Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
How Brain Waves Influence Your Memory

Key points Brain waves influence cognitive control and memory formation, informing how the brain manages memory. Working memory stores and manipulates information temporarily for tasks like learning and decision-making. Phase-amplitude coupling neurons synchronize with brain waves, aiding cognitive control and memory retrieval. New findings…
Does sleep clear more toxins from the brain than when we’re awake? Latest research casts doubt on this theory

Eleftheria Kodosaki does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment. Partners University College London provides funding as a founding partner…
Contraceptive Pills Have a Curious Effect on The Fear-Promoting Area of The Brain

(danilo.alvesd/Unsplash) Scientists have found a possible link between using oral contraceptives and changes in parts of the brain that process fear. The findings may help explain fear-related mechanisms that disproportionately affect women . Hormonal changes during a menstrual cycle are currently understood to affect…
Naturally occurring substance in pomegranates can improve treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
A substance naturally occurring in i.a. pomegranates, strawberries and walnuts can improve memory and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, a new study conducted at the University of Copenhagen concludes. Forgetfulness, difficulty finding words and confusion about time and place. These are some of the most…
Hitting the target with non-invasive deep brain stimulation: Potential therapy for addiction, depression and OCD
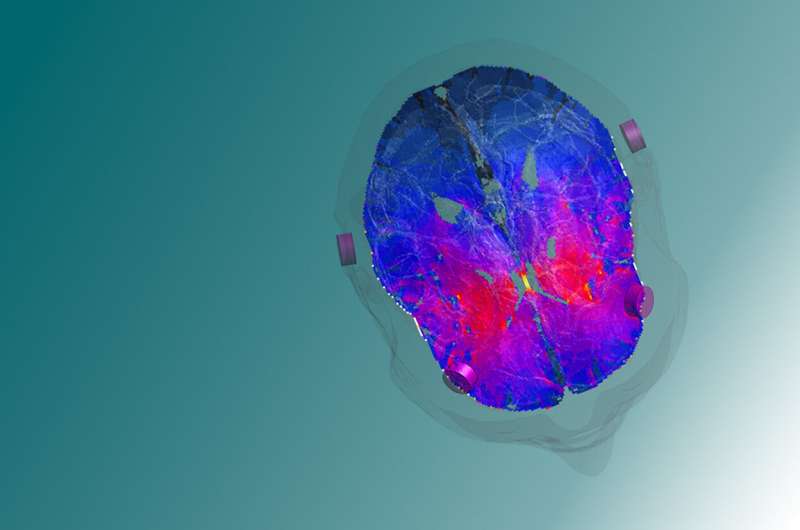
by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne A model image of the targeted deep brain zone, the striatum, a key player in reward and reinforcement mechanisms. Credit: EPFL Neurological disorders, such as addiction, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), affect millions of people worldwide and are…
Turning Back Time: Study Links Key Nutrients to Slower Brain Aging

A novel study highlights the critical role of specific nutrients found in the Mediterranean diet in promoting brain health and slowing cognitive decline, providing a foundation for future nutritional interventions. Participants whose brains aged more slowly had a nutrient profile that was similar to…
Serotonin Affects Behavior and Motivation

Summary: A new study reveals how activating the brain’s serotonin center affects behavior and motivation in awake mice. Using optogenetics and high-field MRI, researchers found that stimulating serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) activates the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia, critical areas…
Eating more ultra-processed foods tied to cognitive decline, stroke, according to study
People who eat more ultra-processed foods like soft drinks, chips and cookies may have a higher risk of having memory and thinking problems and having a stroke than those who eat fewer processed foods, according to a new study published in the May 22,…
Unlocking Memory: Neuroscientists Reveal How the Brain Decides What To Remember

Human Brain Memories Neuroscientists have determined that some daily experiences are transformed into permanent memories during sleep through a process facilitated by the brain. A recent study led by NYU Grossman School of Medicine has identified “sharp wave-ripples” in the hippocampus as the key…
Ultra-Processed Foods Could Lead to Strokes and Dementia, Says Harvard Study

A picture of a meal from a fast food restaurant . A Harvard study has found that eating ultra-processed foods could damage a person’s brain. According to The Times , the study – which was published in the journal Neurology – concluded that consuming…
Ultra-processed foods may raise risk of stroke, dementia

A 10% increase in the amount of ultra-processed foods a person eats is associated with a 16% higher risk of cognitive problems, researchers found. Photo by Adobe Stock/HealthDay News Ultra-processed foods are bad for more than your waistline: New research shows they seem to…
Upgrading brain storage: Quantifying how much information our synapses can hold
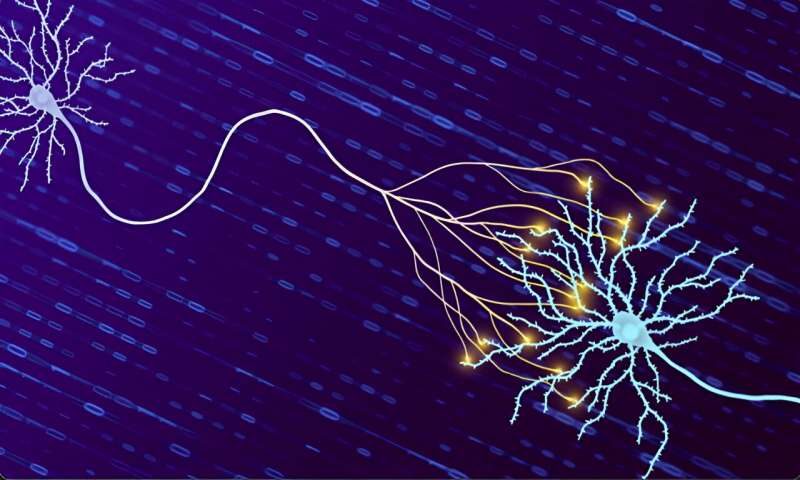
Two neurons, one in full (left, light purple) and one partially out of frame (right, light blue) on top of a background of zeros and ones to symbolize the unit of bits used to quantify information storage in synapses. The neuron on the left…
More Research Links Ultra-Processed Foods to Increased Risk of Cognitive Decline, Stroke

New research on the risks associated with consuming ultra-processed foods, shows a correlation rather than causation between the consumption of ultra-processed foods and these health issues. The findings are published in the current issue of the journal Neurology . Ultra-processed foods, which are characterized…
Ultra-Processed Foods an Independent Risk Factor for Poor Brain Health

0 Consuming highly processed foods may be harmful to the aging brain, independent of other risk factors for adverse neurologic outcomes and adherence to recommended dietary patterns, new research suggests. Observations from a large cohort of adults followed for more than 10 years suggested…
Study shows exercise spurs neuron growth and rewires the brain, helping mice forget traumatic and addictive memories
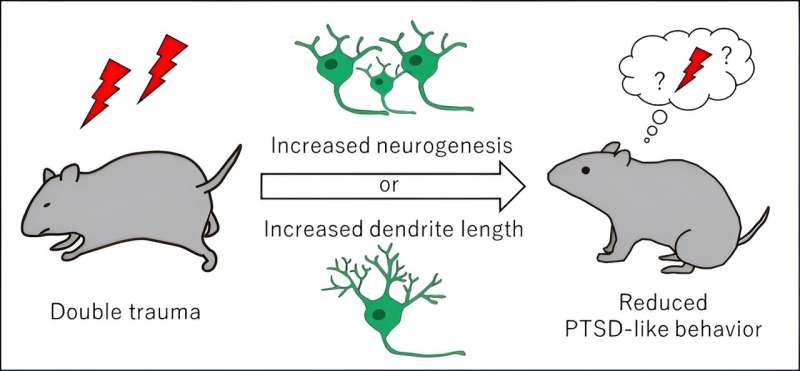
Exercise-induced formation of neurons and genetically-inducted neuron growth rewired neural circuits in the hippocampus, helping mice forget traumatic memories and reducing their PTSD-like symptoms. Credit: Risako Fujikawa, Kyushu University and Hospital for Sick Children Researchers from the University of Toronto, Canada, and Kyushu University,…
Exercise spurs neuron growth and rewires the brain, helping mice forget traumatic and addictive memories
Researchers from the University of Toronto, Canada, and Kyushu University, Japan, have found that increased neuron formation and the subsequent rewiring of neural circuits in the hippocampus through exercise or genetic manipulation helps mice forget traumatic or drug-associated memories. The findings, reported on May…
Study: Certain nutrients may slow brain aging
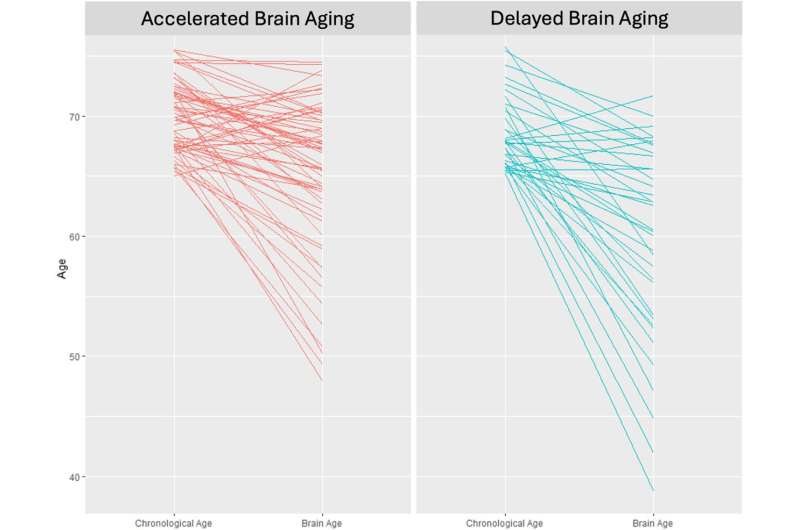
Chronological versus brain age. Credit: npj Aging (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41514-024-00150-8 Scientists have long been studying the brain with the goal of aiding healthier aging. While much is known about risk factors for accelerated brain aging, less has been uncovered to identify ways to prevent…
Unique brain circuit is linked to Body Mass Index
Why can some people easily stop eating when they are full and others can’t, which can lead to obesity? A Northwestern Medicine study has found one reason may be a newly discovered structural connection between two regions in the brain that appears to be…
A Wild New Study Sheds Light On Why Exercise Is So Good For Our Brains

Researchers unearth exercise secrets from a biomolecular soup of synthetic innervated muscle tissue. SrdjanPav/E+/Getty Images It’s no secret that regular exercise is great for the body and the brain . Scientific studies have shown, time and time again, that physical activity has both short…
High BMI Linked to Weak Smell-Eating Circuit in Brain

Summary: A new study reveals a novel brain circuit linking the sense of smell and eating behavior. The weaker the connection between these regions, the higher a person’s Body Mass Index (BMI). This discovery suggests a potential neural mechanism underlying overeating, where disrupted circuits…
