Learn about brain health and nootropics to boost brain function
How the “Little Brain” Fuels Motivation and Addiction
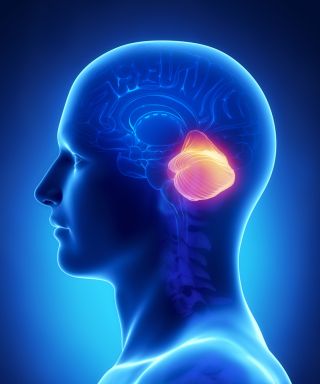
Key points First-of-its-kind research shows how the cerebellum modulates dopamine release within the basal ganglia. Motivation and addiction are both fueled by dopamine activation in the basal ganglia’s substantia nigra. Too little dopamine causes Parkinson’s disease. Stimulating the cerebellum may be a new treatment…
Study finds brain mechanism that may explain how physical exercise improves mood
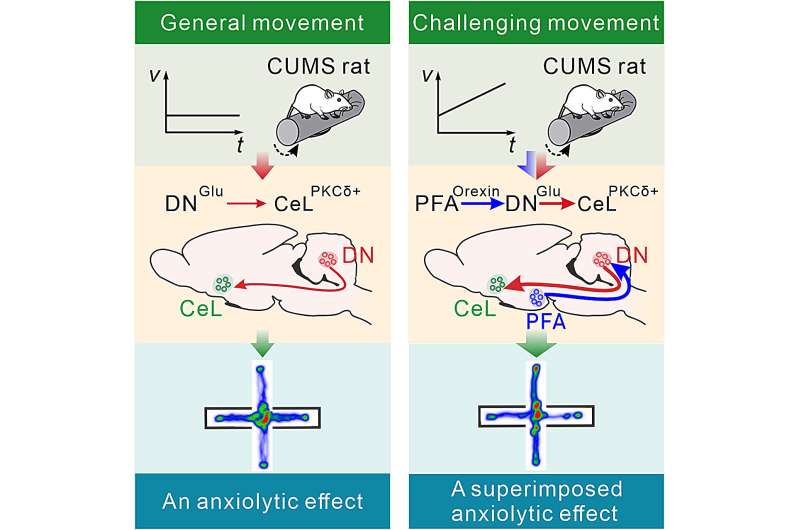
by Nanjing University School of Life Sciences Challenging movement can improve anxiety more effectively by recruiting the hypothalamic-cerebellar orexinergic circuit which more strongly activates the cerebello-amygdalar glutamatergic monosynaptic projections. Credit: Neuron (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.01.007 “Only exercise can remove all kinds of doubts,” Goethe said….
New Tech Could Record Deep-Brain Activity From Surface
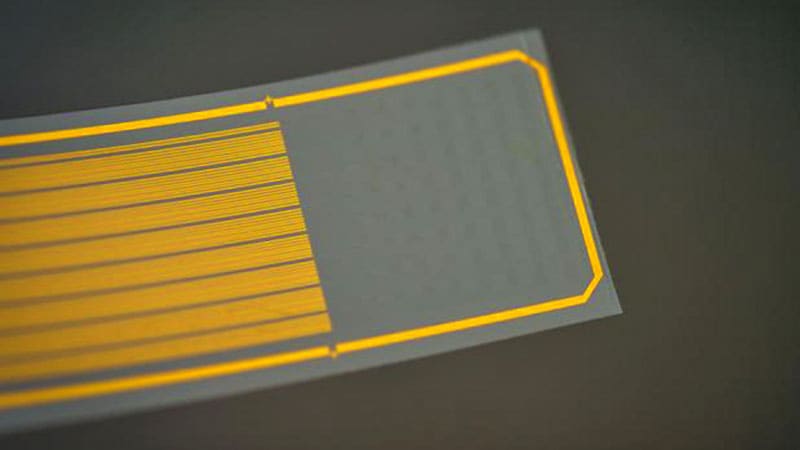
0 Modern technology for recording deep-brain activity involves sharp metal electrodes that penetrate the tissue, causing damage that can compromise the signal and limiting how often they can be used. A rapidly growing area in materials science and engineering is to fix the problem…
You must remember this: VT discovery may lead to keeping good memories, removing bad ones

A protein in the brain may pave the way for targeted therapeutic interventions to enhance memory or alleviate negative memories. Virginia Tech researchers discovered a new function for a common protein in the brain — a development that sheds new light on the mysteries…
Neuroscientists just uncovered a fascinating link between sleep, memory, and breathing
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have discovered a significant link between breathing patterns during sleep and the brain’s ability to consolidate memories. This finding, published in Nature Communications , sheds light on how the simple act of breathing might play a pivotal role in…
This Graphene-Based Brain Implant Can Peer Deep Into the Brain From Its Surface
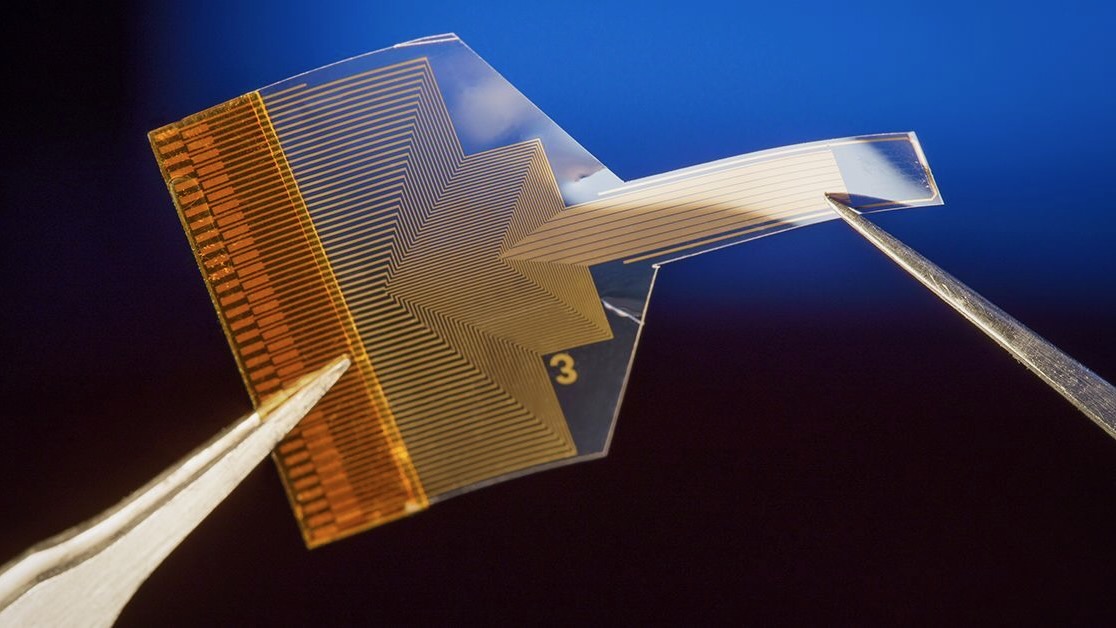
Finding ways to reduce the invasiveness of brain implants could greatly expand their potential applications. A new device tested in mice that sits on the brain’s surface—but can still read activity deep within—could lead to safer and more effective ways to read neural activity….
Study challenges traditional views on how the brain processes movement and sensation
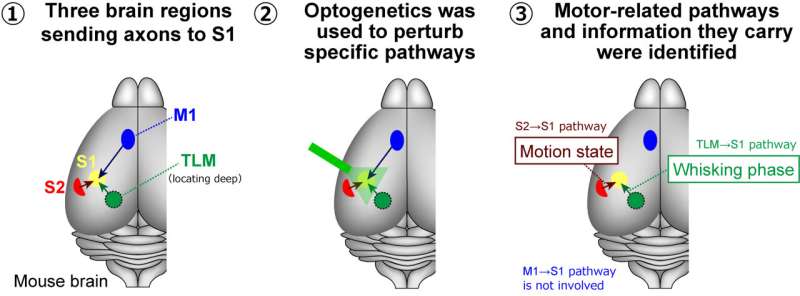
Utilizing optogenetics, researchers at Fujita Health University have selectively deactivated neural pathways with light, revealing new insights into how sensory and motor areas of the mouse brain communicate during movement. Credit: Takayuki Yamashita from Fujita Health University Our body movements profoundly impact how our…
Think you’re good at multi-tasking? Here’s how your brain compensates – and how this changes with age

This means better capacity to maintain performance at or near single-task levels.The white matter tract that connects our two hemispheres the corpus callosum also takes a long time to fully mature, placing limits on how well children can walk around and do manual tasks…
Mind Control Breakthrough: Caltech’s Pioneering Ultrasound Brain–Machine Interface

The latest advancements in Brain-Machine Interfaces feature functional ultrasound (fUS), a non-invasive technique for reading brain activity. This innovation has shown promising results in controlling devices with minimal delay and without the need for frequent recalibration. Credit: SciTechDaily.com Functional ultrasound (fUS) marks a significant…
New brain-like transistor mimics human intelligence
Taking inspiration from the human brain, researchers have developed a new synaptic transistor capable of higher-level thinking. Designed by researchers at Northwestern University, Boston College and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the device simultaneously processes and stores information just like the human brain….
There’s a ‘Wave of Death’ in Every Human Brain. Scientists Are Scrambling to Stop It.

Working to Stave Off Brain’s ‘Wave of Death’Ioannis Tsotras – Getty Images Researchers studying the brain’s final moments have gained new insight into the “wave of death” that occurs before a brain’s activity fully flatlines. When neural activity stops, it doesn’t stop abruptly, but…
Brainoware: A breakthrough AI approach using brain organoids for advanced computation

In a study published in the journal Nature Electronics , researchers in the United States of America developed an artificial intelligence (AI) hardware approach named “Brainoware” that employs adaptive reservoir computation of the brain organoid neural networks (ONNs). They found that the approach could…
Brainoware: Organoid Neural Networks Inspire Brain-AI Hardware
Credit: BlackJack3D / iStock / Getty Images Plus “The human brain has 100 billion neurons, each neuron connected to 10,000 other neurons. Sitting on your shoulders is the most complicated object in the known universe.” — Michio Kaku, PhD. Since most examples of brain-inspired…
Unlocking the secrets of the brain’s dopaminergic system
A new organoid model of the dopaminergic system sheds lights on its intricate functionality and potential implications for Parkinson’s disease. The model, developed by the group of Jürgen Knoblich at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, replicates the…
Unlocking the secrets of the brain’s dopaminergic system
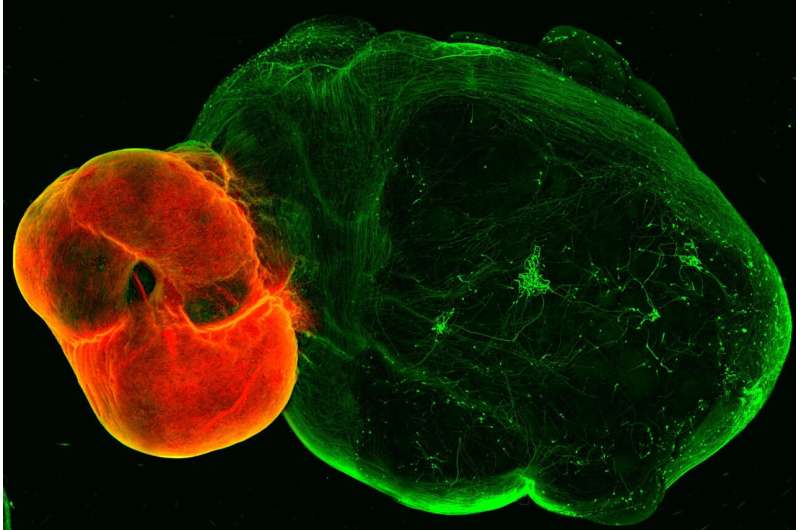
by IMBA- Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences Dopaminergic neurons in the ventral midbrain (red) and ventral midbrain projections into striatal and cortical tissue (green). Credit: (c) Daniel Reumann/IMBA A new organoid model of the dopaminergic system sheds lights on…
Brain’s Reward Pathway Unlocked: Revealing the Secrets of the Dopaminergic System

Scientists developed a revolutionary organoid model of the dopaminergic system, providing significant insights into Parkinson’s disease and the long-lasting effects of cocaine on the brain. This model is a promising tool for advancing Parkinson’s disease treatments and understanding the enduring impact of drug addiction….
Exercise Boosts Brain Power—Neuroscientists Don’t Know How

Key points Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (cardio) increases prefrontal cortex oxygenation and boosts brain power. Even with an insufficient oxygen supply or acute hypoxia, doing cardio can improve cognitive performance. Increased cerebral blood flow alone may not explain why aerobic exercise improves executive function. Vitalii…
Hunger Games: How Gut Hormones Hijack the Brain’s Decision Desk

Scientists have discovered that a hunger hormone in the gut directly influences the brain’s hippocampus, affecting decision-making related to food. The study, conducted on mice, showed that hunger hormones modify brain activity to either inhibit or permit eating based on the animal’s hunger level….
Heartbeats and brain activity: Study provides insight into optimal windows for action and perception
(Photo credit: OpenAI’s DALL·E) A new study published in PLOS Biology suggests that our heartbeat plays a crucial role in determining our brain’s ability to perceive and react to the world around us. Researchers have discovered that during the 0.8 seconds of a heartbeat,…
Decoding anxiety: Study reveals brain’s role in behavioral inhibition risks

In a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , a team of researchers in the United States used non-human primate anxious temperament models to investigate the molecular mechanisms and neural systems underlying behavioral inhibition in humans, which is…