Nature Knows and Psionic Success
God provides
Ayurvedic solutions: Sleep industry increasingly being attracted to Ayurveda
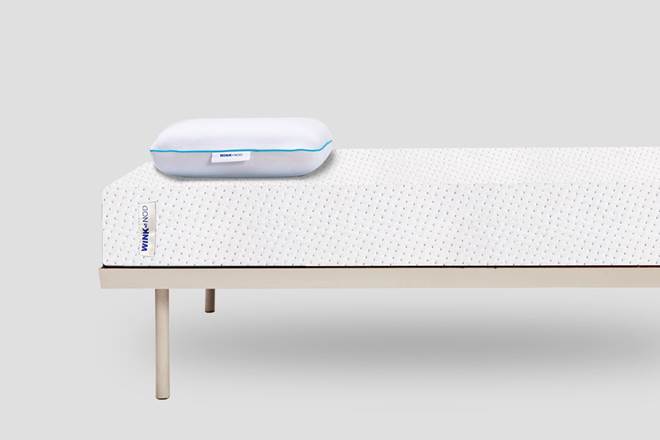

JEEVA mattresses from Wink & Nod come with a lavender-infused cover. (Photo: Wink & Nod) By Sandeep Prasad
Sleep is one of the primary needs as it enables the body to recharge and rejuvenate and maintains our overall health. With stress and tension topping the charts, quality sleep is one of the essential comfort therapies that everyone should receive. Individuals who experience lack or disturbed sleep often suffer from various health issues, including chronic diseases.
Also read | Smokers, it’s never too late! Study shows how quitters can surpass cancer, reverse lung damage
Ayurveda, an ancient science, focuses on leading a healthy life by bringing in changes to the lifestyle. The connection between Ayurveda and sleep is deep-rooted and has been around for a long time. These lifestyle changes include implementing a sleep routine and using other Ayurvedic tips to calm the mind and body.
The sleep industry realizes the importance and link between Ayurveda and sleep. Today, we see more and more companies focusing on Ayurvedic remedies for various issues, sleep being one of them. With the increase in awareness among people with respect to natural remedies, Ayurveda is rapidly gaining traction among customers.
Some Ayurvedic tips to get good sleep are:
Essential oils
Using essential oils like rose and jasmine while taking a bath is extremely helpful before sleeping. According to the principle laid down by Ayurveda, energy – both negative and positive – plays a crucial role in the healing of the body. An excess of negative energy leads to restlessness. Ayurveda states that rose and jasmine have a calming effect on the body as it reduces stress. Smell plays an important role in bringing out good memories and vibes. Hence, nowadays we see people increasingly using scented candles and essential oils to help them sleep.
Massage
Massaging the temples and the naval with ghee has a lot of benefits in Ayurveda. According to Ayurveda, ghee is one of the best substances to massage as it helps to calm and cool the body. Furthermore, it provides hydration and oleation (saturation therapy in Ayurveda). The cooling properties of the ghee increase Pitta and balance Vatta when used to massage the body. Additionally, massaging the feet just before going to bed aids in relaxing the body as there are more than 7,000 nerve endings on each foot. The same theory applies when massaging the scalp.
Practice breathing exercises
Practising Anulom Vilom before going to bed every night assists in reducing the Vatta and balances the left and right hemispheres of the brain. Additionally, concentrating on your breathing helps in meditation and calming the brain, thus ensuring a rested, serene brain before going to bed.
Ayurvedic influence can be seen in companies like GOODWYN TEA selling chamomile tea to help fight anxiety and induce sleep. 1mg is also selling Ayurveda Aswagandhadi Lehyam, which helps increase energy, reduce fatigue and improve stamina, and rejuvenates the body. Additionally, Wink & Nod – an innovative sleep products-focused company, is on the verge of launching JEEVA – Ayurveda mattresses. These companies are ensuring that they incorporate Ayurvedic elements into their products. While chamomile tea from GOODWYN TEA helps fight insomnia and induces natural sleep, JEEVA mattresses from Wink & Nod come with a lavender-infused cover and are made from natural materials, keeping true to the roots of Ayurveda. The memory foam is made from ground oils, and all the components of this mattress are natural and sourced from India.
Companies are going above and beyond to meet the customer’s expectations by providing Ayurvedic solutions to their sleep issues. Hence, it’s evident that the sleep industry is attracted by Ayurveda and its principles. In the coming days, this trend will increase as more and more people are becoming aware of organic products and searching for natural ways to get self-induced sleep. All that is left is to see how companies will come up with more innovative products imbibed with the principles of Ayurveda.
( The author is the Founder of Wink & Nod. Views expressed in the article are personal.)
In the mood: Power of music to lift your spirits

In the mood: Power of music to lift your spirits
Music moves us — not just physically, but emotionally and psychologically, reducing stress and improving mood. And it’s been doing it for centuries, writes Ed Power
In the darkest days of an Irish winter, music feels like a shard of light cutting through the gloom. Intuitively, we all know music has the ability to improve our moods. It can’t make clouds disappear, but it can help disperse the figurative ones.
This sense that music has the potential to nourish the soul and keep blues at bay is supported by research. Studies have demonstrated music may reduce levels of the stress hormone cortisol and boost blood flow in a similar way to statins.
“Research has found that music can benefit the whole person, promoting physical, psychological, emotional, and social well-being,” says Dublin-based singer-songwriter and music therapist Clara Rose.
“In my work as a music therapist I have witnessed first-hand amazing developments in my clients,” she says. “For example, stroke patients who have lost the power of speech still being able to sing.
“This is because we store language and memory in different parts of the brain. The ability to speak may be reduced by a stroke, but the memory of a song is still present.
“Music therapy can be used to aid speech rehabilitation for stroke survivors.”
“The innate musicality of human beings and the healing power of music has been written about and documented from as far back as the writings of Aristotle and Plato,” adds Siân Brown, a music therapist who studied at the University of Limerick. Music is deeply rooted as a healing tool in all cultures and civilisations. The oldest example of the contextual use of music for healing may be the depiction of harp-playing priests and musicians in frescos from 4,000BC. “Music can even affect our heart rate and breathing, and trigger the release of feel-good endorphins, serotonin, dopamine, etc, while also reducing cortisol,” says Brown, who is also a singer/songwriter.
With insomnia on the rise, there is evidence, too, that music can assist with sleep.
“We are all aware of the age-old practice of parents singing lullabies to their children to induce sleep,” says Rose.
“This shows that there is a very natural element of music that helps us sleep. It is a special combination of rhythm, melody, and words that create a safe space for the baby. And when sung by a primary caregiver, this further enhances feelings of safety and security that ‘lull’ them to sleep. Therefore, as adults, we can try to re-create this with our own music choices.
“I have a few created playlists which I use at night to calm the mind and settle me to sleep. Nothing beats the sound of my mother singing lullabies though, although she has quit that at this point, unfortunately.” One theory is that music “selectively activates” neurochemicals associated with positive mood and attention and memory.
“Music moves us,” says Rose. “Whether this is physically, such as dancing/moving to music, or emotionally moving people through what a song or piece of music can trigger for people.
“People also frequently use music to motivate them to exercise. For example, there is research to show that music with 120-140 beats per minute is the most effective to listen to when running.”
Music therapy can take several forms.
“Guided imagery in music” involves a therapist helping to explore life challenges by listening to music of the patient’s choosing. Therapy may also involve singing or playing instruments.
In winter, the transformative powers of music may seem especially potent.
“There are many papers on how music and music therapy can help with depression,” says Brown. “Even if it’s not clinical depression and maybe just a low mood, music can be used for ‘upliftment’.
“January is famous for being a month where most people in this part of the world will feel a little low,” she continues. It’s dark, cold, and everyone feels a bit battered after the madness and overindulgence of Christmas time. Group music-making in music therapy has been shown to be incredibly uplifting for all members. A kind of ‘we’re all in this together’ comfort in community. There is evidence, too, that music can reduce stress and improve well-being for older people experiencing cognitive decline. A 2016 study by the West Virginia University’s School of Public Health found that music was a “powerful tool” for “overall health and well-being”.
“Neurological impairment due to old age can bring disconnection.
“Regions of the brain can be left isolated and impaired, along with body functions, relationships, self-image and social structures,” says Brown.
“Music works on connections between brain cells and between people. Individually and socially, music can be a powerful tool in caring for the elderly.
“As I work with older people in hospital at present, this is a key area of my work,” says Clara Rose. “Many referrals are for older people experiencing cognitive decline and for music therapy to promote cognitive stimulation. This can be through song-singing, music improvisation, songwriting, or learning new songs. Meaningful songs can help older people engage in positive reminiscence about their past experiences. Therefore, music is a useful tool to promote cognitive stimulation.”
Curiously, music doesn’t have to be explicitly upbeat to raise our spirits. “Radiohead got me through my teenage angst years,” says Rose. “I would listen to them and think: ‘That song is about me, how did they know how I’m feeling?’ So what does this say? It can be that music we can relate to on a personal level is the most powerful for us.
“I often find that music therapy clients want to use specific, meaningful music to access their past experiences internally and process them. Sometimes these can be negative, difficult experiences. I worked with a man who had had a road traffic collision in which he had suffered life-altering injuries and he would consistently ask me to play a song for him in his music therapy session. He then told me that this was the song he was listening to when he had the [accident].”“Everyone is different,” agrees Brown. […]
This Keto Diet Plan Will Help Women 50 and Beyone Lose Weight For Good
Getty Images The high-fat, low-carb craze known as keto currently dominates Google’s most-searched diet words and Amazon’s bestseller list. And for good reason: The science backs keto, but the results really speak for themselves. Some women report dropping 11 pounds in seven days, 49 pounds in eight weeks, even 200+ pounds in all!
What makes the keto diet so powerful? It transforms the body metabolically. “At the heart of the keto diet, you limit your intake of carbohydrates to the point where you trigger ketosis — a state where your body burns fat instead of sugar for fuel,” notes cardiologist Bret Scher, M.D., medical director of DietDoctor.com . Indeed, research shows that keto followers increase their fat burn by up to 900 percent. The result: Fat cells shrink as they empty out.
The diet also reverses a slowing metabolism , making it up to 10 times faster, say researchers at Bethel University in Minnesota. Metabolism is determined by muscle tissue. And studies at the University of Southern California show that women lose about one percent of their muscle tissue each year after the age of 30, and the process accelerates as we get older — in fact, by age 60, most women have lost 20 percent of their total muscle mass. So as we lose lean muscle mass, metabolism naturally slows. But the protein and healthy fats included in the keto diet actually combat this natural decline, helping to preserve metabolism-revving muscle, even as excess fat melts away. As a result, you won’t experience slimming slowdowns as the weight comes off.
An added bonus: Keto dieters never feel deprived. “The healthy fats in the keto diet help you feel fuller longer,” Dr. Scher promises, adding that fats increase the production of satiety hormones. And you can enjoy such a wide array of decadent foods (like the Bundt cake on page 68) that you’ll never feel like you’re missing out. “A keto diet is one of the few approaches people can comfortably stick with over the long-term,” says certified obesity medicine specialist Adam Nally, D.O., author of The Keto Cure ( $18.05, Amazon ), who has helped patients drop up to 220 pounds.
As effective as keto is, though, many women struggle on the plan. “A lot of weight-loss strategies are too complex to maintain long enough to create new habits,” explains Dr. Nally. That’s certainly true of the traditional keto diet, which requires keeping track of macronutrients by limiting meals to 5% carbohydrates, 25 percent protein, and 70 percent fat. Indeed, keto dieters report that all the math is daunting, and figuring out what to eat to hit optimal fat levels can be difficult. Worse, this confusion can lead to slip-ups that stall results and derail motivation.
Fortunately, keto dieters have hit upon a strategy that makes it easy to get results. The key is making the diet simple and automated. “You can skip the keto diet math,” promises Denver-based diet expert Jeffry Gerber, M.D., author of Eat Rich, Live Long ( $18.79, Amazon ). Instead, check out these super-easy keto meal plans or create your own meals following Dr. Gerber’s no-stress guidelines: “Start with 2 cups of raw or 1 cup of cooked leafy greens or cruciferous vegetables. Then add 2 to 3 servings of fat from avocado, butter, cheese, nuts, or oils,” he says. “Top it off with a palm-sized serving of protein.”
Speedy slimming is just the start of the benefits. Turns out, the ketogenic diet is also a real heart-saver, reducing artery-harming triglycerides by 300 percent and balancing cholesterol levels. “Research shows that the keto diet improves or reverses type 2 diabetes as well,” adds Dr. Scher. More good news: A keto diet has a beneficial impact on the brain, resulting in a 62 percent improved memory. Plus, increasing your intake of healthy fats has been proven to rein in arthritis pain, stimulate hair growth and tighten skin — which helps women lose big without sagging skin.
This article originally appeared in our print magazine.
Five Natural Ways to Optimize Your Brain Power

In the name of self-care and self-improvement, we are continually looking for ways to feel smarter and healthier to lead a happier and more fulfilling life.
And no matter how old you get, taking care of your mind and optimizing your brain power can be linked to living a much healthier life. Here are five simple ways to improve your brainpower:
Exercise
Exercise gets the blood flowing. Which helps your brain get all the oxygen and nutrients it needs for top performance. Getting about 30-60 minutes of exercise three times a week helps improve blood flow to the area of the brain responsible for memory retention.
Sleep
We all deserve a nap from time to time. And it’s good for you, too! Rest is the body’s natural way of rebooting your brain and other organs, helping you improve your mood and brain. Napping also helps make new connections in the brain, which can help with creativity and problem-solving. Try to get at least 8 hours of sleep every day but limit your naps to 20 minutes tops.
Eat a big breakfast
It is never a good idea to skip breakfast. Many studies have shown that eating a big healthy breakfast in the morning has been linked to improved memory and people who eat breakfast perform better than those who don’t. So get a kick start in your morning with a healthy breakfast.
Learn new things
Keeping your brain busy with crossword puzzles may not boost your cognitive functions, but learning new things definitely will. Trying new activities of learning about new things shows a significant improvement in brain function. The brain is very much like a muscle. The more you use it, the stronger it gets. So find a new exciting hobby and challenge yourself. You’d be surprised at how focused you’ll become.
Meditate
When in distress, your brain releases the hormone cortisol, which actually can destroy brain cells, causing memory loss and slow cognitive features, that’s why people who suffer from depression and anxiety struggle the most with chronic memory loss and difficulty concentrating. Meditation is a brain boost. It allows you to control your stress levels and suppress the production of cortisol. In addition to this, the happier you are, the happier your brain is.
expert reaction to study looking at flavonols and Alzheimer’s disease
Tweet
Research, published in the journal Neurology, reports that the antioxidant flavonol may be linked to lower risk of Alzheimer’s.
Dr Ada Garcia, Lecturer in Public Health Nutrition, University of Glasgow, said:
“This study shows that when elderly people, in particular females, self-reported to eat foods that contained about 15mg of favonols in their diet (for comparison a cup of black tea will provide that amount) then their risk for developing Alzheimer’s over a period of 6 years was reduced by about 44 percent. However, when the authors considered the effect of consuming other nutrients such as omega-3, vitamin E, folate and lutein, which have similar actions to flavonols, then the protective effect of flavonoids was no longer present. These types of studies are informative but need to be consider carefully before making public health recommendations. They rely on participants memory to report what foods were consumed over a period of time, this is in particular difficult in elderly participants because reduction in cognitive function is a normal process of ageing.
“Following a ‘healthful diet pattern’ which includes a variety of foods such fruits, vegetables, oily fish, seeds, nuts, legumes is known to be a good approach to chronic disease prevention rather than focusing on particular nutrients. This is important because the general public might interpret this study wrongly and think about the term “antioxidant” as a magic pill that will prevent the onset of dementia. It is important to remember that consuming isolated flavonols or extracts of flavonol rich foods, for example tea extracts, will not work on isolation to reduce risk of disease but high doses can also have negative effects on health.”
Prof Bart De Strooper, Director, UK Dementia Research Institute, said:
“The relationship between food and health always draws a lot of attention from the public. This new study suggests that specific components in fruit, vegetables and tea are protective against Alzheimer’s Dementia. For studies of this sort we must however not forget that it only describes an association which was observed in a small group of individuals. Association does not demonstrate that there is a real biological or causal link. To give confidence in this observation it must first be repeated in other groups. Many studies in the past have shown however that such observations do not replicate well. So, in general one should be careful not to overstate the importance of such findings.”
Dr Adrian Ivinson, Director, UK Dementia Research Institute, said:
“We’ve long known that there are links between what we eat and our health. This new study suggests tea could be added the equation and shows that the general health benefits may extend to brain health. However, it only describes an association, so further work is needed to see if there are true biological links. But Alzheimer’s disease is exceptionally complex. Whilst diet may help stack the odds in our favour, we need to do discovery research to understand the disease and from there develop ways of preventing or slowing it.”
Dr James Pickett, Head of Research, Alzheimer’s Society, said:
“Early-stage research in mice does show flavonols might reduce the build-up of toxic proteins in the brain we know are involved in Alzheimer’s. This new study in people isn’t definitive about whether flavonols can lower dementia risk, and it definitely doesn’t provide enough evidence to say that drinking tea, and eating food rich in flavonols, will ward off dementia. But the study results do suggest we should keep investigating the potential of flavonols.
“Our researchers are currently looking at a specific flavonol called Epicatchin to understand exactly which components are responsible for slowing the build-up of toxic proteins. This will help fill in the missing pieces of the puzzle as to whether flavonols have any protective effects against Alzheimer’s.
“In the meantime, we can say for sure that eating a balanced diet, with lots of fruit and vegetables, and getting enough exercise is a proven way to reduce your risk of dementia.”
Dr Ana Rodriguez-Mateos, Lecturer in Nutritional Sciences, Kings College London, said:
“This research reports an association between flavonols and lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease. To estimate flavonol intake in this population, researchers used a type of food questionnaire which is not the best tool to measure food intake, as it relies on what people remembered they ate over a year.
“The intake of flavonols in this study is very low, between 5 and 15 mg/day. A big limitation of this study is that they did not report associations with other flavonoids and phytochemicals present in the same foods as flavonols. This is particularly important because flavonols tend to be present in foods in much lower amounts than other phytochemicals. For example, tea is very abundant in other flavonoids and phytochemicals, such as thearubigins, theaflavins and flavanols, while red wine is very rich in other flavonoids such as anthocyanins and flavanols. Olive oil is very rich in phenolic compounds such as tyrosols. In comparison, the amount of flavonols in such foods are tiny.
“The estimated flavonoid intake in the UK for example is typically between 500-1000 mg of flavonoids/day, and existing meta-analysis of clinical studies investigating the efficacy of flavonols have used typically amounts of flavonols between 100 to 700 mg/day. It looks more feasible that the effects observed here are related to the consumption of foods containing flavonols and to other phytochemicals and bioactives present in such foods than to the flavonols themselves.”
Prof Tara Spires-Jones, UK Dementia Research Institute Programme Lead and Deputy Director, Centre for Discovery Brain Sciences, University of Edinburgh, said:
“This paper by Dr Holland and colleagues provides more evidence that a healthy diet rich in vegetables is associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Scientists followed over 900 people for up to 12 years and found that people who reported they ate a diet rich in flavonols (found in vegetables including onions, kale, broccoli, and spinach) were less likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than people who ate lower levels of these compounds. This study was well conducted and […]
Best Caffeine Pills 2020

Caffeine permeates society in more ways than we realize.
It’s not just a Starbucks on every corner or the flourishing energy drink industry.
Rather, caffeine, as the ingredient that sparks natural stimulation within the body, fuels the majority of Western productivity.
But what exactly is caffeine?
In its pure chemical form, trimethylxanthine , caffeine occurs naturally in plants as an evolutionary defense mechanism.
In short – it’s meant to be mildly poisonous to insects so that the plant doesn’t get eaten.
However, when ingested by humans, it acts as a central nervous system stimulant .
That means that it, ironically, has the opposite of its intended effect – making us want to harvest caffeine-producing plants for nootropic use.
If isolated from its parent plant, caffeine stands as a white, odorless solid. Isolating caffeine by itself is a bit more complicated than, say, brewing tea leaves.
Fortunately, caffeine is highly water-soluble, making it an ideal ingredient for drinks.
On the flip side, the caffeine concentration in plants like coffee and tea varies greatly. Especially after roasting, soaking, and brewing, it’s hard to know the exact caffeine content of coffee, tea, yerba mate, and other drinks .
That’s where caffeine pills come in.
Thanks to modern science, we’re able to isolate caffeine from natural sources, measure out a specific quantity, and place it within a pill.
It’s a quick and easy way to reap the benefits of caffeine at the right dose, thanks to modern caffeine pills.
However, with so many options out there, you want to make sure you choose a supplement featuring the right dose without any dangerous add-ons.
In fact, the best ones can even upgrade the power of caffeine.
Within this article, you’ll discover:
> What makes up a caffeine pill
The benefits of caffeine pills (and how they stack up against coffee)
Ways to utilize your caffeine pills
Potential side effects
…and finally our choice for the Best Caffeine Pills 2020
* If you want the quick answer, then go straight to our #1 caffeine pills this year: Performance Lab Stim .
What are Caffeine Pills?
Caffeine is one of the most common compounds that people ingest that acts on the brain.
As a result, most people are familiar with the classic (but necessary) cup of coffee in the morning to wake up.While the taste of coffee is certainly comforting, the compound that actually acts as a stimulant to your brain is caffeine.Caffeine stimulates your brain and nervous system which, in turn, usually makes people feel more awake.Coffee beans – what makes coffee – are notorious for containing caffeine. But it’s also found in other natural ingredients such as tea leaves and kola nuts.The makers of caffeine pills either extract natural caffeine from these plant sources or manufacture it synthetically.The result? A perfectly calculated and measured energy buzz in pill form . Benefits of Good Caffeine Pills Caffeine is classified as a nootropic for its cognitive enhancing abilities.Not only can it wake you up in the morning, but a good caffeine pill also has the following benefits: Enhanced focus Improved creativity Sharpened memory Sustained energy Increased power output Better workouts Improved fat-burning ability Decreased depression and improved mood …and obviously reduced fatigue Since most of us take caffeine to fight fatigue, let’s start there. Caffeine pills hit your system quickly and target your adenosine receptors.Adenosine, as part of the energy molecule ATP, gets used up by the body when we’re energetic and awake.However, it slowly builds within the brain as we wind down towards sleep.When this adenosine links up with its receptors, it’s like a car pulling into its parking spot for the night. The more the cars are parked, the more tired we feel.Caffeine blocks those parking spots, so adenosine is left to roam freely, keeping us alert and awake. This action influences other stimulatory systems within the brain, much like a full parking lot would leave trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles scrambling around.Due to the aforementioned effects, caffeine increases catecholamine signaling.Your catecholamines, such as adrenaline, norepinephrine, and dopamine, regulate mood, focus, and attention levels.Therefore, by targeting these areas, caffeine pills help us concentrate on the task at hand .Too much adrenaline, however, can result in hyperstimulation and anxiety. That’s why it’s important to take caffeine pills with an effective dose. Finally, caffeine pills can improve your workouts. For example, doses of 400-600mg increase acute strength due to excited nervous systems.Research shows that caffeine improves anaerobic power in exercises such as weight lifting and sprinting. It also has a short-term thermogenic effect, meaning it increased heat production within the body.By doing so, caffeine pills mobilize fats to burn calories, potentially accelerating weight loss . Are Caffeine Pills better than Coffee? There are plenty of reasons to love coffee.Its warm, rich aroma wafting through your kitchen like a wake-up call. The bitter-yet-delicious taste of the hot brown liquid in your mug as you drive to work. Or the camaraderie of the timeless tradition of enjoying a cup of joe with your friends.Personally, I love coffee for all the above reasons and more. But some people just don’t like the way it tastes, or they have to cover it in cream and sugar to enjoy it.Other times, coffee is simply inconvenient. And if you’re just looking for a caffeine boost, it’s pretty inconsistent. If you don’t take your coffee black, even a harmless pinch of cream or sugar can add up . In a Western world whose obesity rates seem to be climbing, those calories might be unnecessary.For those looking to lose weight, removing liquid sugars is often the first step. Sodas, fruit juices, wine, and beer all fit the bill.But if you enjoy a few cups of coffee every day, it could be holding you back from your results.Even if you add artificial sweeteners and creamers, those contain dangerous ingredients as well.Fake sweeteners can hurt your metabolism, while trans fats and emulsifiers cause inflammation and can clog arteries .Now, the obvious solution is to just drink your morning coffee black, but why force yourself to drink something you don’t […]
Natural health: ‘What can I do to improve my eye health?’
Natural health: ‘What can I do to improve my eye health?’
What can I do to improve my eye health? I’ve recently been prescribed reading glasses and don’t want my eyesight to deteriorate further.
Although you don’t mention your age, changes to your eyesight are a natural part of the ageing process.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are two carotenoids which are crucial to eye health. Lutein is present in leafy green vegetables such as spinach, kale, collard greens, brussels sprouts and broccoli, while zeaxanthin can be found in yellow and orange produce. Eggs contain both lutein and zeaxanthin.
It is important to include healthy fats such as nuts, seeds, avocado, seafood or cold-pressed oils with your eggs, brightly coloured vegetables, and leafy greens since lutein in particular needs fats present for bioavailability. Healthy fats When it comes to eye health, the trans fats found in processed and fried foods are particularly damaging and increase the risk for macular degeneration and other issues.
One of the most beneficial fats for eye health is DHA, (docosahexanoic acid). DHA is present in the retina and has a number of proven benefits for both eye and brain health, protecting against a number of degenerative eye conditions. Fatty fish contains DHA, or you can choose a supplement form, particularly if you are looking for plant-based sources. Most health stores have a wide range of DHA supplements to choose from.
Along with getting the right essential fatty acids in your diet, you will need to make sure that you eat plenty of foods rich in vitamins A, C, E and the minerals selenium and zinc. This is also easily achieved by eating all of the foods mentioned earlier.
Strengthen eye muscles by choosing a close object to focus on (you can use your thumb) and hold it about 25cm/10in away from your face. Now choose a distant object – about 4.5m/15ft away from you. With each breath switch your focus between the near and far objects.
Improve flexibility by rolling your eyeballs in the shape of the infinity symbol. Move your eyes, slowly tracing the infinity pattern in one direction for 2 minutes, then switch to the other direction for 2 minutes.
Blinking is important, and many of us don’t do it often enough now that we spend more time looking at screens. Simply blink, count to three, then blink again, repeating this for two minutes.
Palming your eyes is both beneficial and relaxing, helping to relieve stress in the eye area. Sit at a desk or table and breathe deeply. Rest your elbows on the table and close your eyes. Place your palms over your eyes and cup your eye sockets for a couple of minutes. Ensure that the pressure is gentle – the point is relaxation and stress relief.
I’m finding it difficult to concentrate at work. I often end up taking work home. Is there a remedy you could recommend?
Concentration, focus, and memory are areas where gentle exercise can have a significant benefit. Qi Gong is a form of breath and movement therapy that will help to re-energise your system and shift your vital force. This should not only help with concentration issues, but also a general sense of wellbeing and clarity.
Qi gong helps significantly with managing stress and anxiety, which have been shown to interfere with concentration, memory, and recall. As an additional bonus, this work can help bring your hormonal systems into balance. Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) are also required to support mood, concentration, and focus along with regulating inflammation within the body.
Nuts, seeds, fatty fruits, and oily fish are all great sources. The omega-6 fatty acids are particularly important in brain health, while the omega-3 fatty acids are useful in regulating inflammation.GABA (Gamma Aminobutyric Acid) is found naturally in our brains, a neurotransmitter that is key to neuron activity – basically helping your brain cells relay and communicate effectively. There are certain types of tea, in particular, oolong tea, that have been shown to contain significant levels of GABA.
This high-protein, brain-boosting trail mix is going to be your new favorite snack

This healthy trail mix is guaranteed to be your new energizing snack of choice. Here’s .
The 4 p.m. slump is one of the most persistent banes of existence. Unless you live in Spain and are allowed daily siestas to recharge your batteries, you’re likely well aware of the brain fog that sets in a few hours before you’re actually allowed to vacate the duties of your job. It’s intensely frustrating and difficult to combat, especially given that for many of us, caffeine is not a good idea that late in the day.
Personally, the only thing that works for me is a mid-to-late afternoon sweat sesh, but since most office workers can’t jet out for an hour to recharge with a workout, herbalist, founder, and host of Well+Good’s video series offers a more widely-adoptable solution: nootropic trail mix.
“Nootropics are another way of describing herbs, supplements, foods, and compounds that are great for our brains,” Robinett says. “This recipe is designed for the times of day…you’re feeling the lethargy or lowness or brain fog.”
One of two key ingredients in her brain-boosting blend is cordyceps mushrooms. Robinett explains that while all are great sources of antioxidants, cordyceps mushrooms are especially adept at providing the body with energy. “Cordyceps also enhance our cells’ ability to use oxygen, which is very important for brain circulation and cognitive function,” she says.
The second key ingredient is rosemary. “Rosemary is my personal favorite for use in the afternoon, when I want a pick-me-up and I’m not going to have caffeine,” Robinett says. “It’s pretty common to hear about the benefits of rosemary for memory or cognition, and for brain clarity—this comes from its ability to throughout the body, and especially the brain.”
Plus, the mix contains , which are packed with protein and fiber and help to stabilize blood sugar, as well as , which are protective against free radicals, anti-inflammatory, and good for heart health.
Watch the video to discover the fascinating origin story of cordyceps, discover rosemary’s impressive role in libido (and how this it linked to its impact on the brain) and, of course, get the recipe to this powerhouse trail mix so you don’t *have to* move to Spain in order to survive the day.
Digging the herbal edge offered by Robinett’s concoctions? , , or .
Non-negotiable needs for struggling learners

Share this article When teachers and other IEP team members work tirelessly to accelerate struggling learners’ (SLs) rates of progress, they often fall short of their goals. Often, progress regresses, stagnates, or crawls forward by only small inches rather than the 10 yards the IEP team had deemed realistic.
Why regression? Why stagnation? Why only a few inches? Some of these SLs try hard but unsuccessfully to succeed. Some don’t focus, some lack energy, some show little interest, some angrily resist instruction, and some disrupt instruction with ingenious antics.
Depending on the day, time, and situation, some show several of these characteristics. If their teachers and IEP support staff work hard, know the curriculum, and are highly competent in using, adapting, and supplementing basic and specialized programs, this makes no sense. What’s undermining success? What’s undermining success?
The factors undermining success originate both outside and inside of school. Though schools can’t control outside of school factors they can often influence them.
To a greater or lesser degree, one or more of the following factors can undermine success, like gaping holes in a ship’s hull can sink it.
> Poor sleep
Poor nutrition
Insufficient physical activity
Heavy demands on willpower
Poor expectations of success
Poor expectations of satisfaction
A mechanical, impersonal environment
Poor progress monitoring
Functional disregard of the EARS principles ( E asy, A ttractive, R elevant, S ocially Supported)
Just one of these affects some SLs’ dramatically, some moderately, and some mildly. In my 50-plus years in special education, I’ve met only a few students who seemed impervious to these factors.
Let’s briefly examine the first three factors. In a follow-up article, I’ll examine the rest. Poor sleep
For anyone, including children, the consequences of night-after-night of poor sleep is devastating.
” Healthy sleep is critical for children’s psychological well-being…. Continually experiencing inadequate sleep can eventually lead to depression, anxiety and other types of emotional problems. Parents, therefore, need to think about sleep as an essential component of overall health in the same way they do nutrition, dental hygiene and physical activity…. ‘There are multiple emotional processes that seem to be disrupted by poor sleep… For example, our ability to self-monitor, pick up on others’ nonverbal cues and accurately identify others’ emotions diminishes when sleep is inadequate. Combine this with less impulse control, a hallmark feature of the teenage years, and sleep deprivation can create a ‘perfect storm’ for experiencing negative emotions and consequences’”
“ Sleep plays a critical role in thinking and learning. Lack of sleep hurts these cognitive processes in many ways. First, it impairs attention, alertness, concentration, reasoning, and problem solving. This makes it more difficult to learn efficiently…. During the night, various sleep cycles play a role in ‘consolidating’ memories in the mind. If you don’t get enough sleep, you won’t be able to remember what you learned and experienced during the day.”
Though schools cannot control SLs’ sleep — e.g., when they get into bed, when they shut off their cell phones — they can influence it. Asking these questions can help SLs:
1. Has the school psychologist, learning consultant, or school nurse administered a sleep rating scale to assess the SL’s sleep? Has it been administered to the parent (or guardian) and when appropriate, the student?
2. Has the school conducted professional training sessions to inform all staff, including custodians and food handlers, about sleep and how to identify students who may have sleep problems?
3. Has the school conducted parent and community training sessions to sensitize the community about helping children (and adults) minimizing or eliminating sleep problems? Poor nutrition
As with sleep, consistently poor nutrition can wreak havoc on children’s health, development, and academic achievement.
“We have found that there is increasing evidence of a link between a poor diet and the worsening of mood disorders, including anxiety and depression.”
“According to the Society for Neuroscience , recent studies reveal that diets with high levels of saturated fats actually impair learning and memory. Unfortunately, foods with saturated fats are often the most affordable and widely available in schools. French fries, sugary desserts, cheeseburgers, chicken nuggets, and other cafeteria staples are filling kids with food that actually lower their brain power before sending them back to class…. Malnutrition can result in long-term neural issues in the brain, which can impact a child’s emotional responses, reactions to stress, learning disabilities, and other medical complications.”“Unhealthful dietary patterns that typically lead to obesity, diabetes, and other physical health problems can also contribute to poor mental health .”And like sleep, schools cannot control nutrition, but often they can provide healthy meals and influence parents’ choices and actions. Asking these questions can help SLs:1. Has the school’s dietician or nurse administered a rating scale to assess the child’s nutrition. Has it been administered to the parent (or guardian) and when appropriate, to the student?2. Has the school conducted professional training sessions to inform all staff, including custodians and food handlers, about proper nutrition and how to identify students who may have difficulties getting or choosing proper nutrition?3. Has the school conducted parent and community training sessions to sensitize the community about helping children (and adults) get and choose nutritional foods?4. Has the school conducted parent and community training sessions about using government resources to secure proper nutrition? Insufficient physical activity The national Centers for Disease Control (CDC) is quite clear about the need for frequent physical activity:“ Regular physical activity can help children and adolescents improve cardiorespiratory fitness, build strong bones and muscles, control weight, reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, and reduce the risk of developing health conditions such as heart disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, [and] obesity.”In addition, “ students who are physically active tend to have better grades, school attendance, cognitive performance (e.g., memory), and classroom behaviors (e.g., on-task behavior) …. Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.But what about the critical area of mental health?“Research has shown […]
Dementia care: Drinking this fruit juice may reduce your risk of developing the condition

Dementia is an umbrella term for a cluster of symptoms associated with brain damage that mainly affects people over the age of 65, although it is not a natural part of ageing.
The condition disrupts the brain’s cognitive functions, causing symptoms such as memory loss and a decline in mental sharpness.
There’s no certain way to prevent dementia but groundbreaking research is shedding a light on lifestyle interventions that may reduce your risk.
Dementia: Could this drink improve memory?
Dementia care: This ‘alternative’ exercise may reduce your risk
Blueberries are rich in flavonoids, a plant compound possessing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Antioxidants are substances that thought to counter “oxidative stress”, a chemical imbalance in the body that is believed to play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurological brain condition that is the most common form of dementia.
To gather the findings, 26 healthy adults were divided into two groups: Twelve were given concentrated blueberry juice – providing the equivalent of 230g of blueberries – once a day, while 14 received a placebo.
DON’T MISS
Best supplements for muscle gain: The dietary supplement proven to retain muscle strength [TIPS]
Libby Clegg health: Dancing on Ice star’s deteriorating eye condition explained [INSIGHT]
Best supplements for blood pressure: Three natural remedies proven to lower your reading [TIPS]
Dementia test: The hand exercise which could determine your risk
Before and after the 12-week period, participants took a range of cognitive tests while an MRI scanner monitored their brain function and resting brain blood flow was measured.
Compared to the placebo group, those who took the blueberry supplement showed significant increases in brain activity in brain areas related to the tests.
Commenting on the findings, Dr Joanna Bowtell, head of Sport and Health Sciences at the University of Exeter, said: “Our cognitive function tends to decline as we get older, but previous research has shown that cognitive function is better preserved in healthy older adults with a diet rich in plant-based foods.
“In this study we have shown that with just 12 weeks of consuming 30ml of concentrated blueberry juice every day, brain blood flow, brain activation and some aspects of working memory were improved in this group of healthy older adults.” Dementia: Scale of Britain’s health crisis revealed in damning report
Dementia: Study found that aerobic exercise may help to preserve memory The study was a small proof-of-concept trial of people ages 55 and older with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is the stage between the expected cognitive decline of normal ageing and the more serious decline of dementia.
Although both groups preserved their cognitive abilities for memory and problem solving, brain imaging showed people from the exercise group with amyloid buildup lost slightly less volume in the hippocampus — a brain region that deteriorates as dementia progresses.
Amyloid is a naturally occurring protein that clumps together to form plaques that collect between neurons and disrupt cell function in a brain damaged by Alzheimer’s.
Blue light may aid recovery after concussion

A study that the United States military funded concludes that blue light can help heal mild traumatic brain injury simply by helping the person sleep better. By improving sleep, blue light may aid recovery from mild traumatic brain injuries. Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), or concussion, can result from a range of causes, from a car accident to fights, falls, or sports.
Following such an injury, people might see stars, become disoriented, or even lose consciousness briefly, but many come round without realizing that they have been concussed at all.
However, for some, mTBI can result in weeks or months of symptoms, including headaches, mental fogginess, dizziness, memory loss, fatigue, and disturbed sleep. According to the researchers behind the current study, some 50% of people with mTBI complain of chronic sleep problems after the injury, which affects their ability to think and recover.
And 15% of those with mTBI have symptoms that last for at least 1 year.
Scientists believe that these symptoms occur due to the stretches and tears that the impact inflicts on microscopic brain cells.
“Your brain is about the consistency of thick Jell-O,” explains lead author William D. “Scott” Killgore, a psychiatry professor at the University of Arizona in Tucson. “Imagine a bowl of Jell-O getting hit from a punch or slamming against the steering wheel in a car accident. What’s it doing? It’s absorbing that shock and bouncing around. During that impact, microscopic brain cells thinner than a strand of hair can easily stretch and tear and rip from the force.”
Such injury can also occur during explosive blasts, when shock waves hitting the soft tissue of the gut push a surge of pressure into the brain, damaging blood vessels and brain tissue.
“Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), which is commonly known as concussion, is one of the most common injuries experienced by military personnel and is a major health concern worldwide,” Killgore told Medical News Today . Stay in the know. Get our free daily newsletter
Expect in-depth, science-backed toplines of our best stories every day. Tap in and keep your curiosity satisfied.
“At present, there are virtually no effective treatments for concussion,” said Killgore. “We sought a nonpharmacologic (or nondrug) method to help people.”
Killgore and his research team received funding from the U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command to conduct the study, which features in the journal Neurobiology of Disease .
The solution that they set out to prove effective was sleep.
“Because sleep is so important for brain health and recovery, we reasoned that improving sleep timing and duration could lead to a more rapid recovery from mTBI,” said Killgore. “Considerable evidence suggests that sleep is important for brain repair processes,” he added.
Killgore explained that scientists have shown that following an injury, sleep facilitates the production of new insulating brain cells called oligodendrocytes.
“Without sufficient restorative sleep, the repair of brain tissue will likely be slowed or incomplete,” Killgore said.
The recent clinical trial, which involved 32 adults with mTBI, focused on solidifying the participants’ circadian rhythm — the natural process that dictates our 24 hour sleep-wake cycle.
The researchers achieved this by exposing the participants to blue light from a cube-like device for 30 minutes early each morning for 6 weeks. The participants in the control group used amber lights instead of blue.
Scientists have shown that blue light suppresses the brain’s production of melatonin, a chemical that makes us sleepy.
“Blue light is one of the brain’s primary timekeepers,” explained Killgore. “Exposure to blue light, such as sunlight at sunrise, tells the body that it is morning and time to stop sleeping. That makes you more alert during the day and starts the clock ticking to tell you when to go to sleep later.”
By using blue light, the participants reset the brain’s inner clock, helping participants fall asleep earlier and stay asleep. The most restorative, and therefore beneficial, sleep occurs when it is in tune with the body’s innate circadian rhythm.
On average, participants using the blue light therapy fell asleep and woke up 1 hour earlier than before the trial and were less drowsy during the day. Their brain-processing speed and efficiency were improved, and they showed an increase in visual attention.
“Our findings suggest that morning blue light exposure helps reset the normal sleep-wake cycle each day, and this maximizes the ability to get better sleep during the night, thus leading to better recovery from concussion.”
William D. “Scott” Killgore
The reason why blue light from phones, computers, and televisions gets a bad rap is timing. Blue light at night can trick your brain into thinking that it is morning, thereby messing with sleep.
Researchers are also looking at the effect of blue light on the sleep of those with emotional disturbances, such as post-traumatic stress disorder, as well as the potential of blue light to boost the alertness of healthy individuals.
Does “bad cholesterol” have a role in early-onset Alzheimer’s disease?
( Natural News ) Alzheimer’s disease is a chronic illness that robs a person of his memory and thinking skills. In the US, as many as five million adults suffer from this debilitating illness, with most symptoms appearing after age 60, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . However, there are some cases where people develop symptoms of the disease in their 40s and 50s , a condition called early-onset Alzheimer’s.
The etiology for Alzheimer’s — as well as other forms of dementia — is unclear, but a recent study in JAMA Neurology highlights the role of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and the risk of developing early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. In their paper, researchers from Emory University School of Medicine , together with the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Atlanta, investigated the association between the two to identify any underlying potential risk factors.
Earlier studies have concluded that a link between high levels of LDL cholesterol and the onset of Alzheimer’s disease does exist. Also known as “bad” cholesterol, too much LDL cholesterol in the body causes clogged arteries, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol can also affect Apolipoprotein E (APOE) E4 expression, a genetic variant linked to cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
“The big question is whether there is a causal link between cholesterol levels in the blood and Alzheimer’s disease risk,” explained Thomas Wingo, a neurologist at Atlanta VA and the study’s lead author. “The existing data have been murky on this point.”
The team looked at genetic data from over 2,000 participants, around 650 of whom had early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. They looked at APOE E4 expression and other potential genetic variants that have a link with early-onset Alzheimer’s. They also looked at associations between Alzheimer’s and plasma cholesterol levels by examining samples collected from research centers in Emory and the University of California (UC) , San Francisco .
Based on the results, around 10 percent of people with early-onset Alzheimer’s had the APOE E4 variant. Moreover, the participants with elevated plasma LDL cholesterol were more likely to be diagnosed with early-onset Alzheimer’s than those with lower cholesterol levels. The association was consistent, even as the team adjusted their data to account for APEO E4 expression, which increases the risk independently. (Related: Alzheimer’s hits more than just the memory; patients experience immune system dysfunction as well .)
This suggests a potentially causal link between bad cholesterol levels and the disease – a hypothesis they are looking to explore in the future.
“One interpretation of our current data is that LDL cholesterol does play a causal role. If that is the case, we might need to revise targets for LDC [sic] cholesterol to help reduce Alzheimer’s risk,” Wingo added.
“Our work now is focused on testing whether there is a causal link.” Prevent Alzheimer’s now by changing your diet
For many people, Alzheimer’s disease is a death sentence. But you can do something about it now , by increasing your intake of these healthy foods. (h/t to MindBodyGreen.com )
> Cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts , bok choy and cauliflower are packed with carotenoids that help lower homocysteine, an amino acid linked to cognitive impairment.
Leafy greens: Spinach, kale , collard greens and mustard greens contain folate, which boosts brain health.
Fatty fish: Fatty fish are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce the likelihood of developing brain lesions that cause dementia.
Spices : Turmeric, cumin , sage and cinnamon break down harmful plaques in the brain, as well as reduce brain inflammation.
Nuts: Aside from being rich sources of omega-3s, nuts like almonds, cashews, hazelnuts, walnuts and pecans contain vitamin E, folate and magnesium.
Other things you should consider to reduce your risk of Alzheimer’s are regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, stress management and proper sleep hygiene. Get more tips on how to keep Alzheimer’s disease at bay by following Alzheimers.news .
Sources include:
CDC.gov
Applying pressure to the arms and legs shown to improve brain blood flow, reveals study
( Natural News ) As you age, your brain will experience changes that could affect your mental function. With cognitive decline being quite common, it is important to maintain brain function by keeping your brain as healthy as it can be. Now, recent evidence suggests that a simple squeeze to your arms and legs might be beneficial for your brain .
A study published in the journal Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology , found that people who restricted their blood flow by wearing blood pressure cuffs on their arms and legs exhibited signs of more controlled blood flow to the brain. This process is referred to by the authors as remote ischemic preconditioning.
Previous research has established that “training” the organs by using remote ischemic preconditioning to restrict blood flow may make the heart more resilient and resistant to changes in blood flow and the damage caused by lack of oxygen during a heart attack.
“Since previous studies have shown benefits to the heart, we wanted to determine if remote ischemic preconditioning could also be beneficial to the brain,” said corresponding author Yi Yang from the First Hospital of Jilin University in China. “Our study found such preconditioning temporarily improved dynamic cerebral autoregulation, which is the brain’s ability to regulate and ensure adequate blood flow to the brain despite blood pressure changes. We also found an increase in biomarkers in the blood that can be protective to the nervous system and brain.” Under pressure
Scientists from China aimed to determine the effects of remote ischemic preconditioning on dynamic cerebral autoregulation and various blood biomarkers in healthy adults. In this new study, the researchers enrolled 50 healthy adults who were, on average, 35 years of age. Each participant went through two consecutive days of monitoring with the first day done without preconditioning. On the second day, the participants were equipped with blood pressure cuffs strapped on one upper arm and one thigh. These cuffs were inflated for five minutes and then deflated for another five minutes, with the process repeating four times.
The researchers measured the brain blood flow regulation of each participant by measuring and analyzing each ones’ blood pressure taken at the start of the day and periodically throughout the next 24 hours. They also used ultrasound to measure the blood flow in the two main arteries in the brain. (Related: Is your brain not getting enough blood flow? Natural ways to improve brain circulation .)
Based on the results, the researchers discovered that participants exhibited improved brain blood flow regulation or cerebral autoregulation only six hours after conducting the cuff compressions. These improvements maintained itself for at least 18 hours after the initial compressions.
In addition, researchers collected blood samples from each participant at the start of the day and one hour after performing cuff compressions. They found that participants experienced increased numbers of specific biomarkers — molecules that signal the presence of certain conditions in the body — one hour after preconditioning compared with their levels before the experiment.
To be specific, the researchers found an increase in two biomarkers that are known to protect the nervous system. One of these biomarkers is called the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, which has been previously found to protect your body against diseases like stroke and help regenerate damaged neurons.
They also noted an increase in four biomarkers involved in regulating inflammation in the body alongside lower levels of one biomarker that responds to inflammation.
“While our results are exciting, obviously we can’t know when someone will have a stroke and when this could be beneficial. We hope to use these results to help develop a new medication or treatment that will help all people better resist stroke or other neurological diseases,” said Yang. “It’s important to emphasize that people should not try to restrict blood flow on their own because, unless under the care of a physician, they could cause themselves harm. In addition, our study was small and much more research needs to be done to confirm our findings before recommendations can be made to physicians to use such preconditioning as a therapy.”
For more information and related stories about brain health and improving brain flow, visit Brain.news .
Sources include:
Adderall Side Effects, Addiction, Abuse & Withdrawal

Adderall is a psychostimulant amphetamine drug that is most commonly prescribed to reduce symptoms of ADHD. Unfortunately, it is also widely abused due to its supposed “cognitive-enhancing” effects, which can lead to addiction and other serious negative consequences. Read on to learn about its potential adverse side-effects and other risks associated with it!
Disclaimer: This post is not a recommendation or endorsement for Adderall. This medication is only FDA-approved for the treatment of certain specific medical disorders, and can only be taken by prescription and with oversight from a licensed medical professional. We have written this post for informational purposes only, and our goal is solely to inform people about the science behind Adderall’s effects, mechanisms, current medical uses, and potential risks. Adderall Side Effects
Given that Adderall has met FDA approval for official medical use, the majority of scientific evidence supports the overall safety and effectiveness of Adderall when used as prescribed, and under the supervision of qualified medical professionals .
Nonetheless, like any drug, there is always at least some potential of experiencing adverse side-effects, and so it’s important to be aware of these.
In general — and similar to many commonly-used pharmaceutical drugs — the rate of adverse side-effects tends to increase at progressively higher doses [ 1 ].
Adderall is a commonly prescribed medication for ADHD that has a good safety profile compared to other stimulants when used properly.
If you experience any of the following symptoms occur after taking Adderall, contact your doctor immediately [ 2 , 3 ] : Seizures (convulsions)
Changes in vision or blurred vision
Pupil dilation (mydriasis)
Allergic reactions: symptoms of this can include itching or hives, swelling of the mouth, face, or hands, difficulty breathing, feeling like you are about to pass out, or tightness in the chest.
Fever or sweating
Muscle problems such as spasms or twitching
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
Hallucinations (visual and auditory)
Fainting
Extreme energy
Confusion
Agitation
Signs of heart problems (can be fast, slow, or uneven heartbeats)
Signs of circulation problems (unexplained bruises, numbness, cold , color changes, or pain in fingers or toes)
Finally, abuse of Adderall by athletes may be especially dangerous, as it can cause dramatically elevated body temperature ( hyperthermia ), which may, in turn, induce heat stress . The dangers are further increased because the subjectively “stimulating” and “energizing” effects of Adderall abuse can cover-up (“mask”) the symptoms of heat stress — such as sudden exhaustion or fatigue — which, when ignored or unnoticed, can result in major medical emergencies [ 4 ].
Serious side effects like seizures, confusion, elevated body temperature, changes in perception, and heart problems are rare. Get immediate medical help if you experience any of them.
The following side-effects are not as severe, but have been reported to occur slightly more frequently in patients taking Adderall [ 2 ]: Dry mouth
Dizziness
Loss of appetite
Weight loss (Although weight loss may potentially be counteracted through the use of other (complementary) medications such as cyproheptadine , or even simply by consuming a higher-calorie diet [ 5 ]) Insomnia Stomach pain According to one report, Adderall may impair short-term memory in some users [ 4 ].Adderall may also lead to “antisocial” feelings, keeping users from enjoying or participating in interactions with others [ 6 ].Some of the psychological side-effects of Adderall may occur due to the greatly elevated levels of dopamine that Adderall (and other amphetamines and stimulants) cause throughout the brain — a mechanism that is also shared by other major psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia. For example, according to one study of 14 amphetamine-dependent patients, 12 were reported to go on to develop psychosis. This reportedly led to a number of schizophrenia-like symptoms, such as intense paranoia and hallucinations [ 7 , 8 ].According to one study of 56 child and adolescent ADHD patients, one of the most commonly reported negative side-effects of Adderall was weight loss. This was more prominent at higher doses [ 1 ].Although Adderall-induced weight loss is usually not severe, in some cases it has been reported to lead to anorexia. For example, one study of 584 children found that anorexia occurred in 21.9% of psychostimulant patients. Similarly, a study of 287 teens reported the occurrence of anorexia in as much as 35.6% of the treated ADHD patients [ 1 , 9 , 10 ].However, in some relatively rarer cases, Adderall may actually cause weight gain . For example, the authors of a single case study of an 11-year old boy reported that Adderall use increased one young boy’s weight by 8.8 lbs. in just 6 weeks. Changing the timing of Adderall consumption from right after meals to 45 minutes before meals reportedly helped to normalize this sudden and severe weight gain [ 11 ].Mild weight loss is among the most common side effects, although weight gain has also been reported. Psychological side effects, such as anxiety and antisocial feelings, are also possible but rarely severe.One of the most dangerous side-effects of treatment with amphetamines — including Adderall and others — can be a heart attack or stroke. Although these side-effects can potentially occur in anyone, patients with a personal or family history of heart conditions are believed to be at an especially elevated risk of experiencing such complications [ 12 , 13 ].These heart problems and other adverse cardiovascular side-effects may be brought about by the significant changes in heart rate and blood pressure that are commonly seen following Adderall consumption. On average, Adderall increases heart rate by 1-2 beats per minute. As the dose is increased, heart rate increases proportionately — and this can result in dangerously elevated heart rate or blood pressure [ 14 , 5 ].Adderall also stimulates β-adrenergic receptor sites all over the body, which causes the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine . Norepinephrine is believed to play a prominent role in stimulating increased heart rate and blood pressure, which may further contribute to some of Adderall’s potential cardiovascular risks [ 3 , 15 ].Additionally, some researchers […]
Brain hacks, implants, enhancers and nootropics: the Silicon Valley pioneers trying to live higher-performing lives
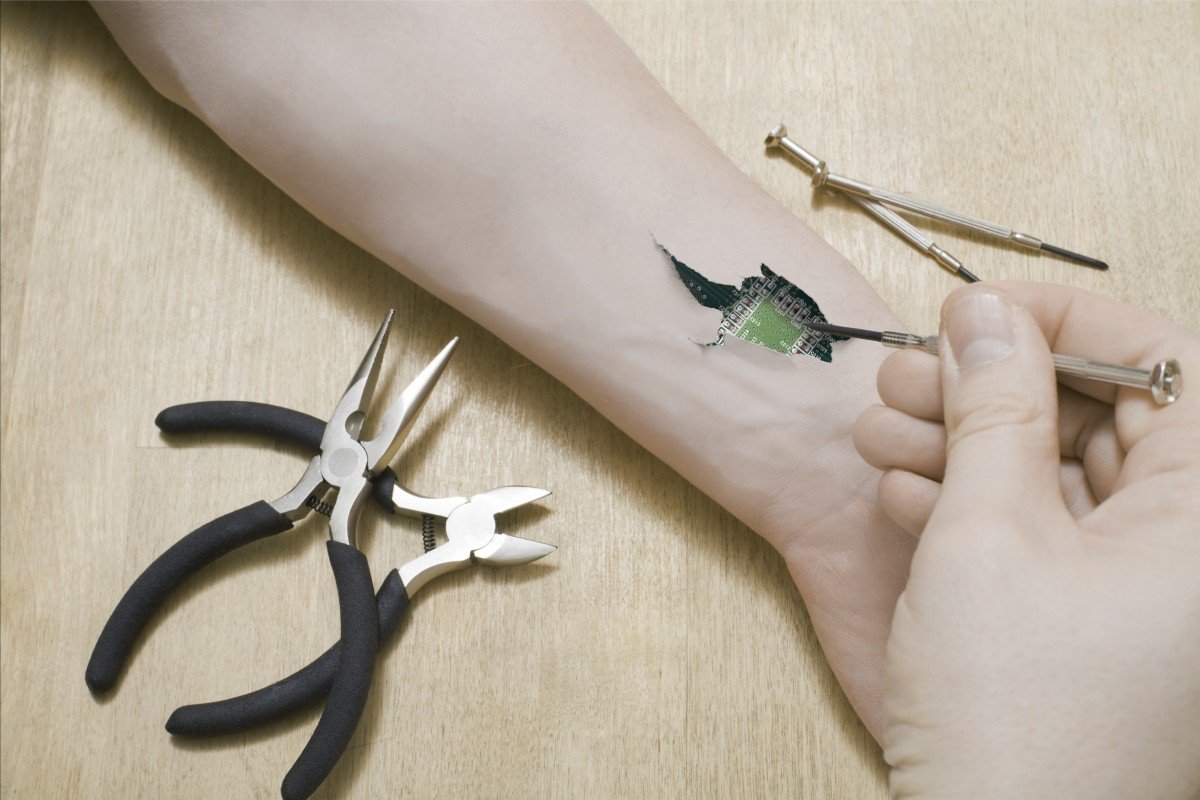

Few go as far as Zoltan Istvan, who dreams of a brain implant to connect him to the internet, but many in Silicon Valley use technology to improve their bodies
We chart some of the latest developments in biohacking, implants, experimental biology and nootropics – all intended to improve cognitive ability and health
Implants such as a chip in your hand or wrist that could send messages and open your front door are one of the more extreme visions of biohackers. Photo: Shutterstock How binaural beats work: the sounds said to tune our moods, boost productivity, lower stress. The science is shaky, doctor says
‘Brain-tuning frequencies’ known as binaural beats are gaining credence as a tool to encourage mindfulness, boost productivity and even relieve stress
While the scientific evidence for their beneficial effects is slim, doctors agree exposure to binaural beats can create changes in the brain’s degree of arousal
Binaural beats are being used as a way to encourage mindfulness and boost productivity – but can sound frequencies make real changes to our brain states and moods? Photo: Shutterstock
Is a healthier gut microbiome the master key to longevity?

( Natural News ) Researchers now believe that boosting the health of the gut microbiome may be the secret to living healthier in old age . In a study published in the journal Nature Communications , researchers looked at how fecal transplantation from young mice to older ones stimulated the gut microbiome and revived the gut’s immune system.
The gut, more so than many other internal organs, can be severely weakened by the effects of aging, and many age-dependent changes to the gut microbiome have been linked to inflammation, frailty and an increased susceptibility to potentially life-threatening intestinal disorders. As you age, these changes to the gut microbiome happen just as your gut’s immune system fails to function at peak efficiency. Before the results of this study, undertaken by immunologists from Cambridge’s Babraham Institute , were published, scientists weren’t entirely sure whether those two changes to the gut microbiome were connected.
Marisa Stebegg, lead researcher, said that the gut microbiome is made up of hundreds of different bacteria that are essential for optimal health. These gut bacteria play a role in metabolic function, brain function and in the immune system’s response to threats such as foreign pathogens.
“Our immune system is constantly interacting with the bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract,” said Stebegg. “As immunologists who study why our immune system doesn’t work as well as we age, we were interested to explore whether the make-up of the gut microbiome might influence the strength of the gut immune response.”
In this study, the researchers either co-housed young and older mice in order to stimulate their natural desire to sample the fecal pellets of other mice, or they directly performed fecal transfers from young to older mice. This boosted the gut immune system of the older rodents and it partly corrected their age-related decline. Michelle Linterman, one of the researchers, remarked that co-housing alone was enough to make the gut immune response of the aged mice nearly indistinguishable from that of their younger roommates. A healthy gut means a healthy life
What this study showed is that the decreasing quality of the gut’s immune response is not irreversible. This immune response can be strengthened by challenging it with the appropriate stimuli. For older mice, it meant co-housing with and sampling the fecal matter of younger mice. For humans, it may be a healthy diet that involves the consumption of probiotics. (Related: Gut bacteria “signatures” predict how the body will respond to poor food choices, predicting risk for diabetes, heart disease .)
Furthermore, the study is relevant because it confirmed the link between the effects of the aging and deteriorating immune system and the age-related changes that occur within the gut microbiome. Interventions, if you want them to be successful, have to focus on having a positive impact on the composition of the gut microbiome.
The food you eat can nourish the gut bacteria. These bacteria then produce the nutrients your body needs to strengthen the immune system and fight off pathogens. This immune response needs to be kept at peak performance and this can be done through eating foods that specifically nourish the gut microbiome, such as probiotics.
Other studies support the theory of Stebegg, Linterman and their team. One such study, published in the journal Scientific Reports , found that feeding fruit flies a combination of probiotics and herbal supplements can prolong their life by 60 percent and protect them from age-related chronic diseases. More research provides even more evidence to suggest that a healthy gut may make the difference between aging poorly and having a good quality of life in your twilight years.
Sources include:
Nature.com 1
Nature.com 2
24 Potential Uses of Neurofeedback Therapy (incl. ADHD)
“ Neurofeedback ” is a form of biofeedback training that aims to help people learn how to consciously control certain aspects of their brain activity. This promising new technology has been proposed to be a potential treatment for a wide variety of different conditions, from depression, ADHD, chronic pain, headaches, and even some symptoms of PTSD and schizophrenia. Does it work? Read on to learn more. What is Neurofeedback?
“ Biofeedback training ” is a growing trend in healthcare, where people are hooked up to devices for measuring different aspects of bodily functions in order to see how these processes are taking place in real-time. People can then be trained to learn to control the way these processes are carried out [ 1 , 2 ].
“ Neurofeedback ” is a specific form of biofeedback training, which is based on the idea that people can consciously alter the way their brains function by using training programs to help them to visualize and learn to change the patterns of electrical activity taking place in their brain [ 3 ]. Purported Benefits of Neurofeedback Therapy
While a considerable amount of early research has been done on neurofeedback, it is still a relatively new technology, and not much is known about the exact mechanisms underlying each different form of neurofeedback training.
There is also another major limitation that is worth noting about much of the existing research: because neurofeedback requires a person to be hooked up to complex devices and extensively trained, it is often difficult, impractical, or even impossible to have proper “control” groups to compare the effects to. This means that it’s possible that many of the reported findings so far are simply due to the “placebo” effect [ 4 ].
Therefore, due both to a general lack of adequate research so far, as well as methodological limitations when it comes to ruling out possible “placebo” effects, all of the purported uses described below are currently considered to have “insufficient evidence” to come to any firm conclusions about the efficacy of neurofeedback training. None of the uses below have been FDA-approved, and much more research will be needed before any of the proposed uses below could become officially approved and accepted as valid medical approaches to treating the various conditions and other biological functions discussed below.
With that in mind, let’s review what some of the preliminary research so far has to say about the potential effects of neurofeedback training!
Some researchers have proposed that neurofeedback may help to enhance neuroplasticity (the capacity of the brain to change and adapt). This, in turn, could possibly help to slow or reverse the natural declines in cognitive function that occur over aging [ 5 ].
For example, one early study reported that neurofeedback training improved cognitive processing speed and executive function in elderly subjects [ 6 ].
Other studies have reported that certain specific types of neurofeedback training, such as decreasing sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) beta rhythms, may help improve reaction time [ 7 ].
According to another preliminary study, subjects who were able to learn to boost their alpha brain wave activity via neurofeedback were reported to perform better at a visual-spatial reasoning task (mental object rotation) [ 8 , 9 ].
While these early results are promising, little is known about how long-lasting these changes might be, or how significant any changes in overall cognitive functioning might be. Therefore, considerably more research work will still be needed to verify and extend these preliminary findings further.
Neurofeedback is under investigation for its potential to affect cognitive function and neuroplasticity, but studies have been limited in both scope and term so far.
Problems with working memory are often associated with issues with attention and short-term memory.
According to some preliminary findings, healthy individuals have reported to improve their working memory and extend their attention spans by increasing certain types of brain wave activity (in this case, alpha-, theta-, and SMR waves) [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 ].
Another study in 32 human subjects reported that EEG-based neurofeedback improved attention and working memory in older patients, while younger subjects improved their concentration and attention (executive functioning). This led some researchers to suggest that neurofeedback may be an effective way to prevent age-related cognitive impairment – although more research will be needed to find out for sure [ 15 , 16 ].
In one other study, fMRI-based neurofeedback training (a type of MRI that can be used to monitor brain responses in real-time) was used to help 18 healthy adults learn to control their blood oxygen level-dependent signals, and was reported to lead to improved working memory abilities [ 17 ].
Some researchers are investigating whether neurofeedback could improve problems with attention and working memory. So far, the evidence is insufficient to support any claims.
Some early evidence suggests that EEG-based neurofeedback training may have potential to enhance the acquisition and organizations of new memories (both short- and long-term memory) [ 18 ].
According to one preliminary study in 50 healthy adults, using an EEG-based neurofeedback program to boost alpha wave strength was reportedly associated with increases in the accuracy of multiple types of memory (episodic, working, short-term). The stronger the boost in alpha waves, the more memory enhancement each subject showed [ 19 , 20 ].
In another study, EEG-based neurofeedback training (targeting SMR and upper alpha waves) was reported to improve verbal memory, short-term visual memory, and working memory in 70% of the subjects (including 17 stroke patients and 40 healthy control subjects). This neurofeedback training was reported to be more effective than traditional cognitive training, and the study’s authors proposed that neurofeedback could potentially benefit patients suffering from brain damage (such as the stroke patients in their study) [ 21 ].
Finally, another study in 27 healthy human subjects reported that EEG-based neurofeedback improved memory consolidation during sleep [ 22 ].
In a few small clinical studies, neurofeedback affected the acquisition and organization of new memories, but it’s unclear whether these results have any reliable clinical application.
In a few preliminary studies, EEG-based neurofeedback was used […]
Cannabis use disorder more common in adults with pain

A new study published in the journal American Journal of Psychiatry reports that the use of cannabis for non-medical indications is much more common in adults who have pain than in others. This includes those who use marijuana very often or heavily enough to be considered to have a problem with dependence. What is marijuana?
Marijuana is the term used for the dried leaves, flowers, stems and seeds of the Cannabis sativa or Cannabis indica plants. These are used as mind-altering drugs due to components such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which have profound psychological effects. Marijuana is currently the Number 1 psychotropic drug, and only alcohol is more commonly used. Many young people, including students in middle and high school, are using marijuana, and it is becoming a substance used in e-cigarettes as well. Image Credit: Lifestyle discover / Shutterstock Marijuana can now be used for medical or recreational purposes in 34 and 11 states of the USA, respectively. However, many papers have reported that using large doses of cannabis can heighten the risk of vehicle accidents, mental symptoms, breathing distress and cannabis use disorder, like addiction. Nonetheless, cannabis is still considered to be a harmless drug and many people use it without a medical indication almost every day. In particular, more students today say they think regular use of marijuana is not a risky act. Effects of marijuana
Marijuana smoking produces both short-term and long-term effects. THC from smoke quickly enters the blood, reaches the brain and other organs, and acts on endocannabinoid receptors. These are receptors that are designed to react to natural substances which act like THC and are important in the natural growth and development of the brain. When marijuana is ingested, the effects are delayed in onset, generally seen after 30 minutes to an hour.
THC activates brain regions with the highest number of these receptors, causing the person to feel a high, as well as to experience more vivid sensations, mood changes, difficulties with movement and cognitive processing (thinking, judgment, memory and logic), hallucinations and delusions. Frank psychosis, or mental imbalance, can also occur and is most likely if the individual is on highly potent preparations of marijuana on a regular basis.
The long-term effects include impaired brain development. If the drug is first begun in adolescence, the developing brain is vulnerable to impairments of cognition, causing difficulties with learning, memory and thinking. It seems to affect the nerve connections that are normally grown between the different brain regions that act together to execute these complex tasks. It is still unclear if these changes are transitory or persist over time.
Other problems include respiratory difficulties due to lung irritation, a higher heart rate, lower fetal weight as well as a higher risk for poor brain and behavioral development if the drug is used in pregnancy, and intense vomiting. The study
The purpose of this study was to find out what factors drove the risk of cannabis addiction. The researchers drew data from the National Epidemiologic Surveys on Alcohol and Related Conditions in 2001-2002 and 2012-2013, related to the use of cannabis. They looked at the patterns of use for non-medical reasons in adults, both those who had and those who did not have pain. The findings
The study shows that about 20% of individuals in either survey said they had pain of moderate to severe degree. The use of non-medical marijuana went up to almost 10% in 2013, from 4% in 2002. The scientists also observed that the increase in frequency was significantly skewed towards patients with pain compared to those without, at 5% vs 3.5%. The same was the case with the risk of addiction, which occurred in over 4% in those with pain but in less than 3% in those without it.
The researchers point out the paradox that most meta-analyses of the efficacy of cannabis in the treatment of pain show mixed results, even while 2 out of 3 American adults believe that it helps significantly to manage one’s pain. In view of the fact that about a fifth of the adult population has moderate to severe pain, the number of adults who are at risk for cannabis addiction because of their non-medical use of the drug is very high. It should be noted that marijuana preparations available today are steadily becoming more potent compared to earlier times, which is one factor behind the increasing number of emergency room visits following the use of this drug. The regular use of high-potency cannabis also increases the risk that the person will become addicted and also the risk of psychosis. The solution
The study authors recommend a balanced reporting about the effects of marijuana and the issues associated with its use. Says researcher Deborah Hasin, “Greater balance is needed in media reporting of marijuana issues, including messages that convey credible information about the nature and magnitude of health risks from non-medical cannabis use, including among the large group of US adults with pain. Psychiatrists and other mental health professionals treating patients with pain should monitor their patients for signs and symptoms of cannabis use disorder.”
U.S. Adults With Pain, A Group Increasingly Vulnerable to Nonmedical Cannabis Use and Cannabis Use Disorder: 2001–2002 and 2012–2013 Deborah S. Hasin, Dvora Shmulewitz, Magdalena Cerdá, Katherine M. Keyes, Mark Olfson, Aaron L. Sarvet, and Melanie M. Wall American Journal of Psychiatry, https://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.19030284
20 Best Mushroom Coffees That Boost Immunity And Energy

Best Mushroom Coffees To Try That Boost Immunity And Energy It’s smooth with added health benefits.
Most of the adult and now even the adolescent population depend on coffee each morning and throughout the day for energy. And while it’s great for a morning or afternoon boost, drinking too much coffee can be a problem, leading to coffee addictions and increased heart rate.
So, why not make your daily cup a little healthier with mushroom coffee? What is mushroom coffee?
Says Lisa Richards, a nutritionist and author of The Candida Diet , “Various medicinal mushrooms have been prepared in such a way that they are able to be added to coffee and boost the nutrient content of the drink. The extract from medicinal mushrooms are added to coffee to fortify or enhance the caffeinated drink’s health benefits through extra nutrients.”
And the benefits of these nutrients include better sleep, reduced inflammation, and enhanced immunity. But it’s not just because of the medicinal mushrooms. Adds Richards, “A major component of the health benefits of mushroom coffee come from replacing artificial sweeteners and high calorie creamers with nutrient rich mushrooms.” While some may consider mushroom coffee a fad, adding mushroom extract from reputable sources to your coffee is worth giving a try.
RELATED: The Pros And Cons Of Drinking Coffee (And How It Really Affects Your Health) 1. Sacred 7 Mushroom Extract Powder
Reishi, Maitake, Cordyceps, Shiitake, Lion’s Mane, Turkey Tail and Chaga — 7 different species of mushrooms, each with unique healing properties, utilized for centuries throughout the world. This easy-to-mix powder adds a powerful nutrient boost to your coffee, tea, smoothie, pre- and post-workout shakes, and even culinary dishes.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 2. Four Sigmatic Adaptogen Coffee
Probably the most popular mushroom coffee brand on the market, it has half the caffeine, plenty of adaptogens to master stress, and is Adaptogen coffee mixed with organic instant coffee, organic tulsi, organic ashwagandha, and organic eleuthero to stay calm, cool, and collected. Adaptogens help your body to balance and fight occasional stress.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 3. Sun Alchemy Mushroom Coffee
Mushroom coffee is mixed with organic fair-trade instant coffee and 1,000mg of Organic Lion’s Mane, Reishi, Chaga, and Cordyceps dual-extracted mushroom powders. Lion’s Mane mushroom is packed with incredible benefits: it’s a cognitive supporting powerhouse, and boosts your energy and mood. And Lion’s Mane extract gives you a mental pick me up and removes brain fog.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 4. Tiger 5 Mushroom Coffee
This mushroom coffee boasts powerful ingredients of all natural mushroom with 100 percent Arabica coffee. In addition to increase in energy, Tiger Mushroom coffee has been traditionally used to help reduce inflammation, improve mental clarity, increase stamina, slow the aging process and lower cholesterol.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 5. NeuRoast Classic Roast Mushroom Coffee
NeuRoast is made with artisan-roasted mushroom coffee enhanced with 100 percent USDA-Certified Organic Cordyceps, Lion’s Mane, Reishi, Turkey Tail, and Chaga mushroom extracts for better focus and mental clarity. It contains Lion’s Mane, Cordyceps, Reishi, Chaga, and Turkey Tail.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 6. RaHygge Reishi Mushroom Coffee
This is a low-acid medicinal mushroom coffee, which combines craft roasted specialty coffee with medicinal mushrooms. These medicinal mushrooms act as Adaptogens, which balance the caffeine effect on the body, reducing the side effects associated with caffeine intake such as accelerated heart rate, adrenaline rate and gastric acidity. Adaptogen plants help the body to better manage stress, exhaustion and overwork.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 7. Wildcrafter Botanicals Organic Coffee
This organic energy coffee blend is infused with herbs like Rhodiola, Lion’s Mane Mushroom and Maca Root to help increase mental and physical performance, improve your memory, and give you the stamina to get through your work day.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 8. Organic Nootropic Mushroom Coffee by I’m Stamina Coffee
This coffee has lower caffeine, high energy mushrooms that balance caffeine and stress. Sharpen mental clarity and focus, boost immunity, and improve health. The coffee is whole bean, has no mycotoxin, is 100 percent arabica, and is low-acid, vegan, and non-GMO.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 9. Ganoderma Reishi Mushroom Coffee
Reishi mushroom has antioxidant properties to support immune function and well-being. This mushroom blend is loaded with adaptogenic mushrooms to help your body balance in times of stress. For boosting energy, add one teaspoon to your morning cup, or take it to the next level by combining it into your oatmeal, soup, or dessert recipes.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 10. Canetic Mushroom Coffee with Reishi Powder
Packed with powerful nutrients that enhance your energy and provide the mental pick up you need, this mushroom coffee has Creatine, Beta Alanine, Citrulline, and L-Theanine that all work wonderfully together in support of your brain function.
(Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) RELATED: Mushroom Coffee Is The Latest Health Craze That Allegedly Prevents Sickness —This Recipe Puts That Theory To The Test 11. MUDWTR Mushroom Coffee MUDWTR is a coffee alternative consisting of organic ingredients lauded by cultures old and young for their health and performance benefits. With 1/7th the caffeine of coffee, mud gives you natural energy, focus and more without the jitters and crash. It includes Cacao, Masala, Chai, Turmeric, Sea Salt, Cinnamon, and mushrooms Chaga, Cordyceps, Reishi, and Lion’s Mane. ( MUDWTR , $40) 12. SOLLO 100% Chaga Coffee Pods This ynique blend of Arabica coffee beans and herbal extracts increase power and digestive systems support for your body, and help you achieve your goals. Organic mushroom coffee is a great home remedy and immune support, as Chaga mushrooms are nutrient dense, contain a wide variety of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. (Check prices and reviews on Amazon ) 13. Dodjivi Reishi Mushroom Coffee Made from Ganoderma Lucidum Mushroom, 100 percent Arabica coffee, and a rich blend of other potent herbal extracts, this […]
Healthy food trends for 2020

In getting a fit and healthy body, diet is everything. One cannot achieve optimum health without considering the importance of nutrition. One’s health mostly depends on what you feed your body and, to start your health plans right, here are the lists of healthy food trends predicted by Frances Largeman-Roth, RDN, published in www.today.com and Khristine Thomason published in Womenshealthmag.com. Even more plant-based protein
TWENTY-NINETEEN saw more plant-based options than ever before, especially when it came to protein sources. And that train isn’t slowing down any time soon. “They’ve always been around, but as people become more conscious about the sourcing of foods, plant-based proteins will likely gain more momentum in 2020,” said Laura Iu, RD.
The Whole Foods 2020 Trend Report touts mung bean, hempseed, pumpkin, avocado, watermelon seed, and golden chlorella as protein sources to look out for in the New Year, as they offer a spectrum of plant-based amino acids.
“Overall, consumers have been encouraged to consume less red meat and food companies/restaurants are responding,” said Keri Gans, RD. “Perhaps, more ‘hot dogs’ and ‘chicken tenders’ will be next!” Plant-based, but not plant-exclusive
While there’s definitely an influx of vegan options hitting the shelves, there will likely be an increased focus on plant-based eating for omnivores and flexitarians in 2020.
There will likely be more hybrid products that incorporate veggies in 2020. For example, Whole Foods’ 2020 Trend Report notes that some brands are creating their meat products with 25 percent to 30 percent vegetables. A new era of mocktails
While “Dry January” is a popular way to start the year on a healthier note, more and more people are jumping on the booze-free train year-round these days. “Millennials and Gen Z are drinking less in general,” said Moon. “It was only a matter of time before someone came up with a creative solution. Enter “zero-proof” drinks.”
More and more brands are introducing alcohol-free spirits, wines and beers. Plus, countless restaurants and bars around the country are including mocktails on their menus, and there are even some nonalcoholic bars opening up across the country, according to Yelp’s 2020 Trend Forecast Report. You’ll learn the term nootropics
“As of 2020, we’re just one short decade away from every baby boomer being retirement age, making 1 in 5 Americans 65 years or older,” said Moon. As a result, “people are increasingly concerned about brain health and staying sharp.” That’s where ’nootropics’ may be able to help.
Nootropics are compounds that help improve brain function, including memory and cognitive function. They come in supplement or drug form, but there are also a number of nootropic foods that boost cognitive health, like turmeric, wild blueberries, salmon, broccoli, walnuts, egg yolks and seaweed.
Plant-based eating is a big trend for 2020. More non-dairy milk alternatives
TWENTY-NINETEEN was certainly the year of oat milk—you can now find the vegan-friendly beverage in supermarkets and coffee shops across the country. And with so much of the population switching to a vegan or plant-based diet, the need for alternative milk won’t slow any time soon Goodbye flour, hello veggies
According to the Grubhub’s “Taste of 2019” report, cauliflower pizza was the most ordered food of the year. That’s not surprising considering the breadth of cauli products on the market, and Gans predicts you’re going to see a lot more flour options in 2020. “From chickpea flour and almond flour to sorghum flour, I think more food companies will be baking with these nutrient dense flours versus basic white flour,” she says. The Whole Foods Trend Report also suspects there will be more packaged products going alt-flour as well—think: tigernut flour in chips and snack foods, and pastries made with seed flour blends. Fresh snacks>packaged
While the word “snack” may seem synonymous with processed pretzels and chips, Sonya Angelone, RD, predicts there will be a lot more healthy snacking choices in the New Year. Particularly, snacks you store in your fridge. The Whole Foods 2020 Trend Report similarly notes, “The refrigerated section is filling up with the kind of wholesome, fresh snacks typically prepared and portioned in advance at home: hard-boiled eggs with savory toppings, pickled vegetables, drinkable soups, and dippers of all kinds, all perfectly portioned and in convenient single-serve packaging.” That extends to protein bars, too, like the brand Perfect Bar which contains a number of fruits and veggies and, therefore, requires refrigeration. CBD is here to stay
A year ago, CBD may not have even been on your radar. Now, it’s in skin care, muscle-soothing lotion and even clothing. CBD has certainly made an impact on the food world. Products include candy, seltzers, gum and even coffee. Spotlight on truly natural sweeteners
According to the International Food Information Council, the No. 1 thing Americans are doing to eat healthier is limiting sugar intake but the National Institutes of Health shows while Americans have cut back, they are still getting way too many added sugars from foods like white bread and pasta, sodas and pastries.”
The Whole Foods 2020 Report predicts that brands will likely launch more “syrupy reductions from fruit sources like monk fruit, pomegranates, coconut, and dates” to add flavor to desserts, meat glazes and marinades. Carbs are back…sort of
There’s no denying 2019 has been very anti-carbs (looking at you, keto diet).
Make no mistake, keto will likely still linger in 2020, but Moon predicts people will be a bit more accepting of healthy carb choices. Carbs from healthy whole grains, pulses, starchy vegetables and fruit are amazing. Sweet potato is the new cauliflower
Sweet potatoes are rich in fiber and packed with nutrients like vitamin A and vitamin C. This nutritious tuber has long been a staple at holiday meals but it’s about to get the cauliflower treatment. Fish is going faux
Tuna looks like canned tuna but it’s actually made from soy protein and other flavorings.
If 2019 was the year of the Impossible Burger, 2020 may just be the year of plant-based fish.
Eating seafood is touted by most […]
