Learn about brain health and nootropics to boost brain function
Olive Leaf Extract (Oleuropein & Hydroxytyrosol) Benefits
The phenolic compounds present in olive leaves, especially oleuropein, have been found to have therapeutic effects for many conditions. Olive leaf extract can help with high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, Alzheimer’s, or heart disease. It’s even known to prevent genetic damage and cancer growth. If you suffer from any of these conditions, find out how olive leaf extracts can help you!
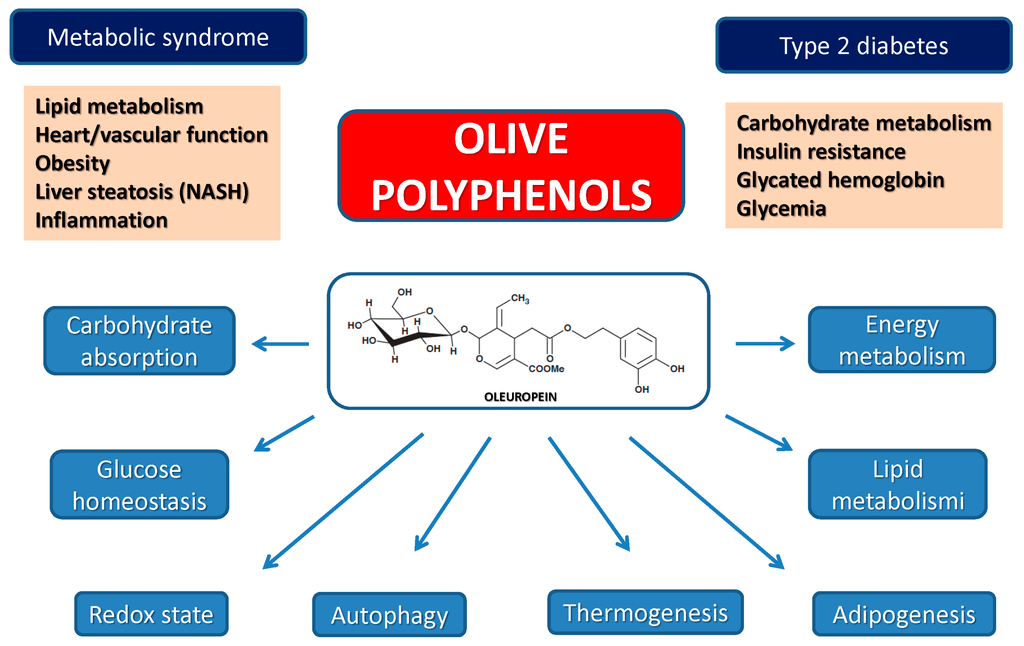
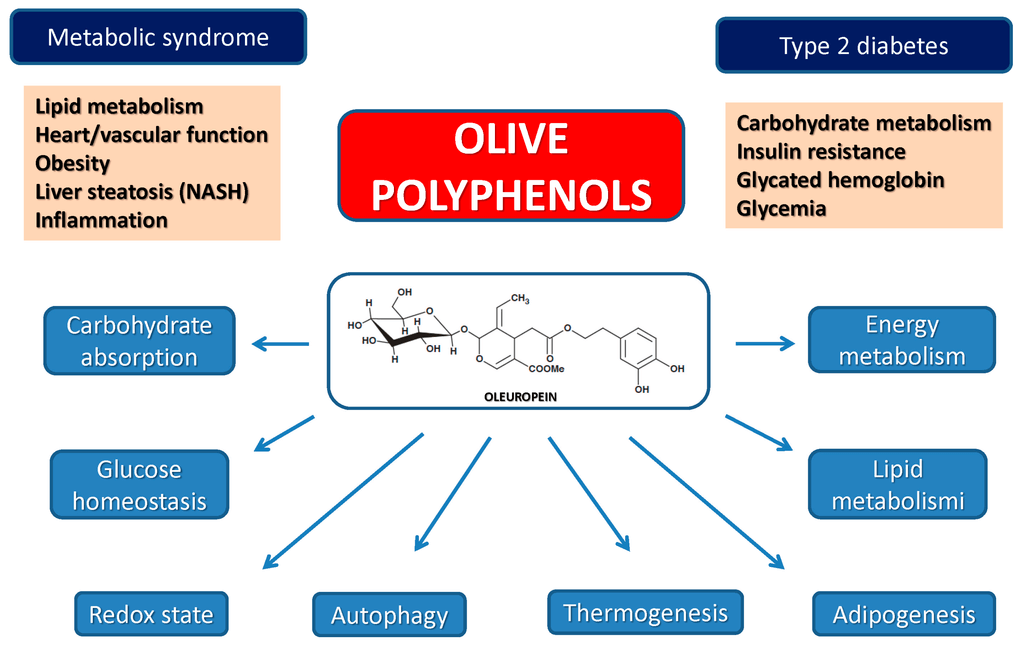
Olive leaf extract is characterized by a high content of polyphenols, which are micronutrients we get through our diet (such as eating olive oil) [1].
Olive phenols and their derivatives are associated with many therapeutic properties. The health benefits gained from these polyphenols depend on how much is consumed, and on how much the body can absorb [2].
The ability of olive leaf extracts to scavenge reactive oxygen species is associated with the protection against heart diseases and metabolic disorders [3].
- Great antioxidant
- Protects the heart
- Strengthens bones
- Lowers blood pressure
- Has anti-cancer properties
- Cognitive benefits
- Protects the brain from toxins
- Good for an array of conditions
- May interact with blood pressure medication
- May interact with blood sugar medication
- Enhanced differentiation into osteoblast; Increased gene expression of osteoblastogenesis markers RUNXII, osterix, collagen type 1, osteocalcin, and alkaline phosphatase [4].
- Prevented the reduction of left ventricular developed and systolic pressures, the rate of increase/decrease of left ventricular pressure, stroke volume, ejection fraction and cardiac output, and serum superoxide dismutase and glutathione reductase [7].
- Prevented the increase of serum malondialdehyde, interleukin-1β, TNF-α, creatine kinase-MB, and troponin I, lactate dehydrogenase, and infarct area [7].
In a study of men with high blood pressure, oleuropein significantly lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It also lowered fat and cholesterol levels in the blood [9].
Oleuropein delayed the onset of an irregular heartbeat and decreased blood pressure in anesthetized rats [10].
In patients with high blood pressure, taking 500 mg of oleuropein twice a day for 8 weeks effectively lowered both systolic and diastolic blood pressure [11].
In both a rat model and in cell study of heart damage caused by oxidative stress, olive leaf extracts prevented the death of heart cells and maintained mitochondrial functions [12, 13].
Longtime consumption of olive leaf extract in rats with high blood pressure lowered systolic blood pressure, lowered heart rate, and reduced enlargement of the heart and kidney tissues. Overall, rats treated with olive leaf extract experienced improved blood vessel function, especially in the heart [14].
In mouse models of heart attack, oleuropein prevented heart damage and heart failure [7].
Oleuropein prevented the production of pro-inflammatory molecules.
Oleuropein reduced the amount of tissue death caused by a local lack of oxygen in the heart [7].
Many studies support the idea that phenolic compounds, such as those found in olive leaf extract, play an important role in preventing cancer.
A recent study shows that olive leaf extract kills bone cancer cells and prevents them from multiplying [15].
In cells, oleuropein prevented cancer cells from replicating, spreading, and invading other parts of the body, effectively reducing the size of tumors within 2 weeks [16].
Olive leaf extract prevented DNA damage in human blood cells. This suggests that olive leaf extracts may prevent the development of cancer by protecting genetic material [17].
A mouse study found that olive leaf extract prevents cancerous cells from multiplying and forces them to die [8].
The concentrations of olive leaf extract that are effective against DNA damage could easily be reached with normal consumption of olive oil [17].
However, there have not been clinical studies evaluating olive leaf for cancer humans, so it’s unknown if it has anticancer effects found in animals and cells.
In a rabbit model of diabetes, oleuropein lowered and restored normal blood glucose levels and MDA [6].
In a study of rats induced with diabetes, oleuropein reduced body weight, fat tissue mass, and liver fat [18, 3].
Oleuropein improved insulin sensitivity and increased the uptake of blood sugar in mouse models of diabetes [3].
Diabetic rats experienced reduced blood sugar levels when treated with oleuropein.
It seems that olive leaf extract can help fight obesity by preventing the body from generating more fat cells [19].
In a study of rats induced with diabetes, oleuropein reduced body weight, fat tissue mass, and liver fat [18, 3, 20].
Another study found that oleuropein reduced fat-cell production in human bone marrow stem cells [4].
Oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol prevent pre-fat cells from maturing into true fat cells [21].
Studies conducted both in cells and in animals revealed that the phenolic compounds found in olive leaf extract (mainly oleuropein aglycone, and oleocanthal) have the potential to slow or prevent the onset of brain disease.
Amyloid diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, are caused by a buildup of misfolded proteins in tissues that cause the tissues to experience inflammation and to degenerate [22].
However, olive leaf extracts can prevent these misfolded proteins from entering the brain. This effectively reduced toxicity and tissue damage in mouse studies [23].
In a rat model of Parkinson’s Disease, olive leaf extract rescued brain cells from cell damage and cell death [24].
Oleuropein reduced spatial memory impairment and improved cognition in rats with anesthesia-induced oxidative stress [25].
Even in the late stages of Alzheimer’s, mice experienced improved brain cell function after being treated with oleuropein aglycone. This suggests that olive leaf extract can be used not only as a preventative measure but also as a therapeutic treatment [23].
During eye surgery, it’s important to keep the pressure within the eye consistent, and inflammation to a minimum. When rabbits were fed a diet high in olive leaf extract, researchers found that eye pressure was significantly decreased. This could help to reduce risk during eye surgery [26].
In a study of mice injected with cisplatin to induce kidney damage, oleuropein countered the damaging effects of cisplatin. Oleuropein lowered creatinine and blood urea nitrogen to normal levels. Oleuropein also reduced inflammation and prevented kidney cell death [27].
In a human brain cell model, olive leaf extracts prevented inflammation [28].
Furthermore, studies associate oleuropein to an anti-inflammatory effect in the trauma of the bone marrow [19].
Surprisingly, oleuropein not only reduced inflammation at skin injury sites in aged mice, but it also promoted rapid healing [5].
Olive leaf extract has been tested for antibacterial action against lactic acid bacteria. Oleuropein was not inhibitory, but two of its hydrolysis products, the aglycone, and oleanolic acid inhibited the growth of the four species of lactic acid bacteria tested [29].
An in-cell study of cells infected with a common opportunistic fungus found that hydroxytyrosol (an olive leaf extract) was effective in limiting and preventing its growth [1, 30].
Toxoplasmosis is inhibited by oleuropein treatment in kidney cells and in mice. Oleuropein effectively prevented cell death and tumor formation in mouse spleens and livers [31].
In an experiment with mice poisoned by arsenic, oleuropein reduced oxidative damage in blood, liver, kidney, and brain tissues [32].
Hydroxytyrosol is the olive leaf phenol that is most effective at acquiring unpaired electrons and neutralizing free radicals, followed by oleuropein and then tyrosol [33].
Studies suggest that olive tree products could prevent age-related bone loss.
A study on human bone marrow stem cells found that oleuropein increased bone cell production [4].
In mice whose ovaries were removed, talc-induced inflammation increased bone loss and loss of bone density. However, olive oil and its main polyphenol oleuropein prevented this bone loss [34, 35]
Pinoresinol of olive oil may prevent the absorption of vitamin D in the intestines. This may cause or increase the severity of gastrointestinal disorders [36].
Olive oil and its extracts may lower blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Taking olive oil extracts in addition to medication for diabetes may cause blood sugar levels to drop too low. Taking olive oil extracts in addition to medication for high blood pressure may cause blood pressure to drop too low [9, 10, 11].
If you’re interested in natural and more targeted ways of lowering your inflammation, we at SelfHacked recommend checking out this inflammation wellness report. It gives genetic-based diet, lifestyle and supplement tips that can help reduce inflammation levels. The recommendations are personalized based on your genes.
SelfDecode is a sister company of SelfHacked. This section contains sponsored links, which means that we may receive a small percentage of profit from your purchase, while the price remains the same to you. The proceeds from your purchase are reinvested into our research and development, in order to serve you better. Thanks for your support!

Click here to view full article