Learn about brain health and nootropics to boost brain function
11 Factors That Disrupt the Blood-Brain Barrier
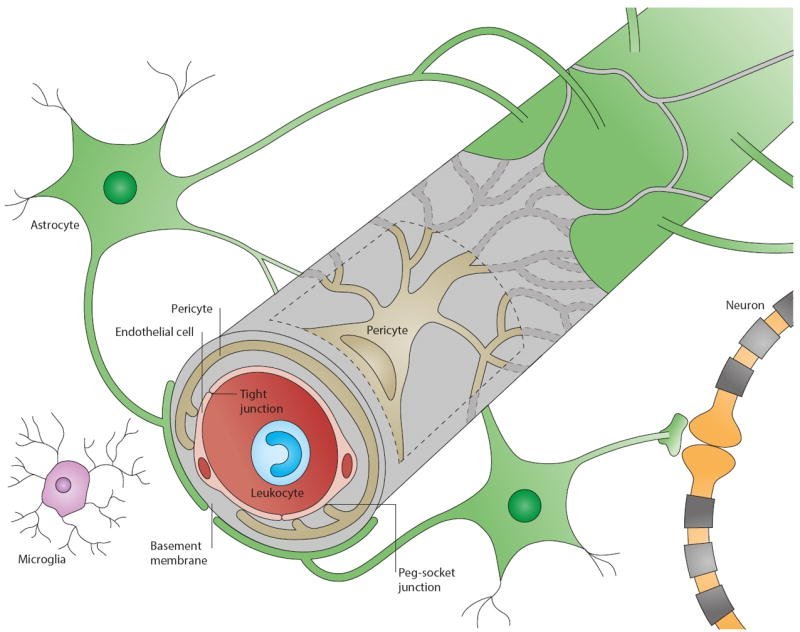
A leaky blood-brain barrier (BBB) is thought to play a role in different neurological and psychiatric disorders, including “ brain fog ”, Alzheimer’s disease , depression , schizophrenia, and more. However, the research in this field is still young, and scientists are yet to unravel potential connections.
When discussing issues with the BBB, it is important to note that a problem does not always start in the brain. Diseases and other problems elsewhere in the body, such as diabetes or gut inflammation, may trigger a “leaky brain.” In this post, we cover the top 11 factors that can disrupt the blood-brain barrier. Brain Injuries
1) Stroke
Strokes cause a lack of glucose and oxygen. This leads to a rise in potassium , the depletion of ATP, and a release of glutamate , which all contribute to blood-brain barrier disruption [ 1 ].
Under stroke conditions, the tight junctions that help prevent substances from entering the brain have compromised integrity. This means that the tight junctions are weaker and increase BBB permeability [ 2 ].
After a stroke, reperfusion (restoration of blood flow to the brain or tissue) occurs. Reperfusion may cause additional tissue damage and an increase in inflammation, which also worsens the BBB condition [ 1 ]. In a study of human brain tissue from five cases of fatal strokes, MMP9 levels were higher in the affected areas. Higher MMP9 levels are a good indicator of increased BBB permeability [ 3 ]. 2) Traumatic Brain Injury https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25624154
After traumatic brain injury, the blood-brain barrier also becomes dysfunctional. This leads to the leakage of proteins and negatively affects immune cells [ 4 ].
BBB breakdown may last from several days to weeks after head trauma. In some cases, the BBB can be dysfunctional for years [ 5 ].
Head trauma injures blood vessels in the brain. It leads to impairments in brain-blood flow, BBB permeability, and metabolic processes. It also reduces oxygen levels in the brain, which further induces BBB breakdown [ 5 ].
Traumatic brain injuries also cause damage to the neurovascular unit. When the nerve cells die quickly, it causes another cycle of injury after the initial brain injury [ 6 ].
After traumatic brain injury, excessive superoxide reacts with nitric oxide to form peroxynitrite. Peroxynitrite contributes to BBB leakage [ 6 ].
In traumatic brain injury-induced adult male rats, treatment to reduce peroxynitrite also decreased BBB leakage. S-nitroso- glutathione (GSNO) helps stop BBB dysfunction and provides protection to nerve cells [ 6 ]. 3) Brain Tumors
There is a loss of tight junction molecules in brain tumor blood vessels. Tumors also affect cell formation and prevent the release of factors necessary for blood-brain barrier (BBB) function [ 7 ].
Brain tumors also cause fluid to leak into the brain. The open tight junctions cause brain edema [ 8 ].
In a study of 10 patients with brain tumors, brain scans showed an increase in BBB permeability [ 9 ].
Another study of mice with brain tumors had similar results. The mice had an increased BBB permeability to sodium fluorescein (a marker for BBB integrity). BBB breakdown is also associated with faster cancer growth [ 10 ].
It is difficult to treat brain tumors because the BBB prevents the transport of drugs into the brain. Scientists are currently studying new therapies that are able to cross the blood-brain barrier [ 10 ]. 4) Hypertensive Encephalopathy
An increase in brain blood pressure may cause hypertensive encephalopathy . Symptoms include severe headache , confusion, and impaired judgment and memory. Coma, convulsions, and other brain problems can occur afterward [ 11 ].
Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) during increased brain blood pressure leads to reduced blood flow and excess fluid in the brain [ 12 ].
Normally, hypertension (high blood pressure) activates pathways to maintain the BBB. However, in animal models of hypertensive encephalopathy, hypertension overrides the BBB [ 13 ].
During hypertensive encephalopathy, BBB dysfunction is widespread. It can cause brain edema, which is the life-threatening excess accumulation of fluid in the brain. Although there are methods to stop brain edema, there are no treatments that specifically target the BBB [ 12 ]. Dietary and Metabolic Factors
4) Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
The obesity-induced inflammation may cause problems in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) [ 14 ].
Diet-induced obesity leads to an increase in proinflammatory cytokines, which increases BBB permeability [ 14 ].
Obesity also increases C-reactive protein levels. In rats, high doses of C-reactive protein increase BBB permeability, which impairs brain function. It mainly affects tight junction function [ 15 ].
High-fat diets and obesity cause blood vessel problems, damaging the BBB integrity. In a study of male rats, in comparison to mice fed a healthy diet, a high-fat diet increased BBB permeability [ 16 ].Moreover, the results of this study suggest that vitamin D supplementation helps protect the BBB. Although it does not seem to have any effect on the control group, vitamin D treatment significantly improved BBB integrity in rats fed a high-fat diet [ 16 ].The rats fed a high-fat diet but did not receive vitamin D supplementation had higher BBB permeability [ 16 ]. 5) Diabetes Blood-brain barrier permeability is increased in diabetic patients and animals. Diabetes may result in the disruption of the blood-brain barrier [ 17 , 18 ].Elevated glucose levels increase oxidative stress in the brain and pericytes. This kills the pericytes (by apoptosis) and disrupts the blood-brain barrier. By blocking glycolysis (the breakdown of glucose), BBB pericytes are protected [ 18 ].During diabetes mellitus, reactive oxygen species accumulate at the blood-brain barrier. This causes oxidative damage, further damaging the BBB and increasing its permeability [ 19 ].Researchers tested BBB selectivity in diabetes-induced rats. Results indicated that diabetes caused the loss of tight junction proteins and increased MMP-9 activity, which led to an increase in BBB permeability [ 20 ]. Infections and Inflammation 6) “Leaky Gut” “Leaky gut” happens when the permeability of the intestine increases. This may also contribute to a leaky brain [ 21 ].The blood-brain barrier […]