Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Top-Line Results of Phase 2 SIGNAL Study in Huntington’s Disease Support Potential for Cognitive Benefit of Pepinemab
K ey cognitive endpoint s trending towards but did not reach statistical significance in early manifest population . O verall study does not meet pre-specified co- primary endpoints
Results support continued development in Alzheimer’s disease and in mid-stage Huntington’s disease patients with greater cognitive deficits
Company to host investor conference call today, September 22, at 8:30 a.m. EDT
To access the call and webcast, please click h e re .
ROCHESTER, N.Y., Sept. 22, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Vaccinex, Inc. (Nasdaq: VCNX), a clinical-stage biotechnology company pioneering a differentiated approach to treating cancer and neurodegenerative disease through the inhibition of SEMA4D, today announced topline results from the early manifest treatment arm (Cohort B1, N=179) of the Phase 2 double-blind, placebo-controlled SIGNAL trial of its lead clinical candidate, pepinemab, in patients with early manifest and prodromal Huntington’s disease (HD).
Maurice Zauderer, Ph.D., president and chief executive officer of Vaccinex remarked on the trial results, “HD affects multiple regions of the brain and disease progression impacts many critical functions including cognition and motor activity. The results reported today strongly support a cognitive benefit to treatment with pepinemab and indicate that treatment with pepinemab antibody potentially targets cortical centers, including those that govern cognition. The first sign of HD is often chorea and cognitive disturbances generally follow later in disease progression. We believe the data, therefore, suggest that patients at a somewhat more advanced stage of HD may derive the greatest benefit from pepinemab.” Dr. Zauderer further noted that, “The insights gained from this study also suggest that pepinemab might be an important treatment option for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases known to primarily affect frontal cortex and to impact cognition. As previously reported, imaging data indicate that these are the brain regions most affected by pepinemab treatment. The company has, accordingly, initiated screening and expects to begin enrolling patients this month in a new Alzheimer’s disease study of pepinemab at 15 clinical sites in the United States. In line with the Company’s ongoing efforts in Alzheimer’s, as well as in head and neck cancer, the Company also intends to examine and, as appropriate, prioritize and balance its budget and expenditures.”
Dr, Zauderer concluded, “We are profoundly grateful to the patients and their families for their initiative and enthusiasm in participating in this study and their courage in confronting the burdens of this disease.”
The study had two co-primary endpoints, a family of two cognitive assessments from the Huntington’s Disease Cognitive Assessment Battery and Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGIC). Although the study did not meet pre-specified co-primary endpoints, the results of each of the two cognitive assessments demonstrated a strong trend for beneficial change (OTS, p=0.028 and PTAP, p=0.06). These cognitive assessments reflect changes in planning ability and memory associated with disease progression. Similarly, a trend of benefit in CGIC did not show a statistically significant difference between the placebo and pepinemab-treated groups, possibly due to small group size in this phase 2 study.
Pepinemab was well-tolerated with remarkably low treatment discontinuation and study drop-out rates over the extended 18 month treatment period. Additional results including a broader examination of motor activity and outcomes for a smaller group of 86 prodromal subjects will be reported in detail at the upcoming 2020 Huntington’s Study Group Conference on October 30 and at subsequent medical conferences.
Conference call details:
Vaccinex management will host a conference call and webcast today, September 22, at 8:30 a.m. EDT. To access the call and webcast, please click here .
About the SIGNAL trial
SIGNAL was a multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of pepinemab as a potential treatment for people with Huntington’s disease, a devastating neurodegenerative disease with currently no effective disease modifying treatment. The study had two sequential Cohorts. The primary outcome of Cohort A was safety and pepinemab appeared to be well-tolerated. Additional data from SIGNAL Cohort A demonstrated that pepinemab treatment results in an increase in FDG-PET signal, a measure of brain metabolic activity, primarily in cortical regions. This is in contrast to the decrease observed in the placebo group and that has been described in the natural history of this and other neurodegenerative diseases. The design of the subsequent Cohort B was informed by the results of Cohort A and enrolled 265 subjects, 179 early manifest patients (Cohort B1) and 86 late prodromal subjects (Cohort B2) for randomized treatment of at least 18 months duration.
About Pepinemab
Pepinemab, also known as VX15/2503, is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds and blocks the activity of semaphorin 4D (SEMA4D) which is an extracellular signaling molecule that regulates the migration and function of immune and inflammatory cells. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that the biological activities associated with antibody blockade of SEMA4D promote immune cell infiltration into tumors and prevent neurological damage in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disease models. Vaccinex is focused on the development of pepinemab for the treatment of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases including Huntington’s and Alzheimer’s disease. As previously announced, encouraging results have been obtained in a study of pepinemab in combination with avelumab checkpoint inhibitor in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. A new collaboration with Merck to test the combination of pepinemab with pembrolizumab in Head & Neck Cancer is expected to begin in early 2021. Pepinemab is an investigational new drug that has not yet been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or other regulatory authorities for any indication.
About Vaccinex, Inc.
Vaccinex, Inc. is a clinical-stage immunotherapy company engaged in the discovery and development of targeted biotherapeutics to treat serious diseases and conditions with unmet medical needs, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and autoimmune disorders, with currently active clinical trials in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Huntington’s and Alzheimer’s disease and a recently announced collaboration with Merck for combination therapy with pepinemab and pembrolizumab in Head & Neck cancer. Vaccinex is based in Rochester, New York.
Forward Looking Statements
To the extent that statements contained in this press release are not descriptions of historical facts regarding Vaccinex, Inc. (“Vaccinex,” “we,” […]
5 Herbs That Help To Boost Your Stamina by Jessica K

Image par congerdesign de Pixabay
The fast-paced schedules of today demand stamina to perform the best. With deadline goals at work and non-stop chores at home, it is essential to have energy and stamina to go through the day and deliver the best in everything. Stamina is not only of the body and physical stamina but also mental stamina and strength to keep the body and the mind functioning coordinately. As such, there are many ways to boost stamina and endurance. Herbs are one of them!
Natural herbs are a perfect way of boosting energy and sustaining the driving force for the day. It gives the much-needed boost that coffee and energy drinks cannot give for the entire day. Herbs give a balanced energy power and boost the energy reserve of the body to deliver efficiently . There are primarily three categories of herbs that boost energy: Tonics- that creates a balance and relaxes the body.
Adaptogens- that adapt to the varied conditions of the body and maintain proper physiological balance in the body.
Stimulants- that boost the energy in a controlled form.
The following are some of the essential herbs that effectively boost energy in the human body.
Eleuthero
The Eleuthero herb, also known as the Siberian Ginseng, is an adaptogenic herb found in China, Russia, Korea, and Japan. The herb is in use for years in traditional Chinese medicine. It is proven to boost the energy levels of the body and calm a person during stressful times . The herb also creates a right balance between the mental and physical functioning of the human body. Additionally, it is also useful in increasing blood circulation and improving memory retention and concentration power. Eleuthero also boosts the body’s healing processes and prevents the occurrence of ulcers. You can take Eleuthero herb as a root powder supplement in foods.
Rhodiola Rosea
This herb is famous as the ‚golden root‘ and available in Europe, Russia, Canada, and the Arctic. It is mostly used by athletes and military professionals to boost stamina and strengthen the body. The herb can thrive in colder and hostile climates. As per a study, Rhodiola Rosea enhanced brain function and showed increased mental capacity in soldiers. You can take the Rhodiola Rose as supplements in the form of tablets or eat the root raw. The herb is also available as a form of tea.
Kratom
Kratom is a tropical herb found in Southeast Asia. The herb contains specific compounds that have psychotropic effects. The leaves of the Kratom herb are used as a recreational drug and supplement to boost stamina in the human body. The herb is perfect for people who have rigorous schedules and require them to be on their toes always. It is believed that using kratom strains like Malay kratom,maeng da kratom as a pre-workout supplement will give you an energy boost, focus & stamina required to last throughout the entire activity time. Ideally, taking up to 5 grams dosage 45 minutes prior exercise could benefit you. You can take bulk Kratom as a pill, powder supplement, or as a capsule. The leaves of the herb can also be eaten raw.
Ginseng
Ginseng is a famous tonic herb used widely across Asia and the US for its energy-boosting and anti-inflammatory properties. It is one of the popular herbal supplements and has its original roots in China. The Ginseng herb is a good supplement for increasing stamina in everyday life. Studies also showed that ginseng is effective in improving erectile dysfunction in men. Ginseng also boosts the health of cancer patients who go through regular chemotherapy sessions. You can eat the Ginseng root raw, steam it, or mix it with foods. It can also be simmered in hot water and taken as tea.
Brahmi
The Brahmi or the Water Hyssop is a perennial stimulant herb that has its original roots in India. It has stimulating mental effects and is also available in the Caribbean and Australia. The herb consists of phytochemicals, which cause the inotropic effects in the human body. It can also be taken as a powder with hot water as a herbal drink. The herb mostly thrives in aquatic conditions and is a storehouse of antioxidants. Brahmi is an essential aid of enhancing brain function, memory retention, and in reducing ADHD symptoms. You can take Brahmi in tablet form or as a powder mixed with foods.
Conclusion:
Herbs are the right way of enhancing the strength and endurance of a person.Moreover if taken in the long term,these act as a powerful immunity booster.You can take these herbs as supplements to your regular diet to absorb their benefits. Take them as powder or tablet form and boost your power for any rigorous schedule come what may!
3 Ways Exercise Benefits Your Mental Health

When you work your body, you boost your mind in three essential ways. Cognition
A new report from researchers at the University of Basel in Switzerland and the University of Tsukuba in Japan has found that coordinated and challenging sports with fellow players, like tennis or soccer, have a greater effect on cognitive abilities than solo fitness activities. The report analyzed 80 studies covering various types and aspects of exercise—including strength training, endurance training, and exercise intensity—and how they impact cognitive performance. While all types of exercise were found to increase cognitive abilities, the greatest benefit came from sports that combined complex sets of movements and interaction with other players. Increased benefit came in the form of growth of new brain cells and neural connections in the frontal lobe.
University of Basel researcher Sebastian Ludyga, PhD, who cowrote the report, says that partner sportsare particularly valuable to cognition because they force our brains to react quickly under pressure to “the somewhat unpredictable movements of our teammates or opponents.”
The report refuted the idea that the more exercise you do, the more mentally fit you’ll become. According to the findings, the type of exercise is more important for cognitive improvement than its frequency or duration. Memory
Aerobic exercise in particular plays a big role in your memory, says Wendy Suzuki, PhD, professor of neural science and psychology at New York University’s Center for Neural Science. “When you exercise, your body pumps out a wide range of neurochemicals, including growth factors that stimulate the birth of brand-new brain cells in the hippocampus. That’s the area of the brain that’s critical for storing long-term memories,” she says. “I use that as my personal motivation to keep working out every day.”
A recent study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found a 47 percent improvement in memory scores among the group who did aerobic exercise for a year versus those who only did stretching exercises. Aerobics were shown to increase blood flow to the hippocampus, which may help protect against memory loss for those at risk of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. Mood
Just a single session of exercise can improve your mood, Suzuki says. Each time we exercise, it encourages our brain to release chemicals like serotonin (which regulates mood, sleep, and hunger) and our natural mood lifters, endorphins. A 2019 study published in Preventive Medicine found that people who did strength training or aerobic activities like walking, running, and cycling reported fewer depressive symptoms. Research also shows that exercise can improve the quality and length of sleep, which is important for mental health and mood. Cumulative exercise can even permanently change the structure and function of our brains for the better, Suzuki says.
“The good news is that we can do an easy form of self-experimentation to decide which type of movement puts us in the best mood,” she says. “For some, it will be dancing to a favorite song in the living room; for others, it will be a five-mile run in nature.”
25 Ways You Make Yourself Sick Without Realizing It

Sure, you know that eating junk food, avoiding exercise, and drinking like a fish isn’t going to do any favors for your health, especially during a pandemic. However, did you know there are many other habits, rituals, and practices most of us engage in that are also damaging our well-being—only we have no idea? Read on to hear the top health and medical experts around the country reveal all the ways that you’re inadvertently harming yourself. Read on, and to ensure your health and the health of others, don’t miss these Sure Signs You’ve Already Had Coronavirus . Shutterstock You might think you are eating a super-healthy diet, but are in fact consuming dangerous chemicals. “Most grain and soy products in North America are sprayed with glyphosate, a known carcinogen and gut microbiome disruptor,” explains Dr. Steven Gundry, MD , medical director at The International Heart and Lung Institute Center for Restorative Medicine and the New York Times best-selling author of The Plant Paradox and The Plant Paradox Cookbook . Basically, we unwittingly eat glyphosate while eating “healthy” whole grain products. He points out that even new plant-based hamburger meat products may have glyphosate in them—as well as most of our animal products like chicken, beef or pork, as most are fed with these same tainted grains and/or soy.
The Rx: In order to avoid eating foods tainted by glyphosate, there are a number of things you can do. Eat organically, eat locally by shopping at your farmer’s market for meat and produce, or grow your own produce. Shutterstock Dr. Gundry points out that the vast majority of whole grain products are loaded with plant proteins called lectins which are part of the plant’s defense system against being eaten. “As The Plant Paradox series show, lectins are major causes of leaky gut, arthritis, depression, weight gain and brain and heart disease as well as autoimmune diseases,” he explains.
The Rx: Reduce your gluten consumption. “As I have reported at The American Heart Association, most patients who remove gluten and other lectin-containing foods resolve autoimmune issues and leaky gut within months,” he says. Shutterstock Artificial sweeteners might be a zero-calorie sugar-free alternative, but they aren’t doing any wonders for your digestive system. “Most people who use artificial sweeteners have no idea that they are destroying and altering their gut bacteria, the microbiome with every packet, the same bacteria that have the potential to keep them lean and happy,” Dr. Gundry says.
The Rx: Try to avoid artificial sweeteners. If you need a boost of sweet, you can always opt for a natural sweetener such as stevia. Shutterstock You might not realize it, but certain positions while sleeping can damage your health. “Many people will sleep every night on their sides in the fetal position. While this seems harmless, this sleeping position can actually be detrimental to your health,” points out David Greuner, MD , of NYC Surgical Associates. “When you sleep like this, it cuts your diaphragm’s free range down which can cause back pain as well as issues with your lungs.”
The Rx: Try another sleeping position. According to the National Sleep Foundation , the healthiest way to sleep in on your back. Shutterstock It can be hard to remember to drink enough fluids. But try and remember it can be hazardous to your health. “Vein insufficiency can be amplified due to dehydration,” explains Dr. Greuner. “When you are hydrated your blood is thinner and flows better. When your blood is thicker, it can make vein insufficiency problems worse.”
The Rx: Drink lots of fluids! The Institute of Medicine of the National Academies of Sciences recommends 2.7 (11 cups) liters to 3.7 liters (nearly 16 cups) per day . “Make sure to stay hydrated to keep your entire body healthy including your veins!” says Dr. Greuner. Shutterstock Just because a product is called “organic” doesn’t mean it is good for you. “Many packaged products are highly processed, and may contain many unhealthy ingredients,” points out Talia Segal Fidler , MS, HHC, AADP, nutritionist at The Lodge at Woodloch. For example, they may contain a high sugar content. “Even though it is organic, it is still sugar and still a processed product.”
The Rx: Remember that processed food is processed food and sugar is sugar—even if it has an organic label on it. Shutterstock Most of us were raised believing that drinking fruit juice was actually good for you. However, Fidler points out that many fruit juices are loaded with sugar and high fructose corn syrup. “There are hardly any connections between the fruits and that beverage,” she explains. “You are basically only consuming sugar!”
The Rx: If you are going to drink juice, look for ones that are 100 percent juice and no added sugar. Better yet, eat a piece of fruit instead, so you get the belly-filling fiber. Shutterstock Eating yogurt that has added fruits, or giving it to children thinking it is a good thing, is pretty common. Unfortunately, Fidler points out that those “fruits” are loaded with unhealthy sugar which defeats the purpose.
The Rx: “A better choice is to buy plain organic yogurt and add freshly cut fruits to it,” Fidler suggests. “For extra sweetness you can add a bit of local honey.” Shutterstock Sure, many fish are high in good fats and can be a great addition to your diet. However, Fidler points out that size matters when it comes to just how healthy a swimmer is. “The larger the fish, the more likely that it may have a high mercury levels and other toxins,” she explains. This is due to the fact that the fish has lived longer and accumulated toxins overtime.
The Rx: Fidler suggests eating smaller fish, such as sardines, mackerel anchovies etc. Or, opt for a deep-water fish that isn’t exposed to the same toxins. Shutterstock While farm raised salmon may boast health benefits in the form of omega 3 fatty acids, they can also be contaminated with toxins, explains […]
Feeling tired after enjoying a cup of coffee? You should probably limit your caffeine intake, advise researchers

( Natural News ) A lot of people rely on coffee to keep them awake and improve their focus. That’s because coffee contains caffeine, a natural stimulant that’s also found in tea and cacao plants.
But if you’re a frequent coffee drinker and notice you’re feeling more tired, you might need to lay off coffee – experts say that caffeine can make some people feel more tired and sleepy than energized.
Not everyone reacts to a certain foods or drinks the same way. For example, some people can drink multiple cups of coffee a day and experience little to no unwanted effects. But some people can experience adverse effects after drinking just one cup of coffee.
The list below describes how coffee makes you feel tired: 1. Caffeine blocks adenosine from binding to its receptors
Adenosine is a brain chemical that plays a vital role in facilitating sleep; when it binds to its receptors, neural activity slows down and a person feels sleepy. Adenosine levels increase during wake hours and decrease during sleep.
When you drink coffee, caffeine binds to adenosine receptors. But it does not halt the production of adenosine or the body’s ability to make more adenosine receptors. As a result, there’s a buildup of adenosine waiting to bind to its receptors. This can lead to sleepiness and feelings of tiredness once the effects of coffee wear off.
The length of time that caffeine stays in the body varies from one person to another. Some people may be more susceptible to this unwanted effect than others. 2. Coffee drinkers develop caffeine tolerance
Habitual drinkers of coffee may develop caffeine tolerance, which occurs when caffeine becomes less effective as a stimulant. That’s because the body may learn to adapt by producing more adenosine receptors. This allows more adenosine to bind to its receptors and offset the effects of caffeine.
Research also showed that regular intake may lead to caffeine tolerance. One study looked at the effects of continuous caffeine consumption on the cycling performance of 11 adults. In the beginning, the participants demonstrated higher heart rates and greater cycling power after consuming caffeine. After 15 days, researchers observed that the effects of the stimulant began to decrease. 3. Coffee can raise blood sugar levels
Caffeine in coffee has been found to increase blood sugar levels. A meta-analysis found that it can temporarily reduce insulin sensitivity. Meanwhile, another study concluded that consuming 100 mg of caffeine impaired glucose metabolism in 10 healthy males with excess weight.
In turn, high levels of blood sugar can lead to a host of conditions, such as fatigue, headaches and difficulty in concentrating.
The amount of sugar in your coffee can also contribute to higher levels of blood sugar. Sugar may take the form of whipped cream or shots of syrup, which are a standard in specialty drinks. You may try adding less sugar if you find limiting coffee consumption difficult. 4. Coffee is a diuretic
Caffeine is considered a diuretic, a substance that makes you urinate more often. Therefore, your body can lose great amounts of fluid, which can lead to dehydration.
Coffee-drinkers who go to the bathroom more frequently than usual can get stuck in a cycle of dehydration that can make them feel more tired.
For one, water loss can lead to a decrease in blood volume . This puts excess pressure on the heart to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the organs, including the muscles. The body makes do with low fluid levels, leading you to feel tired and sluggish.
While some people need coffee to boost their day, caffeine in the drink may cause tiredness and sleepiness. If you notice these symptoms, try limiting drinking coffee and opt for other energizing foods such as dark chocolate , whole grains and meat.
Learn more about ways of preventing fatigue at Prevention.news .
Sources include:
Healthline.com
Managing depression: 5 mood boosting oils that help

Essential oils can help you come out of your depression by relaxing your mind and body and relieving you of anxiety and stress. @Shutterstock Feeling sad and depressed is a part of life and everybody goes through low phases in their lives once in a while. But when this feeling of sadness, anger and loss goes on for a long time, you need to sit up and take notice. Chronic depression is a debilitating condition that can interfere with your daily life. It can lead to job losses and relationship problems. In some cases, it can also drive a person to suicide. There are many reasons behind this condition. But whatever the reason, if you are depressed you need to get advice from a doctor. Simultaneously, you may also try and get relief with some home remedies. One such natural treatment for depression is aromatherapy, which involves the use of essential oils. Also Read – Ayahuasca: Know the benefits and side effects of this trending psychoactive brew
Essential oils are extracts of herbs and plants that have potent therapeutic properties. These oils can rejuvenate and energise you. Some can even help you come out of your depression by relaxing your mind and body and relieving you of anxiety and stress. These oils work by influencing the brain’s limbic system. This is the part of the brain that controls emotions, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and smell. These essential oils help in preventing depression and anxiety. Also Read – What is CBD oil and why it is increasingly gaining attention from researchers?
Here, we reveal a few such oils that you can use to get relief from your condition. Also Read – Fight depression by making the right food choices Lavender Oil
This essential oil has been used for relaxation since ancient times. Even the Romans are said to have added it to their bath for this very reason. It also uplifts your mood and makes you more happy. By bringing down your anxiety levels and making you calmer. It induces better sleep too, which is so important for a patient of chronic depression. This oil can also boost your immunity and make you body more resilient to infections and diseases. Just add a few drops of lavender oil to your bath water and soak in it for as long as you are comfortable. This will also make your skin soft and supple. Alternatively, you may also use this oil in your oil diffusor while sleeping at night. If you feel you need an instant mood boost, just inhale the perfume directly from the bottle. You will be surprised at the effects. Jasmine oil
According to scientists, jasmine oil can have a calming effect and reduce anxiety, stress and aggression significantly. It induces a general feeling of wellness and makes you more energetic. However, pregnant women must stay away from this oil as it can induce early labor. You can dab this oil on to your wrists or add it to your oil diffusor. A quick whiff from the bottle will also do the trick. Rose oil
This prevents anxiety and depression. The sweet scent of roses can boost self-esteem, make you more confident and productive. It also stimulates your libido and induces a general sense of happiness and well-being. Add a few drops of this essential oil to your diffuser every day. You can also smell the perfume directly from the bottle for a quick mood boost. Basil oil
This essential oil, which is rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, has a calming effect on your nervous system. At the same time, it also stimulates your adrenal glands. This prevents sluggishness and increases your motivation and drive. This is very important if you are a patient of chronic depression. This oil makes you more happy, helps relieve stress and anxiety, makes you energetic and also more productive. But avoid it if you are pregnant as it can lead to premature contractions. Just add this oil to your diffuser every morning. Lemon oil
Need an instant mood boost? Then this is the oil for you. Lemon essential oil makes you happier a happier person by boosting your dopamine and serotonin level, hormones that are responsible for your overall happiness. It also makes you more mentally alert and improves concentration and productivity. This oil will improve mood and prevent depression. All you need to do is add a few drops to your diffuser.
18 healthy herbal teas worth buying

Who doesn’t enjoy a comforting cuppa every now and again? Whether you’re sipping a dried herbal tea, brewing fresh leaves, or trying one of the many healthy tea options from your local health store, there’s nothing quite like a fresh pot to soothe the soul.
Traditional teas – which include green tea , black tea, white tea, and oolong tea – are all brewed from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, and vary only in terms of the way they are processed.
Herbal tea, meanwhile, is made from various fruits, flowers, spices and herbs, or a combination of them, so they’re incredibly diverse in flavour. Even though herbal tea has been used as a natural medicine for centuries, the health properties of these teas are only just being established in scientific literature. 18 healthy herbal teas
We asked Dr Tim Bond of the Tea Advisory Panel to talk us through the emerging evidence-backed benefits of a variety of healthy teas. 1. Hibiscus tea
There are several hundred species of hibiscus that vary according to location and climate, but Hibiscus sabdariffa is most commonly used to make hibiscus tea. Known for its tart flavour, hibiscus tea – made from the deep red flower of this tropical plant – is rich in powerful antioxidants and has been shown to be beneficial for heart health.
‘A systematic review of nine randomised controlled trials (RTCs) and six laboratory studies found that hibiscus tea can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health and wellness, particularly blood pressure,’ says Bond. ‘Emerging research also reveals potential benefits in terms of its ability to favourably impact lipid profiles, inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance.’ 2. Echinacea tea
Echinacea – also called coneflower – refers to a group of flowering plants that form part of the daisy family. Packed with beneficial plant compounds, it’s been linked to health benefits that range from fighting inflammation to reducing blood sugar levels. Echinacea tea, which is made from both the upper parts and roots of the plant, is frequently used as a cold and flu remedy.
‘Echinacea is high in antioxidants,’ says Bond. ‘Some research suggests that echinacea may help stimulate immune activity to shorten bacterial infections and viruses. A study in 95 people found that five to six cups of echinacea tea daily at early onset of cold and flu symptoms was effective for reducing symptoms compared with placebo.’ 3. Sage tea
Delicate, sweet and earthy, sage tea is made from the leaves of the common sage plant, a perennial evergreen shrub that forms part of the mint family. This aromatic herb is rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds, says Bond, including rosmarinic acid and carnosol.
‘Sage tea may help to boost heart health,’ he continues. ‘A small, four-week study in six women, drinking 10 x 300ml mugs of sage tea twice daily resulted in 16 per cent lower total cholesterol, 20 percent lower ‘bad’ LDL cholesterol , and 38 per cent higher ‘good’ HDL cholesterol.’
Sage tea may also be beneficial for people with diabetes and women experiencing menopause. ‘A two-month study in 105 adults with type 2 diabetes found that sage extract three times daily improved blood sugar and HBA1c – a measure of blood glucose control over the previous three months,’ says Bond. ‘A 2017 review suggested that sage might reduce menopausal symptoms of hot flushes.’ 4. Lemon balm tea
Lemon balm is a lemon-scented herb from the mint family. It’s best known for its stress-soothing properties. ‘Lemon balm tea may help you to relax and unwind,’ says Bond. ‘One small pilot human study showed a 42 per cent reduction in insomnia symptoms after participants received 600 mg of lemon balm extract per day for 15 days.
Lemon balm has been shown to increase gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in the brain – an inhibitory neurotransmitter known for reducing overwhelming feelings of anxiety – in laboratory studies , ‘which may explain its sedative effects,’ Bond says. Like sage, lemon balm may also reduce menopausal symptoms of hot flushes. 5. Rose hip tea
Rose hips are small, round ‘fruits’ found just below rose petals. While there are hundreds of species of rose plants, rose hip research has focused mainly on the Rosa canina variety. Rose hip is rich in plant polyphenol antioxidants, and contains antioxidant vitamins C and E, says Bond.
‘Rose hips have the highest vitamin C amongst fruit and vegetables, although amounts vary,’ he says. ‘Vitamin C is an immune function nutrient. There is evidence from laboratory studies that rose hip can benefit immune function parameters though research in humans is so far lacking.’ 6. Passionflower tea
There are about 500 known species of passionflower, known collectively as Passiflora. A natural sleep aid, passionflower – specifically Passiflora incarnata – has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and insomnia by boosting GABA levels in the brain.
‘Traditionally, passionflower has been used to help relieve anxiety and improve sleep ,’ says Bond. ‘One study in 40 healthy adults found that those who drank passionflower tea daily for one week reported significantly better sleep quality compared to participants who did not drink the tea.’ 7. Chamomile tea
An herb that comes from the daisy-like flowers of the Asteraceae plant family, Chamomile is commonly regarded as a mild sedative, and is often consumed as tea before bed to promote sleep . The plant’s calming effects may be attributed to an antioxidant called apigenin, which is found in abundance in chamomile tea, says Bond – apigenin binds to specific receptors in the brain that may decrease anxiety and initiate sleep.
‘A study of 60 nursing home residents found that those who received 400mg of chamomile extract daily had significantly better sleep quality than those who did not receive any,’ he says. ‘Another study involving women who had given birth to a baby and who had poor sleep quality found that those who drank chamomile tea for a two-week period reported overall better sleep quality than those who did not drink chamomile tea.’ 8. Rooibos tea
Also known as red tea […]
9 Health Benefits of Coffee and the Best Ways to Drink It

If you are a big coffee lover but keep hearing from people that it is bad for you, we have great news. There are many health benefits of Coffee if consumed in moderate amounts, of course. Seeing as how billions of cups of joe are consumed daily worldwide, plenty of people have already come to this realization.
So, if you are already obsessed with coffee, keep reading to learn more about it. On the other hand, if you are a tea drinker that is resisting coffee because you heard it’s not healthy, it might be time to give it a try. Take a look below for some tips on the best ways to drink it as well. What are the health benefits of coffee?
If you’re still debating whether you should choose tea over coffee , you need to know that they are similar in many ways and offer similar health benefits. The only difference is the taste, which means that the choice is entirely up to you. With that in mind, what are these health benefits you will get to enjoy if you drink coffee regularly? Reduced risk of cancer
There is plenty of research that links drinking coffee with a reduced risk of developing several types of cancer, which people who advise against this activity are probably not aware of. This is due to caffeine’s ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. A study from 2017 suggests that one cup a day reduces the risk of hepatocellular cancer by 20%. Moreover, as it can regulate insulin and reduce inflammation, drinking coffee regularly can also lower prostate and colorectal cancer risk. Studies also show that chances of breast cancer reoccurring are smaller among people who consume at least two cups of joe per day. Finally, there is less possibility of developing melanoma and basal-cell carcinoma. Seeing as how cancer is the second leading cause of death on a global level, the fact that doing something as simple as drinking coffee regularly can prevent it means a lot. Lower risk of stroke
Besides various types of cancer, moderate coffee intake can also help lower the possibility of suffering a stroke. Every year, over 11 million people worldwide are affected by stroke in one way or another. Sometimes they result in disability while sometimes the outcome is death, unfortunately. According to research, drinking coffee while having a healthy and balanced diet that includes fruits and vegetables, fish, and dairy can reduce stroke risk. Protection from heart disease
While there are studies that concluded that people who consume a lot of this beverage have higher levels of cholesterol and blood lipids, there are also those who have concluded that coffee in moderate amounts can protect from heart disease. What is more, even though some claim that the risk of heart failure is increased by drinking coffee, researchers have disproved them. However, moderation is key. One or two cups a day have their benefits, but more than five is not advised. Photo by The Lazy Artist Gallery from Pexels Decreased chances of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s
Cancer, stroke, and heart disease are not the only health issues that coffee can reduce the risk of. Many diseases that affect people on a large scale, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, still have no cure. Parkinson’s can cause tremors, mobility issues, and speech problems, while Alzheimer’s is the leading cause of dementia. Seeing how medical professionals have still not found a way to cure these, prevention is essential. Regular exercise and a healthy diet combined with regular coffee intake can lower the risk of these issues. Studies found that coffee drinkers are up to 60% less likely to develop Parkinson’s and 65% less likely to have Alzheimer’s . Reduced risk of type-2 diabetes
Type-2 diabetes is another major health condition that impacts millions of people’s lives all over the world. People with a reduced ability to secrete insulin that results in elevated levels of blood sugar can turn to coffee as researchers concluded that a single cup of this beverage a day could reduce the risk of developing type-2 diabetes by 7%. Naturally, drinking coffee with loads of sugar and cream reduces its beneficial effects. Studies have found that black coffee can reduce the risk of this condition by up to 67%. Smaller chances of depression
The number of people struggling with depression keeps rising globally and this issue can seriously reduce the quality of one’s life. While therapy and medication are of great help, it’s also good to know that coffee can act as a mild antidepressant and boost the brain’s feel-good neurotransmitters. A Harvard study from 2011 showed that women that consume four cups a day are at a lower risk of developing depression by 20%. Another study concluded that people who drink that same amount are 53% less likely to try to commit suicide. As it releases serotonin and dopamine, it also helps prevent mood swings and makes people generally happier . Energy and focus boost
Being energized is probably the first thing that comes to mind when thinking about coffee’s benefits, right? That comes as no surprise. Many people drink it as soon as they get out of bed to get through the day. What is more, people who need to pull an all-nighter to study before an exam or work to get a task finished on time also rely on this beverage to help them. Caffeine is a natural stimulant that promotes focus and alertness once absorbed into the bloodstream. This is why people drink it to perk up when they start feeling fatigued or need to figure out a problem they’ve been struggling with. Plus, it also boosts short-term memory. In addition to increasing mental performance, a cup of java can improve physical performance and reduce post-workout pain in the muscles. While this substance is often associated with anxiety and sleep deprivation, research shows that it comes with an abundance of health benefits when consumed in appropriate amounts. Burning fat
[…]
Glyphosate Toxicity Alert: How America’s #1 Weedkiller Tricks Your Body Into Absorbing It

When you’re creating a meal or spraying a stray dandelion in your yard, you probably don’t think about glyphosate toxicity. Still, glyphosate is the most commonly used agricultural pesticide in the world — and a go-to weedkiller in lawns and gardens across America. And although you would never purposely add it to your food or drinking water … you’re still probably consuming it every day. (It’s used so heavily, it’s now detected in rain samples , too.)
The unfortunate truth is, glyphosate is virtually impossible to avoid, so you and your loved ones are probably at risk from its toxic effects right now — unless you take active steps to defend yourself. The Inside Track on Glyphosate
Glyphosate’s primary use involves killing weeds, but it was first patented as a metal chelator (remover) because it binds to minerals (like calcium) to clear them out of pipes. That’s great for pipes, but not for people who need essential minerals to stay strong and healthy.
The herbicide also causes a devastating impact on our internal ecosystem. It kills off beneficial bacteria (probiotics) while giving dangerous pathogens a competitive edge. Research indicates that glyphosate creates and speeds up antibiotic resistance in disease-causing bacteria such as salmonella and E. coli.
In its central role, glyphosate is the most widely used agricultural pesticide in the world, but it’s often combined with other toxic herbicides including: Atrazine
2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid)
Dicamba
Neonicotinoid insecticides
That’s why the vast majority of our conventional food supply is contaminated with glyphosate , almost always along with other toxins. And as we’re finding, these dangerous combinations spell disaster for our personal and planetary health. Glyphosate Toxicity: The Many Dangers
Glyphosate poses an enormous health risk because of our constant exposure. And though each instance of contact with glyphosate may seem small, they all add up — especially since this everyday toxin “tricks” your body into storing it, by mimicking other essential nutrients.
That puts you at higher risk for many troubling health issues, including: Deficiencies in essential minerals such as manganese and iron that can lead to diabetes, dementia, and anemia symptoms
Overgrowth of pathogens in the gut (dysbiosis or “leaky gut”), which disrupts immune function and increases inflammation, putting you at risk for dozens of chronic diseases
Disruption of vital biochemical processes (like detox methylation ), which can lead to toxin overload, autoimmune disease and cancer
Reduced neurotransmitter production, which can cause depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline
Since glyphosate contamination is extremely difficult to avoid, you need to defend yourself against it every day. Pesticides Taint Most Foods
Most plant foods sold in the U.S. come bathed in pesticides. According to the USDA , more than 225 different pesticides can be found on fruits, vegetables, and grains commonly consumed in the U.S. (See the Dirty Dozen list for more details.) Even organic foods are not always spared, since pesticides like glyphosate and others can find their way into organic farms via wind drift or other means.
Glyphosate itself contaminates hundreds of the most common foods. Even though each food may contain only trace amounts of glyphosate, those traces add up to an oversized daily dose. Here’s just a small taste of foods that contain glyphosate in popular brands: Granola bars
Bottled orange juice
Rolled oats
100% whole grain pasta
Hummus
While it may seem impossible to avoid glyphosate and other pesticides, there are things you can do to protect yourself and your family from the harm these toxins can cause. Emphasizing organic foods and products is an important first step. Even though organic produce may still contain some pesticide or toxin residues, levels will be far lower than conventionally-grown items.
There’s also a new, independent certification that manufacturers can obtain to verify products as glyphosate-free. While still in the early stages, this new certification may be something to keep an eye out for, as awareness about the dangers of glyphosate continues to climb. Protect Yourself from Glyphosate Toxicity
There are several things you can do to minimize — and even eliminate — glyphosate contamination, but the most important is to protect your body with natural defenders. That way, as we are chronically exposed to glyphosate, our bodies can safely deal with it before long-term damage is done.
The most effective glyphosate defense team includes:
Citrus pectin: A soluble fiber known to detoxify heavy metals and clear cholesterol through its superior binding powers A lginates (purified from kelp): Proven to protect against pesticide toxicity and effectively remove heavy metals and toxins Glycine: An amino acid needed to create glutathione — a powerful detoxifier and antioxidant that also protects the liver against toxicity. Interestingly, the body can mistake glyphosate for glycine during protein synthesis, tricking it into storing toxic glyphosate in tissues and organs. By supplementing with extra glycine, we can prevent glyphosate from being stored, enhance glutathione activity, and help support healthy protein production.The top glycine-rich sources include collagen and bone broth, but it’s also found in legumes, meat, dairy, poultry, eggs and fish. Even some fruits and vegetables contain glycine, like spinach, cabbage, kale, bananas and cauliflower. Gingko biloba: An ancient herb found to be a powerful protector against glyphosate toxicity Organic Iceland kelp: A rich source of protective minerals including iodine, which prevents the absorption of radioactive ions and toxic pesticide halogens like fluoride, bromide, and chlorine Probiotics and prebiotics : Needed to restore beneficial gut bacteria killed off by glyphosateIn my practice, I recommend a targeted detox formula with these detox binders, to safely remove glyphosate and other agricultural toxins, prevent them from being stored in the body, and support thyroid, GI health, and other areas.Pesticides and environmental toxins represent a daily problem that require daily solutions—especially since our levels of exposure are on the rise. Supporting your body with safe, natural detoxifiers offers the best defense against glyphosate along with other pesticides and toxins, with additional protective benefits for long-term health and wellness.
The incredible science-backed health benefits of cumin

( Natural News ) Merchants in early civilizations traded a host of prized possessions. Many of them include spices, treasured not only for their culinary uses but also for their medicinal properties.
One such spice is cumin, which is made from the dried seeds of the Cuminum cyminum plant of the parsley family. Various cultures around the world use cumin seeds and powder as both a spice and a powerful healing agent. In India, for example, cumin has long served as a staple in natural medicine and as a traditional ingredient in curry.
Modern science has recently become privy to the potential health benefits of cumin. Research into the matter is growing, with studies demonstrating that the spice is a powerful superfood that may help treat a host of medical conditions, including diabetes and bacterial and yeast infections.
Some of the health benefits of cumin include: 1. Helps treat bacterial infections
Cumin has antimicrobial properties that can help treat infections and enhance the effectiveness of current antibiotics.
One study found that cumin seed oil inhibits the growth of the bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae by decreasing biofilm formation, a defense mechanism used by the bacteria against antibiotics. It also enhanced the antimicrobial activity of conventional antibiotics such as ciproflaxins.
Other studies also found that cumin seed oil and alcoholic extracts can be effective at fighting the superbug Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and three different strains of the yeast Candida albicans . 2. Helps manage diabetes
Cumin’s anti-diabetic properties help treat diabetes and reduce its symptoms, including diabetes associated cataracts.
According to one study, the methanolic extract of cumin seeds can lower blood sugar levels comparably to glyburide, a drug used to treat Type 2 diabetes . Cumin was also found to be effective at fighting oxidative stress and reducing advanced glycated end products (AGEs).
AGEs are harmful compounds that are formed when protein or fat combine with sugar in the bloodstream. They are implicated in a variety of diseases, including diabetes – people with high blood sugar levels are prone to produce more AGEs. 3. Improves cognition
Cumin enhances cognition by reducing stress and improving memory .
A study on mice looked at the effects of cumin extract on signs of stress and found a lower stress response in mice that received cumin extract. The researchers added that they also demonstrated faster recall.
The researchers attributed their findings to the antioxidant properties of cumin, which helped fight oxidative stress that could affect brain health. 4. Helps prevent blood clotting
Cumin helps prevent blood clotting, or thrombosis. Research explored the potential anti-aggregatory agents in cumin extract and found that it inhibits platelet aggregation, suggesting that it may be useful for preventing blood clots. 5. Improves cholesterol levels
Cumin helps improve cholesterol levels, which are an important biomarker for heart disease.
A study on overweight adults examined the potential benefits of cumin and found that taking 3 g of cumin powder a day led to lower levels of triglycerides and low-density lipoproteins or “bad” cholesterol. In addition, it led to higher levels of high-density lipoproteins or “good” cholesterol.
Oil extracts of black cumin seeds are also rich in healthy fatty acids that help maintain healthy cholesterol levels. These include linoleic acid and oleic acid, which are unsaturated fatty acids that are found to be good for heart health. 6. Improves gut health
Research also shows that cumin can relieve an upset stomach and improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
A study looked at the effects of consuming cumin essential oil drops on the symptoms of IBS. Participants reported experiencing improvements including reduced stomach pain and bloating after taking cumin for four weeks. (Related: Black Cumin Seeds for Cancer, Autoimmune Disorders, Asthma, and More .)
Cumin , a spice known not just for its culinary use, is a powerful superfood that’s highly beneficial to health. Incorporate more of this spice into your meals and see its health benefits work wonders on your body.
Sources include:
Healthline.com 1
Healthline.com 2
18 healthy herbal teas worth buying

Who doesn’t enjoy a comforting cuppa every now and again? Whether you’re sipping a dried herbal tea, brewing fresh leaves, or trying one of the many healthy tea options from your local health store, there’s nothing quite like a fresh pot to soothe the soul.
Traditional teas – which include green tea , black tea, white tea, and oolong tea – are all brewed from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, and vary only in terms of the way they are processed.
Herbal tea, meanwhile, is made from various fruits, flowers, spices and herbs, or a combination of them, so they’re incredibly diverse in flavour. Even though herbal tea has been used as a natural medicine for centuries, the health properties of these teas are only just being established in scientific literature. 18 healthy herbal teas
We asked Dr Tim Bond of the Tea Advisory Panel to talk us through the emerging evidence-backed benefits of a variety of healthy teas. 1. Hibiscus tea
There are several hundred species of hibiscus that vary according to location and climate, but Hibiscus sabdariffa is most commonly used to make hibiscus tea. Known for its tart flavour, hibiscus tea – made from the deep red flower of this tropical plant – is rich in powerful antioxidants and has been shown to be beneficial for heart health.
‘A systematic review of nine randomised controlled trials (RTCs) and six laboratory studies found that hibiscus tea can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health and wellness, particularly blood pressure,’ says Bond. ‘Emerging research also reveals potential benefits in terms of its ability to favourably impact lipid profiles, inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance.’ 2. Echinacea tea
Echinacea – also called coneflower – refers to a group of flowering plants that form part of the daisy family. Packed with beneficial plant compounds, it’s been linked to health benefits that range from fighting inflammation to reducing blood sugar levels. Echinacea tea, which is made from both the upper parts and roots of the plant, is frequently used as a cold and flu remedy.
‘Echinacea is high in antioxidants,’ says Bond. ‘Some research suggests that echinacea may help stimulate immune activity to shorten bacterial infections and viruses. A study in 95 people found that five to six cups of echinacea tea daily at early onset of cold and flu symptoms was effective for reducing symptoms compared with placebo.’ 3. Sage tea
Delicate, sweet and earthy, sage tea is made from the leaves of the common sage plant, a perennial evergreen shrub that forms part of the mint family. This aromatic herb is rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds, says Bond, including rosmarinic acid and carnosol.
‘Sage tea may help to boost heart health,’ he continues. ‘A small, four-week study in six women, drinking 10 x 300ml mugs of sage tea twice daily resulted in 16 per cent lower total cholesterol, 20 percent lower ‘bad’ LDL cholesterol , and 38 per cent higher ‘good’ HDL cholesterol.’
Sage tea may also be beneficial for people with diabetes and women experiencing menopause. ‘A two-month study in 105 adults with type 2 diabetes found that sage extract three times daily improved blood sugar and HBA1c – a measure of blood glucose control over the previous three months,’ says Bond. ‘A 2017 review suggested that sage might reduce menopausal symptoms of hot flushes.’ 4. Lemon balm tea
Lemon balm is a lemon-scented herb from the mint family. It’s best known for its stress-soothing properties. ‘Lemon balm tea may help you to relax and unwind,’ says Bond. ‘One small pilot human study showed a 42 per cent reduction in insomnia symptoms after participants received 600 mg of lemon balm extract per day for 15 days.
Lemon balm has been shown to increase gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in the brain – an inhibitory neurotransmitter known for reducing overwhelming feelings of anxiety – in laboratory studies , ‘which may explain its sedative effects,’ Bond says. Like sage, lemon balm may also reduce menopausal symptoms of hot flushes. 5. Rose hip tea
Rose hips are small, round ‘fruits’ found just below rose petals. While there are hundreds of species of rose plants, rose hip research has focused mainly on the Rosa canina variety. Rose hip is rich in plant polyphenol antioxidants, and contains antioxidant vitamins C and E, says Bond.
‘Rose hips have the highest vitamin C amongst fruit and vegetables, although amounts vary,’ he says. ‘Vitamin C is an immune function nutrient. There is evidence from laboratory studies that rose hip can benefit immune function parameters though research in humans is so far lacking.’ 6. Passionflower tea
There are about 500 known species of passionflower, known collectively as Passiflora. A natural sleep aid, passionflower – specifically Passiflora incarnata – has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and insomnia by boosting GABA levels in the brain.
‘Traditionally, passionflower has been used to help relieve anxiety and improve sleep ,’ says Bond. ‘One study in 40 healthy adults found that those who drank passionflower tea daily for one week reported significantly better sleep quality compared to participants who did not drink the tea.’ 7. Chamomile tea
An herb that comes from the daisy-like flowers of the Asteraceae plant family, Chamomile is commonly regarded as a mild sedative, and is often consumed as tea before bed to promote sleep . The plant’s calming effects may be attributed to an antioxidant called apigenin, which is found in abundance in chamomile tea, says Bond – apigenin binds to specific receptors in the brain that may decrease anxiety and initiate sleep.
‘A study of 60 nursing home residents found that those who received 400mg of chamomile extract daily had significantly better sleep quality than those who did not receive any,’ he says. ‘Another study involving women who had given birth to a baby and who had poor sleep quality found that those who drank chamomile tea for a two-week period reported overall better sleep quality than those who did not drink chamomile tea.’ 8. Rooibos tea
Also known as red tea […]
15 Ways How Aniracetam Improves Your Brain
Photo by Robina Weermeijer
Have you heard about Aniracetam ? What does Aniracetam have to do with Piracetam and GABA? What are the ingredients of Aniracetam nootropics? This prescription drug is a nootropic. Its properties include improving memory and the brain’s cognitive function in healthy individuals.
Aniracetam is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the US, and you can buy it in Europe only with a prescription. Above all, the benefits of this nootropic include alertness, better mood, and neuroprotection.
If you want to find out more about nootropics and memory supplements – their history, recommendations, and properties – make sure to check out our Ultimate Nootropics Guide .
At Goodlife Engineering , we strive to help you construct your own well-being. For instance, through Ultimate Guides and specific articles, we want to make you an expert in the niches of nootropics, technology, and many more.
What are the ingredients of Aniracetam ?
What is this nootropic comprised of? What is the chemical structure of Aniracetam nootropics?
It is technically known as N-anisoyl-2-pyrrolidinone . You can come across other brand names of Aniracetam nootropics , such as Draganon, Ampamet, or Referan.
In the 1970s, Hoffman-La Roche combined Aniracetam ingredients for the first time. This nootropics can be made in two ways: either a reaction of 2-pyrrolidone with anisoyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine , or gamma-aminobutyric acid can react with anisoyl chloride .
According to the prerequisites of nootropics formulated by Giurgea, the ingredients of Aniracetam have to be non-toxic and safe in order to call them nootropics.
GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid is one of the major metabolites in Aniracetam. In a study, GABA mimicked the effects of this nootropic.
Both substances – Aniracetam and GABA – showed how they impact serotonin release in the body. Serotonin is sometimes called the happy hormone . Both GABA and Aniracetam work as mood-boosters and can be of great help in fighting depression or anxiety. [1]
Both Aniracetam and Piracetam are a part of the racetam family of nootropics. The substances are very similar when it comes to their chemical structure, yet they have different effects on the body and the mind.
> Aniracetam is absorbed more quickly
Piracetam stays in the organism for longer
Piracetam is better for beginners
Aniracetam can reduce anxiety and depression
In conclusion, Aniracetam and Piracetam are both strong cognitive-enhancing nootropics because they help you learn and concentrate.
Sugar, touchscreens, displays – they all make us sluggish and sleepy. Taking Piracetam or Aniracetam nootropics can help you stay alert against the odds.
It may help you to stay attentive, hence making every challenge less scary. It can be useful especially for university students and working professionals, who are willing to excel at their careers or exams.
Being able to focus on one task among thousands of distractions is difficult. Especially students may find it troublesome to sit down and study.
Aniracetam’s ingredients and chemicals affect the brain, hence making it easier to focus on what you have to do.
Scientists have taken a deeper look into Aniracetam’s effects on sleep. In fact, studies show that these nootropics can be helpful in treating various sleep impairments and disorders. [2]
When it comes to post-stroke patients, Aniracetam nootropics can improve the quality of the REM phase of dreaming. In conclusion, it might have some effects on the sleeping habits and quality of sleep in healthy people, yet no conclusive studies exist as of now.
Research on pigeons and mice have shown that these nootropics have no effect on the animals’ working memory whatsoever. [3, 4]
Nonetheless, the very same study suggested that Aniracetam or Piracetam may improve memory in individuals with cognitive impairment, along with improving different aspects of the brain’s cognitive function.During a study on two control groups, researchers proved that it can be used in the treatment of dementia, similarly to Pramiracetam . [5] Apart from that, these nootropics are easily absorbed and tolerated by the human organism, in comparison to Piracetam (though their chemical ingredients are quite similar).By keeping you attentive and focused, this nootropic helps you stay concentrated on one task or switch your attention between tasks more easily.Piracetam and Aniracetam give you a similar feeling of concentration, but your organism absorbs the latter faster.Benefits such as ease of focusing, staying attentive, improved memory – these nootropics are great cognitive enhancers that boost the cognitive function of your brain.If you want to learn about other brain-enhancing substances, check out our Ultimate Nootropics Guide and dive into the world of nootropics and memory supplements.These nootropics can help the brain recover after traumatic brain injury. For instance, Aniracetam’s ingredients are helpful in post-injury treatment, as research on rats indicates. [6] Aniracetam and GABA regulate the level of serotonin in your organism. For this reason, these nootropics can help you fight fear and anxiety.In fact, these nootropics can make you more sociable. Without social anxiety, it’s far easier to interact with people.The level of the happy hormone can be regulated by GABA nootropics. These smart drugs will give you a mood boost, hence making you feel more confident and happier.Aniracetam and GABA work as neuroprotectors. In addition, it helps patients recover from mild brain injury and shield the brain from degeneration. [7] The chemical ingredients of these nootropics have a lot of potential in brain-related treatment, such as treating memory deficits. [8] By improving the cognitive function of the brain, these nootropics are of great help when learning.In other words, Aniracetam and Piracetam are used by students to do better at exams and tests. They enhance the learning ability through tweaking memory and concentration.Research proves that Aniracetam is effective in the treatment of mild Alzheimer’s disease. Its effects are long-term and safe. In addition, scientists say that this nootropic is a “promising option for patients with cognitive deficit of mild severity.” [9] Studies show that its ingredients may support the neurotransmission of GABA. Aniracetam nootropics modulate the transmission of GABA in the human organism. [10] The chemical ingredients of GABA and Aniracetam nootropics facilitate the production of serotonin, the happy […]
How much damage blue light actually does to your eyes

One thing you can do is to check your monitor’s settings to see if there is a “eye saver” feature. Once you turn it on it the screen will look different/dimmer at first but give it a few minutes. Your eyes will adjust and after that you won’t even notice it is on.
A 2nd tip is to set the nighttime setting in windows. Click the start button and type in “night”. Click on night light. There is a scheduling option to have it automatically adjust the blue light at a certain time. This way your computer screen won’t keep you up all night. Similarly to the eye saver feature of your monitor, the screen will look weird for a couple minutes but your eyes will quickly adjust. You will actually notice a difference in your tiredness also as your subconconscious stops to think it is daytime. The blue light in the monitor makes your mind think it is daytime and so it prevents your body from releasing melatonin. -Corey
Begin article excerpt:
There’s no escaping blue light in the modern world. From digital devices, computers and phone screens, to fluorescent bulbs and LED lights, blue light is everywhere we turn. And the biggest source of it? Natural sunlight.
With the number of blue-light-blocking products being touted in the market today , it’s easy to assume that blue light is physically harmful to our eyes. But how much damage does it actually do?
“The truth is, nobody knows with certainty,” says ophthalmologist Dr Claudine Pang, founder of Asia Retina Eye Surgery Centre.
“There have been no human studies to document retinal damage by blue light. For this reason, we tend to err on the side of caution and try to limit excessive blue light exposure to our eyes.” Some amount of blue light exposure is good for us
“It is unscientific to equate all blue light as harmful. We actually need some amount of blue light to regulate normal circadian rhythms , boost alertness and memory, and prevent development of myopia,” says Dr Pang.
“Blue light deprivation has even been shown to be associated with depression-like changes in the brain.”
What most of us should be worried about is excessive, prolonged exposure – but to be fair, almost everything is harmful in excess. And because our retina can’t block blue light at all, that’s where specialised lenses and screens come in.
According to Dr Pang, blue-light-blocking lenses are able to block 20-70% of blue light, depending on their quality. Blue light occupies the 400-490 nm wavelength, and the yellow tint of blue-light-blocking lenses filters out wavelengths less than 450 nm, which may increase eye comfort when viewing digital devices for extended periods of time. The negative consequences are more behavioural than physical
The real concern with blue light is actually behavioural.
“The most conclusive consequence of prolonged exposure of blue light is that it affects the normal secretion of melatonin at night and disrupts our normal sleep cycle. Therefore, we should reduce the use of electronic devices especially at night for better sleep,” says Dr Pang.
This disruption of our natural circadian rhythms affects the quality of our sleep, which has a host of other consequences like increased risk of obesity, heart disease and diabetes.
And the tiredness we feel after looking at our screens for too long has more to do with digital eye strain than any physical damage caused by blue light exposure. Spending too much time looking at a screen reduces blinking, which results in dry eyes, discomfort, and blurry vision.
These issues are exacerbated by poor lighting, such as when you’re scrolling through social media in bed.
The important thing to remember when it comes to eye health to take regular breaks between screen time. There is a simple 20-20-20 rule you can follow: look away from your screen at least once every 20 minutes, looking 20 metres into the distance for at least 20 seconds.
In Dr Pang’s parting words, “As with most things in life, regulating blue light exposure is about moderation.”
Cannabidiol (CBD) found to alleviate seizures in those with neurodevelopmental conditions: Study

( Natural News ) Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the 113 organic compounds in the Cannabis sativa plant, commonly known as hemp. Previous studies on CBD have focused on its medicinal uses for pain relief, epileptic seizures, insomnia and Parkinson’s disease.
But a recent study from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC) found that CBD could also benefit children and adults suffering from Angelman syndrome (AS).
First author Bin Gu and his colleagues tested the effects of CBD on seizures, motor deficits and brain abnormalities in a mouse model of the said neurogenetic disorder.
Their experiments demonstrated that CBD treatment can reduce the severity of seizures in mice with AS . In addition, CBD also caused mild sedation and restored the mice’s normal brain rhythms.
Gu is hopeful that their findings, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation , could inspire further research into the use of CBD as a treatment for seizures caused by AS and other neurological disorders. CBD reduces seizures and causes mild sedation
AS is a rare neurogenetic disorder that occurs in one in 15,000 live births, or about 500,000 people around the globe. It tends to cause developmental problems that become noticeable when an infant reaches six to 12 months of age.
AS can also cause other abnormalities, such as seizures, balance disorders and speech problems. Because of the rare nature of AS, there is scant research on possible treatments and therapies.
Benjamin Philpot, the associate director of the UNC Neuroscience Center and the study’s senior author, said that there is an unmet need for better treatments for children suffering from the disorder. In response to this need, he and his colleagues created genetically modified mouse models of AS that they could use to find a possible treatment.
The researchers chose to test CBD because of its anti-epileptic properties. In 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of CBD as a treatment for seizures caused by two rare forms of epilepsy. (Related: Treating neurological disorders in children with oriental herbal medicine .)
To assess the effects of CBD on AS symptoms, the researchers injected the genetically-modified mice they created with various doses of CBD an hour prior to behavioral testing. Regardless of dose, CBD did not have a major impact on motor coordination or balance.
However, injection of a standard anti-convulsant dose of CBD caused mild sedation in the mice and reduced the severity of their experimentally triggered seizures. CBD also helped stabilize brain pulses linked to neural deficits and abnormalities.
These results expand the therapeutic spectrum of the anti-epileptic effects of CBD . The researchers also believe that their study could help address the need for better treatments for children with AS. CBD reduces seizures and autism-like behaviors in a mouse model of another childhood brain disorder
This isn’t the first time that scientists attempted to assess the therapeutic effects of CBD on rare and less-studied neurological disorders.
In 2017, researchers from the University of Washington (UW) used CBD to treat mice with Dravet syndrome (DS), a severe type of epilepsy characterized by prolonged seizures that begin in the first year of life.
But unlike AS patients whose symptoms tend to improve with age, DS patients tend to suffer from worse intellectual impairments, autism-like behaviors and other debilitating neurological problems over time.
DS is also a rare and life-long condition that affects one in 20,000 to 40,000 people worldwide. Its drug-resistant nature has further complicated the development of treatments and therapies for it.
The UW researchers assessed the effects of CBD treatment on a mouse model of DS. Their experiments showed that high doses of CBD could reduce the severity, frequency and duration of DS-induced seizures.
In addition, mice treated with low doses of CBD spent more time interacting with other mice compared with the untreated mice, indicating an improvement of autism-like behaviors. However, this effect was lost at the higher doses needed to reduce seizures .
Nephi Stella, the founder of the UW Center for Cannabis Research and a member of the research team, said that their findings highlight the need for a treatment that could confer both benefits at once.
Nevertheless, the researchers noted that their findings contribute to the emerging data supporting the use of CBD in the treatment of drug-resistant and debilitating neurological conditions.
Read more about the medicinal uses of CBD at CBDs.news .
Sources include:
ScienceDaily.com 1
ScienceDaily.com 2
JCI.org
51 Fibre-Rich Foods Which May Help Lose Weight Easily

Fibre is an important plant-based nutrition that primarily helps promote weight loss along with maintaining digestive and bowel health, reducing unwanted cravings, lowering blood sugar levels, fighting constipation and reducing the risk of stroke. Fibre-rich foods help bulk up the stomach and make the digestion slow to prevent sudden glucose and cholesterol spike in the body. [1]
Overweight is a major issue as many of the health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease and obesity are due to increased body fat. Reducing the quantity of food or starving is not the solution for losing weight as it may cause a deficiency of many essential nutrients in the body.
The best way to lose weight while maintaining the nutrient balance in the body is by eating fibre-rich foods. They not only help in weight management but also provide vital nutrients for the proper functioning of the body. Take a look at essential foods that help lose weight easily. Also remember, it is always good to combine both exercise and fibre-rich foods for a healthy weight loss journey. Fruits
1. Pears
Pears are among the top fruits which are densely packed with dietary fibre. They are also enriched with antioxidants and phenolic compounds. [1]
Dietary fibre in pears (100 g): 3.1 g
How to use: Eat pears directly with the skin. You can add them to your fruit bowl or consume after roasting them. 2. Avocado
Avocado contains healthy fats and other essential nutrients such as vitamins, magnesium, fatty acids and potassium. It is also an excellent source of phytochemicals that may help in weight management and prevent heart-related diseases. [2]
Dietary fibre in avocado (100 g): 6.7 g
How to use: Add avocados in a fruit salad. You can also simply slice the fruit, sprinkle some black pepper and consume. 3. Blackberry
A low-fibre diet can cause digestive problems such as constipation and bloating while high-fibre foods primarily help in weight loss as well as in controlling blood sugar and reducing cholesterol. This is why blackberries are mostly consumed for healthily losing weight.
Dietary fibre in blackberry (100 g): 5.3 g
How to use: Consume blackberries with Greek yoghurt, oats or porridge. You can also include them in your fruit bowl. 4. Fresh Figs
Figs are packed with dietary fibre. Including fresh figs in the diet helps lower blood cholesterol that may further help maintain body weight and proper blood flow in the body. Fresh figs also help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. [3]
Dietary fibre in fresh figs (100 g): 2.9 g
How to use: Either eat fresh figs or soak them in water for overnight and consume. You can add them to your cakes and puddings as they act as a natural sweetener. 5. Raspberry
Raspberry helps prevent fatty liver and obesity. It is best known to decrease body weight and hepatic triacylglycerol due to the presence of essential nutrients along with dietary fibre. [4]
Dietary fibre in raspberry (100 g): 6.5 g
How to use: Eat raspberries as a snack with Greek yoghurt, oatmeal or make smoothies out of them.
The Longevity Diet: What To Eat And How Does It Work? Know More About This Diet Plan 6. Coconut
Both raw and dried coconut have multiple health benefits. The fruit helps stabilise glucose level and has antidiabetic effects.
Dietary fibre in coconut (100 g): 9 g
How to use: Add coconut pulp in a fruit bowl or roast them and consume. 7. Guava
This seasonal fruit is an excellent source of fibre and low in calories. Studies say that the fruits can help maintain proper weight by regulating cholesterol and sugar levels in the body.
Dietary fibre in guava (100 g): 5.4 g
How to use: Consume guava without peeling. You can also sprinkle some salt on the fruit and eat. 8. Kiwi Kiwi contains both soluble and insoluble fibre. When consumed, the fruit gives us a feeling of fullness and prevents us from eating unhealthy foods that increase weight. Dietary fibre in kiwi (100 g): 3 g How to use: Eat kiwi after peeling them. You can add them to oats, porridge or a fruit bowl. 9. Pomegranate The essential nutrients in pomegranate such as antioxidants, anthocyanins and tannins may help reduce obesity and cholesterol levels. The fruit also prevents the growth of cancerous cells. Dietary fibre in pomegranate (100 g): 4 g How to use: Consume a glass of pomegranate juice every day. You can also add pomegranate seeds to oats or porridge. 10. Banana Bananas can help maintain a perfect waistline. It is rich in carbohydrates and contains low calories. Besides, eating a single banana gives a feeling of fullness and reduces hunger. Consumption of banana not only promotes weight loss but also helps replenish the lost energy from the body during physical activities. [5] Dietary fibre in banana (100 g): 2.6 g How to use: Toss a few slices of banana in a fruit bowl. You can also prepare banana smoothies or add them to your oats.Diet And Depression: Healthy Foods That May Help Fight Depression 11. Grapefruit Grapefruit is low in calories and rich in vital nutrients. It helps reduce weight with the help of an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase. The enzyme boosts metabolism and utilises stored fat and sugar for producing energy in the body. [6] Dietary fibre in grapefruit (100 g): 1.1 g How to use: You can consume half grapefruit a day. 12. Apple Apple is a major source of dietary fibre and polyphenols. It significantly helps reduce belly fat in people who are obese. Polyphenols in the fruits also help with digestion. [7] Dietary fibre in apple (100 g): 2.4 g How to use: Add apples to your breakfast by including them in a fruit salad, oats or porridge.7 Ways To Include Apple In Your Diet 13. Mango Mango makes for healthy snacks that promote satiety. It contains beta-carotene, which helps reduce the risk of cancer. Mangoes are also a rich source of vitamins C, B and […]
Which herbal remedy is best for you?
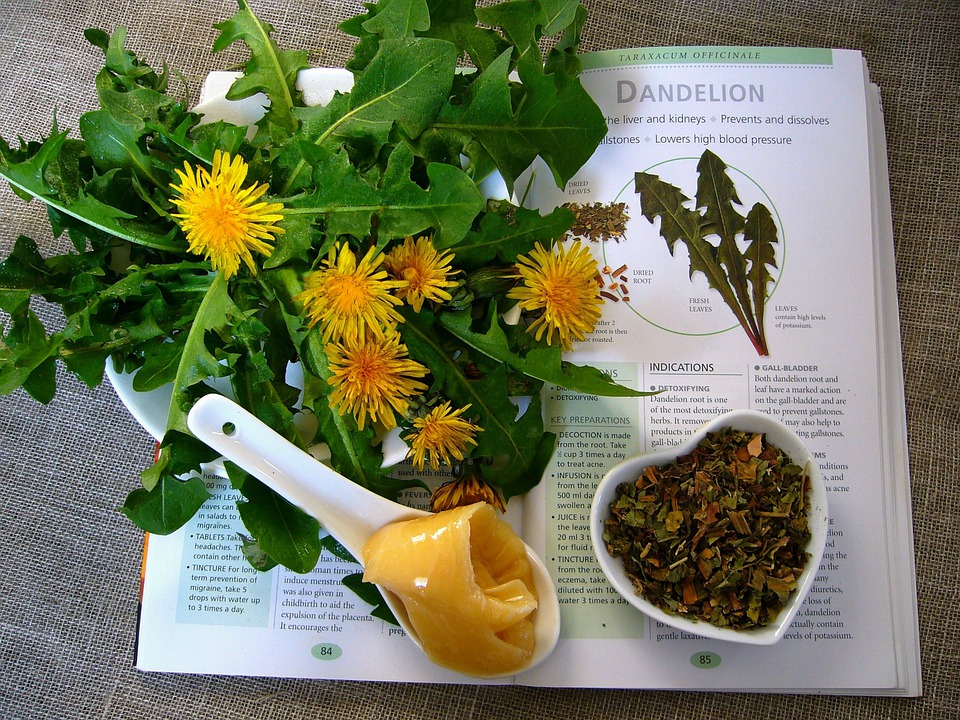

DANDELION: May combat water retention and treat urinary tract infections. CREDIT: Pixabay The market is awash with natural and herbal remedies which can help treat almost every condition from anxiety to high blood pressure.
But with so many remedies to choose from, how do we know what we should take?
Herbal medicines are those with active ingredients made from plant parts, such as leaves, roots or flowers.
But being ‘natural’ doesn’t necessarily mean they’re safe to take.
Just like conventional medicines, herbal medicines will have an effect on the body, and can be potentially harmful if not used correctly.
They should therefore be used with the same care and respect as conventional medicines, warns NHS.UK , which recommends if you’re consulting your doctor or pharmacist about health matters, or are about to undergo surgery, always tell them about any herbal medicines you’re taking.
People with serious health conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, should avoid herbal medicines, as should people who are on other medication, and pregnant or breastfeeding women.
While herbs are generally less potent than drugs and have fewer side effects, this does not mean you can simply take them without caution, they need to be used responsibly.
So how do you choose which rememdy is best?
The herbs listed below are believed to have the following properties:
Aloe Vera – reduces inflammation, can help soothe suburn, has anti-bacterial and moisturising properties
Bilberry – anti-oxidant, could improve circulation and repair veins. Considered effective in aiding vision, reducing inflammation, lowering blood sugar levels and may help prevent hardening of the arteries.
Chamomile – often used to treat insomnia, anxiety and digestive disorders.
Dandelion root – may combat water retention and treat urinary tract infections such as cystitis, bladder inflammation or kidney infections.
Echinacea – anti-inflammatory and immune-booster. Not recommended for people with autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis or ME.
Feverfew – can treat fevers, migraines, rheumatoid arthritis, stomach and tooth aches as well as menstrual pain.
Garlic – as well as lowering cholesterol levels, it may help prevent cancer, hardening of the arteries and high blood pressure.
Ginseng – may boost energy levels, reduce inflammation, benefir brain function, improve erectile dysfunction and boost the immune system.
Gingko biloba – an antioxidant which may improve circulation and memory and help prevent tinnitus and macular degeneration
Green tea – antioxidant and tonic (a herb which works on the whole body or organ)
Milk thistle – may repair liver cells and protect against damage from alcohol, hepatitis and chemical toxins.
St John’s Wort – could help relieve mild to moderate depression and anxiety, along with menopause symptoms.
Tea tree oil – a natural antiseptic used for treating skin infections as well as cuts, burns, bites and stings.
Turmeric – an antioxidant
Valerian – a natural sedative used to treat insomnia, anxidety and headaches brought on by stress and tension.
Wild yamcan – may relieve stomach problems like PMT, and menopause symptoms such as hot flushes and vaginal dryness.
Zinc – vital for immune function, metabolism, wound healing, blood clotting and thyroid function. It may reduce inflammation, help prevent muscle cramps and the risk of some age-related disease.
Exercise found to rapidly trigger nootropic effect in younger adults

Using supplements, dieting protocols, special sleeping schedules and more in an effort to boost one’s cognitive abilities is a major trend at the moment. These efforts largely revolve around taking various substances, some lesser-known than others, but that may be overkill for some people — at least if they’re still under the age of 36. According to a new study, exercise in younger adults can rapidly boost one’s ability to learn.
‘Nootropics’ refer to a variety of supplements and other compounds and chemicals that may help improve cognitive abilities, including enhancing memory and learning, through a variety of mechanisms. Some substances, such as CBD, may work by decreasing inflammation and increasing blood flow in key regions of the brain, for example, while other substances have less research to back up claims made about them.
Regardless, supplements and other nootropics are often quite expensive, leading those who are interested in a brain boost to other, cheaper alternatives. Adjusting and refining one’s diet remains a popular method, but perhaps under-appreciated is one that is entirely free: getting exercise on a regular basis.
According to a new analysis of existing studies recently published in Translational Sports Medicine , adults ages 18 to 35 may experience increases in memory and learning ability after a single workout, the varieties of which included things like riding a bicycle, walking, and running.
Based on 13 studies on the topic that were reviewed as part of this latest study, increases in these two aspects of cognition, as well as attention and concentration, were found to improve for up to two hours after 1 hour or less of exercise. The ‘catch?’ This exercise had to be high intensity, meaning a casual stroll or gentle trot won’t help.
How even a short walk can boost your brain: Exercising for just two MINUTES each day can improve concentration, memory and problem-solving skills, study finds

Even two minutes of exercise per day could be enough to improve your brain health and memory, a study has found.
Researchers looking at past studies saw that any amount of exercise, even if it was only a short walk, was good for the brains of people between the ages of 18 and 35.
The NHS recommends that all adults should do at least two hours of moderate activity per week but science suggests a lot less than that could still be worthwhile.
PLAY Top Articles by Daily Mail Coronavirus kills off BRAIN cells About Connatix V54548 Read More Read More Read More Read More Visit Advertiser website GO TO PAGE 1/1 SPONSORED / Coming Next Skip Ad
Exercise was found to be good for the brain because it made nerve cells more active and it increased dopamine levels, helping to sharpen people’s focus and memory.
The effects after short periods of exercise were found to last for at least two hours in the tests, while the researchers added that intense exercise brought long-term improvement.
As well as boosting brain health, exercise at any level is proven to bring a wealth of health benefits including strengthened heart and lungs, and a lowered risk of long-term illnesses such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease.
The Swedish researchers who did the study suggested their findings, which were specific to young people, could help them to learn better in studies or at work. EXERCISE ‘CAN MAKE YOUR BRAIN YOUNGER’
Going for a daily walk or bike ride can shave 10 years off your ‘brain age’, according to a study published in January 2019.
Researchers found that regular aerobic exercise – known more commonly as cardio – boosted essential gray matter in all adults, even those as young as 20 years old.
Even climbing the stairs improve the thinking skills of the students they examined, scientists said.
The positive effect of physical activity increased with age: people aged 40 had the brainpower to match someone 10 years younger, while 60-year-olds seemed 20 years younger, said scientists at Columbia University in New York.
The study of 132 people, published in the journal Neurology, found exercise specifically improved the health of nerves in areas that control executive function.
These relate to a person’s ability to regulate their own behavior, pay attention, organize and achieve goals.
Professor Yaakov Stern said: ‘We found all participants who exercised not only showed improvements in executive function but also increased the thickness in an area of the outer layer of their brain.’
Advertisement
The scientific review looked at people aged between 18 to 35 who exercised by walking, running or cycling at moderate to high intensity.
After exercising they then took tests to analyse their brain power, such as remembering a list of 15 words.
The participants, who exercised in bursts of two minutes, or 15 minutes, half an hour or an hour, all improved on tests and showed better concentration and problem-solving skills.
Findings were pooled together from 13 other studies that were then analysed by researchers from the Jonkoping and Linkoping universities in Sweden.
The authors wrote: ‘This systematic review strongly suggests that aerobic, physical exercise followed by a brief recovery… improves attention, concentration, and learning and memory functions in young adults.
‘The results of this review may have important education‐related implications.
‘Identifying optimal exercise strategies may help students to enhance their learning and memory.’
Exercise is believed to increase levels of a protein called ‘brain-derived neurotrophic factor’ which is thought to be important for memory, the scientists said.
They also suggested that brainpower improvements might come from a ‘sustained’ boost to nerve connectivity in the organ.
And exercising is also known to increase levels of the the feel-good hormone, which works as a neurotransmitter, helping signals to flit quickly around the brain.Higher levels of dopamine, the researchers said, ‘may enhance attention and memory’.But not everyone is a natural athlete or has hours to work out.The review wanted to see if a single bout of exercise could have an effect, so looked at studies exploring this with young adults over ten years.The review, published in the journal Translational Sports Medicine, found any exercise from two minutes to an hour improved memory and thinking skills for up to two hours. HOW MUCH EXERCISE DO YOU NEED TO DO? To stay healthy, adults aged 19 to 64 should try to be active daily and should do: at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity such as cycling or brisk walking every week and strength exercises on 2 or more days a week that work all the major muscles (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders and arms) Or: 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity such as running or a game of singles tennis every week and strength exercises on 2 or more days a week that work all the major muscles (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders and arms) Or: a mix of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity every week – for example, 2 x 30-minute runs plus 30 minutes of brisk walking equates to 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity and strength exercises on 2 or more days a week that work all the major muscles (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders and arms) A good rule is that 1 minute of vigorous activity provides the same health benefits as 2 minutes of moderate activity.One way to do your recommended 150 minutes of weekly physical activity is to do 30 minutes on 5 days every week.All adults should also break up long periods of sitting with light activity.Source: NHS Advertisement
First ‘plug and play’ brain prosthesis demonstrated in paralyzed person

Karunesh Ganguly (right), M.D., Ph.D., discusses ECoG brain recording data with student Stefan Lemke in 2016. In a significant advance, researchers working toward a brain-controlled prosthetic limb at the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences have shown that machine learning techniques helped a paralyzed individual learn to control a computer cursor using their brain activity without requiring extensive daily retraining, which has been a requirement of all past brain-computer interface (BCI) efforts. An ECoG array comprises a pad of electrodes that is surgically placed on the surface of the brain. “The BCI field has made great progress in recent years, but because existing systems have had to be reset and recalibrated each day, they haven’t been able to tap into the brain’s natural learning processes. It’s like asking someone to learn to ride a bike over and over again from scratch,” said study senior author Karunesh Ganguly , M.D., Ph.D., an associate professor of in the UC San Francisco Department of Neurology. “Adapting an artificial learning system to work smoothly with the brain’s sophisticated long-term learning schemas is something that’s never been shown before in a paralyzed person.”
The achievement of “plug and play” performance demonstrates the value of so-called ECoG electrode arrays for BCI applicartions. An ECoG array comprises a pad of electrodes about the size of a Post-it note that is surgically placed on the surface of the brain. They allow long-term, stable recordings of neural activity and have been approved for seizure monitoring in epilepsy patients. In contrast, past BCI efforts have used “pin-cushion” style arrays of sharp electrodes that penetrate the brain tissue for more sensitive recordings but tend to shift or lose signal over time. In this case, the authors obtained investigational device approval for long-term chronic implantation of ECoG arrays in paralyzed subjects to test their safety and efficacy as long-term, stable BCI implants.
In their new paper, published Sept. 7 in Nature Biotechnology , Ganguly’s team documents the use of an ECoG electrode array in an individual with paralysis of all four limbs (tetraplegia). The participant is also enrolled in a clinical trial designed to test the use of ECoG arrays to allow paralyzed patients to control a prosthetic arm and hand, but in the new paper, the participant used the implant to control a computer cursor on a screen.
The researchers developed a BCI algorithm that uses machine learning to match brain activity recorded by the ECoG electrodes to the user’s desired cursor movements. Initially, the researchers followed the standard practice of resetting the algorithm each day. The participant would begin by imagining specific neck and wrist movements while watching the cursor move across the screen. Gradually the computer algorithm would update itself to match the cursor’s movements to the brain activity this generated, effective passing control of the cursor over to the user. However, starting this process over every day put a severe limit on the level of control that could be achieved. It could take hours to master control of the device, and some days the participant had to give up altogether.
The researchers then switched to allow the algorithm to continue updating to match the participant’s brain activity without resetting it each day. They found that the continued interplay between brain signals and the machine learning-enhanced algorithm resulted in continuous improvements in performance over many days. Initially there was a little lost ground to make up each day, but soon the participant was able to immediately achieve top level performance.
“We found that we could further improve learning by making sure that the algorithm wasn’t updating faster than the brain could follow — a rate of about once every 10 seconds,” said Ganguly, a practicing neurologist with UCSF Health and the San Francisco Veterans Administration Medical Center’s Neurology & Rehabilitation Service. “We see this as trying to build a partnership between two learning systems — brain and computer — that ultimately lets the artificial interface become an extension of the user, like their own hand or arm.”
Over time, the participant’s brain was able to amplify patterns of neural activity it could use to most effectively drive the artificial interface via the ECoG array, while eliminating less effective signals – a pruning process much like how the brain is thought to learn any complex task, the researcher say. They observed that the participant’s brain activity seemed to develop an ingrained and consistent mental “model” for controlling the BCI interface, something that had never occurred with daily resetting and recalibration. When the interface was reset after several weeks of continuous learning, the participant rapidly re-established the same patterns of neural activity for controlling the device – effectively retraining the algorithm to its former state.
“Once the user has established an enduring memory of the solution for controlling the interface, there’s no need for resetting,” Ganguly said. “The brain just rapidly convergences back to the same solution.”
Eventually, once expertise was established, the researchers showed they could turn off the algorithm’s need to update itself altogether, and the participant could simply begin using the interface each day without any need for retraining or recalibration. Performance did not decline over 44 days in the absence of retraining, and the participant could even go days without practicing and see little decline in performance. The establishment of stable expertise in one form of BCI control (moving the cursor) also allowed researchers to begin “stacking” additional learned skills — such as “clicking” a virtual button — without loss of performance.
Such immediate “plug and play” BCI performance has long been a goal in the field, but has been out of reach because the “pincushion-style” electrodes used by most researchers tend to move over time, changing the signals seen by each electrode. Also, because these electrodes penetrate brain tissue, the immune system tends to reject them, gradually impairing their signal. ECoG arrays are less sensitive than these traditional implants, but their long-term stability appears to compensate for this shortcoming. The stability of ECoG recordings may be even more important for long-term control of more complex […]