflammation, positively impact growth factors, and increase blood vessel formation [ 25 ]. 7) Pain In a study (DB-RCT) of 80 chemotherapy patients, red light significantly reduced self-reported pain [ 26 ].Red light therapy might treat tennis elbow for a short period of time, but these findings were only shown by one study (RCT) [ 27 ].With […]
The Scary Ways An All-Nighter Messes Your Body And Brain
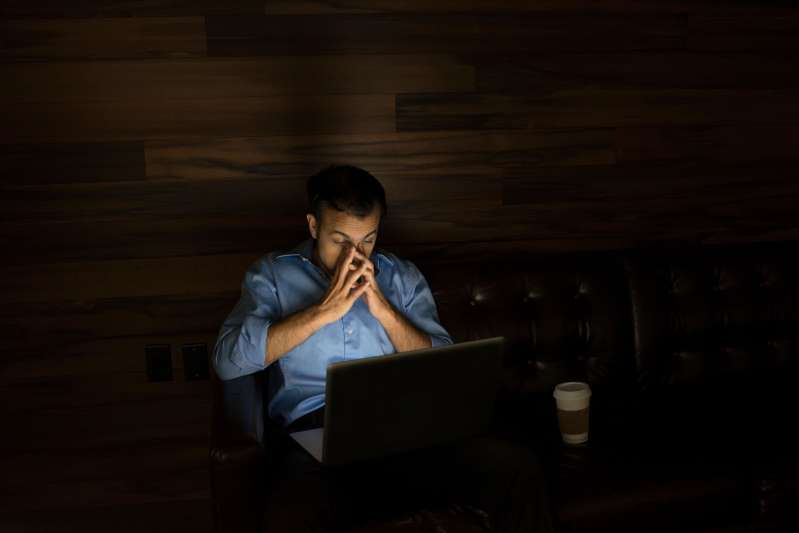

Most people have pulled an all-nighter at least once in their lives, whether it was to meet a school or work deadline or to keep the party going until the morning.
The experience of going at least 24 hours without sleep, otherwise known as total sleep deprivation, obviously does not make you feel good the next day. The physical and mental repercussions are notable.
HuffPost spoke to sleep experts to find out what exactly happens to your body and mind when you pull an all-nighter. You fight your body’s natural drive to sleep.
Pulling an all-nighter requires you to fight your body’s natural drive to sleep by making use of “wake-promoting factors” and avoiding “sleep-permissive factors,” said Roy Raymann, the vice president of sleep science and scientific affairs at Carlsbad, California-based SleepScore Labs .
“Wake-promoting factors include using caffeine, being in a colder environment, being in a well-lit room with plenty of blue-enriched light, and standing,” he said, adding that sleep-permissive factors include darkness, a warm comfortable temperature, reclining and closing your eyes. Your body skips its recovery period.
When you skip a full night of sleep, your body has missed out on a much-needed opportunity to relax, recharge and recover.
“During the night, all kinds of restorative processes happen to bring you back to shape for the next day,” Raymann said. “Cells and tissues are repaired, toxins are removed from your brain, memories and emotions are dealt with and stored and the fatigue that you have been building up during daytime is reduced.”
Pulling an all-nighter or just getting a limited amount of sleep means that this recovery process doesn’t happen or isn’t executed to its full extent, leaving you unrefreshed.
“Cognitive performance degrades and mood can suffer,” said Nate Watson, co-director of the University of Washington Medicine Sleep Center and a SleepScore Labs advisor. “The glymphatic system, which removes the byproducts of a day’s worth of activity from the brain, is not able to perform its function.” Stress hormones spike.
“When you’re not getting sleep, you’re running on stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, so stress levels rise,” said Jon Caulfield, a dentist in Littleton, Colorado, who focuses on airway, sleep and TMJ disorders and a board member and national instructor with the American Sleep and Breathing Academy.
“Sleep loss can cause stress and anxiety,” echoed Terry Cralle, a registered nurse and certified clinical sleep educator in the Washington, D.C. area who serves as a spokesperson for the Better Sleep Council . Cralle cited a recent study from the University of California, Berkeley, found that one sleepless can boost anxiety levels up to 30%.
This can be a vicious cycle: Stress and anxiety often cause people to have trouble sleeping, but then sleep deprivation increases stress and anxiety levels. And around and around you go. Focus and accuracy drop.
“It has been postulated that even during a single night of sleep deprivation, the microstructures in your brain can change,” Raymann said. “Also, there’s now more evidence that during the night you’re getting a brain wash to remove all the debris and toxins that accumulated in your brain during the day. Both these changes ― micro-structure and no brain wash ― lead to impaired communication between your brain cells.”
This impaired communication between brain cells hampers your ability to pay attention or work at an optimal level. A 2007 study from St. Lawrence University in Canton, New York, found that pulling all-nighters was associated with lower grade point averages.
“Sleep deprivation affects your prefrontal cortex, which affects your cognitive abilities. Think of it as being impaired.” Cralle said.
Many experts have even compared sleep deprivation to drunkenness, which is why drowsy driving is so dangerous.
“In addition to a lack of focus, which many call brain fog, there’s a lack of accuracy. You’re likely to get things wrong on a test or miss a shot if you’re playing sports,” said Raj Dasgupta, assistant professor of pulmonary and sleep medicine at the University of Southern California.
This is why it’s dangerous to drive or operate heavy machinery while sleep deprived. You’re more susceptible to injury or accident.
In the wake of sleep deprivation, “the next day you will be less productive. Everything costs more time and takes more effort, and you are likely to make errors,” Raymann said.
He added, “My first mentor during my PhD taught me the wise lesson, when he saw me still late working at my desk: ‘Whatever you try to do at the end of the day after a busy day will cost you a lot of effort and time, and will even most likely lead to something you will not be happy with the next day. Go home, relax and get some sleep. During the next morning, you will resolve that task in a breeze.’” Memory suffers.
“Sleep deprivation’s effect on working memory is staggering,” David Earnest, a professor with the Texas A&M College of Medicine, said in a 2016 report about the effect of all-nighters on health. “Your brain loses efficiency with each hour of sleep deprivation.”
Research has suggested that sleep plays a major role in memory consolidation , the process of short-term memories moving to long-term storage. When you pull an all-nighter, this process is disrupted, and memory recall suffers. You’re likely to make poor decisions.
The prefrontal cortex is also linked to decision-making, so sleep deprivation can lead to poor judgment.
“Decision-making becomes impulsive,” Watson said. “We become less able to assess the potential negative consequences of our decision-making.” You become irritable.
It’s hardly a surprise that people are cranky after not sleeping for a full night. Indeed, sleep deprivation often leads to a bad mood .
“Your interaction with people will be more blunted, and you might become easily annoyed or irritated,” Raymann said. “You will also likely look more tired.” Your immune system is compromised. Sleep deprivation can affect your body’s production of cytokines, which play a big role in your immune response. That could lead to a serious case of the sniffles down the road.“When you’ve stayed up all night, your immune […]
Racetams: An Overview

WN Lifestyle Home – Health
Originally Posted On: https://mindzymes.com/racetams/ A class of Nootropics, known as Racetams, have taken the market by storm, and their users have been sharing stories from around the world. They describe how this amazing… A class of Nootropics, known as Racetams, have taken the market by storm, and their users have been sharing stories from around the world. They describe how this amazing group of supplements can increase cognitive abilities, such as; focus, motivation, creativity and memory. Today, we’re going to break down the Racetam family, and introduce you to a few of the most popular ones on the market. First and foremost
Racetams are manufactured Nootropics, and they contain many of the effective properties found in natural ones. Within the family of Nootropics, Racetams are identified by the similarities in their chemical structures, and they all have a wide array of therapeutic effects on the body. Many of them operate by increasing the flow of blood, oxygen, glucose, or other nutrients throughout the body. The more your brain is supplied with these elements, the better your brain will function. This means heightened concentration and focus, increased brain stamina, and a reduction in the degeneration of brain cells.
For the most part, Racetams trigger the glutamate receptors that are contained within the same cells as the cholinergic receptors. Glutamate and acetylcholine, two important neurotransmitters, play a vital role in cognitive function and human action, and are on the receiving end of these receptors.
Glutamate exists in various parts of the body, but its highest concentration is in the nervous system, and the brain. It is responsible for making sure signals between nerve cells send correctly, and it plays an extremely important role in learning and memory.
Acetylcholine, on the other hand, is the most widely used neurotransmitter in the body, and is responsible for activating cholinergic receptors. At the center of the parasympathetic nervous system, Acetylcholine works to restore the feeling of normalcy after a stressful incident, and works to restore calmness. It’s also the neurotransmitter that signals muscles to contract and/or flex, making it incredibly important for athletes. Most importantly though, the brain uses Acetylcholine for cognition, which gives us the ability to learn, retain and connect memories and information.
Given the importance of these two neurotransmitters, it’s easy to see why the Racetam family of Nootropics can be such an important, and often overlooked, way to improve your well-being.
Racetams also boost the communication between the left and right hemispheres of the brain. By increasing the communication between the two hemispheres, you may enhance the speed of idea formation, which may result in being able to recall memories faster. The strengthened communication between the left and right side of the brain will also lead to a greater level of cognitive function.
There are a variety of Racetam Nootropics available today, and it’s difficult to decide which one might be right for you. Anyone who is considering enhancing their overall mental output must consider the varying experiences Nootropics can offer, in order to create the right plan for their individual biochemistry.
Listed below are a few of the best, and most widely-used Racetams, as well as their recorded benefits, side effects, and stacking recommendations.
Considered to be one of the safest, and mildest Nootropics available, due to its low acute toxicity levels. Piracetam is a good choice to introduce yourself to the use of Racetams, and Nootropics as a whole.
Piracetam is widely considered to improve the blood flow to the brain, and signals essential neurotransmitters to aid in cognitive functions, such as; mental energy, information and memory retention, motivation and increased sensory awareness. Research has shown that taking Piracetam may boost the absorption of neurons in the brain, which makes it more accessible for vital nutrients to enter, and for waste to be easier disposed of. It should be noted, that in order for benefits of Piracetam to show, one must research for the correct usage, and dosage. It may take a couple of weeks of taking the amount needed, in order for a person to begin to notice improvements in memory, creativity and mood. Some benefits of Piracetam include the following:
Research has indicated that taking Piracetam has shown benefits in the treatment of some mental, and physical ailments, such as cognitive decline due to age, alcoholism and schizophrenia.
Binge eating disorder, or BED, is a stress-related disease that has also been studied in regards to Piracetam. BED is described as an intake of large quantities of food during an acute period of time. Because the acetylcholine levels are compromised during an episode of BED, it leads to deficits in cognition and a sharp increase in anxiety. A study performed on animals in 2018 indicated that Piracetam regulates levels of acetylcholine, which decreased BED related cognitive deficiencies, essentially limiting the binge eating behavior and body weight.
Studies of Piracetam have shown that it is also efficient in alleviating symptoms related to stress, anxiety, limited coordination and depression. In fact, in patients who experience drug-resistant depression symptoms, Piracetam may provide an additional therapy that shows compelling, rapid clinical improvement.
Piracetam is primarily known as a cognitive enhancer, and clinical trials indicate that it is extremely effective in boosting brainpower, notably with concentration, and memory. Although the effects of Piracetam in cognition are significant in individuals of all ages, it is most compelling in older adults who are experiencing a decline in cognition due to age.
Piracetam increases synaptic plasticity by improving blood flow in the brain, and raising the function and production of vital brain chemicals, or by creating new connections between neurons, which are important to learning.
Piracetam users have self-reported improved focus, increased energy levels, and a boost in creativity, especially when taken as a stack with choline. Studies have bolstered the self-reports by showing that Piracetam enhances verbal learning in healthy students, in addition to those who have dyslexia.
Piracetam’s benefits are associated with increased blood flow to the brain, and increased cellular membrane fluidity, which when taken with choline, enhances memory in older adults.
In many […]
Marblehead scientist wants to improve your memory

PeiPei Wishnow in her home office, with her new Interceuticals Memory supplements. [Wicked Local photo/Leigh Blander] Hide caption Locals say new supplement is making a difference
Judith Black, of Marblehead, started noticing recently that her brain isn’t quite as sharp as it used to be.
“It’s that loose-around-the-edges thing,” she laughed. “It comes with age.”
So Black, who is 68, decided to try a new supplement, created by Marblehead scientist PeiPei Wishnow, that claims to slow age-related memory problems and enhance brain function.
“It had an authentic effect,” Black said. “I started remembering people’s names better. I suddenly remembered the lyrics to a song I had written 20 years ago. I’m a science-based person and completely skeptical of supplements, but I recommend this to people all the time.”
Wishnow started her company, Interceuticals Inc., 20 years ago, in her Marblehead home. It is now based in Salem. She creates natural supplements for seniors struggling with age-related challenges, including bladder control. In September, she introduced a new product, Interceuticals Better Memory.
“Memory issues are on everybody’s mind,” said Wishnow. “Everybody is worried about Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.”
Inflammation Fighter
Using a study out of UCLA, Wishnow identified curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, as a powerful tool to fight inflammation, which is often blamed for cognitive decline.
“Our research thus far indicates clear cognitive benefits (of curcumin), which may take the form of stabilization of memory abilities and delay of future decline,” said Dr. Gary Small, author of the UCLA study.
Wishnow added a mix of Chinese herbs which she says improve circulation. “That allows for faster results,” she said. “People can see results within six months.”
Wishnow has personal reasons for her work in memory supplements. Her mother has suffered from worsening dementia for years.
“Her personality has completely changed. She’s verbally abusive. I don’t want to be going there, so when I noticed my memory starting to change over the last couple of years, I started to look at the research,” she said.
Wishnow said she was doing yoga and eating a healthy diet and still noticed her memory was deteriorating and her multi-tasking ability was down.
“I suddenly forgot the entrance code to my office. I needed to do something else, something natural and preventative,” she said.
Mental & Physical Effects
Dr. Nancy DeMuth, 63, is a local physical therapist who works with people suffering from inflammation. She started taking Interceuticals Memory about 10 months ago.
“Not because I’m having particular memory problems, but because I’m interested in not developing memory or cognitive problems,” she said.
DeMuth says she’s seen an impact.
“My memory is better,” she said. “I feel like I have a better ability to remember peoples’ names and sequences of numbers, more like my younger brain.”
DeMuth also saw a physical improvement.
“This hip pain that I’ve been having for about a year got dramatically better. I can do things in yoga and dance that I couldn’t do before. That was the most dramatic thing,” she said.
Mike Elkin, Judith Black’s husband, also noticed a physical benefit when he started taking the supplement.
“I have emphysema and chronic back pain and I’ve seen radical improvements in both. I’m breathing a lot better,” Elkin said.
He says his memory is improving, too.
“I’m 77 years old now,” he said. “I’m just generally more aware, sharper, I can keep track of things better.”Supplements are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration.“We don’t try to treat dementia or reverse or stop it,” Wishnow emphasized. “We try to help people just like myself do something extra to protect their memory.”Wishnow will be speaking about curcumin at Abbot Library on Sunday, December 1, at 2 p.m.To learn more about Interceuticals, visit https://bebetternow.com /.
8 Habits You Didn’t Know Were Aging Your Brain

Aging is a natural, inevitable part of life that we cannot escape. However, that doesn’t mean that we need to go out of our way to accelerate the process. In fact, a lot of time and energy is spent in preventing any sort of premature aging in our skin. That said, it’s also important to take the same precautionary measures when it comes to the health of your brain.
As brain health does decline with age, it’s important to be conscious of habits that may cause the brain to age faster. This results in weaker neuron communication, loss of blood flow to the brain as well as inflammation – factors that can results in cognitive decline, particularly increasing your risk of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s.
Therefore, if you want to ensure the health of your brain, and maintain cognitive function for the years to come, then be sure that you’re not partaking in any of the following habits. 1. You’re not exercising
Exercising is important for your overall health and in addition to its various health benefits, protecting your brain health is one of them. In fact, research has found that a sedentary lifestyle can be quite detrimental to your brain health ( 1 ). It appears that living an inactive lifestyle may cause your medial temporal lobe, which is responsible for memory as well as cognitive function, to thin.
Additionally, a separate study published in the journal Neurology found that women who led active lifestyles faced an 88% reduced risk of developing dementia when compared to women who did not exercise.
If you really want to protect your brain health, it’s important that you prioritize getting more active over sitting in front of a screen, watching Netflix. 2. You’re eating a horrible diet
You are what you eat, and that includes your brain health. If you weren’t already aware, a diet rich in processed foods and refined grains is not the best option for your health as it increases the risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Now imagine what it can do for your brain health.
The wrong foods can trigger inflammation, which can then cause the brain to age faster than normal. However, the right food can help to prevent any form of premature again. In fact, research published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association found that the MIND diet can help to reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
The MIND diet refers to the Mediterranean-DASH Intervention diet, which is an eating plan that incorporates both aspects of the Mediterranean and DASH diet. As a result, the diet includes whole grains, berries, leafy green vegetables, olive oil , poultry, and fish. These food groups are each rich in antioxidants, fatty acids and other essential nutrients that will help to protect your brain health. As a result, the study found that following the mind diet would help to reduce the risk of both Alzheimer’s and dementia by 53%. 3. Excessive drinking
Now while a glass of red wine does provide health benefit s, it’s important not to over-consume alcohol.
The hippocampus refers to the area of the brain that helps to regulate both learning and memory. However, according to research published in the journal Neuroscience , excessive drinking can reduce the hippocampus’s functionality by at least 40%. Therefore, if you are looking to enjoy a drink, it’s important to try to stick to a glass a day – preferably of organic red wine. 4. You stop learning
If you really want to prevent your brain from prematurely aging, then it’s important that you keep exercising it so that it doesn’t lose its sharp thinking skills. In fact, research has found that keeping your brain active through brain games like crossword puzzles can help to reduce the risk of dementia ( 2 ).
However, if you are not a fan of crossword puzzles and other brain games, there are other ways in which you can keep your brain active. These can include learning a new language or learning a new skill, such as how to play an instrument . 5. You have a poor social life
Blue Zones are five areas around the world that are inhabited by healthy individuals who go on to live to age 100 and beyond. Additionally, these areas are also virtually free of disease. One of the most notable characteristics of these Blue Zones are the close community bonds that they each have in their respective areas.
According to research, having strong social connections may help to delay your brain from aging. In fact, a study published in the Journal of International Neuropsychology Society found that strong social bonds may help to reduce your risk of cognitive decline by over 50%.
Now while some solitude can provide us with an opportunity to get a better perspective on where we are in life, don’t shy away from calling up a friend for a Saturday lunch. 6. You don’t sleep enough
The body needs at least seven to nine hours of sleep as this gives it ample opportunity to fully recharge and to ensure that it is in proper working order. Unfortunately, a lot of us are guilty of not even getting six hours of sleep, let alone seven. This can then cause the brain to decline faster with age.
In fact, research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that losing even one night of sleep caused an increase of beta-amyloid – a protein in the brain that has been closely linked to cognitive decline as well as Alzheimer’s disease.
If you’re battling with getting enough sleep at night, there are methods you can use to help alleviate this problem. Such methods include the use of essential oils , rearranging your bedroom , or even sleeping on the floo r. 7. You smoke
Smoking can literally damage every aspect of your body, which is why it’s important to quit the habit as soon as possible, especially if you want to both improve and protect your health .
In […]
8 Himalayan Salt Lamp Benefits That Explain Their Popularity

People have made many different claims regarding Himalayan salt lamps in the recent past. They are becoming popular day by day due to their properties. Owning a Himalayan salt lamp is believed to have a number of health benefits.
First of all, these lamps are said to have the ability to release negative ions into the atmosphere, and this is a good thing. While there is no particular scientific research to prove these claims, Himalayan salt lamps still could have health benefits.
As the name suggests, their origin is the Himalayan Mountains. It’s Himalayan pink salts that are being used to manufacture these lamps. So what is their proposed mechanism of action?
They are said to ionize the Himalayan pink salts with the heat from the bulb. As a result, these lamps release negatively charged particles into the environment. Now that you know how they work, here are some of the suggested benefits of having a Himalayan salt lamp.
1. They neutralize electromagnetic radiations
You live in an environment that is flooded by an overflow of electromagnetic radiation from your electrical devices, including your appliances, computers, as well as mobile phones.
There are thus many positive ions floating around, and these may subject you to long-term adverse health effects. These effects may include; an increase in stress levels, chronic fatigue as well as a decrease in your body’s response to pathogens.
When you have a Himalayan salt lamp, the released negative ions negate most of the effects of the EM radiation on your health. Although neutralization is more of an overstatement, salt lamps do a great work of reducing the harmful emissions in the atmosphere. 2. Help reduce allergy symptoms and asthma
These salts are said to tremendously decrease bronchitis and asthma, which is another reason for their increased popularity. HPS lamps have been known to filter out any microscopic dust, pet dandler particles, mildew, and mold particles in your indoor air.
Many people argue that adding a lamp in your room will help alleviate your allergy symptoms. Some people who have asthma have also testified to benefitting from these lamps in terms of their respiratory health. 3. Purify the air
Those who appreciate natural living have boasted that the core benefit of having a Himalayan salt lamp is its incredible ability to remove cigarette smoke, pollen and other contaminants from the air.
The hygroscopic nature of the salts in HPS lamps is said to achieve this by trapping the pollutants in the air into their salt crystals. The air in your home may, therefore, become cleaner and healthier for you to breathe . 4. Increase energy levels
Because of the way positive ions sap the energy out of your body, the negative ions from the HPS lamps are said to have the ability to make you more energetic.
The same way being in nature rejuvenates you, is the same way lighting a Himalayan salt lamp benefits your mental health and works to your advantage. This is because both nature and these salts have an abundance of negative ions that invigorate your body. 5. Improve breathing and sleep
A controversial statement claims that negative ions increase the ciliary activity in your lungs, while positive ions affect it negatively. Cilia are the tiny hairs lining the windpipe. In other words, when the air has more negative ions, the air getting into your lungs is cleaner. This makes it easier for you to breathe.
Salt lamps are also believed to help you to enjoy better sleep . It happens because there is more oxygen getting into your blood as a result of the reduction in contaminants. Better oxygen intake means the better circulation of oxygen into your brain, thus more regular sleeping patterns. 6. Improve your mood and reduces stress
If you are a person who suffers from seasonal depression, you might benefit immensely from the salt lamps . Apart from seasonal depression, it could also help with other forms of depression too. This is because of the proposed effect of a high density of negative ions from the Himalayan salt lamps, which is said to result in mood improvement .
According to claims, the salts put your body in a comfortable, relaxed state. Another thing that the lamps are said to do to help improve your mood is reducing the levels of stress that you are experiencing.
In your day to day experiences, you may come across situations that subject you to stress. The situations may be just the nature of the actual work that you do. Or it could also be an extraordinary event that happens while you are doing your job.
Exposure to positive ions from different origins might contribute to stress. The lamp releases negative ions that possibly counteract the effects of stress on your body. 7. Alleviate colds and symptoms of coughing
The negative ions which emanate from the Himalayan salt lamps have a way of protecting you against airborne germs. According to claims, they remove the contaminants from the air but also improve how your body filters air.
The salts in the lamps enable your body to purify the air going into your lungs by blocking foreign particles. This is effective in preventing the worsening of common symptoms of a cold, including coughing and sneezing. 8. Improve concentration
One of the proposed effects of negative ions from an HPS lamp is to reduce your levels and enhance your concentration. An increased blood and oxygen supply to the brain means that you experience an improvement in your concentration span.
When you are able to concentrate more, it means that it also boosts your brain’s capacity to interpret and retain information. Improvement in concentration, therefore, directly translates into a better memory. When you are able to recall events and information, you will be able to carry out your duties and responsibilities more easily.
These are just a few of the suggested benefits of having a Himalayan salt lamp in your home or office. While there is no conclusive scientific evidence to confirm them, it’s undeniable that such a lamp would be a […]
Marblehead doctor to host memory lecture at library

RYAN MCBRIDE/Staff photoDr. Peipei Wishnow in her Marblehead home. She is the founder and president of Interceuticals, a Salem-based company that specializes in herbal supplements that aim to help slow the progression of memory loss and dementia. MARBLEHEAD — Dr. Peipei Wishnow, founder of Interceuticals in Salem, will lead a lecture and discussion on memory at the Abbot Public Library in Marblehead this Sunday.
Titled “Protecting Brain and Memory As We Age,” the talk will focus on the doctor’s research and her product, Better Memory. Wishnow says the natural supplement, made from theracurmin curcumin, aims to slow age-related memory issues.
Curcumin, the main active ingredient in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, according to a UCLA study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. Researchers reported a 28% increase in memory functions in participants who took theracurmin curcumin twice a day for 18 months.
A native of Hangzhou, China, Wishnow came to the U.S. in 1985 to pursue a doctorate in biology. After conducting post-doctoral studies at MIT and the California Institute of Technology and serving as a research scientist in the pharmaceutical industry, she moved to Marblehead with her husband.
“I grew up in a family that understands the value of traditional Chinese medicine,” she said while describing her grandfather, an herbalist in China.
Drawing on her roots, Wishnow founded Interceuticals in 1997. Since then, she’s worked to combine Eastern and Western medical practices in an attempt to help the aging process for both men and women. Her earlier supplements included BetterMan for bladder control and stamina, followed by BetterWoman.
“We’re doing all of these things, what else can we do?” Wishnow asked. “I want to help myself and help the people I love.”
Since developing Better Memory, Wishnow says she’s given the supplement to her 93-year-old mother, who was displaying dementia-related symptoms. After six months, she says her mother became more engaged and was able to recognize family members and recite a new poem from memory. Wishnow has also started taking the daily supplement to aid her concentration and multitasking abilities.
Patricia J. Rogers, director of the Abbot Public Library, says she’s excited to hear Wishnow discuss her story and her knowledge of Eastern and Western medicines. Wishnow will lead a lecture and short discussion before opening a Q&A session. The library hosts more than 70 public programs each year, the director says, but this is the first time Wishnow is coming to speak.
“She’s a very well-grounded scientist,” said Rogers. “The topic is of great interest, and I’m happy to have the opportunity to share this information.”
Wishnow will speak at the Abbot Public Library, located at 235 Pleasant St. in Marblehead, on Sunday, Dec. 1, at 2 p.m. The event is free and open to the public and no registration is required.
Staff writer Alyse Diamantides can be reached at 978-338-2660 or adiamantides@salemnews.com .
5 Health benefits of acai berry that make it a real superfood

( Natural News ) While they may look like a cross between blueberries and grapes, acai berries are technically not berries — they’re drupes. Drupes are fruits that have a central pit rather than a bunch of tiny seeds surrounded by fruit flesh. Other fruits under this classification include cherries, apricots, olives, peaches, and plums. Acai berries have grown in popularity globally over the years, with some people hailing them as a superfood. This is due to their high antioxidant content and a number of other health benefits, such as supporting heart health, improving digestion, and preventing skin aging . Acai berries: nutrition and benefits
Acai berries are dark-purple berries that grow on the acai palm ( Euterpe oleracea ), a tree widely found in the Amazonian rainforests of South and Central America. The acai palm can reach 50 to 100 feet tall, with stems that can produce four to eight bunches of berries every year. Unfortunately, acai berries are rarely found fresh in your local grocery stores. This is because they’re not easy to transport and have a short shelf life. Acai berries also start to ferment within 48 hours of harvest, even when chilled in the refrigerator. (Related: Acai berries actually come from palm trees .)
Acai berries have a unique flavor profile, and some people may find them tart, not sweet. Others would say they taste like a combination of blackberries and dark chocolate. Acai berries also have a unique nutritional profile, being high in fat but low in sugar. Here’s what you can get from 100 grams of organic acai berry puree : Discover how to prevent and reverse heart disease (and other cardio related events) with this free ebook : Written by popular Natural News writer Vicki Batt, this book includes everything you need to know about preventing heart disease, reversing hypertension, and nurturing your cardiac health without medication. Learn More. Calories: 70 kilocalories
Fat : 5.26 grams
Sugars : 0
Dietary fiber : 5.3 grams
Carbohydrates : 5.26 grams
Acai berries also contain various trace minerals like zinc, iron, copper, magnesium, and potassium . These minerals, together with various antioxidant compounds, are responsible for acai berries’ many health benefits, some of which are listed below: They have anti-cancer properties
Some foods can prevent cancer cells from developing or spreading. Acai berries contain pigments called anthocyanins that give them their deep purple color. These pigments are also potent antioxidants that can help neutralize the damaging effects of free radicals, preventing the development of diseases like diabetes, heart disease and cancer .
In a study published in the Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry, researchers gave 12 healthy volunteers acai juice, acai pulp, applesauce and a non-antioxidant beverage at four different times. They then analyzed blood samples from the participants. The researchers found that acai pulp and applesauce significantly increased the participants’ blood antioxidant levels, suggesting that the antioxidants found in acai berries can be easily absorbed in the gut. They keep your skin healthy
The antioxidants in acai berries support skin health by fighting off free radicals which could potentially damage your skin. Eating antioxidant-rich foods regularly is important for repairing skin cells as people are constantly exposed to free radical sources like pollution, stress and even poor nutrition. They can support heart health
An animal study suggests that acai pulp could help improve heart health by reducing “bad” LDL and total cholesterol . This is mostly because of plant sterols — cholesterol-like compounds found in plants — that prevent the absorption of dietary cholesterol.
A study published in Nutrition Journal evaluated the effects of acai fruit pulp on overweight participants . The researchers fed 10 overweight adults 100 grams of acai pulp twice a day for one month. They observed that the participants had lower insulin levels and fasting blood sugar levels at the end of the study. They also found that eating acai pulp caused significant reductions in LDL cholesterol. They aid in digestion
Acai berries contain antioxidants and dietary fiber, both of which are useful for promoting gut health. A study published in Food Chemistry examined the effects of acai berries on the human digestive tract . Researchers found that half of the polyphenols in acai berries are able to travel as far as the colon. This suggests that acai berries can confer prebiotic and DNA-protective benefits throughout the gastrointestinal tract. They can protect your brain
Plant compounds like polyphenols have the potential to protect the brain from common brain diseases. Researchers from The University of Adelaide in Australia found that acai berry extract could protect brain cells from the harmful effects of beta-amyloids. The accumulation of these proteins in the brain is linked to the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Thanks to the antioxidant content and nutrient profile of acai berries, they can provide a variety of health benefits that could improve your overall health. This makes acai berries worthy of their “superfood” title .
Sources include:
ScienceDirect.com 1
ScienceDirect.com 2
ScienceDirect.com 3
13 Benefits of White Mulberry (Morus Alba)

Morus alba has many claimed benefits, including lowering blood sugar and fat levels, supporting brain function, and preventing bone loss. In addition, the herb has few reported side effects. Read this post to learn about all its potential health benefits and mechanisms. What Is White Mulberry ( Morus alba )?
White mulberry ( Morus alba ) is a small tree native to northern China. During ancient times its primary uses were to feed silkworms and treat various illnesses.
White mulberry contains many unique active compounds and flavonoids that confer a broad range of potential benefits.
Its leaves and roots can be prepared in a tea, while its berries can be eaten whole or made into wine. Constituents
White mulberry contains many natural polyphenols and flavonoids, which have potential antioxidant , anti-inflammatory , anticancer , and antibacterial properties [ 1 , 2 ].
Compared to the stems and fruits, the leaves contain more phenolic compounds and flavonoids [ 3 ]. Apigenin
Morin
Isoquercitrin
Anthocyanins
Caffeic acid
Gallic acid
Umbelliferone
Additionally, white mulberry contains many constituents that are unique to the plant: Moracin has potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties [ 2 ]
Snapshot
Proponents
May lower blood sugar
May reduce the risk of heart disease
May support brain function
Few mild adverse effects reported
Skeptics
Insufficient evidence for most benefits
May interact with antidiabetic and immunosuppressant medication
Health Benefits
Possibly Effective for:
Diabetes
In 4 clinical trials on 101 healthy people, white mulberry leaf extract reduced carbohydrate digestion and absorption, resulting in decreased blood sugar and insulin spikes after meals [ 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 ].Similarly, the extract reduced fasting sugar levels and sugar and insulin spikes after meals in 3 clinical trials on 84 people with type 2 diabetes or at risk of developing this condition [ 15 , 16 , 17 ].A nutraceutical complex with white mulberry extract, red yeast rice , and berberine l owered fasting glucose , blood insulin, and hemoglobin bound to sugar (glycated hemoglobin) in 2 trials on almost 400 people with high blood fat levels, possibly reducing their risk of developing type 2 diabetes [ 18 , 19 ].White mulberry leaf extract also improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in obese mice. In cels, it decreased glucose levels by increasing the production of its transporter GLUT4 [ 20 , 21 ].White mulberry extract may also help with diabetic complications. It improved the antioxidant status and blood fat profile in a clinical trial on 60 diabetic people with kidney damage, possibly slowing the progression of the disease. In diabetic mice, its antioxidant and sugar-lowering activity protected the eyes against cell death [ 22 , 23 ].All in all, the evidence suggests that white mulberry may help lower blood sugar levels. You may discuss with your doctor if it may be helpful in your case. Importantly, never take white mulberry supplements in place of the antidiabetic medication prescribed by your doctor . Insufficient Evidence for: 1) Preventing Heart Disease In 2 clinical trials on 48 people with high blood fat levels, white mulberry extract lowered triglycerides , total cholesterol , “bad” ( LDL ) cholesterol, and markers of inflammation ( CRP ) and oxidative damage (8-isoprostane), while increasing “good” ( HDL ) cholesterol [ 24 , 25 ].Similarly, a nutraceutical complex with white mulberry, red yeast rice, and berberine lowered total and LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure in 2 trials on almost 400 people with this condition [ 19 , 18 ]White mulberry extract also decreased fat buildup in the blood vessels and lowered blood pressure in animal studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 ].Although the results are promising, only 4 clinical trials have been carried out (two of which combined white mulberry extract with other compounds that may lower cholesterol and blood pressure). Larger, more robust clinical trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results. 2) Improving Memory and Learning In a study of 60 adults, 1-2.1 grams per day of white mulberry leaf extract enhanced brain function and memory [ 29 ].In mice, white mulberry extract increased NGF levels, leading to increased brain cell growth . The mice then had enhanced learning and memory (as seen by their improved retention and object recognition time) [ 30 ].In another study, rats treated with white mulberry extract showed improved memory , as well as increased brain cell density and reduced oxidative stress in the brain [ 31 ].A single clinical trial and some animal research cannot be considered sufficient evidence to claim that white mulberry improves memory and learning. Further clinical research is required. 3) Whitening the Skin Both white mulberry root bark and leaves can whiten the skin, suggesting their potential application in skin-lightening cosmetics [ 29 +].A 75% white mulberry oil reduced skin pigmentation in a clinical trial on 50 people with a condition that causes dark patches on the skin (melasma) [ 32 ].Mulberroside F is likely responsible for this effect. In mouse cells, it inhibited melanin formation and tyrosinase activity [ 33 ].Again, only one clinical trial is insufficient to support this potential use of white mulberry. More clinical trials on larger populations are needed. 4) Obesity In a clinical trial on 46 overweight people eating a low-calorie, balanced diet, supplementation with white mulberry extract enhanced weight loss by approximately 3x (10 kg versus 3.2 kg in the placebo group) [ 34 ].The combination of white mulberry with other plant extracts suppressed appetite and lowered fat levels in mice [ 35 , 36 ].White mulberry may also protect against obesity-related diseases . In mice, its leaf extract kept Nrf2 levels at a balance. This may balance fat production, produce antioxidant enzymes, and prevent obesity -related fatty liver diseases [ 37 ].Once again, only a small clinical trial and some animal research support the use of white mulberry to reduce obesity and its complications. More clinical research is needed. 5) Bone Loss A combination o white […]